Abstract
In addressing the global challenge of rural healthcare delivery, this study highlights fundamental principles and strategies to enhance accessibility and outcomes. The study found that understanding rural communities’ socio-cultural, economic, and geographic nuances is the first step for public health specialists to adapt their methods effectively. Community engagement fosters trust and active participation, reducing health inequities. Interdisciplinary teamwork involving doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and community health workers amplifies healthcare delivery’s reach and effectiveness. Telemedicine and technology offer remote areas access to high-quality healthcare, with telemedicine, electronic health records, and mobile apps enabling consultations and information exchange. Customised health education programs empower rural communities by raising awareness and promoting prevention, reducing preventable diseases through improved health literacy. Implementable strategies include mobile clinics for remote access, rural hubs for expert consultations, and incentives to sustain a rural healthcare workforce. Collaborations between governments, businesses, and NGOs ensure comprehensive rural healthcare. Data-driven policy decisions optimise resource allocation and healthcare efficiency. A holistic approach grounded in contextual awareness, community engagement, and technological innovation is vital for rural healthcare improvement. Public health practitioners can enhance rural health outcomes by applying these concepts and strategies.
Keywords: Health care; Health outcome; Public health; Rural posting
Introduction
Rural healthcare delivery is integral to global public health practices [40,61,62]. However, it frequently presents unique challenges necessitating specialised approaches and strategic planning. To address healthcare disparities experienced by rural populations, rural posting deploying healthcare professionals to remote areas to provide essential services is critical. In this comprehensive examination, we explore the principles and strategies that underpin successful rural postings within the realm of public health practices.
Geographical isolation, inadequate infrastructure, limited healthcare resources, and a shortage of healthcare personnel often characterise rural areas. Consequently, rural residents face barriers to accessing healthcare services, increasing morbidity rates and exacerbating healthcare disparities. Rural posting is vital to address these issues, ensuring that underserved communities receive the healthcare they require and deserve.
In many developing countries, clinical experience in rural settings is integral to medical education. This practice aims to train medical students and equip them to meet the healthcare needs of rural populations. The primary purpose of rural posting is to acquaint medical students with the challenges and realities of delivering healthcare in rural areas, fostering a sense of social responsibility and dedication to supporting underserved communities.
Typically, rural postings have set durations, ranging from several weeks to months, depending on the medical school's curriculum and policies. Students are usually assigned to work in rural healthcare institutions, such as rural hospitals, clinics, or health centres, often located in remote or underserved regions, limiting residents' access to medical care.
Additionally, medical students gain valuable clinical experience by diagnosing and treating patients under the guidance of experienced healthcare professionals during rural placements [12]. They encounter various medical conditions, including those more prevalent in rural areas, such as infectious diseases and injuries related to agricultural work. Moreover, students actively engage with the local community, learning about its people, culture, customs, and the social determinants influencing rural populations' health. This engagement offers a comprehensive understanding of rural healthcare systems and emphasises the significance of interdisciplinary teamwork in healthcare delivery [68].
Furthermore, rural postings significantly influence students' career choices. Exposure to rural healthcare during training often leads students to pursue careers in rural or underserved areas upon graduation [78]. In some developing countries, government-sponsored programs offer scholarships or preferential job placements in rural areas, encouraging medical students to consider rural postings [70].
Rotating through rural settings is an indispensable component of the education for medical students in developing nations. It makes students aware of rural populations' unique challenges and healthcare needs, nurturing a sense of social responsibility and contributing to the training of a healthcare workforce better equipped to serve underserved communities. This paper focuses on the principles and strategies of public health practices during rural postings.
Principles of Rural Posting in Public Health Practice
Regarding public health practices, rural posting is guided by a few essential ideas that strive to serve rural communities' healthcare requirements successfully [2]. These guiding principles help guarantee that healthcare professionals are adequately trained to work in rural areas and contribute to the general improvement of the health and well-being of communities in rural areas. The following are the fundamental tenets of rural posting in the context of public health practices (Figure 1).
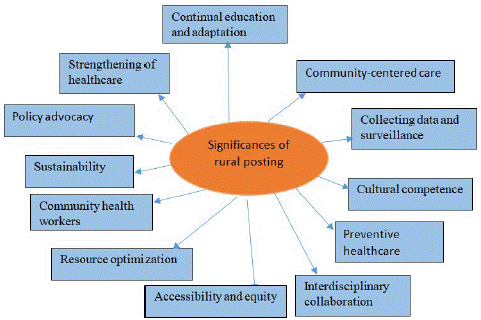
Figure 1: Principles of rural posting in public health practice.
Accessibility and Equity
Rural health postings aim to increase accessibility and equity in medical care [18]. To fulfil the medical requirements of underserved communities and lessen the gaps in access to medical services, healthcare professionals are being relocated to more rural locations.
Community-Centred Care
Care that is centred on the community is given top priority by public health professionals stationed in rural areas [36]. This encourages community engagement and participation. They collaborate closely with local communities to understand the members' requirements, priorities, and values, and they involve community members in the decision-making process and activities that promote health. A thorough awareness of the community's needs and objectives should be the foundation for any rural position. To create and implement programs and interventions that are pertinent and successful, public health experts should collaborate closely with community people and leaders [7].
Cultural Competence
Medical professionals working in rural areas are expected to demonstrate cultural competence by respecting the customs, traditions, and beliefs of the populations they serve [67]. They should also be aware of rural communities' unique challenges, such as poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and geographic isolation. By speaking with residents and leaders, reading books and articles about rural culture, and visiting cultural events, public health professionals can gain knowledge about the cultural norms and traditions of rural areas. They can create therapies and programs that are culturally relevant with the aid of this understanding [58,65,66]. These contribute to the development of trust and make for more effective communication.
Preventive Healthcare
Healthcare focusing on preventing illness rather than treating it is called preventive healthcare. Preventive healthcare techniques include health education, vaccination drives, and early disease detection. Rural public health approaches focus primarily on disease prevention and promoting healthy lifestyle choices and behaviours.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Rural health teams sometimes include professionals from various fields, such as physicians, registered nurses, workers in public health, nutritionists, and social workers. Professionals from these fields must work together to handle complex health challenges comprehensively. Furthermore, rural posting is most effective when it is done in collaboration with regional institutions and groups [84]. Public health professionals should collaborate with community health centres, hospitals, schools, and other institutions to offer complete and integrated services [9]. Thus, public health experts can collaborate with regional businesses and institutions by creating collaborative programs and initiatives, pooling resources, and cross-training employees. By doing this, it may be possible to guarantee that communities receive complete and integrated services.
