
Case Report
Austin J Clin Case Rep. 2019; 6(4): 1156.
Plasmocytoma of Lymph Nodes: A Rare Extramedullary Involvement of Multiple Myeloma
Naoufal AS1*, Abdelkhalak MA1, Naoual EL1, Jihane SM1, Amal CH1, Fadoua ME1, Mohamed JI1, Jamal FA1, Mohamed Amine ES2 and Mohamed OU2
¹Department of Internal Medicine, Mohamed V Military Hospital, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University Mohammed V Rabat, Morocco
²Department of Histopathology, Mohamed V Military Hospital, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University Mohammed V Rabat, Morocco
*Corresponding author: Naoufal AS, Department of Internal Medicine, Mohamed V Military Hospital, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University Mohammed V Rabat, Morocco
Received: September 10, 2019; Accepted: October 17, 2019; Published: October 24, 2019
Abstract
Multiple myeloma is a disseminated malignant disease in which a clone of transformed plasma cells proliferates in the bone marrow, disrupting its normal functions and invading the adjacent bone. However, in rare cases, patients can develop extramedullary disease.
The involvement of lymph nodes is a rare condition that illustrates the diagnostic challenge that practitioner could face sometimes in their daily routine.
Here, we report a case of a 66-year-old female patient who was admitted to our hospital for further examination of chronic fever and palor. A computed tomography (CT) revealed retroperitoneal and mesenteric lymph node enlargement. Biopsies of the cervical lymph node showed a plasma cell infiltrate positive for, CD138, kappa light chain.
Multiple myeloma with lymph nodes extramedullary localization was diagnosed.
Our case demonstrates a rare presentation of extramedullary involvement of multiple myeloma, which it could have been misdiagnosed with lymphoid malignancy.
Keywords: Multiple myeloma; Extramedullary; Computed tomography (CT); Lymph node
Background
Multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by a proliferation of malignant plasma cells with strong dependence on the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment [1]. Although it usually is confined to the bone marrow and surrounding bones, some patients develop extramedullary disease (EMD) in the form of soft tissue plasmacytomas [2]. EMD involves commonly the upper respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tracts, skin, and lung [3,4] and in rare cases lymph nodes (less than 1% of all EMD) [5]. Here, we present the case of a patient with EMD involving the cervical thoracic, and the abdominal lymph nodes at the time of MM diagnosis.
