
Special Article - Pediatric Dentistry
Austin J Dent. 2018; 5(6): 1122.
Dental Considerations and Management of Children with Renal Diseases - An Over View
Nirmala SVSG*
Department of Paedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Professor, Narayana Dental College & Hospital, India
*Corresponding author: Nirmala SVSG, Department of Paedodontics & Preventive Dentistry, Narayana Dental College & Hospital, India
Received: October 29, 2018; Accepted: November 26, 2018; Published: December 03, 2018
Abstract
Kidneys are vital organs for maintain a stable internal environment, prevalence of renal disease is increasing universally. Nephritic syndrome is a clinical manifestation of any glomerular lesion that causes more than 35g of proteinuria/ day. Chronic renal disease is defined as a progressive and irreversible decline in renal function associated with a reduced glomerular filtration rate. Common renal disorders seen in children include congenital nephropathies, nephrotic syndrome, Chronic Renal Failure (CRF), glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis, and multicystic renal dysplasia, which ultimately lead to End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). Children usually show growth retardation, bleeding tendency due to capillary fragility and thrombocytopenia is positive, pale and anaemic. This article discuss about the etiology, clinical features and dental management of children with renal diseases.
Keywords: Children; Dental Management; Oral Health; Renal Diseases
Introduction
Kidneys play an important role in sustain physiologic balance; regaining homeostasis and fluid electrolyte acid-based balance, drug metabolism and elimination, blood pressure control through the renin-angio-tensin system, red blood cell production through erythropoietin production, and vitamin common renal disorders seen in children are nephritic syndrome, chronic renal failure, chronic pyelonephritis, chronic glomerulo nephritis which ultimately leads to end stage of renal failure [1].
Nephrotic Syndrome (Nephrosis)
It is a condition that indicates exogenous or endogenous glomerular injury. Acute nephritic syndromes occur most frequently in children and are classically associated with post streptococcal glomerulo nephritis, commonly preceded by a beta-hemolytic streptococcal oropharyngitis. Typically l-2 weeks after the pharyngitis. Since the advent of penicillin therapy, acute nephritic syndrome has been observed less frequently aher streptococcal pharyngitis [1].
The aetiology of this syndrome is unknown but there is a reasonable possibility that it is an autoimmune disease. The onset is often at the age of about 2 to 3 years and the duration may be months or years. There are glomerular changes and a loss of protein. Oedema is an important feature which recurs during the course of the disease and secondary anaemia may be present. These children are very susceptible to infection and upper respiratory infections are common. Exacerbations of the renal condition may occur on these occasions [3,4] (Table 1).
Localised
Obstructive
Systemic
Proliferative membranous glomerulonephrothy
Upper respiratory tract obstruction
Benign/malignant
Chronic pylonephritis
Hydronephrosis
Polyarteritis nodosa
Tubercular pylonephritis
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Dessiminated lupas erythematosis
Renal caliculi
Neoplasm
Primary and secondary amyloidosis
Congenital nephritis
Adenoma
Potassium deficiency
Polycystic disease
Urethral stricture
Hypercalcemia
Medullary cystic disease
Urethral valves
Oxalosis
Renal hypoplasia
Bladder neck obstruction
Thrombiotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Renal tubular hypoplasia
Neurogenic bladder
Lead poisoning
Diabetes
Table 1: Etiology of CRF.
Clinical features over 50% cases are subclinical or mild, usually producing slightly abnormal renal function that lasts less than a week. Sudden onset characterized by fever malaise. Children are ill with concurrent findings of oedema, oliguria, azotemia, and dark or coffee ground color urine (hemnturia). The hypertension is usually mild to moderate and elevates the systolic blood pressure about 20 to 40 mmHg. When the blood pressure as markedly elevated and the oedema and electrolyte imbalance become persistent, nephritic syndrome can lead to convulsions. Congestive heart failure or cardiac arrythmias. Progressive cardio-respiratory symptoms include cough, dyspnca. onhopnea, edema, rules, and gallop rhythm [5].
