
Research Article
Austin J Clin Pathol. 2015; 2(3): 1037.
Co-Overexpression Myc and Bcl-2 Predicts Inferior Survival in Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Wirian ML1,2, Yao M1,2, Xu X1,2, Chen K1,2, Hu L1,2, Feng Y2,3, Huang H1,2, Huilanrao2,3 and Cai Q1,2*
1Department of Medical Oncology and Cancer Center, University of Sun Yat-sen, China
2Department of State Key Laboratory of Oncology, University of Sun Yat-Sen, China
3Department of Pathology and Cancer Center, University of Sun Yat-sen, China
*Corresponding author: Cai Q, Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Center and State Key Laboratory of oncology, University of Sun YatSen, China
Received: November 03, 2015; Accepted: November 19, 2015; Published: November 25, 2015
Abstract
Background: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is found in 5–10% of all non- Hodgkin’s lymphomas. It is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma whose molecular pathogenesis is translocation t (11;14) (q13;q32), resulting in constitutive over-expression of cyclin D1 and subsequent dysregulation of the cell cycle. However, Cyclin D1 overexpression alone is not sufficient to trigger lymphoma genesis. Oncogenic such as MYC and BCL-2 are also involved in developing spontaneous lymphomas. In this study, we assessed the correlation between over expressions of Myc and Bcl-2 proteins with survival in MCL patients to aid in risk-stratification for MCL management.
Materials and Methods: We determined the expression of Myc and Bcl-2 proteins by Immunohistochemistry (IHC). The expression of Myc and Bcl-2 was correlated with clinicopathologic characteristics in MCL patients.
Results: In our study (n = 34), Myc and Bcl-2 proteins were detected in 29% and 47% of patients, respectively. Concurrent expression (Myc positive/Bcl-2 positive) was present in 20% of all patients. No correlation between Myc protein expression and Ki-67 proliferation index was found in our study (Spearman’s = 0.223, P = 0.206). Myc protein overexpression was associated with inferior Overall Survival (OS) and Progression-Free Survival (PFS) when Bcl-2 protein was co-over expressed (both P-values are 0.002). Moreover, high Myc score affect both OS and PFS of MCL patients while Bcl-2 score is only shown as a predictive factor for OS.
Conclusion: Co-overexpression of Myc and Bcl-2 predicts inferior survival in MCL. Assessment of Myc and Bcl-2 expression by IHC represents a robust, rapid, and inexpensive approach to risk-stratifying patients with MCL at diagnosis.
Keywords: Mantle cell lymphoma; Myc; Bcl-2; Co-overexpression; Survival
Introduction
Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) is an aggressive B-cell Non- Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) that originates from the follicular center of lymph nodes, accounting for 5%-10% of the NHL. Its molecular pathogenesis is partially attributed to the characteristic genetic feature of translocation t (11;14) (q13;q32), which leads to the overexpression of cyclin D1 and dysregulation of the cell cycle [1]. The clinical manifestation of MCL is invasive, and its prognosis is poor [2]. Although most of the first-line treatments are effective, the response duration is short and there is no standard treatment strategy for MCL [3].
MYC gene is a group of cancer genes first found in Burkitt’s Lymphoma (BL), consisting of C-MYC, N-MYC, and L-MYC, which are located on chromosome 8, chromosome 2 and chromosome 1, respectively. It can be activated by chromosomal translocation, mostly through the translocation of chromosome 2, chromosome 22 and chromosome 14. In some studies, it was found that Myc was also abnormally expressed in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and other B cell lymphomas [4].
The members of Bcl-2 gene family can be divided into two major categories. One is an anti-apoptotic group, mainly including Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, Bcl-W, Mcl-1, CED9, et al., the other is the apoptotic type, mainly including Bax, Bak, Bcl-Xs, Bad, Bik, Bid, et al., These genes play a vital role in the process of cell apoptosis. Bcl-2, as a negative regulator of cell death, can protect cells from apoptosis when there is an external stimulation. Over-expression of Bcl-2 directs cells to avoid apoptosis and continue proliferating in the Germinal Center (GC) [5,6].
