
Case Report
Austin J Clin Case Rep. 2022; 9(7): 1267.
Cholecystitis in Young Age due to Cholesterolosis: A Case Report Study
Chinifroush Asl M¹ and Nabighadim M²*
¹Assistant Professor of Pathology, Medical School, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran
²Medicinestudent, Medical School, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran
*Corresponding author: Mahsan Nabighadim, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran
Received: November 01, 2022; Accepted: November 24, 2022; Published: December 01, 2022
Abstract
Cholesterolosis of the gallbladder is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol esters and triglycerides in macrophages on the surface of the gallbladder wall, as well as hyperplasia of the mucous villi. As cholesterolosis and acute cholecystitis are uncommon in young people and can result in complications. We will present a case of cholecystitis caused by cholesterolosis in a young woman in order to illustrate how to diagnose and treat such a case and differentiate it from other causes. The patient was a 21-year-old married woman who complained of upper abdominal discomfort (stomachache). She reported experiencing intermittent pains for approximately two months, which were intensifying and radiating to her side and shoulder. Cholesterolosis was identified through an abdominal ultrasound. After undergoing cholecystectomy and spending two days in the hospital, the patient was discharged.In the sample sent to pathology, the final diagnosis of acute or chronic cholecystitis with villous metaplastic mucosal change & cholosterlosis was given. Cholesterolosis is a benign condition andlaparoscopic cholecystectomy is an effective treatment for it. Ultrasound and cholecystectomy are typically used for diagnosis. Given the rarity of this condition in young people, physicians should consider it and apply an effective treatment procedure.
Keywords: Cholecystitis; Strawberry gallbladder; Cholesterol; Cholesterolosis; Ardabil; Iran
Introduction
Cholesterolosis of the gallbladder, also known as strawberry gallbladder, is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol esters and triglycerides in macrophages on the surface of the gallbladder wall, as well as hyperplasia of the mucous villi. The gallbladder can be affected as a polypoid or diffuse form. This condition is identified in a small number of cholecystectomy specimens [1-3]. Cholesterolosis is occasionally associated with symptoms and complications similar to those caused by gallstones; however, there is no correlation between the development of cholesterolosis and the risk factors associated with gallstone formation [4]. Acute cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease of the gallbladder that can occur alongside chronic cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, diverticulitis, colitis, and appendicitis [5,6]. It may cause complications such as perforation of the gallbladder (biliary peritonitis), necrosis and abscesses around the gallbladder, and internal biliary fistula [7]. Acute cholecystitis is rare among young individuals. However, it is one of the most common conditions requiring emergency abdominal surgery in older adults [8]. As cholesterolosis and acute cholecystitis are uncommon in young people and can result in complications, we will present a case of cholecystitis caused by cholesterolosis in a young woman in order to illustrate how to diagnose and treat such a case and differentiate it from other causes.
Case Presentation
The patient was a 21-year-old married woman who complained of upper abdominal discomfort (stomachache). She reported experiencing intermittent pains for approximately two months, which were intensifying and radiating to her side and shoulder. Cholesterolosis was identified through an abdominal ultrasound. After undergoing cholecystectomy and spending two days in the hospital, the patient was discharged.
In the pathology report of the specimen obtained from cholecystectomy, the macroscopic signs are as follows: RIF, consist of a previously opened greenish colored gall bladder, M:6.5 ×2.5 ×1.5 cm with velvety greenish colored internal mucosa & 2-4 mm thickness of the wall; SOS=4/1 E=10%. Also, the microscopic signs are as follows: Section show intermittent congested atrophic & villous metaplastic changed mucosa with moderately lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and focal foamy aggregation with vascular congestion through full wall thickness. Rocky-tanskey-aschoffsinuses are also noted (Figure 1).
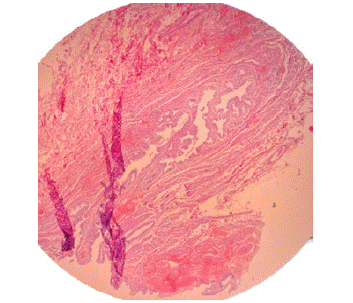
Figure 1: Cholecystitis with villous metaplastic mucosal change & cholosterlosis.
Discussion
In the present study, we introduced a young woman who underwent cholecystectomy due to cholesterolosis and acute or chronic cholecystitis. This is a rare case among young people and primarily affects older individuals [8,9]. A similar case report [10] described a 20-year-old woman who complained of right hypochondrial pain and was clinically diagnosed with cholecystitis despite the absence of any risk factors. She underwent an elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy and recovered without complication after the procedure. The histopathological examination revealed cholesterolosis and chronic calcific cholecystitis [11]. Cholesterolosis is asymptomatic and benign and can occur alone or in conjunction with gallstones. Ultrasound and cholecystectomy are typically used for diagnosis [12,13]. The primary microscopic characteristic of cholesterolosis is the presence of fat-filled macrophages in the villi, which causes these hyperplastic villi to swell and form small yellow nodules under the epithelium. In approximately two-thirds of cases, they cause diffuse cholesterolosis and give mucus a grainy appearance, whereas one-third of cases involve larger nodes with a polypoid appearance [3,14]. Cholesterolosis could be effectively treated with laparoscopic cholecystectomy [15].