Resource Optimization
Because of the limited resources that are frequently present in rural locations, medical professionals who work in these settings need to learn how to make the best possible use of the available resources. They may need to modify their strategies to fit the local environment and get inventive to compensate for the lack of resources [39,59,60].
Strengthening of Healthcare Infrastructure
Public health professionals in rural areas frequently play a part in developing a more robust healthcare infrastructure [31]. This includes raising the quality of laboratory and diagnostic services and improving the standard of healthcare facilities in rural areas.
In modern medicine, the laboratory diagnosis of diseases is paramount, employing a wide array of techniques to identify pathogens, anomalies, and disease-specific markers. These techniques encompass various categories such as hematology (including complete blood counts and blood chemistry) [5,6,22-28], microbiological tests (including culture and sensitivity, as well as Gram staining), molecular biology techniques, serological tests, histopathology, imaging studies, flow cytometry, electrocardiograms, urinalysis, and toxicology screens. The choice of which test to employ is contingent upon the suspicion of a particular disease, the patient's presenting symptoms, and the treatment considerations at hand. Healthcare professionals utilize these diverse techniques in combination to ensure precise disease diagnoses and the formulation of effective treatment strategies.Additionally, this includes guaranteeing a steady supply of vital medications.
Community Health Workers
Rural health postings need to make use of the expertise and experience of community health workers [1]. Typically drawn from the local community, these workers assist with health education and outreach activities. Their role is to act as a bridge between medical experts and the community.
Collecting Data and Conducting Surveillance
Monitoring and responding to health trends and outbreaks in rural regions requires gathering and conducting surveillance [79]. Data should be used to inform decision-making and prioritise health interventions, and healthcare providers should do so.
Sustainability
Sustainability is an important consideration that needs to be considered while designing rural health programs. By educating local staff, creating local financing sources, and increasing community capacity, public health professionals can endeavour to create sustainable programs and interventions [75]. This can aid in ensuring that initiatives and programs carry on after public health specialists have left.
Continual Education and Adaptation
Public health professionals in rural areas should be willing to engage in lifelong education and be flexible enough to modify their practices in response to shifting demographics and evolving conditions. In the field of rural healthcare, adaptability is essential for success.
Policy Advocacy
Policy Advocacy Healthcare providers in rural areas may be able to enhance rural healthcare systems by engaging in policy advocacy to address structural concerns [76]. They are in a position to push for additional financing, improved infrastructure, and policies that are helpful on both the regional and national levels.
Strategies of Rural Posting in Primary Health Care
Rural posting in primary healthcare in developing countries requires specific strategies to address rural populations' unique healthcare needs and challenges effectively. These strategies aim to provide comprehensive, accessible, quality healthcare services in rural areas. The strategy for rural posting in primary healthcare are summarised in Figure 2.
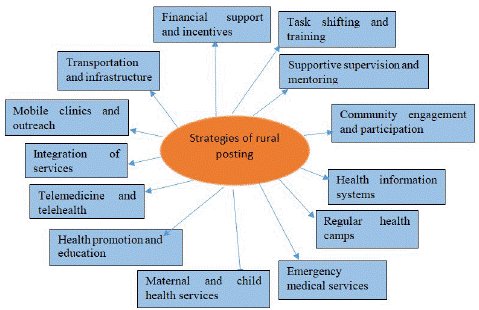
Figure 2: Strategies of rural posting in primary health care in developing country.
Community Engagement and Participation
Community engagement and participation during rural healthcare assignments in public health practice refer to involving local communities in healthcare initiatives and decision-making, particularly in underserved rural areas [29]. This involvement is of particular significance in rural contexts. It entails collaborative efforts with community members, leaders, and organizations to plan, execute, and evaluate public health programs and interventions tailored to the specific needs and preferences of the community [13]. This approach fosters a sense of partnership and shared responsibility, ultimately leading to more effective and sustainable public health interventions in rural regions. Thus, the local communities of the area's indigenous people are involved in healthcare decision-making. Establishing community health committees or councils to provide input and guidance on healthcare priorities is essential [51]. Furthermore, Regular community meetings to gather feedback and ensure services of the rural posting align with local needs and preferences.
Mobile Clinics and Outreach
Mobile Clinics and Outreach in Rural Public Health encompass strategies and services designed to provide healthcare in remote or underserved regions where access to medical facilities is limited [77]. These approaches are particularly significant in rural areas, where inadequate infrastructure can hinder healthcare access. Consequently, these methods play a crucial role in rural public health practice by surmounting geographical barriers and ensuring that even the remotest communities have access to essential medical services and health education. Mobile clinics and various outreach initiatives are pivotal in reducing health disparities and enhancing overall health outcomes in rural areas [80]. Therefore, regular health camps and outreach programs provide healthcare services directly to rural communities.
Task Shifting and Training
In public health, concepts and practices such as Task Shifting and Training in Rural Posting are crucial in enhancing healthcare delivery in underserved or remote areas. Task Shifting involves reassigning specific healthcare tasks and responsibilities from highly specialized professionals, like doctors or nurses, to healthcare workers or community health workers with lower levels of training but adequate skills for these tasks [30]. This approach becomes particularly valuable in rural regions with limited access to highly trained healthcare professionals. By utilizing healthcare workers with suitable skills, task shifting optimizes the use of available personnel, facilitates healthcare access in remote areas, and is especially effective for tasks that don't require advanced medical expertise.
Training in Rural Posting pertains to the targeted training and education provided to healthcare professionals or community health workers assigned to serve in rural or remote locations [21]. This training encompasses specialized fields such as rural medicine, emergency care, telemedicine, or health conditions prevalent in rural populations. Its objective is to equip healthcare providers with the knowledge and skills necessary to address rural communities' unique healthcare challenges and needs [87]. Additionally, training programs may incorporate cultural sensitivity training to help healthcare workers better understand and effectively serve the local population.
These strategies are instrumental in rural public health as they bridge the healthcare gap in areas where highly specialized professionals may be scarce [20]. By implementing task shifting and offering specialized training, healthcare services can be efficiently and effectively delivered to rural populations, leading to improved health outcomes and increased access to care in these underserved regions.