Cyclin D1 overexpression alone is not sufficient to trigger lymphoma genesis. Oncogenic such as MYC and BCL-2 are involved in developing spontaneous lymphomas [7]. Double-hit B-cell lymphoma is defined as a B-cell lymphoma associated with chromosomal breaks targeting the MYC gene located at chromosome 8q24 in combination with additional rearrangements affecting another gene, such as BCL2 or BCL6.With the availability of anti-Myc antibodies suitable for IHC staining in paraffin-embedded tissues, Green et al., and Johnson et al. showed that DLBCL patients with Myc/Bcl-2 co expression have a poorer prognosis with or without MYC or BCL-2 gene rearrangements [8,9]. Oberley et al., showed that Myc protein expression is independently predictive of clinical outcomes in MCL [10].
In this study, we used IHC to assess the prognostic value of Myc and Bcl-2expression, and particularly Myc/Bcl-2 co-expression. We also evaluated the possibility of using Myc and Bcl-2 protein expression level as a new prognostic index for MCL patients.
Materials and Methods
Case selection
With approval from the Ethics Committee, the pathologic archives of the Sun YatSen University Cancer Center were searched for cases of MCL diagnosed from January 2000 to December 2013. Cases were included if patients were pathologically diagnosed with MCL, older than 18, initially treated, had available Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue, and had complete clinical data and follow-up information. 34 patients were identified to have archival FFPE tissues from pre-treatment diagnostic biopsies and fulfilled the selection requirements.
Immunohistochemical staining and quantification
For Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of Myc, Bcl-2and Ki-67 expressions in the MCL tissue, 4 μm-thick sections from each Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue block were deparaffinized with xylem and rehydrated through a graded series of alcohol. Antigen retrieval was achieved by autoclaved 3 min at 121°C. Anti-Myc, anti-Bcl-2andanti-Ki-67 (ZSGB-Bio Company, Beijing, China) is used for primary antibodies staining. After incubation with the primary antibodies, the ChemMateTMDAKOEVisionTM+/ HRP/DAB Rb and Mok it was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sections were counterstained with haematoxylin and then mounted. Myc and Ki-67expression showed a distinct nuclear pattern with no background cytoplasmic staining, whether Bcl-2 expression exhibited a cytoplasmic pattern. The positive tumor cells were stained yellow-brown or brown.
Statistical analysis
Normality distribution test was used to determine the distribution of MYC and Bcl-2 IHC results. Spearman test was used to evaluate the relation between Myc and Ki-67 index [11]. Progression Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS) were assessed by the Kaplan-Meier method and life table, while log rank test was used for comparison. Prognostic factors for PFS and OS were analyzed by multivariate analysis. All tests were two-sided. Statistical significance was set at P <0.05. The SPSS statistics 21.0 was used for all analyses.
Results
Patient characteristics
The clinical and pathological features of 34 cases are listed in (Table 1). The median follow-up time of this cohort was 75 months (95 % CI: 25-125 months). All 34 patients received combined chemotherapy regimen, mostly CHOP and CHOP-like regimens. Patients included in this study were treated with relative similarity: 79% received frontline rituximab-containing chemotherapy regimens.
Clinical characteristics
n
Percentage (%)
gender
male
30
88
female
4
12
age
≤ 60
18
53
> 60
16
47
B symptom
yes
17
50
no
17
50
Serum LDH level
< 245 U/L
26
76
≥ 245 U/L
8
24
IPI score
Low risk
4
12
Low-intermediate risk
15
44
High-intermediate risk
15
44
MIPI score
Low risk
23
68
Intermediate risk
9
26
High risk
2
6
Spleen involvement
yes
11
32
no
23
68
Estranodal involvement
yes
22
65
no
12
35
Bone marrow involvement
yes
7
21
no
27
79
Ann Arbor stage
II
5
15
III
10
29
IV
19
56
Treatment
Frontline rituximab-containing polychemotherapy
27
79
Table 1: Clinical characteristics of 34 MCL patients.
Assessment of MYC, Bcl-2 and Ki-67 staining
The proportion of positive Myc tumor cells in MCL cases ranged from 1% to 30%, with a median of 8%; the proportion of Bcl-2 positive tumor cells ranged from 0 to 95%, with a median of 80%; and the proportion of positive Ki-67 tumor cells ranged 3-90%. Normality distribution test was used to examine if the MYC and Bcl-2 IHc results were continuous. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test showed P<0.05, which indicates that the variables were non-normal distribution. Based on this, we chose median values as the cut-off values, 8% for Myc and 80% for Bcl-2 (Figure 1).