In a study of patients who underwent cholecystectomy for chronic cholecystitis, the authors discovered that the incidence of cholesterolosis was higher among those with metabolic syndrome, dyslipoproteinemia and chronic pancreatitis. According to them, cholesterolosis is accompanied by alterations in the blood vessels of all layers of the gallbladder wall (in endothelial cells and pericytes of both large and microcirculatory vessels), as well as redistribution of blood in the circulatory system, arteries, and veins. Moreover, it is sometimes significantly associated with the spread of stasis symptoms. Changes in the dystrophic endothelium result in edema, bleeding, and, eventually, the development of sclerotic processes [16]. No correlations have been found between blood cholesterol level, gallbladder ejection fraction, gender and age distribution, and gallbladder cholesterolosis development [2,9,16]. Cholesterolosis is not linked to acute inflammation, but it is linked to metaplasia. Routine histopathological examination is very important. Surgeons must carefully interpret histopathology reports containing unusual or exceptional cholecystectomy specimen findings [17].
In a cross-sectional study of the results of histopathological examinations of the gallbladder caused by cholecystectomy for cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis was found to be the most prevalent pathological finding, followed by cholesterolosis of the gallbladder. In addition, there was a significant correlation between cancer presence, age over 60, and wall thickness of 0.3 cm [9].
Cholecystitis is a collection of diseases with varying etiologies, severities, clinical courses, and management strategies. Care for a patient with gallbladder disease necessitates a comprehensive understanding of acute and chronic cholecystitis syndromes as well as an awareness of potential complications [18].
During the first two to four days after cholecystitis, also known as the edematous cholecystitis stage; congestion and edema are prominent symptoms. Necrotizing cholecystitis characterized by hemorrhage and necrosis, develops within 3-5 days. The disease reaches its purulent stage, also known as purulent cholecystitis, within 7 to 10 days. If not treated at this stage, the disease will progress to subacutecholecystitis and then chronic cholecystitis [7]. In the majority of cases, laparoscopic cholecystectomy performed within three days of diagnosis is the first line of treatment for acute cholecystitis [19].
Conclusion
Cholesterolosis is a benign condition for which laparoscopic cholecystectomy is an effective treatment. Ultrasound and cholecystectomy are typically used for diagnosis. Given the rarity of this condition in young people, physicians should consider this condition and apply an effective treatment procedure.
Patient Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient.
References
- Jacyna M, Bouchier I. Cholesterolosis: a physical cause of” functional” disorder. British Medical Journal (Clinical research ed). 1987; 295: 619-620.
- Dairi S, Demeusy A, Sill AM, Patel ST, Kowdley GC, Cunningham SC. Implications of gallbladder cholesterolosis and cholesterol polyps?. Journal of surgical research. 2016; 200: 467-72.
- Zakko WF, Zakko SF. Gallbladder polyps and cholesterolosis. Monografía en Internet] UpToDate[Consultado en Diciembre 2014] Disponible en. 2013.
- Il’chenko A, IuN O. Cholesterosis of the gallbladder: review of literature. Eksperimental’naia i Klinicheskaia Gastroenterologiia. Experimental & Clinical Gastroenterology. 2003; 155: 83-90.
- Kim SW, Kim HC, Yang DM, Won KY, Moon SK. Cystic duct enhancement: a useful CT finding in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis without visible impacted gallstones. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2015; 205: 991-8.
- Jones MW, Genova R, O’Rourke MC, Carroll C. Acute Cholecystitis (Nursing). 2021.
- Adachi T, Eguchi S, Muto Y. Pathophysiology and pathology of acute cholecystitis: A secondary publication of the Japanese version from 1992. Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sciences. 2022; 29: 212-6.
- Escartín A, González M, Cuello E, Pinillos A, Muriel P, Merichal M, et al. Acute Cholecystitis in Very Elderly Patients: Disease Management, Outcomes, and Risk Factors for Complications. Surgery research and practice. 2019; 2019: 9709242.
- Holanda AKG, Lima ZB. Gallbladder histological alterations in patients undergoing cholecystectomy for cholelithiasis. Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes. 2020; 46.
- Irct201604084613N. The impact of mother education on Maternal Self Efficacy and Newborn Discharge Preparation. http://wwwwhoint/trialsearch/ Trial2aspx?TrialID=IRCT201604084613N19. 2016. PubMed PMID: CN- 01843771.
- Soundrapandian F, Durairaj B, Kashyap AR, Jose R. Strawberry gallbladder: a case report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2016; 5: 1313-5.
- Cocco G, Basilico R, Delli Pizzi A, Cocco N, Boccatonda A, D’Ardes D, et al. Gallbladder polyps ultrasound: what the sonographer needs to know. Journal of Ultrasound. 2021; 24: 131-42.
- Damore LJ, Cook CH, Fernandez KL, Cunningham J, Ellison EC, Melvin WS. Ultrasonography incorrectly diagnoses gallbladder polyps. Surgical Laparoscopy Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques. 2001; 11: 88-91.
- Feldman M, Feldman Jr M. Cholesterosis of the gallbladder: an autopsy study of 165 cases. Gastroenterology. 1954; 27: 641-8.
- Gamal A K, Salman Y G, Khalid R M. Cholesterolosis: incidence, correlation with serum cholesterol level and the role of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. 2004; 25: 1226-8.
- Petrushenko V, Grebeniuk D, Liakhovchenko N, Gormash P. Gallbladder cholesterolosis in patients with metabolic syndrome and chronic pancreatitis. Reports of Morphology. 2021; 27: 58-65.
- Yaylak F, Deger A, Ucar BI, Sonmez Y, Bayhan Z, Yetisir F. Cholesterolosis in routine histopathological examination after cholecystectomy: What should a surgeon behold in the reports? International Journal of Surgery. 2014; 12: 1187-91.
- Elwood DR. Cholecystitis. Surgical Clinics of North America. 2008; 88: 1241- 52.
- Gallaher JR, Charles A. Acute Cholecystitis: A Review. JAMA. 2022; 327: 965-75.