Clinical Image
Austin J Clin Ophthalmol. 2018; 5(1): 1087.
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Peau D’orange and Angioid Streaks
Lin M1,2,3 and Anesi SD1,2*
1Massachusetts Eye Research and Surgery Institution, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA
2Ocular Immunology and Uveitis Foundation, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA
3State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China
*Corresponding author: Stephen D. Anesi, 1440 Main Street, Suite 201 Waltham, MA 02451, USA
Received: February 08, 2018; Accepted: March 05, 2018; Published: March 22, 2018
Clinical Image
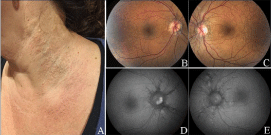
A 43-year-old lady with pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) presented for fundus exam. Her parents noticed rash-like lesions on the side of her neck when she was 9-years-old. She was diagnosed with PXE by skin biopsy. Genetic analysis revealed autosomal recessive mutation in the ABCC6 gene. She was followed yearly as a child, and diagnosed with angioid streaks as a teenager. Physical exam showed small, yellowish papular lesions and cutaneous laxity mainly affecting the neck (A). Color fundus photography showed “peau d’orange” appearance involving Bruch’s membrane just posterior to the retina in both eyes (B and C) (Figure 1). Angioid streaks, linear breaks in Bruch’s membrane seen better on fundus auto fluorescence, radiated out from the optic nervewithout involving the fovea (D and E). She has been followed for over 30 years without need for treatment. Skin lesions progressed slowly. Vision remains unaffected, but she continues to be followed for possible secondary neovascularization.