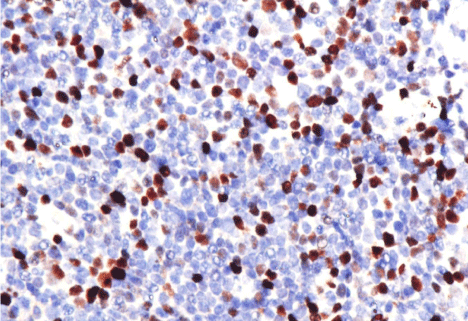
Figure 1: A, 20% positive cells of MYC protein x 400. B, 3% positive cells
of MYC protein x 400. C, 90% positive cells of BCL-2 protein x 400. D, 60%
positive cells of BCL-2 protein x 400.
Relation myc with Ki-67 proliferation index
Using Spearman test, we evaluated the correlation between Myc protein expression and Ki-67 proliferation index. Results showed that ρ=0.223, P=0.206. Thus, we conclude that the expression level of Myc protein was not associated with Ki-67 proliferation index.
Myc and/or Bcl-2 protein expression predicts poor prognosis in MCL
Using median values of 8% and 80% as the cut-off values for Myc and Bcl-2, respectively, 29% were positive for Mycover-expresssion (Myc>8%) and 47% were positive for Bcl-2over-expresssion (Bcl- 2>80%) (Table 2). Concurrent over-expression (Myc>8%/Bcl- 2>80%) was present in 20% of 34 patients.
Pathologic result
n
Percentage(%)
Type
Blastic
3
9
Pleomorphic
2
6
Classic
29
85
MYC
MYC >8%
10
29
MYC ≤8%
24
71
Bcl-2
Bcl-2 >80%
16
47
Bcl-2 ≤80%
18
53
Table 2: Immunohistochemical staining of 34 MCL patients.
In the Cox regression model used to analyze prognostic factors, we got MYC protein expression less than 8% can be used as predictor factor for both PFS and OS (all P values less than 0.05, respectively), whether BCL-2 protein expression less than 80% only can be used as predictor factor for OS (P value less than 0.05) (Table 3). Myc and Bcl-2 protein co-overexpression (>8%, >80%, respectively) in MCL had adverse impact on patient survival (Figure 2) (Table 3). The 5-year Overall Survival (OS) and the 5-year Progression-Free Survival (PFS) of MCL patients with Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression were 18 months (P=0.002) and 14 months (P=0.002), respectively, which were the shortest among all patients (Figure 2). The results also showed that Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression was an adverse prognostic factor for OS (P<0.05) (Table 3). When assessed separately, patients with Mycor Bcl-2over-expression in MCL had significantly inferior OS and PFS (Figure 2) compared with patients with Myc <8% or Bcl-2 <80%. The Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the patients whose Myc protein expression was more than 8% had shorter PFS (14 months vs 48 months, P<0.000) and shorter OS (25 months vs. 75 months, P=0.040) (Figure 2). Similarly, patients whose Bcl-2 protein expression was more than 80% had shorter PFS (17 months vs. 48 months, P=0.030) and shorter OS (25 months vs. 84 months, P=0.006) (Figure 2).
PFS
OS
HR
95%CI
P
HR
95%CI
P
Male (men)
0.361
0.073 - 1.780
0.210
0.889
0.096 - 8.199
0.917
Age (≤60)
0.835
0.169 - 4.115
0.824
0.049
0.005 - 0.531
0.013
B symptoms (+)
1.474
0.480 - 4.522
0.498
2.941
0.283 - 30.536
0.366
Serum LDH level (<245U/L)
0.530
0.061 - 4.595
0.565
0.027
0.001 - 0.524
0.017
MIPI (low risk)
7.801
1.456 - 41.795
0.016
34.228
3.255 - 359.973
0.003
Spleen involvement (–)
2.666
0.802 - 8.857
0.110
11.559
0.986 - 135.487
0.051
Extranodal involvement(+)
1.124
0.355 - 3.556
0.843
0.456
0.059 - 3.541
0.453
Bone marrow involvement(–)
0.354
0.080 - 1.556
0.169
0.127
0.009 - 1.708
0.120
Ann Arbor stage (IV)
0.450
0.093 - 2.185
0.322
0.050
0.004 - 0.684
0.025
MYC> 8% & Bcl-2 >80%
2.401
0.621 - 9.278
0.204
79.143
5.608 - 1116.977
0.001
Table 3: Multivariate analysis of 5 year PFS and OS.