Telemedicine and Telehealth
Telemedicine and telehealth are innovative healthcare delivery methods that leverage technology to provide medical services and information to individuals situated at a distance, offering particularly valuable solutions in public health roles within rural settings where access to conventional healthcare facilities and specialized healthcare providers may be limited [50].
Telemedicine is a specific practice within telehealth that focuses on delivering clinical consultations, diagnosis, treatment, and post-treatment care through various communication technologies, such as secure messaging, videoconferencing, and remote monitoring tools [55]. It allows healthcare professionals to provide medical care to patients in remote areas without necessitating physical visits to healthcare facilities. Telemedicine encompasses direct patient-provider interactions as well as the transmission of medical data and images to enable remote diagnosis and treatment planning [17].
Telehealth, on the other hand, is a broader category encompassing a wide array of methods for disseminating healthcare information and services [10]. It goes beyond clinical care and includes health promotion, the remote monitoring of vital signs, and administrative tasks associated with healthcare management. In the context of rural public health, telehealth initiatives can involve the use of mobile health applications for tracking and managing chronic conditions, facilitating online discussion boards, conducting webinars on health-related topics, and offering continuing education opportunities both in person and online [42].
Both telemedicine and telehealth are instrumental in rural public health settings as they enhance healthcare access, eliminate geographical barriers, and ensure that individuals residing in remote areas receive timely and appropriate medical care and support. These technologies are indispensable tools for addressing the healthcare disparities faced by underserved rural communities [73]. They signify the use of electronic communication technologies to provide healthcare services within each respective domain, playing pivotal roles in closing the healthcare gap in rural regions with limited access to medical professionals.
Health Promotion and Education
In order to promote preventative healthcare practices and improve overall health, it is essential to conduct health education campaigns. These campaigns aim to increase awareness about various aspects of health, including nutrition, hygiene, and family planning. Additionally, community training sessions and workshops play a crucial role in disseminating important health information.
These efforts are particularly important in developing countries like Nigeria, especially in rural areas where primary healthcare is a primary focus [2]. These public health programs, often carried out during rural postings, encompass a range of initiatives. These include immunization programs, which provide vaccines to safeguard children against preventable diseases like measles, polio, and diphtheria. There are also maternal and child health programs that offer care and support to pregnant women, mothers, and children, covering prenatal care, childbirth, and follow-up care. Furthermore, nutrition programs educate people about healthy eating and physical activity, contributing to disease prevention and overall health improvement.
Maternal and Child Health Services
Maternal and Child Health Services encompasses a range of healthcare programs and interventions specifically aimed at promoting the well-being of mothers (including pregnant women and new moms) and their children (infants, toddlers, and young children). These services are geared towards ensuring a healthy pregnancy, safe childbirth, and proper care during the early years of a child's life. The components of Maternal and Child Health Services are summarized in Figure 3.
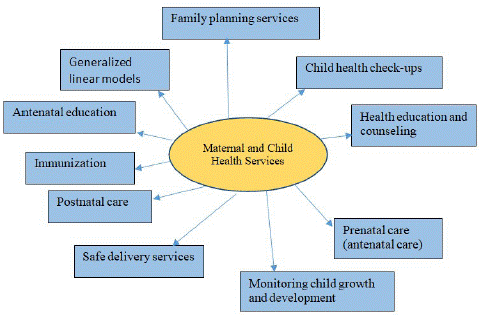
Figure 3: Maternal and child health sciences as a strategy in rural posting in public health practices.
This means medical care for pregnant women to monitor their pregnancy, address potential complications, and provide guidance on healthy practices during pregnancy [83]. Educational and counseling sessions for expectant mothers and their families on topics like breastfeeding, childbirth preparation, and nutrition during the antenatal period. Ensuring access to qualified healthcare professionals and facilities for safe childbirth, including emergency obstetric care when needed. Providing medical attention and emotional support to mothers and infants immediately after childbirth to assess their health and address postpartum issues [43]. Administering vaccines to protect newborns and children from preventable diseases. Keeping track of a child's physical, mental, and emotional growth to identify and address any developmental delays or concerns [47]. Offering guidance on appropriate infant and child nutrition, with a focus on promoting and supporting breastfeeding. Providing information and access to contraception to help families plan and space pregnancies according to their preferences. Conducting regular medical examinations for children to detect and manage potential health problems early on. Offering information and counseling on various aspects of maternal and child health, including hygiene, child safety, and family planning [48].
These services are vital for reducing maternal and infant mortality rates, promoting healthy pregnancies, and ensuring the optimal development of children in their early years. They are typically delivered through healthcare facilities, clinics, and community health programs, with the overarching goal of improving the overall health and well-being of both mothers and children. Therefore, during rural posting prioritizing maternal and child health services, including prenatal care, safe deliveries, immunizations, and nutrition support [74]. Train healthcare providers in essential obstetric and neonatal care.
Integration of Services
Integration of Services in public health postings within rural areas refers to a deliberate effort to blend and coordinate various healthcare services and initiatives in remote or rural regions [14]. The goal is to establish a more comprehensive and efficient healthcare system that enhances the effectiveness, efficiency, and accessibility of healthcare for rural residents.
This integration entails combining a variety of healthcare services, such as primary care, preventative measures, specialist consultations, diagnostic services, and support programs, into a unified and well-coordinated healthcare system. It aims to break down traditional service delivery barriers by fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals, community organizations, and public health authorities. The objective is to provide healthcare services that are holistic, patient-centred, and consider both immediate medical needs and the socio-economic factors that impact rural populations.
The process may involve sharing patient information, resources, and infrastructure to minimize duplication of services and optimize the allocation of healthcare resources [4]. Additionally, this integration effort often includes improvements in referral systems, simplifying administrative processes, and enhanced communication among healthcare professionals.
Integration of services is particularly crucial in rural areas where challenges such as a shortage of healthcare workforce, long distances to healthcare facilities, and inadequate infrastructure are prevalent [85]. Overall, the aim is to create a healthcare system that is more efficient, accessible, and patient-focused, tailored to the specific needs and constraints of rural communities, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes for rural residents.
Therefore, integrate primary healthcare services with other sectors like nutrition, water and sanitation, and education to address the social determinants of health [86]. Provision of integrated care for common conditions, such as tuberculosis and HIV, to reduce the burden on patients and healthcare systems.
Emergency Medical Services
In underserved rural areas, using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) as a technique in rural postings for public health practices can substantially influence both access to healthcare and the outcomes of that care [49]. Often, rural areas face unique difficulties, such as a lack of access to healthcare facilities and personnel. Solving these problems and improving public health practices may be possible by successfully implementing EMS in these locations. The critical aspect of EMS is summarized in Figure 4.
