
Case Report
Austin J Clin Case Rep. 2021; 8(4): 1204.
Gingival Tumor in Young Female Patient: A Case Report
Rithul P¹, Rao PK¹*, Kini R¹ and Gonsalvis N²
¹Oral Medicine & Radiology, A.J Institute of Dental Sciences, Karnataka, India
²Oral Pathology, A.J Institute of Dental Sciences, Karnataka, India
*Corresponding author: Dr. Prasanna Kumar Rao, Oral Medicine and Radiology, A.J Institute of Dental Sciences, NH 66, Kuntikana, Mangaluru 575004, Karnataka, India
Received: March 15, 2021; Accepted: March 31, 2021; Published: April 07, 2021
Abstract
Pyogenic granuloma is one of the inflammatory hyperplasias seen in the oral cavity. This term is a misnomer because the lesion is unrelated to infection and in reality arises in response to various stimuli such as low-grade local irritation, traumatic injury or hormonal factors. Clinically, oral pyogenic granuloma is a smooth or lobulated exophytic lesion manifesting as small, red erythematous papules on a pedunculated or sometimes sessile base, which is usually hemorrhagic. The surface ranges from pink to red to purple, depending on the age of the lesion Conservative surgical excision is usually curative but recurrence is not unusual. Lasers and cryotherapy may also be employed.
Keywords: Pyogenic granuloma; Pregnancy; Oral cavity; Inflammatory reactive hyperplasia
Introduction
Pyogenic Granuloma (PG) is a kind of inflammatory hyperplasia. The term “inflammatory hyperplasia” is used to describe a large range of nodular growths of the oral mucosa that histologically represent inflamed fibrous and granulation tissues [1]. It includes fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia (clinical fibroma, epulis fissuratum, and pulp polyp), palatal papillary hyperplasia, giant cell granuloma, pregnancy epulis and Pyogenic granuloma [2]. Pyogenic granuloma is a common tumor-like growth of the oral cavity or skin that is considered to be non-neoplastic in nature. Occurrence of pyogenic granuloma in man was first described in 1897 by Poncet and Dor. At that time, it was called botryomycosis hominis. Pyogenic granuloma has been referred to by a variety of other names such as granuloma pediculatum benignum, benign vascular tumor, pregnancy tumor, vascular epulis, Crocker and Hartzell’s disease. It was given its present name by Crocker in 1903 [3]. However, some researchers believe that Hartzell in 1904 introduced the term “pyogenic granuloma” that is widely used in the literature, although, it does not express accurately the clinical or histopathologic features [4]. The name pyogenic granuloma is a misnomer since the condition is not associated with pus and does not represent a granuloma histologically. It is a reactive inflammatory process filled with proliferating vascular channels, immature fibroblastic connective tissue, and scattered inflammatory cells. The surface usually is ulcerated, and the lesion exhibits a lobular architecture.
Case Presentation
A 16 year old female patient came to the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology with complains of pain in relation to the upper right back teeth region since three months. Patient was apparently normal one-year back then she noticed growth, it was small in size and progressive to present size. She had history of pain while chewing and during brushing and also bleeding on touch. Patient had undergone treatment for the same since one-year back and they excised the lesion completely. On extraoral examination reveals Gross asymmetry noted. Swelling seen over of size approximately 2*1.5 cm extending superiorly from right ala of the nose to the upper lip and mediolaterally from the midline to the corner of the lip. Extension of a growth seen on the right side corner of the mouth, pink in colour. (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Patient profile with right facial asymmetry.
On clinical examination well defined swelling seen on the maxillary region in relation to the 12 and 13 size of approximately 3x2 cm. It was reddish pink in color with oval shape, surface was smooth and surrounding area appears normal. On palpation swelling was afebrile, bleeding present on touch, varying consistency noticed, soft in consistency in relation to the base region (12 and 13 region) and firmer in consistency in relation to the lobulated margin. Swelling was pedunculated in nature (Figure 2). Chair side investigation diascopy was done and it shows negative result. Based on the clinical examination provisional diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma in relation to 22 and 23 is given. Excision biopsy was done. Histopathological features shows proliferation of vascular channel with ulcerated area and it reveals it to be pyogenic grnuloma in relation to 22 and 23 region (Figure 3 & 4).
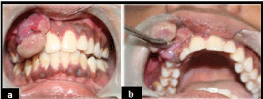
Figure 2: Shows two lobulated soft tissue masses in relation to maxillary right
lateral incisor and canine. (a and b).
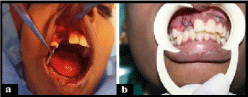
Figure 3: Shows after excision of lesion with removal of maxillary right lateral
incisor and canine.