Treatment by corticosteroid therapy has greatly changed the course of this disease. Its duration is much reduced and chances of complete recovery considerably improved. This therapy is likely to be intensive and prolonged and may be continuous or interrupted. The use of antibacterial agents has reduced the number of deaths due to infection.
Oral condition
Enamel hypoplasia occurs in some of the children with this condition, and there may be some degree of discoloration of the teeth by tetracyclines [6].
Dental treatment
In view of the prolonged nature of the disease and its relationship to infection, maintenance of dental health is of importance. In remission periods the patient leads a relatively normal life and dental treatment should be carried out regularly at that time. Dental sepsis should be eliminated including any teeth which are doubtful. Root canal therapy is contraindicated. All extractions should be done with suitable antibiotic cover and consultation with the physician in charge will be necessary to establish the existing state of the corticosteroid therapy and whether to supplement it General anaesthesia ust be an in-patient procedure. Enamel hypoplasia is treated as necessary and the patient may seek improvement of the appearance of the permanent incisors when they are badly discolured by frequent tetracycline therapy during the early years [7].
Oral manifestation and dental considerations
They develop persistent oropharyngitis that involves the tonsillar tissues, uvula, and 501% palate. lntensely painful pharyngeal erythema and areas of necrosis may be observed. Healing occurs 1 to 2 weeks after the initiation of penicillin therapy.
Dental care for the patient with nephritic syndrome should be delayed until acute symptoms resolve. Consultation with the physician is advised prior to commencing dental treatment, to determine the patient’s renal status [8].
Chronic Pyelonephritis
Though most cases appear to be due to an ascending infection, there are some which are caused by a blood-bome infection of the coccal type from a distant focus. Recurrent or persistent infection results in scarring and loss of function of the kidney, but in some there is also a pre-existing obstructive lesion. Treatment is usually by prolonged courses of antibiotics or sulphonamides. Hypertension may be a feature.
Oral condition
There are no special dental features associated with this condition.
Dental treatment
This should be directed towards the elimination of septic foci and the maintenance of dental health.
Extractions should be done under prophylactic cover, the choice of which should take into account previous or current therapy preferably in consultation with the patient’s physician [9].
Postoperative bleeding may be a problem in cases with hypertension. General anaesthesia is generally contraindicated unless the patient can be admitted to hospital for it, but local anaesthesia is acceptable.
Root canal therapy in a non-vital tooth is best avoided, though a vital extirpation may be acceptable if routine follow-up is certain [10].
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
This condition may follow either the acute type or the nephrotic syndrome in children or may have an insidious onset without demonstrable cause. There are often acute exacerbations following upper respiratory infections of B haemolytic streptococci and each attack causes further renal damage. Many of the glomeruli may be damaged, the tubules atrophic or cystic, and extensive scar tissue and other degenerative changes present. There may be complete failure at the time of puberty. The condition produces a significant state of fatigue and anaemia may be present. The prognosis is a downward one and death may follow cerebral damage or heart failure. Current types of treatment do not materially alter the prognosis, but modern development in transplant surgery may well change this. These patients are highly susceptible to infections and any measures which prevent this will prolong life and keep the patient in a better mental state [11].
Oral condition
There are no special dental features associated with this condition [12].
Dental treatment
Elimination of dental sepsis must be the first consideration and in view of the susceptibility to infection, any doubtful teeth are better removed. This must be done under antibiotic cover and consultation with the physician in charge is advisable.
Local anaesthesia would be the method of choice and general anaesthesia should only be used as an in-patient procedure [13].
Once the septic and doubtful teeth have been removed, dental health should be maintained.
Treatment plans should be simple and not prolonged in view of the prognosis, but the patient should not be denied simple orthodontic treatment if desired.
Such measures not only maintain good oral conditions but help to promote a hopeful attitude in the patient and root canal therapy is contraindicated [14].
