
Research Article
Austin J Dermatolog. 2023; 10(1): 1104.
Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Prurigo Nodularis: A Real-World Study
Xiaoli Li*
Department Head, School of Computer Science and Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore
*Corresponding author: Xiaoli LiDepartment Head, School of Computer Science and Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore Email: anjala@163.com
Received: February 02, 2023; Accepted: March 21, 2023; Published: March 28, 2023
Abstract
Prurigo Nodularis (PN) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by severe itching accompanied by multiple nodules throughout the body. There is currently no effective drug-targeted treatment for PN. Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody which can suppress the Th2 inflammatory reaction. We aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of dupilumab in PN. There were 29 PN patients who received dupilumab treatment for four months. Serum total Immunoglobulin E (Ig E), eosinophil counts, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), and Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) were assessed on patients before and after treatment. And we count the vaccination of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) in patients and the impact on skin diseases and treatment measures after vaccination. Plotting was performed using GraphPad Prism8, and statistical analysis was performed using PASW Statistics18.
The eosinophil counts in patients higher decreased to normal, and the Ig E levels gradually decreased and tended to normal levels after receiving dupilumab injection. The average DLQI score at baseline was 23.93±0.66, and decreased to 11.66±0.55 (P<0.01) and 1.83±0.22 (P<0.01) at 1-month and 6-month follow-up of treatment, respectively. The average NRS score at baseline was 9.79±0.08, and decreased to 3.52±0.23 (P<0.01) and 0.31±0.15 (P<0.01) at the 1-month and 6-month follow-up of treatment, respectively. Our study shows that dupilumab has achieved good efficacy in PN with few adverse reactions and high safety. We can recommend that patients follow the advice of specialists to be vaccinated and under the condition of stable disease, separated from dupilumab treatment for one week.
Keywords: Prurigo nodularis; Dupilumab; IL-4 and IL-13; Novel coronavirus pneumonia; Vaccine
Abbreviations: PN: Prurigo Nodularis; HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus; FDA: US Food and Drug Administration; IL-4Ra: IL-4 Receptor Subunit a; AD: Atopic Dermatitis; Ig E: Immunoglobulin E; DLQI: Dermatology Life Quality Index; NRS: Numeric Rating Scale; COVID-19: Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia
Introduction
Prurigo Nodularis (PN) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease with symmetrical distribution of nodules as typical skin lesions and severe itching as the main symptom [1]. It occurs on the trunk or extremities, especially on the lower legs the range in number from a few to hundreds [2]. Histopathological examination of the skin of PN lesions shows a dense infiltration of eosinophils, T lymphocytes, and mast cells that release multiple proinflammatory cytokines [3]; however, the incidence and prevalence of PN is not very clear, but some surveys show that it occurs more frequently in women and the elderly [4], and can also occur in children [5]. The quality of life of patients with this disease is severely reduced, and many studies have found that PN is significantly associated with insomnia, anxiety, and depression [6].
The exact pathogenesis of PN is unclear, but it is currently thought to be related to immune abnormalities caused by T lymphocytes, eosinophils, and mast cells, as well as potential interactions between neurons and neurohumor, resulting in intractable, malignant pruritus - scratching cycles-which subsequently lead to characteristic pruritic nodules [7]. Additionally, many factors are associated with PN, including eczema, psychiatric diagnoses, and chronic diseases such as malignancy, chronic liver and kidney failure, diabetes, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection [8-10]. There is currently no US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved drugs specifically targeting the treatment of PN, and clinicians often offer treatments, primarily targeting the underlying immune and neurological disorders [11]. Different treatment methods are used for different patients, and the curative effects varies greatly [12].
Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that blocks IL-4 receptor subunit a (IL-4Ra), and resulting in dual inhibition of IL-4 and IL-13 [13]. To date, dupilumab has been approved for patients with moderate-to-severe Atopic Dermatitis (AD) aged ≥six months [14], however, it has not yet been approved for PN. The collective role of Th2-related cytokines in the pathogenesis of PN suggests that dupilumab may be an effective treatment for this disease.[13] The objective of our study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of off-label use of dupilumab in PN in the real world.
Patients and Methods
Patients
This study collected patients with PN in our center from October 2020 to May 2022. Inclusion criteria are: PN was diagnosed by clinical presentation and skin biopsy; systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressive therapy are ineffective; refusal to use corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents and there are contraindications to use. Exclusion criteria: receiving and effective treatment with systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressants; poor patient compliance; hospitalization during treatment for severe allergies, systemic infectious diseases, or other diseases. After obtaining informed consent from patients and their families, the following information was collected for each patient: demographic and clinical data (sex, age, and disease duration), other comorbidities, previous medication history, etc.