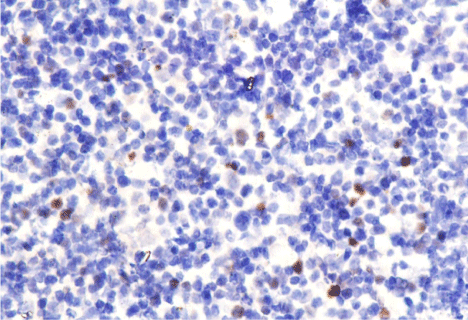
Figure 2: A-B, Progression-free survival and overall survival based on the
Myc protein expression in patients with MCL. C-D, Progression-free survival
and overall survival based on the Bcl-2 protein expression in patients with
MCL. E-F, Progression-free survival and overall survival based on the Myc
and Bcl-2 protein expression in patients with MCL.
Discussion
In this study, we show that patients with MCL characterized by Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression have a poor clinical outcome. Myc/ Bcl-2 co-overexpression is an adverse prognostic factor for OS. Approximately 20% of 34 MCL cases demonstrated Myc/Bcl-2 cooverexpression in our study. A study by Hu et al. reported that Myc/ Bcl-2 co-expression is more common in Activated B-Cell (ABC) type DLBCL and is associated with a poor prognosis [12]. Study by Chloe et al., showed that Myc overexpression is a negative predictor of MCL patient outcomes [13]. This is the first study that depicted the prognostic significance of Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression in MCL patients.
Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma whose molecular pathogenesis is partly attributed to the characteristic feature of t (11;14) (q13;q32), resulting in the translocation of protooncogene CCND1, overexpression of cyclin D1 and subsequent dysregulation of the cell cycle [7,14-16]. Although gene translocation and cyclin D1 overexpression play a vital role in MCL lymphoma genesis, several clinical observations have indicated that these mechanisms may not be sufficient for the transformation of the cells and aggressive behavior of the tumor. Initial studies on cultured rat cells show that cyclin D1 may function as an oncogene, but its oncogenicity and transforming activity are less effective than other oncogenes [17,18]. Transgenic mice in which cyclin D1 was linked to Ig gene regulatory elements did not spontaneously develop lymphomas. Lymphoma genesis in these models required cooperation with other oncogenes such as MYC or BCL-2. The abnormality of BCL-2 can is found in up to 70%-95% of Follicular Lymphoma (FL). This translocation leads to unusual overexpression of Bcl-2 protein in Germinal Center (GC) during the differentiation of normal B cells [8,16,19-21]. Translocations and amplifications of the MYC gene and over-expression of Myc RNA can be found in 40% of MCL patients and are associated with a poor clinical outcome [17,22]. In the study of Oberley et al., they assessed the expression of Myc protein in MCL patients, and they reported that the protein expression was associated with poor prognosis and survival rates. Recent studies have reported that over-expression of Myc and Bcl-2 proteins are found not only in BL and FL, but also in other B-cell lymphoma subtypes such as Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), B Cell Lymphoma Unclassifiable (BCLU), and MCL [8,19-21]. These gene aberrations cause aggressive clinical behaviors, drug resistance, and poor prognosis, indicating that abnormality of Myc is only partially the reason for cell proliferation. Therefore, we hypothesize that Myc and Bcl-2 may cooperate to develop MCL. Immunohistochemical staining is a simple, accurate and reproducible method [10,23]. Oberley et al., and previous studies have confirmed that immunohistochemical assessment of Myc protein expression in MCL can be reliably performed and is predictive of clinical outcomes [8,10,12]. Our study also used the same methods to evaluate Myc and Bcl-2 protein expression level, and whether they had an impact on prognosis and survival rates [8,10,12,23].
The thirty-four tissues of pre-treatment MCL patients showed the positive Myc tumor cells in range from 0 to 30% and positive Bcl-2 tumor cells in range from 0 to 95%. At present, there is still no standard cut-off value for positive Myc expression. In DLBCL, some literature reported that the cut-off value of 40% of the nuclear Myc expression can be considered as positive [23]. Cognizant that the number of MCL cases in our study was insufficient to establish a reliable cut-off value, according to the studies of Oberley [10] and Shimin Hu [12], we performed an unbiased dichotomization of the cases at the median as the cut-off point: Myc>80% and Bcl-2>8% for positive expression [10,12]. There were 29% of patients with Myc protein expression more than 8%, 47% of patients with Bcl-2 protein expression more than 80%. The cut-off point was lower than that of previous studies reported. The discrepancy may be a consequence of the differences in age, disease stage, MIPI score, and other clinical characteristics of the patients [10,12].