Chronic Renal Failure
It is also known as chronic kidney disease as it develops slowly, with few initial symptoms and is a long term result of irreversible acute disease or untreated disease progression. CRF is characterized by gradual reduction in the number of functional nephrons sufficient to produce alterations in the well-being and hampering the organ function. GRF rate falls less than 60ML/min. Failure of kidney failure depend upon the degree of intoxication. Children nephritic syndrome is often caused by minimal change glomerulonephm” that is, nephritic syndrome with minimal glomerular changes as seen by light microscopy [15-18,20] (Figure 1) (Table 2 and Table 3).
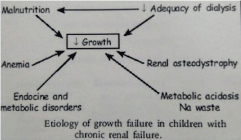
Figure 1: Etiolology of growth failure in children with chronic renal failure [20].
Clinical
Radiographic
JAWS
TEETH
Candidiasis and oral petechiae
Total or partial loss of lamina dura
Pulpal narrowing
Mucosal pallor
Demineralisation of boner
Pulp calcification
Extrinsic discoloration of teeth
Localised radiolucent lesions
Dentinal bridging
Enamel hypoplasia
Loss of distinct cortical border of hard palate
Intra dentinal radiolucency
Decreased rate of dental caries
Oral calcification
Root resorption
Mobility of teeth leads to Premature loss of teeth
Arterial calcifications in facial artery and carotid artery.
Uremic stomatitis with painful ulcers
Intraoral hematoma with tendency to bruise
Chronic marginal gingivitis
Uremic odour
Table 2: Showing clinical and radiographic findings of renal disorders [26-27].
Patients with a history of penicillin therapy within the previous six months
Patients who are sensitive to penicillin should be given erythromycin or tetracycline (not Cephaloridine)
Patients without a history of penicillin therapy
Cephaloridine by intramuscular injection 30 minutes before operation followed by erythromycin orally 6- hourly for 3 days.
Erythromycin orally commencing 12 hours before operation and taken 6-hourly for 4 days.
Triplopen in a single intramuscular injection 30 minutes before operation
Tetracycline orally commencing 12 hours before operation and taken 6 hourly for 4 days. (Children under 8 years of age should be given oxy tetracycline rather than any of the others in view of the dental side effects).
procaine penicillin and benzyl penicillin by intramuscular injection 30minute before, operation followed by oral penicillin V taken 6 hourly for 3 days
Oral penicillin V commenced 12 hours before operation and continued 6 hourly for 4 days
Note: In each group the type of antibiotic cover are given in order of preference, the first being the most effective.
Antibiotic
Route
presentation
Up to 1 year
1-5 years
6-12 years
Adult
Frequency
Penicillin
IM injection
Injection suspension
150 mg
300mg
600mg
300-900mg
Maintain single injection of both followed by oral penicillin
-procaine
300mg per ml
Combined preparation of fortified procaine penicillin BP
Penicillin- Benzyl
IM injection
Injection suspension
62.5 mg
150 mg
300mg
Up to 1.5G
150mg per ml
Penicillin-V
Oral
Capsules or tablets 125mg, 250mg
125mg
250mg
250mg
6 hourly for at least 4 days
Penicillin-V
Oral
Mixture125mg per ml
62.5mg
125mg
6 hourly for at least 4 days
Penicillin-Triploen
IM injection
Vials containing
1 Vial
1 Vial
1 Vial
1 Vial
2 doses at 48 hours interval
Benethamine pen 250mg
Sodium-penicillin G 300mg
Cephaloridine
IM injection
Vials
125mg
250mg
0.5-1G
Single initial dose followed by oral erythromycin for 3 days
250mg
500mg 1G
Erythromycin
oral
Tablets
100mg
200mg
250mg
6 hourly for at least 4 days
100mg, 250mg
Erythromycin
oral
Mixture
50 mg
100mg
200mg
250mg
6 hourly for at least 4 days
100mg per 5ml
Oxytetracycline
oral
Tablets
100mg
150mg
250mg
6 hourly for at least 4 days
100mg, 250mg
Oxytetracycline
oral
Syrup
62.5mg
125mg
150mg
250mg
6 hourly for at least 4 days
125 mg per 5ml
Table 3: Types of antibiotic therapy.