Case Presentation
A 66-year-old woman who initially presented with arthralgia and fever reported to have been appearing over the previous two months. The patient had neither any remarkable past medical history, nor a family history relevant to such a complaint.
On physical examination, palpable left subclavicular and axillary lymph nodes with hepatomegaly and splenomegaly were noted.
Cervical, thoracic and Abdominal computed tomography showed submandibular, axillary, mediastinal and abdominal lymphadenopathy (the largest lymph node was 23mm in diameter) (Figure 1).
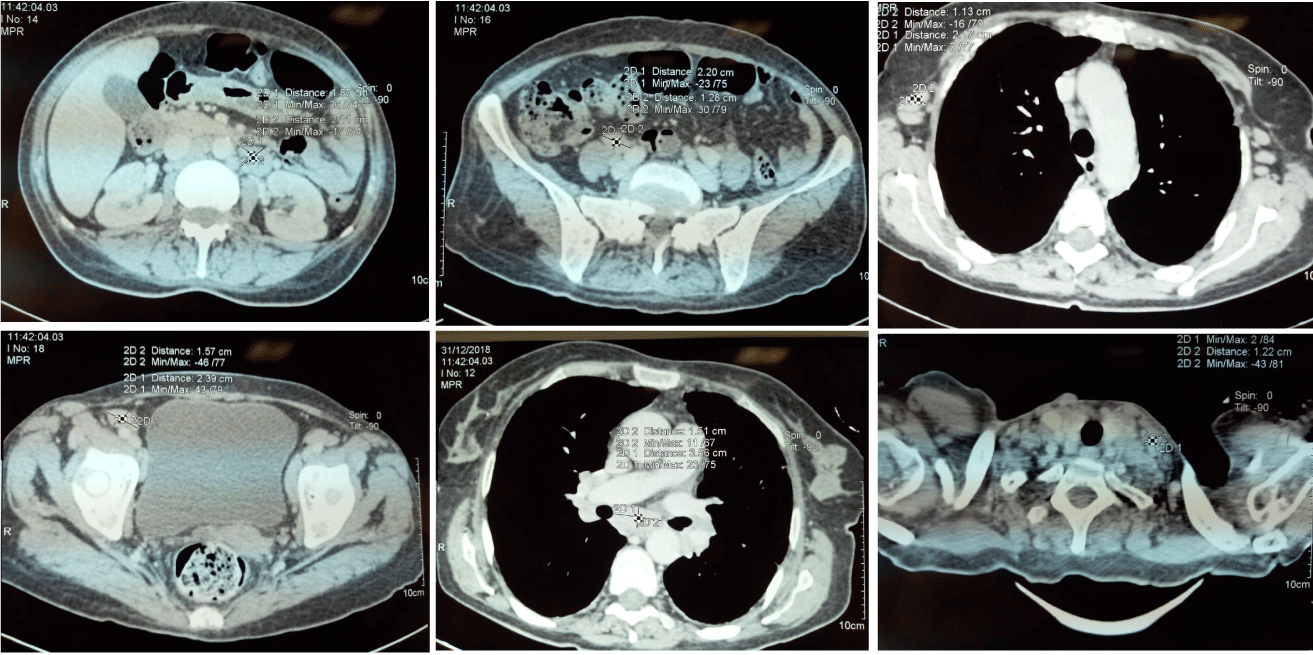
Figure 1: Cervical and thoracic abdominal computed tomography (CT). CT scans showing hepatosplenomegaly and multiple lymphadenopathy.
The patient’s haemoglobin was 6.7g/100ml; white blood cell and platelets counts were 1.900 and 113.000 per cubic millimetre, respectively; and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 100mm/h. Ferritin level was very high 1478 (normal range: 11–306,8 ng/ml). Her serum lactate-dehydrogenase level was normal at 181U/L (normal range: 125-243 U/L) Blood urea, creatinine, calcium, inorganic phosphate and other values for biochemical analyses and parameters of haemostasis were within the normal range.
Tests for HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) and HCV (hepatitis C virus) antibodies and HBV (hepatitis B virus) antigen were negative. Tests for tuberculosis (GeneXpert) were negative as well.
A biopsy of the subclavicular lymph node has been performed and the histopathological examination of the specimens revealed mature plasma cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and round eccentric nuclei where tumor cells are strongly positive for CD138, and Monoclonal κappa light chain is strongly positive in the plasma cells (Figure 2). A bone marrow biopsy showed Clonal marrow plasma cell percentage of 77% and the tumor cells are strongly positive for CD138.
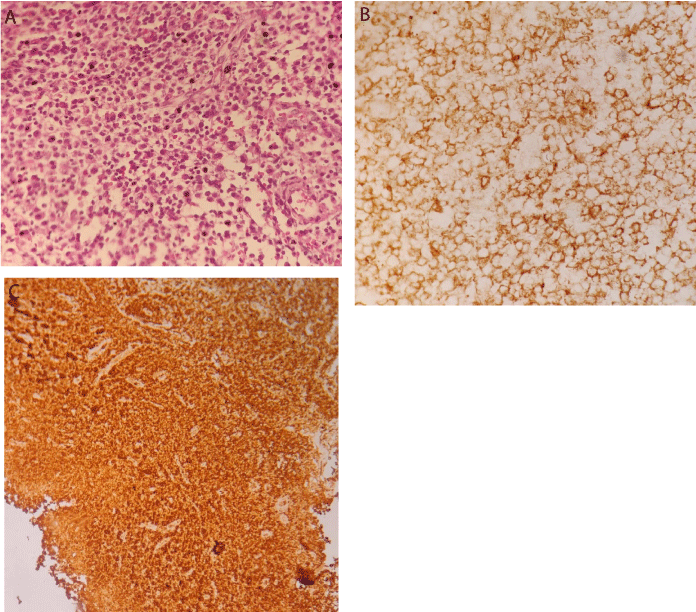
Figure 2: Histological and immunohistochemical examination of the
subclavicular lymph node. A) Mature plasma cells with abundant eosinophilic
cytoplasm and round eccentric nuclei (hematoxylin-eosin, original
magnification × 25). B) Tumor cells are strongly positive for CD138 (IHC,
original magnification x 25). C) Monoclonal κappa light chain is strongly
positive in the plasma cells (IHC: original magnification × 25).