Genetic rearrangement of B-Cell Lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) could be found in 70-95% of FL patients. Continuous expression of Bcl-2 can be found in B-lymphoma cells with BCL-2 rearrangement. Visco et al., found that 60 patients (18.3%) out of 327 DLBCL patients had a BCL-2 mutation, and the presence of Bcl-2 was associated with GCB subtype, aggressive-phase and significantly shorter PFS. High expression of Bcl-2 protein was significantly correlated with shorter PFS (P=0.01) and OS (P=0.02). In our study, the PFS (17 months vs. 48 months) and OS (25 months vs. 84 months) were significantly shortened in patients with Bcl-2 protein expression over 80% (P<0.05). In the study by Oberley et al. [10], multivariate analysis demonstrated that the expression level of Myc protein was an independent prognostic factor for prognosis. Patients with higher Myc protein expression level had shorter PFS and OS. A study by Shimin Hu et al. [12], of DLBCL found that patients with positive Myc or Bcl-2 had shorter PFS and OS, particularly those with co-expression of Myc and Bcl- 2. Based on IPI score, co-expression of Myc and Bcl-2 still had an impact on prognosis. Similarly, in our study, Cox regression analysis showed that co-overexpression of Myc and Bcl-2 proteins could be used as a predictor of OS, and the expression level of Myc protein could be used as a predictive factor for PFS. Patients with Myc protein expression higher than 8% had a shorter median PFS (14 month vs. 48 months). Patients with Bcl-2 protein expression higher than 80% had shorter median PFS (17 month vs. 48 months) and OS (25 months vs. 84 months). We further combined Myc and Bcl-2 protein expression level as prognostic factors and the results showed that 7 patients with Myc/Bcl-s co-overexpression had the shortest PFS (14 months, P=0.002) and OS (18 months, P=0.002). Our results demonstrated that MCL with Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression is a unique subset of MCL with dismal clinical outcome. The potential molecular basis behind the dismal outcome may be seen through the role of Myc and Bcl-2 proteins and their unknown confounding effect.
Myc protein is a transcription factor associated with high Ki-67 proliferation index [7,15,22,24,25]. Using Spearman test, we found that Myc protein expression and Ki-67 proliferation index was not significantly correlated (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient ρ= 0.223, P = 0.206). This is in consistent with the study of Oberley [10], in which they found that there was a weak correlation between Myc protein expression and Ki-67 proliferation index. This indicates that in MCL, the proliferation of tumor cells is not only due to the carcinogenic effect of MYC gene, but also due to another mechanism such as inhibiting the apoptosis pathway mediated by TP53 [26,27]. Likewise, the discrepancy of Ki-67 proliferation index, Myc protein expression and morphological changes were also observed in DLBCL patients [11,28-30].
Other features that can be used as prognostic factors were LDH level, MIPI score, bone marrow and spleen involvement, which is in consistent with the previous studies of MCL and DLBCL [10,12,21].
In conclusion, MCL with Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression characterizes a subset of MCL patients with poor prognosis in our study. MCL with Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression expands the spectrum of Myc/Bcl-2 double-hit B-cell lymphoma defined genetically. However, it should be emphasized that MCL with Myc/Bcl-2 co-expression are not equivalent to Myc/Bcl-2 double-hit B-cell lymphoma. Gene arrangement in MYC and Bcl-2 are not common in other B-cell lymphoma subtypes. Oberley et al., investigated the association between Myc over expression and MYC gene rearrangement using FISH, and remarkably found that none of the 57 MCL cases showed evidence of MYC rearrangement [10]. Additional molecular abnormalities may involve in these double-expression lymphomas. Further study is needed to explore the mechanisms for Myc/Bcl-2 co-overexpression in other B-cell lymphoma subtypes. A larger cohort study is also warranted to confirm the potential cut-off value for risk-stratification and the relationship between Myc/Bcl-2 protein and Ki-67 index in MCL.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.81372883), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2015A030313020), Young Talents Project of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (to Cai Qingqing), Young Talents Key Project of Sun Yat-sen University (2015ykzd13, to Cai Qingqing), and the Sister Institution Network Fund of MD Anderson Cancer Center (to RaoHuilan).
References
- Campo E, Rule S. Mantle cell lymphoma: evolving management strategies. Blood. 2015; 125: 48-55.
- Räty R, Franssila K, Jansson SE, Joensuu H, Wartiovaara-Kautto U, Elonen E. Predictive factors for blastoid transformation in the common variant of mantle cell lymphoma. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39: 321-329.