Clinical manifestations [21-24]
Oedema is the most frequent complaint of patient seeking medical treatment, is usually localized to the lower extremeties, peri-orbital region, and abdominal wall, but infrequently, It can involve the pericardial sac. Left untreated edema may cause patients to complain that their legs feel cold, heavy, numb, and swollen. Lethargy, tiredness, muscle wasting, and hypertension. Fmthy urine due to proteinurai and lipiduria. Reduced urine volume and increased thirst. “Muerke’s lines”, a transven white bands of the finger nails and toe nails are Oedema is the most frequent complaint of patient seeking medical treatment, is usually localized to the lower extremeties, peri-orbital region, and abdominal wall, but infrequently, It can involve the pericardial sac. Left untreated edema may cause patients to complain that their legs feel cold, heavy, numb, and swollen. Lethargy, tiredness, muscle wasting, and hypertension. Fmthy urine due to proteinurai and lipiduria. Reduced urine volume and increased thirst. “Muerke’s lines”, a transven white bands of the finger nails and toe nails are
Oral manifestations
In children the periorbital edema can be severe enough to prevent the eyelids from opening.
Although these features may be dramatic, after a short course of corticosteroid therapy, the oedema usually wanes [13,14].
Symptoms of CRF [25-30]
General Symptoms of CRF include:
Increased level of urea in the blood may lead to
- Nocturnal urination
- Frequent urination in smaller amounts
- Pale urine
- Foamy for bubbly urine
- Difticulty in urinating
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Blood in urine
- Muscular cramps
- Itching
- Bone damage
- Muscular paralysis
- Disturbed heart rhythm
- Weakness
- Loss of memory
- Dizziness
- Hypotension
- Difficulty in concentrating
- Shortness of breaths due to overload on lungs
- Edema of face, eyelids, ankle and feet
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Loss of appetite due to altered taste
- Hyper pigmentation of skin
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Gingival inflammation has been reported, due to plaque accumulation and poor oral hygiene habits
Increased levels of phosphates may cause
Accumulation of potassium may lead to Hyperkalemia
Increased production of erythropoietin ultimately resulting in anemia that causes
Failure to remove excess fluids results in-
Polycystic kidney disease may give pain in the back or side due to accumulation of arge, fluid cyst on kidney
Other symptoms include
Conclusion
Renal disease patients present a complex clinical problem with multi-system involvement, including several oral disturbances. Paediatric and general dentists should be aware of the severity of clinical manifestations related to CRF as well as the modem treatment possibilities and their repercussions on the lives of these children. Since the number of CRF children is constantly increasing, the need for dental treatment as an integral part in managing the CRF child is also rising. It is important for dentists to be familiar with this complex clinical problem, and its effect on the dental treatment, for provision of optimal dental care.
References
- Glodny B, Unterholzner V, Tafemer B, Hofmann KJ, Rehder P, Strasak A, et a1. Normal kidney size and its influencing factors-a 64-slice MDCT study of 1.040 asymptomatic patients. BMC Urol. 2009; 9: 19.
- Johnathan B, Vize Peter D, Woolf Adrian S. The Kidney: From Normal Development to Congenital Disease. Boston: Academic Press. 2003.
- Olivas-Esca rcega V, Rui-Rodri guez Mdel S, Fonseca-Leal Mdel P, Santos- Díaz MA, Gordillo-Moscoso A, Nernández-Sierra JF, et al. Prevalence of oral candidiasis in chronic renal failure and renal transplant pediatric patients. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2008; 32: 313-318.
- Bagga A, Mantan M. Nephrotic syndrome in children. Indian J Med Res. 2005; 122: 13-28.
- Warady BA, Chadha V. Chronic kidney disease in children: The global perspective. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007; 22: 1999-2009.
- Hamid MI, Dummer CD, Pinto LS. Systemic conditions, oral findings and dental management of chronic renal failure patients: General considerations and case report. Braz Dent J. 2006; l7: 166-170.
- Proctor R, Kumar N, Stein A, Moles D, Porter S. Oral and dental aspects of chronic renal failure. J Dent Res. 2005; 84: 199-208.