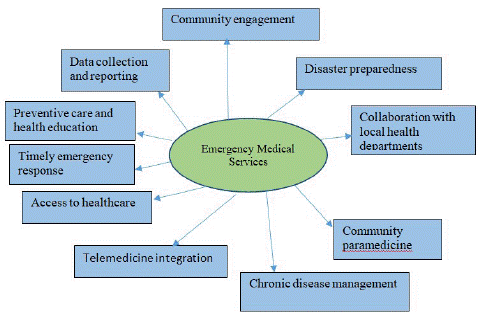
Figure 4: Emergency Medical Services as a strategy in rural posting in public health practices.
Emergency Medical Services are essential in promptly responding to medical emergencies, accidents, and natural disasters. In rural locations, where medical institutions are frequently located some distance from towns, emergency medical services EMS can dramatically cut response times, which is essential for doing so to save lives in the event of an emergency [8].
Access to Healthcare It's possible that people who live in rural areas have a more limited ability to get to medical facilities and specialists. Emergency medical services can help bridge this gap and ensure that patients can reach the proper healthcare facilities for treatment and follow-up care by offering transportation services to people living in remote areas.
Emergency medical services teams can participate in community outreach and education programs to encourage the use of preventive care measures [53]. They can provide information regarding vaccinations, health screenings, diet, and lifestyle choices to promote the community's general health.
By incorporating telemedicine capabilities into EMS, it is possible to provide inhabitants of rural areas with access to remote consultations with medical professionals [37]. Because to advancements in technology, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care can all be provided remotely, eliminating the need for considerable travel.
Emergency medical services professionals can assist in managing chronic conditions by providing patients with frequent checkups, helping patients manage their medications, and educating patients on how to take care of themselves. This preventative approach can help prevent complications and reduce the number of patients admitted to the hospital.
Some rural regions have implemented community paramedicine programs that extend the role of EMS providers [16]. These programs involve paramedics providing non-emergency services within the community, such as medication management, wound care, and chronic disease monitoring.
Preparedness for Natural Disasters Rural areas are more likely to be affected by natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires than urban ones. EMS can play a significant part in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery, ensuring that communities are ready for any crisis that may arise.
Emergency medical services can potentially provide public health organizations with valuable data. These data can assist in identifying health trends, evaluating community needs, and forming public health initiatives and policies in rural areas.
EMS agencies and local health departments need to work together closely. They can collaborate on the creation and execution of public health initiatives, emergency response plans, and disaster preparedness strategies that are specifically adapted to meet the requirements of rural areas.
Participation in the community, particularly with community leaders and members, is essential in rural locations. EMS providers can cultivate trust and partnerships within the community, thus increasing the likelihood that patients would positively respond to the healthcare services they receive and making the services more culturally competent.
To successfully integrate EMS into rural public health practices, rigorous planning, resource allocation, and training are required [90]. In addition, it requires solving the particular difficulties present in rural areas, such as rugged terrain, a lack of infrastructure, and a lack of available labor. Nevertheless, EMS has the potential to become a vital resource for rural areas if they are provided with an effective plan that aims to expand access to medical treatment and strengthen public health policies.
Regular Health Camps
There are several reasons why holding routine health camps can be a helpful technique in rural public health practice. Rural areas often face difficulties in the healthcare field, such as limited access to healthcare facilities and practitioners [19]. The rural population's general health and sense of well-being can be improved by using health camps, which can assist in addressing some of these difficulties [45]. Regular health camps can be an effective strategy, and the potentials are summarized in Figure 5.
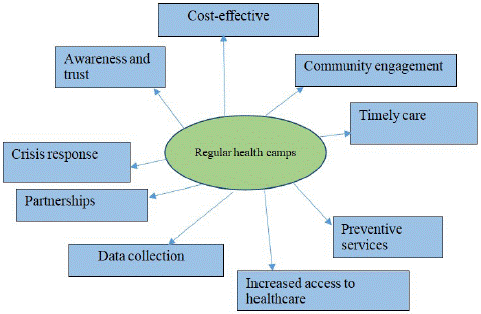
Figure 5: Regular health camps as a strategy in rural posting in public health practices.
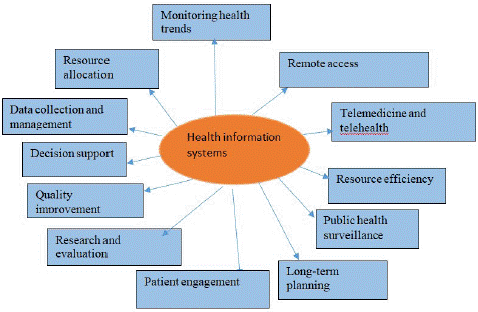
Figure 6: Implementing health information systems as a strategy in rural posting in public health practices.
Health information systems makes possible the effective collection and management of data connected to healthcare, such as patient records, illness prevalence, vaccine coverage, and healthcare utilization [69]. These facts serve as the foundation for making decisions in an informed manner.
Health information systems allow medical professionals working in remote areas to view patient data, medical histories, and treatment guidelines from a distance [11]. This is especially helpful when coordinating care with metropolitan healthcare facilities or speaking with medical professionals. The HIS helps keep track of disease outbreaks and monitor health trends in real-time. This information is essential for the early diagnosis and prompt response to disease outbreaks in rural areas, where they are more likely to occur.
The HIS can assist public health professionals in successfully allocating resources to the health requirements of rural communities [35]. This includes determining which regions have a more significant disease load or particular health requirements.
Health information systems can facilitate telemedicine and telehealth services, connecting patients in remote areas with healthcare providers in other parts of the country [44]. Because of this, access to specialized care and consultations may be improved. Health information systems can give tools for decision support that aid healthcare personnel in diagnosing and treating patients, which is especially helpful in regions with few healthcare resources [56]. Health information systems can assist in determining where there are voids in the delivery of healthcare services and can monitor the level of care offered in rural health institutions [81]. Applying this knowledge can lead to initiatives to continuously enhance the quality.
Health information systems has the potential to increase the efficiency of healthcare delivery in rural regions by lowering the amount of paperwork that must be completed and streamlining the administrative chores that must be completed. This would enable healthcare providers to focus more on patient care. The HIS provides support for public health surveillance initiatives. These efforts assist authorities in detecting and responding to disease outbreaks, monitoring the effectiveness of immunization programs, and assessing the impact of public health policies [57]. The data from the HIS can be used to inform long-term planning for public health, including the development of infrastructure, the training of healthcare workforces, and the distribution of funds for healthcare projects in remote areas.