Assessments
Laboratory test results for serum total Immunoglobulin E (Ig E) and eosinophil counts were collected at baseline, one and six months after starting treatment. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) were determined at baseline, one and six months after starting treatment. At the same time, the patients were followed up to observe whether there was any discomfort during treatment.
Medication
All patients were administered an initial dose of 600mg, subcutaneous injection, followed by a maintenance dose of 300mg every two weeks. The treatment continued for at least 4 months. There were two female pediatric patients (one 13 and one 14 years old) weighing >60kg, and experts recommended the initial the dose was 600mg, followed by a maintenance dose of 300mg every two weeks. Patients can be treated in the hospital or at home. During dupilumab treatment, other treatment modalities were discontinued. However, patients can be treated with topical glucocorticoids for not more than two weeks in the early stage of treatment, topical antipruritic ointment without hormones can be used for no more than one month.
Regarding the Situation of the Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (COVID-19) Vaccine
Since COVID-19 swept the world in late 2019, it has seriously threatened human life and health and caused huge medical, financial, and social damage globally. In the absence of specific treatment methods, vaccines are the most effective means of global prevention and control of COVID-19, and countries have invested heavily in vaccine development [15]. According to different research and development strategies, they can be divided into three categories: protein vaccines; gene-based vaccines; and combining protein- and gene-based methods to generate one or more protein antigens in vitro and in vivo, typically represented by live attenuated virus vaccines [16]. Since December 15, 2020, China has started large-scale vaccination work. Inactivated vaccines, adenovirus vector vaccines (type 5 adenovirus vector), and recombinant subunit vaccines (CHO cells) have been used urgently or approved for marketing under certain conditions [17]. Here we count the vaccination of patients and the impact on skin diseases and treatment measures after vaccination.
Statistical Analyses
Plotting was performed using GraphPad Prism8, and statistical analysis was performed using PASW Statistics18. Data represent mean ± sem. multiple sample means were compared using analysis of variance with repeated measures design data. Differences between data were considered statistically significant when P<0.05.
Results
29 patients were finally included in our study. There were 22 males (76%) and seven females (24%). The youngest age was 13 years, the oldest was 86 years, and the average age was 56.55±3.23; the shortest duration of the disease was half a year, and the longest was 20 years, with an average of 4.87±0.94. Four patients (13.79%) had hypertension, two patients (6.90%) had diabetes, one patient (3.45%) had coronary heart disease, and one patient (3.45%) had Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection. Among them, three patients (10.34%) had concurrent allergic rhinitis, and 11 patients (37.93%) had previously been diagnosed with eczema. Two patients (6.90%) had a family history of allergic diseases and one patient (3.45%) had a family history of eczema. Laboratory test results showed that seven patients (24.14%) had eosinophil counts higher than 0.52*109/L, and six patients (20.69%) had blood Ig E levels higher than normal levels (in adults ≥100IU/mL, in children 10-15 years old ≥200IU/mL). The eosinophil counts in these patients decreased to normal levels, and Ig E levels gradually decreased and tended to normal levels after receiving dupilumab treatment. All patients had previously treated with antihistamines and topical glucocorticoids; 18 patients (62.07%) had received oral and/or intramuscular glucocorticoids, six patients (20.69%) had received oral thalidomide tablets, and four patients (13.79%) had received micro-needling. Seven patients (24.14%) had received at least three of the above treatments but only had a short-term therapeutic effect. Patient details are shown in (Table 1).
Variable
Value n (%)
Sex
Male
Female
22(76%)
7 (24%)Age
56.55±3.23
Disease duration
4.87±0.94
Comorbidities
Hypertension
Diabetes
Coronary heart disease
Allergic rhinitis
Eczema
Human immunodeficiency virus
Family history
Allergic diseases
Eczema
4(13.79%)
2(6.90%)
1(3.45%)
3(10.34%)
11(37.93%)
1 (3.45%)2(6.90%)
1(3.45%)Laboratory examination
Elevated eosinophil count
Elevated Ig E levels
7(24.14%0
22(20.69%)Previous treatment
Antihistamine treatment
Topical glucocorticoids
Oral and/or intramuscular injection glucocorticoids
Oral thalidomide
Micro-needle therapy
29(100%)
29(100%)
19(65.52%)
6(20.69%)
4(13.79%)
Table 1: Basic information of patients with prurigo nodularis.
In our study, all patients were treated for at least four months, and the patients with the longest treatment were treated for 8 months. We followed up and observed the DLQI and NRS scores of the patients at baseline, one month, and six months after starting treatment, respectively. The average DLQI score at baseline was 23.93±0.66, and decreased to 11.66±0.55 (P<0.01) and 1.83±0.22 (P<0.01) at 1-month and 6-month follow-up of treatment, respectively. The average NRS score at baseline was 9.79±0.08, and decreased to 3.52±0.23 (P < 0.01) and 0.31±0.15 (P<0.01) at the 1-month and 6-month follow-up of treatment, respectively.