- de Francisco AL, Otero A. Occult chronic renal failure: EPIRCE study. Nefrologia. 2005; 25: 66-71.
- Davidovich E, Davidovits M, Eidelman E, Schwarz Z, Bimstein E. Pathophysiology, therapy, and oral implications of renal failure in children and adolescents: an update. Pediatr Dent. 2005; 27: 98-106.
- Jover Cerveró A, Bagán JV, Jiménez Soriano Y, Poveda Roda R. Dental management in renal failure: patients on dialysis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2008; 13: E419-E426.
- Leão JC, Gueiros LA, Segundo AV, Carvalho AA, Barrett W, Porter SR. Uremic stomatitis in chronic renal failure. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2005; 60: 259- 262.
- Antoniades DZ, Markopoulos AK, Andreadis D, Balaskas I, Patrikalou E, Grekas D. Ulcerative uremic stomatitis associated with untreated chronic renal failure: Report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101: 608-613.
- Kerr AR. Update on renal disease for the dental practitioner. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 92: 9-16.
- de la Rosa García E, Mondragón Padilla A, Aranda Romo S, Bustamante Ramírez MA. Oral mucosa symptoms, signs and lesions, in endstage renal disease and non-end stage renal disease diabetic patients. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006; 11: 467-473.
- De Rossi SS, Glick M. Dental considerations for the patient with renal disease receiving hemodialysis. J Am Dent Assoc. 1996; 127: 211-219.
- Kho HS, Lee SW, Chung SC, Kim YK. Oral manifestation and salivary flow rate, pH, and buffer capacity in patients with end stage renal disease undergoing renal dialysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999; 88: 316-319.
- Sobrado Marinho JS, Tomás Carmona I, Loureiro A, Limeres Posse J, García Caballero L, Diz Dios P. Oral health status in patients with moderate-severe and terminal renal failure. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007; 12: 305-310.
- Meyer TW, Hostetter TH. Uremia. N Engl I Med. 2007; 357: l316.
- Al Nowaiser A, Roberts GJ, Trompeter RS, Wilson M, Lucas VS. Oral health in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol. 2003; 18: 39-45.
- Saini R, Sugandha Saini S. The importance of oral health in kidney diseases. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010; 21: 1151-1152.
- Seymour RA, Thomason JM, Nolan A. Oral lesions in organ transplant patients. J Oral Pathol Med. 1997; 26: 297-304.
- Lima RB, Benini V, Sens YA. Gingival overgrowth in renal transplant recipients: A study concerning prevalence, severity, periodontal, and predisposing factors. Transplant Proc. 2008; 40: 1425-1428.
- Marshall RI, Bartold PM. Medication induced gingival overgrowth. Oral Dis. 1998; 4: 130-151.
- Hernández G, Arriba L, Frías MC, de la Macorra JC, de Vicente JC, Jiménez C, et al. Conversion from cyclosporin A to tacrolimus as a non-surgical alternative to reduce gingival enlargement: A preliminary case series. J Periodontol. 2003; 74: 1816-1823.
- Ciavarella D, Guiglia R, Campisi G, Di Cosola M, Di Liberto C, Sabatucci A, et al. Update on gingival overgrowth by cyclosporine A in renal transplants. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2007; 12: 19-25.
- Molpus WM, Pritchard RS, Walker CW, Fitzrandolph RL. The radiographic spectrum of renal osteodystrophy. Am Fam Phys. 1991; 43: 15l-158.
- Martins C, Siqueira WL, Guimaraes Primo LS. Oral and salivary flow characteristics of a group of Brazilian children and adolescents with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008; 23: 619-624.
- Nakhjavani YB, Bayramy A. The dental and oral status of children with chronic renal failure. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2007; 25: 7-9.
- Nunn JH, Sharp J, Lambert HJ, Plant ND, Coulthard MG. Oral health in children with renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000; 14: 997-1001.
- Management of chronic renal failure patients: General considerations and case report. Braz Dent J. 2006; l7: 166-170.