Health information systems can incorporate patient portals and mobile health applications that engage patients in managing their own health, booking appointments, and accessing educational resources [71]. This is especially helpful for rural communities. The data from the HIS can be utilized for research and evaluating programs, which will contribute to implementing public health initiatives in rural regions supported by evidence. It is imperative to consider elements such as the following to adopt health information systems in rural public health practices successfully. Ensure sufficient infrastructure to support the installation of HIS, including stable internet connectivity and electricity. Educate healthcare professionals and personnel in remote areas on the most efficient ways to use HIS, including how to enter, retrieve, and analyse data.
Supportive Supervision and Mentoring
Rural public health practices need supportive monitoring and mentoring to promote healthcare and workforce performance [52]. These tips can help rural healthcare providers overcome obstacles and enhance local health. Helpful rural public health supervision and mentoring have many benefits (Figure 7). For instance, Mentoring and supportive monitoring can help rural healthcare workers enhance clinical and public health skills. It includes diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and patient communication training. Mentors can teach rural healthcare workers best practices and evidence-based methods. Regular support and mentoring can boost rural healthcare personnel's confidence and community participation [88]. Supportive supervision and mentorship let healthcare workers discuss daily difficulties with experts. Mentors can assist rural health professionals in improving care with clinical audits and feedback. Mentoring keeps healthcare and public health professionals updated. Mentorship and supervision can boost rural healthcare workers' morale and reduce burnout. Rural healthcare practitioners' settings and demographics can inform mentoring [15]. Supportive monitoring and mentoring can involve the community. Mentors help healthcare workers build trust, engage with communities, and manage cultural differences [54]. Regular performance assessments of healthcare personnel can inform professional development plans and suggest improvements. Mentoring can find and prepare rural healthcare leaders to sustain services.
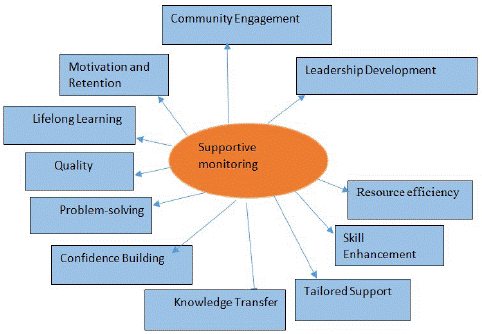
Figure 7: Supportive monitoring as a strategy in rural posting in public health practices.
Through these benefits, rural public health benefits from supporting monitoring and coaching. They can help rural healthcare providers develop confidence to provide high-quality care, improve health outcomes, and boost rural populations' well-being. Planning, structure, and support are needed for strategy success.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Transportation and infrastructure are pivotal in bolstering rural public health strategies, potentially impacting healthcare delivery and overall well-being. The enhancement of transportation and infrastructure catalyses progress in rural public health.
Improved transportation and infrastructure translate into tangible benefits for rural healthcare access and health outcomes [3]. In particular, well-maintained roads and bridges significantly enhance the accessibility of healthcare services in rural areas. Such infrastructure not only expedites patient transport, especially during medical emergencies like childbirth complications or accidents, but also facilitates the deployment of mobile clinics to remote communities that lack permanent healthcare facilities.
Furthermore, robust transportation networks ensure the swift delivery of vaccines, medications, and essential medical supplies to rural health facilities [64]. This is critical in preventing stockouts and ensuring a consistent supply of life-saving drugs. Additionally, clean and well-structured roads and transportation infrastructure enable prompt responses to natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and other emergencies, safeguarding the health and safety of rural residents.
The role of infrastructure extends beyond physical transportation. Reliable internet and telecommunications infrastructure allow rural residents to consult healthcare providers remotely, overcoming geographical barriers. Community centres and meeting spaces can be harnessed for health education and outreach programs, engaging the community in various public health initiatives.
Infrastructure development also encompasses fundamental elements like clean drinking water and sanitation facilities, which prevent waterborne diseases and advance community health. Moreover, access to electricity is indispensable for powering essential medical equipment, maintaining vaccine refrigeration, and ensuring adequate lighting for surgeries and examinations in rural healthcare facilities [38]. In the broader context, robust transportation and infrastructure contribute to the retention and attraction of skilled healthcare professionals in rural areas, mitigating regional healthcare personnel shortages.
Financial Support and Incentives
Financial support and incentives are crucial in bolstering rural postings' effectiveness in public health practices [72]. This strategy aims to attract and retain healthcare professionals in underserved rural regions, with the overarching goal of addressing healthcare disparities and enhancing the overall health of rural populations.
To achieve this, public health organisations can offer various financial incentives, such as bonuses, loan forgiveness programs, or increased salaries, to healthcare workers who choose to serve in rural areas. Doing so incentivises professionals to commit to rural postings, helping alleviate workforce shortages often prevalent in these regions. The result is improved healthcare access and delivery for rural communities.
Furthermore, financial support can extend to infrastructure development in rural healthcare facilities. This ensures these facilities have the resources and capabilities to provide high-quality care [34]. Financial support and incentives serve as essential tools for promoting equitable healthcare access and elevating health outcomes in rural areas.
Advocacy and Policy Support
Advocacy and policy support can enhance rural public health postings, addressing issues like infrastructure, labor, and resources [33]. Through advocacy and policy support, increased financing, incentives, and improved infrastructure for rural healthcare could be achieved. Engage policymakers at all levels to spotlight rural healthcare needs. Promote policies involving communities in healthcare decision-making and worker recruitment. Promote improved telemedicine and tech infrastructure measures, reducing healthcare service gaps [32]. Advocate for policies funding healthcare facility development and maintenance to ensure quality care. Support policies for data collection and research on rural health challenges to inform policymaking [89]. These actions collectively enhance rural healthcare, benefiting both communities and public health practices.