- Iqbal J, Naushad H, Bi C. Genomic signatures in B-cell lymphoma: how can these improve precision in diagnosis and inform prognosis? Blood Rev. 2015.
- Cai Q, Medeiros LJ, Xu X, Young KH. MYC-driven aggressive B-cell lymphomas: biology, entity, differential diagnosis and clinical management. Oncotarget. 2015.
- Kroemer G. The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat Med. 1997; 3: 614-620.
- Iqbal J, Neppalli VT, Wright G. BCL2 expression is a prognostic marker for the activated B-cell–like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24: 961-968.
- Jares P, Colomer D, Campo E. Genetic and molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma: perspectives for new targeted therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7: 750-762.
- Johnson NA, Slack GW, Savage KJ. Concurrent expression of MYC and BCL2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30: 3452-3459.
- Green TM, Young KH, Visco C. Immunohistochemical double-hit score is a strong predictor of outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30: 3460-3467.
- Oberley MJ, Rajguru SA, Zhang C. Immunohistochemical evaluation of MYC expression in mantle cell lymphoma. Histopathology. 2013; 63: 499-508.
- Klapper W, Hoster E, Determann O. Ki-67 as a prognostic marker in mantle cell lymphoma—consensus guidelines of the pathology panel of the European MCL Network. J Hematop. 2009; 2: 103-111.
- Hu S, Xu-Monette ZY, Tzankov A. MYC/BCL2 protein co expression contributes to the inferior survival of activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and demonstrates high-risk gene expression signatures: a report from The International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Blood. 2013; 121: 4021-4031.
- Choe JY, Yun JY, Na HY. MYC overexpression correlates with MYC amplification or translocation, and is associated with poor prognosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Histopathology. 2015.
- Jares P, Colomer D, Campo E. Molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122: 3416.
- Pérez-Galán P, Dreyling M, Wiestner A. Mantle cell lymphoma: biology, pathogenesis, and the molecular basis of treatment in the genomic era. Blood. 2011; 117: 26-38.
- Conacci-Sorrell M, McFerrin L, Eisenman RN. An overview of MYC and its interactive. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014; 4: a014357.
- Hernandez L, Hernandez S, Bea S. C-myc mRNA expression and genomic alterations in mantle cell lymphomas and other nodal non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Leukemia. 1999; 13: 2087-2093.
- Slack GW, Gascoyne RD. MYC and aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Adv Anat Pathol. 2011; 18: 219-228.
- Arcinas M, Heckman CA, Mehew JW, Boxer LM. Molecular mechanisms of transcriptional control of bcl-2 and c-myc in follicular and transformed lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2001; 61: 5202-5206.
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000; 403: 503-511.
- Savage KJ, Johnson NA, Ben-Neriah S. MYC gene rearrangements are associated with a poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP chemotherapy. Blood. 2009; 114: 3533-3537.
- Aukema SM, Siebert R, Schuuring E. Double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2011; 117: 2319-2331.
- Petrich AM, Nabhan C, Smith SM. MYC‐associated and double‐hit lymphomas: A review of pathobiology, prognosis, and therapeutic approaches. Cancer. 2014; 120: 3884-3895.
- Caballero D, Campo E, López-Guillermo A. Clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Recommendations from the GEL/TAMO Spanish Cooperative Group. Ann Hematol. 2013; 92: 1151-1179.
- Gladden AB, Woolery R, Aggarwal P, Wasik MA, Diehl JA. Expression of constitutively nuclear cyclin D1 in murine lymphocytes induces B-cell lymphoma. Oncogene. 2006; 25: 998-1007.
- Tomita N. BCL2 and MYC dual-hit lymphoma/leukemia. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011; 51: 7-12.
- Dominguez-Sola D, Victora GD, Ying CY. The proto-oncogene MYC is required for selection in the germinal center and cyclic reentry. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13: 1083-1091.
- Calado DP, Sasaki Y, Godinho SA. The cell-cycle regulator c-Myc is essential for the formation and maintenance of germinal centers. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13: 1092-1100.
- Determann O, Hoster E, Ott G. Ki-67 predicts outcome in advanced-stage mantle cell lymphoma patients treated with anti-CD20 immunochemotherapy: results from randomized trials of the European MCL Network and the German Low Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2008; 111: 2385-2387.
- Visco C, Tzankov A, Xu-Monette ZY. Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of germinal center origin with BCL2 translocations have poor outcome, irrespective of MYC status: a report from an International DLBCL rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Haematologica. 2013; 98: 255-263.