Figure 4: Histopathological features shows proliferation of vascular channel
with ulcerated area under 40x.
Discussion
Pyogenic Granuloma (PG) is a kind of inflammatory hyperplasia. The term “inflammatory hyperplasia” is used to describe a large range of nodular growths of the oral mucosa that histologically represent inflamed fibrous and granulation tissues [2]. It includes fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia (clinical fibroma, epulis fissuratum, and pulp polyp), palatal papillary hyperplasia, giant cell granuloma, pregnancy epulis and Pyogenic granuloma [1]. Pyogenic granuloma is a common tumor-like growth of the oral cavity or skin that is considered to be non-neoplastic in nature [5]. Hullihen’s description in 1844 was most likely the first Pyogenic granuloma reported in English literature, but the term “pyogenic granuloma” or “granuloma pyogenicum” was introduced by Hartzell [6] in 1904. Although it is a common disease in the skin, it is extremely rare in the gastrointestinal tract, except for the oral cavity where it is often found on keratinized tissue. There are two kinds of Pyogenic granuloma namely Lobular Capillary Hemangioma (LCH type) and non-LCH type, which differ in their histological features [7].
Pyogenic Granuloma (PG) occurs in patients of all ages with a peak incidence in the second and third decades of life [3]. In children, the average age at diagnosis is 6 to 10 years and there is a predilection for males. Mucosal Pyogenic granuloma is more common in adult women than in men or children. About 2% of pregnant women develop an intraoral Pyogenic granuloma in the first five months of pregnancy [4]. Gingiva was the predominant site followed by lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, and hard plate. Other sites were the cheek, lips, tongue, palate, mucobuccal fold, and frenum [8].
The exact aetiopathogenesis of oral pyogenic granuloma is not known. At present it is regarded as an endothelial proliferation of unknown cause. pyogenic granuloma as an “infectious” entity. Kerr has reported staphylococci and botryomycosis, foreign bodies, and localization of infection in walls of blood vessel as contributing factors in the development of the lesion [8]. Regezi et al. suggested that pyogenic granuloma is caused by a known stimulant or injury such as calculus or foreign material within the gingival crevice resulting in exuberant proliferation of connective tissue.
Pyogenic Granuloma is a smooth or lobulated exophytic lesion manifesting as small, red erythematous papules on a pedunculated or sometimes sessile base, which is usually hemorrhagic and compressible [9] and may develop as dumb-bell-shaped masses. However, Epivatianos et al. reported that the two types of PG were clinically different. They found that LCH PG occurred more frequently (66%) as a sessile lesion, whereas non-LCH PG mostly occurred as pedunculated (77%). The size varies in diameter from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Rarely does Pyogenic granuloma exceed 2.5 cm in size and it usually reaches its full size within weeks or months, remaining indefinitely thereafter [10]. Clinical development of the lesion is slow, asymptomatic and painless but it may also grow rapidly. The surface is characteristically ulcerated and friable which may be covered by a yellow, fibrinous membrane and its color ra because they are composed predominantly of hyperplastic granulation tissue in which capillaries are prominent. Thus minor trauma to the lesion may cause considerable bleeding, due to its pronounced vascularity, whereas older lesions tend to become more collagenized and pink. Rarely, Pyogenic granuloma may cause significant bone loss [11].
Microscopic examination of Pyogenic granuloma shows a highly vascular proliferation that resembles granulation tissue. Numerous small and large channels are formed which are engorged with red blood cells and lined by banal flat 170 or plump endothelial cells that may be mitotically active. The blood vessels often show a clustered or medullary pattern separated by less vascular fibrotic septa, leading some authorities to consider Pyogenic granuloma as a polypoid form of capillary hemangioma or nothing more than an inflamed lobular hemangioma; others prefer to use the term granulation tissue-type hemangioma. Some pathologists require these vessels, which are sometimes organized in lobular aggregates, for diagnosis (lobular capillary hemangioma) [12]. At low magnification, particularly at the lateral edges, a lobular arrangement is noted wherein groups of capillaries proliferate but abruptly stop. Each lobule is surrounded by a thin collagen layer. This arrangement is disrupted at the base, where irregularly shaped larger vascular channels reside and presumably communicate with the proliferation. It is here that some anastomosing channels (resembling angiosarcoma) can occasionally be identified, but they are focal rather than an integral part of the lesion. At higher magnification, another discriminating feature of benign vascular lesion is found: the small capillary endothelial-lined spaces are themselves surrounded by a perithelial or pericytic layer of cells. This double layer of cells, also seen in intramuscular angiomatosis, is not seen in the clonal angiosarcoma [13].