Conclusion
Given the ongoing global challenges in this area, understanding the principles and strategies that influence rural healthcare delivery in public health initiatives is essential. This paper highlights critical concepts and innovative approaches for enhancing healthcare accessibility and outcomes in rural settings. The study underscores the significance of comprehending rural populations' socio-cultural, economic, and geographical facets as a foundational step toward adequate rural healthcare provision. Public health specialists must tailor their methods to align with the specific health needs of these communities. Community engagement emerges as a linchpin for success in rural healthcare. Establishing trust and fostering collaboration with residents empowers them to actively participate in managing their healthcare, thus fostering sustainable solutions and diminishing healthcare disparities. Interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and community health workers, is imperative for addressing a broader spectrum of health issues and enhancing the efficiency of healthcare delivery in rural areas. Leveraging telemedicine and technology can bridge geographical barriers. Telemedicine, electronic health records, and mobile health applications enable remote consultations, diagnoses, and information exchange, expanding access to high-quality care. Customized health education programs tailored to rural communities are pivotal in raising awareness, promoting preventive measures, and empowering individuals to make informed health decisions. Health literacy initiatives are indispensable for reducing the prevalence of preventable diseases.
Several actionable strategies can contribute to effective public health practices in rural areas. For instance, deploying mobile clinics ensures that healthcare services reach even the most remote regions. Establishing rural hubs facilitates consultations with urban experts, enabling timely recommendations. Sustainability in rural healthcare requires the provision of financial incentives, training opportunities, and career support to incentivize medical professionals to work in remote locations. Collaborative efforts involving governments, businesses, and non-governmental organizations can deliver comprehensive rural healthcare services. Utilizing data on rural health trends is crucial for evidence-based policy formulation and efficient resource allocation, optimizing healthcare delivery. By applying these principles and strategies, public health practitioners can significantly improve rural healthcare outcomes and access.
References
- Abdel-All M, Angell B, Jan S, Howell M, Howard K, Abimbola S, et al. What do community health workers want? Findings of a discrete choice experiment among Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs) in India. BMJ Glob Health. 2019; 4: e001509.
- Abdulraheem BI, Olapipo AR, Amodu MO. Primary health care services in Nigeria: critical issues and strategies for enhancing the use by the rural communities. J Public Health Epidemiol. 2012; 4: 5-13.
- Aggarwal S. The long road to health: healthcare utilization impacts of a road pavement policy in rural India. J Dev Econ. 2021; 151: 102667.
- Al-Jaroodi J, Mohamed N, Abukhousa E. Health 4.0: on the way to realizing the healthcare of the future. IEEE Access. 2020; 8: 211189-210.
- Allagoa DO, Eledo BO, Dunga KE, Izah SC. Assessment of Some Immune System Related Parameters on Helicobacter pylori Infected Students in a Nigerian Tertiary Educational Institution. Int J Gastroenterol. 2018a; 2: 24-7.
- Allagoa DO, Eledo BO, Okoro MO, Izah SC. Hemostasis status of some female students before and after menstruation. J Thromb Circ. 2018b; 4: 129.
- Altman DG. Sustaining interventions in community systems: on the relationship between researchers and communities. Health Psychol. 1995; 14: 526-36.
- Aringhieri R, Bruni ME, Khodaparasti S, van Essen JT. Emergency medical services and beyond: addressing new challenges through a wide literature review. Comput Oper Res. 2017; 78: 349-68.
- Arora S, Geppert CM, Kalishman S, Dion D, Pullara F, Bjeletich B, et al. Academic health center management of chronic diseases through knowledge networks: project ECHO. Acad Med. 2007; 82: 154-60.
- Backhaus A, Agha Z, Maglione ML, Repp A, Ross B, Zuest D, et al. Videoconferencing psychotherapy: a systematic review. Psychol Serv. 2012; 9: 111-31.
- Bates DW, Ebell M, Gotlieb E, Zapp J, Mullins HC. A proposal for electronic medical records in US primary care. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003; 10: 1-10.
- Billett S. Learning through health care work: premises, contributions and practices. Med Educ. 2016; 50: 124-31.
- Cabassa LJ, Baumann AA. A two-way street: bridging implementation science and cultural adaptations of mental health treatments. Implement Sci. 2013; 8: 90.
- Carmone AE, Kalaris K, Leydon N, Sirivansanti N, Smith JM, Storey A, et al. Developing a common understanding of networks of care through a scoping study. Health Syst Reform. 2020; 6: e1810921.
- Chipeta E, Bradley S, Chimwaza-Manda W, McAuliffe E. Working relationships between obstetric care staff and their managers: a critical incident analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016; 16: 441.
- Choi BY, Blumberg C, Williams K. Mobile integrated health care and community paramedicine: an emerging emergency medical services concept. Ann Emerg Med. 2016; 67: 361-6.
- Daniel SJ, Kumar S. Teledentistry: a key component in access to care. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2014; 14: 201-8.
- Darkwa EK, Newman MS, Kawkab M, Chowdhury ME. A qualitative study of factors influencing retention of doctors and nurses at rural healthcare facilities in Bangladesh. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015; 15: 344.
- Dassah E, Aldersey HM, McColl MA, Davison C. Health care providers’ and persons with disabilities’ recommendations for improving access to primary health care services in rural northern Ghana: A qualitative study. PLOS ONE. 2022; 17: e0274163.
- Dharssi S, Wong-Rieger D, Harold M, Terry S. Review of 11 national policies for rare diseases in the context of key patient needs. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017; 12: 63.
- Dussault G, Franceschini MC. Not enough there, too many here: understanding geographical imbalances in the distribution of the health workforce. Hum Resour Health. 2006; 4: 12.
- Eledo BO, Allagoa DO, Egwugha CT, Dunga KE, Izah SC. Some haemostatic indicators among malaria infected adolescents attending a Nigerian University Teaching Hospital. Open Access Blood Res Transfus J. 2019; 3: 555602.
- Eledo BO, Izah SC. Studies on some haematological parameters among malaria infected patients attending a Tertiary Hospital in Nigeria. Open Access Blood Res Transfus J. 2018; 2: 555586.
- Eledo BO, Allagoa DO, Njoku I, Izah SC. Distribution of haemoglobin variants, ABO blood group and rhesus D among nursing students of Madonna University Nigeria. MOJ Toxicol. 2018a; 4: 398-402.
- Eledo BO, Izah SC, Okamgba OC. Assessment of Some Haemostasis System Blood Indicators among the Elderly Attending a tertiary Health Institution in Nigeria. Arch Blood Transfus Disord. 2018b; 1: ABTD.000518.2018.
- Eledo BO, Izah SC, Okamgba OC. Prothrombin time activated partial thromboplastin time and platelets count among hypertensive patients attending a Tertiary Health Institution in Yenagoa, Nigeria. J Blood Res. 2018c; 9: 117-121.