The DLQI and NRS scores of the patients are shown in (Table 2) (two patients showed moderate improvement in pruritus symptoms). During the treatment, pruritus in two patients (6.90%) (one patient with skin lesions concentrated on the back, the other patient concentrated on the head, face, neck, and upper limbs) worsened after stopped the four months of treatment for one month, and the condition improved after the maintenance dose was given to continue the injection.
Patient
DLQI0
DLQI1
DLQI6
NRS0
NRS1
NRS6
1
18
11
0
10
4
0
2
15
7
0
9
4
0
3
25
15
4
9
4
0
4
27
14
2
10
2
0
5
25
17
2
10
3
0
6
25
13
1
9
3
0
7
27
12
2
10
2
0
8
28
8
2
10
4
0
9
27
12
3
10
2
0
10
24
10
2
10
4
1
11
20
8
1
9
4
0
12
22
15
3
10
2
0
13
26
15
1
10
4
0
14
27
14
1
10
3
0
15
27
10
2
10
2
0
16
27
8
1
10
3
0
17
27
12
1
9
2
0
18
22
14
1
10
5
0
19
23
9
2
10
4
0
20
24
10
2
10
5
1
21
28
14
4
10
4
0
22
21
12
4
10
6
3
23
24
8
2
10
5
0
24
22
9
2
10
1
0
25
16
10
1
10
5
3
26
20
11
1
10
3
1
27
26
18
4
9
4
0
28
23
8
0
10
5
0
29
28
14
2
10
3
0
Table 2: Patient's DLQI and NRS scores.
Overall, we observed that the patient's itching symptoms improved significantly (Figure 1), less scratching, improved sleep quality, gradual regression of skin lesions, and residual hyperpigmentation at the primary site after dupilumab treatment. However, there were still some patients with stubborn nodules that subside slowly. We combined liquid nitrogen freezing and micro-needling therapy to promote the recovery of skin lesions. Interestingly, we found that regression of nodules in the head was slower in some patients than in the trunk and extremities. The patients in this study had no adverse reactions during treatment. Typical cases are shown in (Figures 2 & 3).
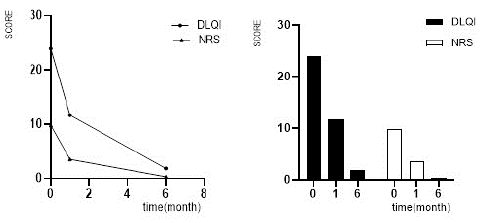
Figure 1: Changes in DLQI and NRS scores of patients.
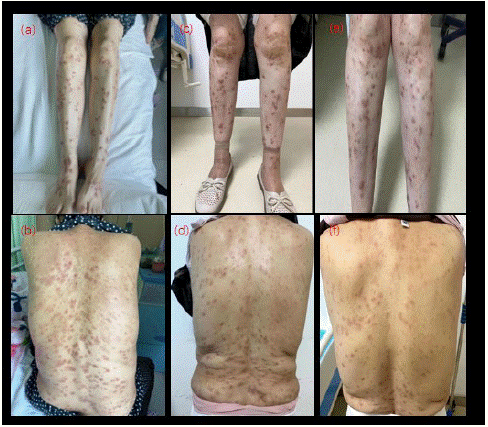
Figure 2: Cutaneous lesions before and after dupilumab treatment. a, b, are the photos before treatment; c, d are the photos after 6 injections of dupilumab; e, f are the photos after 10 injections of dupilumab.

Figure 3: Cutaneous lesions before and after dupilumab treatment. a, e, i are photos before treatment, b, f, j are photos after 5 injections of dupilumab, c, g, k are photos after 7 injections of dupilumab, d, h, l are photos after 10 injections of dupilumab.
In our study, six patients (20.69%) were not vaccinated because of concerns about their condition, 23 patients (79.31%) were vaccinated, and among them, one patient (4.35%) was vaccinated before the disease, two patients (8.70%) reported that the disease tended to aggravate after vaccination, and the remaining 20 patients (86.95%) vaccinated under the advice of doctors and under the condition of stable disease, separated from dupilumab treatment 1 week, and the disease does not worsen. The vaccination status of the patients with COVID-19 is shown in (Figure 4).
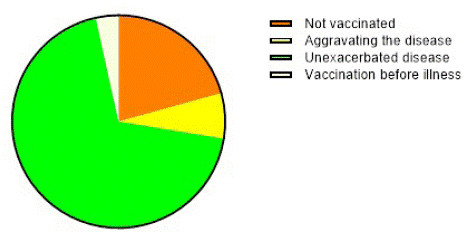
Figure 4: The vaccination status of patients with COVID-19 vaccine.
