
Short Communication
Austin J Clin Trials Open Access. 2018; 1(1): 1001.
Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery through Manubrium Sparing Mini-Sternotomy
Alat I* and Celik E
Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Afyonkarahisar State Hospital, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Alat I, Afyonkarahisar Devlet Hastanesi, Nedim Helvacioglu Bulvari, Kalp ve Damar Cerrahisi Servisi, Afyonkarahisar, Turkey
Received: August 07, 2018; Accepted: September 20, 2018; Published: September 27, 2018
Abstract
The importance of off-pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) surgery through manubrium sparing mini-sternotomy was presented in this article under the light of previous literature and our own technique was mentioned on the basis of an operated case. Off pump CABG surgery with manubrium sparing mini-sternotomy is a plausible choice of surgical treatment for the suitable patients and leads to fast recovery in the postoperative period due to lesser surgical trauma. All of these outcomes will result in the lower cost of hospitalization and higher patient’s satisfaction.
Keywords: Coronary; Sternal; Bypass; Cardiac surgery; Incision; Quality of life
Introduction
Coronary artery bypass surgery which has been changing and progressing very rapidly since 1960s, has come to a point that could not be foreseen at the onset of its history. While in those days, the questions which techniques and which grafts need to be used couldn’t be duly answered [1] and much earlier, in 1910, while Alexis Carrel reported a negative report that would discourage other surgeons to perform this surgery [2], whereas today’s surgeons are now pursuing the questions of what the smallest incision is, how much little invasive it is, and how much cheap and successful the coronary bypass surgery can be done. For example, robotically assisted minimally invasive coronary bypass surgeries are no longer a freak for anyone [3].
On the other hand, when considering the increasing population rate and increasing number of patients today, it is also important that any surgical method has to be as cost effective as less invasive. From this point of view, it is a bit of imagination to hope that the robotic surgeries will become widespread all around the world. The biggest obstacle in this regard is the equipment, requiring high cost and therefore only a limited number of surgeons can have sufficient experience in this area.
For all these reasons, the main objective should be to develop and disseminate surgical methods that are less invasive than open heart surgery but less expensive than robotic surgery.
In this article, we aimed to present our technique in which it’s possible to do smaller skin incision with the sparing of manubrium.
The Short Communication on the Basis of a Patient
When the literature is reviewed, it is possible to see different alternative surgical methods including mini-sternotomy in the surgical treatment of different cardiac diseases in order to achieve this aim. Alternative incisions for aortic or mitral valve diseases, proximal aortic aneurysms or dissections, coronary artery diseases, some congenital heart diseases or some mandatory applications due to special conditions like tracheal stoma can be seen [4-10].
Among these applications, we hereby want to especially present our surgical method on the basis of one of our patients by comparing it to the report [6] of Su and coworkers. According to the report of Su and coworkers, they developed a new surgical method, which is an off-pump coronary artery bypass approach with lower distal ministernotomy (TM-OPCAB) for multivessel coronary revascularization. They compared two different groups to each other. The first group underwent TM-OPCAB and the second group underwent Standard Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (S-OPCAB).
After completing their research, they found significantly shorter periods on ventilation, shorter postoperative in-hospital stays and lower blood transfusion rates in the group of TM-OPCAB. In order to measure graft patency rates, they measure transit-time flow measurement and they observed that there was no significant difference in postoperative graft patency between both groups. They also analyzed that overall survival, the percentage of patients freed from major adverse cardiac, and cerebrovascular events were similar between both groups. When compared to the results of S-OPCAB patients, these successful results including postoperative clinical superiorities of the TM-OPCAB patients resemble the results of previous articles in the literature about mini-sternotomy or other minimal invasive coronary bypass surgeries.
These successful results are due to two different subjects: Offpump surgery instead of open-heart surgery and secondly, the length of the skin incision like an indicator for invasion.In their method for the patients in the TM-OPCAB group, an approximately 14cm midline skin incision was made. The mean length of the skin incision in the patients in the TM-OPCAB group was 15.0cm and 22.6cm in the S-OPCAB group.
Precisely at this point, we herein want to present one of our patients who underwent off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery through a mini-sternotomy incision, and want to mention about the difference of our surgical technique.
A 67-year-old male patient underwent off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting surgery through mini-sternotomy incision for single- vessel coronary artery disease in our center (Left Internal Thoracic Artery (LITA) to left anterior descending coronary artery). The operation was planned and performed by the first author (IA) of this article. As seen in (Figure 1) which was taken in his postoperative period, the skin incision was only 9cm. Total length of his sternum is 23cm as seen between the index fingers of the nurse in the same photograph.
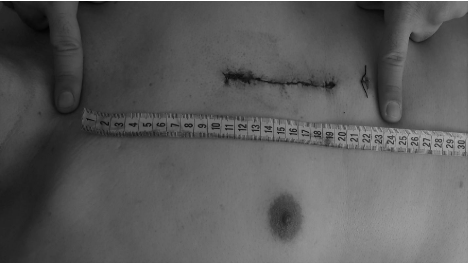
Figure 1: A postoperative photograph of our patient who underwent off-pump
coronary artery bypass grafting surgery through a mini-sternotomy incision.
Please note that the length of the incision is only 9cm. It would be a 23-cmlength
incision, if his sternum was totally incised as indicated by the index
fingers of the nurse.