- Eledo BO, Izah SC, Okamgba OC, Onuoha EC. Assessment of some haemostatic parameters at different stages of pregnancy. Hematoltransfus Int J. 2018; 6: 96-9.
- Eledo BO, Igwe MU, Izah SC. Evaluation of Total white blood cells and Cluster of Differentiation 4 Cells among Post - Menopausal Women in Elele, Nigeria. Mod Res Inflam. 2018e; 07: 21-9.
- Elmusharaf K, Byrne E, O’Donovan D. Strategies to increase demand for maternal health services in resource-limited settings: challenges to be addressed. BMC Public Health. 2015; 15: 870.
- Fulton BD, Scheffler RM, Sparkes SP, Auh EY, Vujicic M, Soucat A. Health workforce skill mix and task shifting in low income countries: a review of recent evidence. Hum Resour Health. 2011; 9: 1.
- Gaede B, Versteeg M. The state of the right to health in rural South Africa. S Afr Health Rev. 2011; 2011: 99-106.
- Gallegos-Rejas VM, Thomas EE, Kelly JT, Smith AC. A multi-stakeholder approach is needed to reduce the digital divide and encourage equitable access to telehealth. J Telemed Telecare. 2023; 29: 73-8.
- Gerein N, Green A, Pearson S. The implications of shortages of health professionals for maternal health in sub-Saharan Africa. Reprod Health Matters. 2006; 14: 40-50.
- Goldman HH, Ganju V, Drake RE, Gorman P, Hogan M, Hyde PS, et al. Policy implications for implementing evidence-based practices. Psychiatr Serv. 2001; 52: 1591-7.
- Grier S, Bryant CA. Social marketing in public health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2005; 26: 319-39.
- Haines A, Sanders D, Lehmann U, Rowe AK, Lawn JE, Jan S, et al. Achieving child survival goals: potential contribution of community health workers. Lancet. 2007; 369: 2121-31.
- Haleem A, Javaid M, Singh RP, Suman R. Telemedicine for healthcare: capabilities, features, barriers, and applications. Sens Int. 2021; 2: 100117.
- Henderson LN, Tulloch J. Incentives for retaining and motivating health workers in Pacific and Asian countries. Hum Resour Health. 2008; 6: 18.
- Ikhajiagbe B, Ogwu MC. Hazard quotient, microbial diversity and plant composition of spent crude oil polluted-soil. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2020; 9.
- Izah SC, Odubo TC, Ngun CT, Ogwu MC. Research needs of medicinal plants used in the management and treatment of some diseases caused by microorganisms. In: Izah SC, Ogwu MC, Akram M, editors. Herbal medicine phytochemistry. Reference series in phytochemistry. Cham: Springer. 2023; 1-27.
- Sylvester Chibueze I, Kurotimipa Frank O, Matthew Chidozie O. Lassa fever in Nigeria: social and Ecological Risk Factors Exacerbating Transmission and Sustainable Management Strategies. Int J Trop Dis. 2022; 5: 1-15.
- Kampmeijer R, Pavlova M, Tambor M, Golinowska S, Groot W. The use of e-health and m-health tools in health promotion and primary prevention among older adults: a systematic literature review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016; 16: 290.
- Kanotra S, D’Angelo D, Phares TM, Morrow B, Barfield WD, Lansky A. Challenges faced by new mothers in the early postpartum period: an analysis of comment data from the 2000 Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) survey. Matern Child Health J. 2007; 11: 549-58.
- Kaplan B. Revisiting health information technology ethical, legal, and social issues and evaluation: telehealth/telemedicine and COVID-19. Int J Med Inform. 2020; 143: 104239.
- Keeton V, Soleimanpour S, Brindis CD. School-based health centers in an era of health care reform: building on history. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2012; 42: 132-56.
- Keeton V, Soleimanpour S, Brindis CD. School-based health centers in an era of health care reform: building on history. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2012; 42: 132-56.
- Leslie LK, Gordon JN, Lambros K, Premji K, Peoples J, Gist K. Addressing the developmental and mental health needs of young children in foster care. J Dev Behav Pediatr JDBP. 2005; 26: 140-51.
- Lindegren ML, Kennedy CE, Bain-Brickley D, Azman H, Creanga AA, Butler LM, et al. Integration of HIV/AIDS services with maternal, neonatal and child health, nutrition, and family planning services. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 12: CD010119.
- Leszczynski PK, Sobolewska P, Muraczynska B, Gryz P, Kwapisz A. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on quality of health services provided by emergency medical services and emergency departments in the opinion of patients: pilot study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19: 1232.
- Lurie N, Carr BG. The role of telehealth in the medical response to disasters. JAMA Intern Med. 2018; 178: 745-6.
- Maluka SO. Strengthening fairness, transparency and accountability in health care priority setting at district level in Tanzania. Glob Health Action. 2011; 4: 7829.
- Manzi A, Hirschhorn LR, Sherr K, Chirwa C, Baynes C, Awoonor-Williams JK. Mentorship and coaching to support strengthening healthcare systems: lessons learned across the five Population Health Implementation and Training partnership projects in sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017; 17: 5-16.
- Martinez J, Ro M, Villa NW, Powell W, Knickman JR. Transforming the delivery of care in the post–health reform era: what role will community health workers play? Am J Public Health. 2011; 101: e1-5.
- McCosker A. Engaging mental health online: insights from Beyondblue’s forum influencers. New Media Soc. 2018; 20: 4748-64.
- Morland LA, Greene CJ, Rosen CS, Kuhn E, Hoffman J, Sloan DM. Telehealth and ehealth interventions for posttraumatic stress disorder. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017; 14: 102-8.
- Mosa ASM, Yoo I, Sheets L. A systematic review of healthcare applications for smartphones. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012; 12: 67.
- Nsubuga P, White ME, Thacker SB, Anderson MA, Blount SB, Broome CV, et al. Public health surveillance: a tool for targeting and monitoring interventions. 2011.
- Ogwu MC. The Significance and Contribution of Conservation Education in Nigeria: an Appraisal and a call for Improvement. In: Babalola F, editor. Proceedings of the maiden seminar of Nigerian Tropical Biology Association. Nigerian Tropical Biology Association and Tropical Biology Association. 2009; 109-14.
- Ogwu MC. Towards sustainable development in Africa: the challenge of urbanization and climate change adaptation. In: Cobbinah PB, Addaney M, editors. The geography of climate change adaptation in Urban Africa. Springer nature, Switzerland. 2019; 29-55.