Radiographic findings are usually absent. However, that in some cases long standing gingival pyogenic granulomas caused localized alveolar bone resorption. Differential diagnosis of pyogenic granuloma includes peripheral giant cell granuloma, peripheral ossifying fbroma, fbroma, peripheral odontogenic fbroma, hemangioma, conventional granulation tissue, hyperplastic gingival inflammation, Kaposi’s sarcoma, bacillary angiomatosis, angiosarcoma, and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice. After surgical excision of gingival lesions, curettage of underlying tissue is recommended. Excision with 2 mm margins at its clinical periphery and to a depth to the periosteum or to the causative agent. Any foreign body, calculus, or defective restoration should be removed as part of the excision. Nevertheless, prognosis for intra-oral pyogenic granulomas is good. Satisfactory outcome has been reported with Laser therapy and Cryosurgery for oral pyogenic granulomas. Interestingly, multiple recurrences of intraoral pyogenic granuloma have been reportedly treated with intra-lesional corticosteroids [14]. Incomplete excision, failure to remove etiologic factors or repeated trauma contributes to recurrence of these lesions. No recurrence in cases treated by surgical excision [15] but few studies observed a recurrence rate of 5.8% [16].
Conclusion
Although pyogenic granuloma is a non-neoplastic growth in the oral cavity, proper diagnosis, prevention, management and treatment of the lesion are very important. Pyogenic granuloma arises in response to various stimuli such as lowgrade local irritation, traumatic injury, sex hormones or certain kinds of drugs, so removal of causative irritants (plaque, calculus, foreign materials, and source of trauma) is the major line of treatment. Excisional surgery is the treatment of choice for pyogenic granuloma.
References
- Greenberg MS, Glick M. Burket’s oral medicine: diagnosis and treatment. 10th edition, BC Decker, Hamilton. 2003; 141-142.
- Eversole LR. Clinical outline of oral pathology: diagnosis and treatment. 3rd edition, BC Decker, Hamilton. 2002; 113-114.
- Bhaskar SN, Jacoway JR. Pyogenic granuloma - clinical features, incidence, histology, and result of treatment: Report of 242 cases. J Oral Surg. 1966; 24: 391-398.
- Angelopoulos AP. Pyogenic granuloma of the oral cavity: Statistical analysis of its clinical features. J Oral Surg. 1971; 29: 840-847.
- Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Oral & maxillofacial pathology. 2nd edition, WB Saunders, Philadelphia. 2002; 437-495.
- Hartzell MB. Granuloma pyogenicum. J Cutan Dis Syph. 1904; 22: 520-525.
- Fowler EB, Cuenin MF, Thompson SH, Kudryk VL, Billman MA. Pyogenic granuloma associated with guided tissue regeneration: a case report. J Periodontol. 1996; 67: 1011-1015.
- Ainamo J. The effect of habitual toothcleansing on the occurrence of periodontal disease and dentalcaries. Suom Hammaslaak Toim. 1971; 67: 63-70.
- Regezi JA, Sciubba JJ, Jordan RCK. Oral pathology: clinical pathologic considerations. 4th edition, WB Saunders, Philadelphia. 2003; 115-116.
- Epivatianos A, Antoniades D, Zaraboukas T, Zairi E, Poulopoulos A, Kiziridou A, et al. Pyogenic granuloma of the oral cavity: comparative study of its clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features. Pathol Int. 2005; 55: 391-397.
- Mills SE, Cooper PH, Fechner RE. Lobular capillary hemangioma: the underlying lesion of pyogenic granuloma. A study of 73 cases from the oral and nasal mucous membranes. Am J Surg Pathol. 1980; 4: 470-479.
- Fechner RE, Cooper PH, Mills SE. Pyogenic granuloma of the larynx and trachea. A causal and pathologic misnomer for granulation tissue. Arch Otolaryngol. 1981; 107: 30-32.
- Sternberg SS, Antonioli DA, Carter D, Mills SE, Oberman H. Diagnostic surgical pathology. 3rd ed, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia. 1999; 69: 174.
- Parisi E, Glick P, Glick M. Recurrent intraoral pyogenic granuloma with satellitosis treated with corticosteroids. Oral Dis. 2006; 12: 70-72.
- Lawoyin JO, Arotiba JT, Dosumu OO. Oral pyogenic granuloma: A review of 38 cases fromIbadan, Nigeria. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 35: 185-189.
- Al-Khateeb T, Ababneh K. Oral Pyogenic granuloma in Jordanians: A retrospective analysis of 108 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61: 1285- 1288.