When compared our skin incision to the skin incisions in the Su’s work, they completed their TM-OPCAB operations through 15cm mean skin incision while it is only 9cm in our patient. In another words, according to their report they had an average sternum length of 22cm, they completed their operation by doing 66% ([15/22.6] × 100 = 66) of total sternal skin incision. In our patient, the skin incision was 9 cm and the operation was completed by doing 39% ([9/23] × 100 = 39) of total sternal skin incision. It is obvious that there is a meaningful difference between 66% and 39%. It might be thought at first that the difference between the percentages of skin incisions are related to the numbers of the bypassed vessels: one patient had threevessel- surgery but the other patient had only single vessel surgery. However, we think that the difference is related to our technique, not the numbers of the vessels.
In order to explain this, firstly we should understand that there are three main factors that affect the length of the mini-sternotomy skin incision in off-pump coronary surgery:
1- The location of the coronary stenotic lesions, which are being planned to be bypassed.
2-Needs for ascending aorta as being the location for proximal anastomoses.
3-To be able to reach the proximal end of LITA (with the division of the first intercostal artery).
It is a classical knowledge that - if the patient is suitable for an off-pump coronary surgery- the problems in item 1 and 2 can be overcome with a “C” or “upside down or reverse L or J” mini-sternal incision. This is same for all kind of operations and independent from the numbers of the vessels. So, it can be said that the most influential factor for the length of skin incision is the need to reach the root of LITA. In our patient, it was achieved by means of cutting a cartilaginous rib and then it was sewed with a steel wire at the end of the operation. In order to reach the proximal root of the LITA, cutting of the cartilaginous rib which is preventing your harvesting can be an enough solution. At the end of the operation, it can be sewed. By means of this application, unnecessary sternal incisions can be prevented. In addition, it is not necessary to make an incision on the skin as much as the sternal incision. We believe that the main reason for the difference between the lengths of the incisions is related to these technical differences. To the best of our knowledge, without using video assisted or robotically assisted methods or instruments, for preventing the excessive lengthening of sternotomy incision, the addition of cutting a rib while harvesting LITA to the ministernotomy incision in an off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting surgery is new in the literature. It is believe that this manuscript will encourage the cardiac surgeons for doing smaller incisions in their patients.
Moreover, when considered the positive notification in the guidelines [11-13] about the off-pump CABG surgery and minimally invasive CABG surgery in regard to reduced hospital stay and costs and improved patient satisfaction with better aesthetic results, it seems that the future of the off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery through manubrium sparing mini-sternotomy is bright. However, it is obvious that the accumulated knowledge and experience by multicenter studies are needed in this area.
Conclusion
Manubrium sparing off-pump coronary bypass grafting surgery leads to not only better esthetical results but also lesser trauma of the whole body of the patient due to lesser invasive procedural applications. These outcomes result in the decreasing of the cost of the operation and the increasing of the patient satisfaction. It is believe that this manuscript will encourage the surgeons to develop smaller incisions to get the same successful results.
References
- Konstantinov IE. The first coronary artery bypass operation and forgotten pioneers. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997; 64: 1522-1523.
- Rocha EAV. Fifty years of coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2017; 32: II-III.
- Cook RC, Fung AY, Percy ED, Mayo JR. A novel approach using computed tomography angiograms to predict sternotomy or complicated anastomosis in patients undergoing robotically assisted minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass. Innovations (Phila). 2018; 13: 207-210.
- Choi JB, Yang HW, Han JO, Choi SH. Manubrium-sparing median sternotomy as a uniform approach for cardiac operations. Tex Heart Inst J. 2000; 27: 3 2-6.
- Abjigitova D, Panagopoulos G, Orlov O, Shah V, Plestis KA. Current trends in aortic root surgery: The mini-Bentall approach. Innovations (Phila). 2018; 13: 91-96.
- Su P, Gu S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Yan J, An X, et al. Off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting with mini-sternotomy in the treatment of triple-vessel coronary artery disease. Int Heart J. 2018; 59: 474-481.
- Sabzi F, Faraji R, Kazeminasab M. Minimal invasive technique in atrial septal defect surgery. Cardiol Res. 2018; 9: 90-93.
- Farhat F, Metton O, Jegaden O. Benefits and complications of total sternotomy and ministernotomy in cardiac surgery. Surg Technol Int. 2004; 13: 199-205.
- Carrozzini M, Bejko J, Guariento A, Rubino M, Bianco R, Tarzia V, et al. Minimally invasive implantation of continuous flow left ventricular assist devices: the evolution of surgical techniques in a single centre experience. Artif Organs. 2018.
- Ricci M, Salerno TA, Houck JP. Manubrium-sparing sternotomy and off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with tracheal stoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000; 70: 679-680.
- Hillis LD, Smith PK, Anderson JL, Bittl JA, Bridges CR, Byrne JG, et al. ACCF/AHA Guideline for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2011; 124: e652-735.
- Patel MR, Calhoon JH, Dehmer GJ, Grantham JA, Maddox TM, Maron DJ, et al. ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS, Appropriate Use Criteria for Coronary Revascularization in Patients With Stable Ischemic Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Heart Association, American Society of Echocardiography, American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 69: 2212-2241.
- Neumann FJ, Sousa-Uva M, Ahlsson A, Alfonso F, Banning AP, Benedetto U, et al. ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur Heart J. 2018; 25.