- Ogwu MC. Value of Amaranthus [L.] species in Nigeria. In: Waisundara V, editor. Nutritional value of amaranth. IntechOpen, UK. 2020; 1-21.
- Ogwu MC, Chime AO, Oseh OM. Ethnobotanical survey of tomato in some cultivated regions in Southern Nigeria. Maldives Natl Res J. 2018; 6: 19-29.
- Ogwu MC, Osawaru ME, Obahiagbon GE. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used for traditional reproductive care by Usen people of Edo State, Nigeria. Mal J Biosci. 2017; 4: 17-29.
- Ogwu MC, Osawaru ME, Aiwansoba RO, Iroh RN. Ethnobotany and collection of West African Okra [Abelmoschus caillei(A. Chev.) Stevels] germplasm in some communities in Edo and Delta States, Southern Nigeria. Borneo J Resour Sci Technol. 2016; 6: 25-36.
- Oigbochie AE, Odigie EB, Adejumo BIG. Importance of drones in healthcare delivery amid a pandemic: current and generation next application. Open J Med Res. 2021; 2: 1-13.
- Osawaru ME, Ogwu MC. Ethnobotany and germplasm collection of two genera of cocoyam(Colocasia [Schott] and Xanthosoma [Schott], Araceae) in Edo State Nigeria. Sci Technol Arts Res J. 2014; 3: 23-8.
- Osawaru ME, Ogwu MC, Omoigui ID, Aiwansoba RO, Kevin A. Ethnobotanical survey of vegetables eaten by Akwa Ibom people residing in Benin City, Nigeria. J Sci Technol. 2016; 4: 70-93.
- Overall PM. Cultural competence: A conceptual framework for library and information science professionals. Libr Q. 2009; 79: 175-204.
- Palumbo R. Contextualizing co-production of health care: a systematic literature review. Int J Public Sect Manag. 2016; 29: 72-90.
- Pandey A, Roy N, Bhawsar R, Mishra RM. Health information system in India: issues of data availability and quality. Demogr India. 2010; 39: 111-28.
- Perna LW, Orosz K, Jumakulov Z. Understanding the human capital benefits of a government-funded international scholarship program: an exploration of Kazakhstan’s Bolashak program. Int J Educ Dev. 2015; 40: 85-97.
- Price-Haywood EG, Harden-Barrios J, Ulep R, Luo Q. Ehealth literacy: patient engagement in identifying strategies to encourage use of patient portals among older adults. Popul Health Manag. 2017; 20: 486-94.
- Ramani S, Rao KD, Ryan M, Vujicic M, Berman P. Hum Resour Health. For more than love or money: attitudes of student and in-service health workers towards rural service in India. 2013; 11: 1-12.
- Rutledge CM, Haney T, Bordelon M, Renaud M, Fowler C. Telehealth: preparing advanced practice nurses to address healthcare needs in rural and underserved populations. Int J Nurs Educ Scholarsh. 2014; 11: 1-9.
- Sahoo KC, Negi S, Patel K, Mishra BK, Palo SK, Pati S. Challenges in maternal and child health services delivery and access during pandemics or public health disasters in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Healthcare (Basel). 2021; 9: 828.
- Shediac-Rizkallah MC, Bone LR. Planning for the sustainability of community-based health programs: conceptual frameworks and future directions for research, practice and policy. Health Educ Res. 1998; 13: 87-108.
- Shroff ZC, Bigdeli M, Meessen B. From scheme to system (part 2): Findings from Ten Countries on the Policy Evolution of Results-Based Financing in Health Systems. Health Syst Reform. 2017; 3: 137-47.
- Skillman SM, Doescher MP, Mouradian WE, Brunson DK. The challenge to delivering oral health services in rural America. J Public Health Dent. 2010; 70: S49-57.
- Smith T, Cross M, Waller S, Chambers H, Farthing A, Barraclough F, et al. Ruralization of students’ horizons: insights into Australian health professional students’ rural and remote placements. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2018; 11: 85-97.
- Thackway S, Churches T, Fizzell J, Muscatello D, Armstrong P. Should cities hosting mass gatherings invest in public health surveillance and planning? Reflections from a decade of mass gatherings in Sydney, Australia. BMC Public Health. 2009; 9: 324.
- Theriault H, Bridge G. Oral Health equity for rural communities: where are we now and where can we go from here? Br Dent J. 2023; 235: 99-102.
- Thompson TG, Brailer DJ. The decade of health information technology: delivering consumer-centric and information-rich health care. Washington, DC: United States Department of Health and Human Services. 2004.
- Vaithiyalingam S, Mohan R, Joseph AA, Jacobe MG, Purty AJ. Morbidity pattern of Kerala flood victims of 2018 in the post flood recovery phase. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2019; 6: 4940.
- Vamos CA, Thompson EL, Avendano M, Daley EM, Quinonez RB, Boggess K. Oral Health promotion interventions during pregnancy: a systematic review. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2015; 43: 385-96.
- Vora KS, Mavalankar DV, Ramani KV, Upadhyaya M, Sharma B, Iyengar S, et al. Maternal health situation in India: a case study. J Health Popul Nutr. 2009; 27: 184-201.
- Weinhold I, Gurtner S. Understanding shortages of sufficient health care in rural areas. Health Policy. 2014; 118: 201-14.
- White F. Primary health care and public health: foundations of universal health systems. Med Princ Pract. 2015; 24: 103-16.
- Wilson NW, Couper ID, De Vries E, Reid S, Fish T, Marais BJ. A critical review of interventions to redress the inequitable distribution of healthcare professionals to rural and remote areas. Rural Remote Health. 2009; 9: 1060.
- World Health Organization. The Delivery of essential health service in Africa, realities and people’s perceptions and perspectives: report submitted for the North West site in Nigeria. 2011.
- Xiu-Xia L, Ya Z, Yao-Long C, Ke-Hu Y, Zong-Jiu Z. The reporting characteristics and methodological quality of Cochrane reviews about health policy research. Health Policy. 2015; 119: 503-10.
- Yancey AH, Fuhri PD, Pillay Y, Greenwald I. World Cup 2010 planning: an integration of public health and medical systems. Public Health. 2008; 122: 1020-9.
- Zundel KM. Telemedicine: history, applications, and impact on librarianship. Bull Med Libr Assoc. 1996; 84: 71-9.