Serum protein electrophoresis with immunofixation identified an immunoglobulin G kappa monoclonal gammopathy (monoclonal spike [M-spike]: 3.8g/dl) and a free kappa protein band. The serum kappa free light chain was slightly elevated at 37.88mg/l (normal range: 3.30-19.4 mg/l), with the serum lambda free light chain within normal range at 7mg/l (normal range: 5.71-26.30 mg/l). The beta-2 microglobulin level was at 9.5mg/L (normal range: 0.7-1.8 mg/l) and serum albumin at 31g/l (normal range: 35-50 g/l).
The patient was diagnosed with multiple myeloma with extramedullary localization in the cervical, mediastinal and abdominal lymph nodes, corresponding to clinical stage IIIA in the Durie & Salmon staging system and clinical stage III in the International Staging System of myeloma.
Unfortunately, the patient died before we could propose appropriate treatment.
Discussion
The extramedullary (EMD) disease shows to be more and more common over the past decade, with 7% to 18% of patient with MM had extramedullary disease (EMD) according to the different studies [2], which simply could be explained, in one hand, by the fact that sensitive imaging techniques such as CT scan, MRI and Pet scan become more affordable and accessible over years [2] and in the other hand by the prolonged survival of patient with multiple myeloma [6].
The infiltration of lymph nodes by plasma cell tumors could be a result of primary lymph node plasmacytomas where there must be no evidence of plasma cell proliferation elsewhere, and no associated malignant lymphoma components [7].
Alternatively, lymph nodes could be involved in the extramedullary spreading of myeloma [8].
The EMD involvement of lymph nodes is more frequently detected in autopsies than in living patient [9]. The reason why could be explained by the lack of symptoms in the most cases [2].
The patient whom case we are reporting had fever and arthralgia associated with high erythrocyte sedimentation rate that led to further investigation, which revealed cervical, mediastinal and abdominal lymphadenopathy by computed tomography, after which a diagnosis was established based on the results of the biopsies.
Conclusion
To conclude, multiple myeloma could have several clinical faces and it is always important to remember that we should never say never especially when you are in front of unusual clinical presentation, which have to push clinician to be more suspicious and double effort to optimally detect extramedullary disease.
References
- Joan Bladé, Carlos Fernández De Larrea and Laura Rosiñol. Extramedullary Involvement in Multiple Myeloma. Haematol. 2012; 97: 1618-1619.
- Zeljko Todorovic1, Milena Jovanovic, et al. Extramedullary Involvement of Lymph Nodes in Multiple Myeloma. Ser J Exp Clin Res. 2017; 18: 257-261.
- Alexiou C, Kau Rj, Dietzfelbinger H, Kremer M, Spiess Jc, Schratzenstaller B, et al. Extramedullary Plasmacytoma: Tumor Occurrence And Therapeutic Concepts. Cancer. 1999; 85: 2305-2314.
- Galieni P, Cavo M, Pulsoni A, Avvisati G, Bigazzi C, Neri S, et al. Clinical Outcome of Extramedullary Plasmacytoma. Haematologica. 2000; 85: 47-51.
- Wu P, Davies Fe, Boyd K, Thomas K, Dines S, Saso Rm, et al. The Impact of Extramedullary Disease at Presentation on the Outcome of Myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009; 50: 230-235.
- Varettoni M, Corso A, Pica G, Mangiacavalli S, Pascutto C, Lazzarino M. Incidence, Presenting Features And Outcome Of Extramedullary Disease In Multiple Myeloma: Longitudinal Study On 1,003 Consecutive Patients. Ann Oncol. 2009; 21: 325-330.
- Soutar R, Lucraft H, Jackson G, Reece A, Bird J, Low E, et al. Guidelines On The Diagnosis And Management Of Solitary Plasmacytoma Of Bone And Solitary Extramedullary Plasmacytoma. Br J Haematol. 2004; 124: 717-726.
- Menke Dm, Horny Hp, Griesser H, Tiemann M, Katzmann Ja, et al. Primary Lymph Node Plasmacytomas (Plasmacytic Lymphomas). Am J Clin Pathol. 2001; 115: 119-126.
- Kazama T, Ng Cs, Giralt Sa. Multiphasic Ct And Mri Appearances Of Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Involving The Stomach, Pancreas, And Bladder. Clin Imaging. 2005; 29: 263-265.