Discussion
The pathogenesis of PN is largely related to the enhanced inflammatory response, and several proinflammatory and pruritic cytokines are elevated in PN lesions, including Th2-related cytokines such as the interleukins IL-31 and IL-4 [4]. Dupilumab inhibits the type 2 immune response by blocking the IL-4 and IL-13 pathways, which can be used to break the pruritus cycle of PN and achieve the purpose of treatment [18]. In our study, a retrospective observational study of PN was performed. The real-world data is closer to clinical reality than the strict inclusion and exclusion criteria of clinical trials. Our study showed that a significant reduction in disease severity as measured by NRS and DLQI scores after four months of treatment, and dupilumab has achieved good efficacy in PN with few adverse reactions and high safety. The results of this study are same to previous studies [12,18,19]. It can quickly reduce itching, prevent the appearance of new nodules, and gradually reduce the number of current nodules [12].
PN is often associated with other allergic diseases, such as AD or chronic pruritus of various origins. In recent years, many scholars believe that PN can be regarded as a clinical manifestation of AD [20]. The study by Staender et al [8] showed that nearly half of PN had atopic predisposition or AD as the single cause of PN or mixed origin.In our study, 11 patients (37.93%) had been diagnosed with eczema in the past, and the conventional treatment was ineffective, long-term repeated scratching of the skin gradually formed nodules.
The efficacy of dupilumab in AD has been confirmed, and it can significantly improve the symptoms of itching, anxiety, sleep disturbance, and improve the quality of life of patients [13]. Although it is not currently approved for PN, our study found that dupilumab can also significantly improve the symptoms of PN, such as itching, sleep disturbance, anxiety. Compared with AD treatment, the skin lesions did not fully recover after four months treatment, the nodules subsided more slowly, and the remaining skin pigmentation was difficult to subside. At the same time, in our study, there were two patients (6.90%) relapsed after stopping treatment, and both patients had a history of eczema. Therefore, we suggest that PN associated with AD required more weeks of treatment than those with PN associated with non-AD. This finding is consistent with the conclusions of previous studies [21]. Therefore, in the absence of standard therapy, Dupilumab appears to be a safe and effective treatment for refractory PN. In our study, there were two patients had aggravated primary disease after vaccination. The patients did not take further measures and continued treatment according to the original plan, and then their condition gradually improved. Many adverse effects of vaccination have been reported in other studies. The most common adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccines are erythema, swelling, tender ness, pain, induration and itching at the injection site, as well as delayed local reactions, urticaria, and measles-like rash [22]. Certain pre-existing chronic inflammatory skin diseases, such as lupus erythematosus, are induced and aggravated after vaccination against COVID-19 [23]. Additionally, It is worth noting that severe systemic allergic reactions cannot be ignored. If pruritus, urticaria, flushing, and angioedema occur within the four hours after vaccination, symptomatic treatment should be given promptly [24]. With the continuous emergence of novel coronavirus variants, the ability of the virus to spread and cause disease has gradually increased. The COVID-19 vaccine remains an effective way to control the spread of the virus and block the epidemic. At present, we can recommend that patients follow the advice of specialists to be vaccinated, pay close attention to the changes after the injection, and provide further treatment if necessary. This study had certain limitations. First, the sample size was small, and only one hospital was selected for observation. In the future, multiple centers should be combined to carry out retrospective studies to increase the sample size and reduce selection bias. Second, there is few laboratory data because the follow-up method is mainly by telephone and the laboratory tests of some patients in the later stage of treatment are not carried out in our center, so specific information cannot be provided. Third, this is a retrospective study, in the future, a long follow-up time and a multicenter prospective cohort study should be conducted to observe the effect of dupilumab. Fourth, this study used the DLQI and NRS scores to evaluate the efficacy, and subjective factors had a greater influence. Therefore, a more objective approach should be sought to assess the efficacy of dupilumab in PN.
Conclusion
Our study is a real word study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the use of dupilumab in patients with PN, and we show that dupilumab appears to be a safe and effective treatment for patients with refractory PN.During the COVID-19 pandemic, we can recommend that patients follow the advice of specialists to be vaccinated during the stable period of the disease, separated from dupilumab treatment one week, pay close attention to the changes in the patient's condition after the injection, and provide further treatment if necessary.
References
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, Kwatra MM, Kwatra SG. Diagnostic Workup and Evaluation of Patients with Prurigo Nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019; 6: 97.
- Pereira MP, Steinke S, Zeidler C, Forner C, Riepe C, et al. European academy of dermatology and venereology European prurigo project: expert consensus on the definition, classification and terminology of chronic prurigo. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018; 32: 1059-1065.
- Williams KA, Roh YS, Brown I, Sutaria N, Bakhshi P, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacological treatment of prurigo nodularis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021; 14: 67-77.
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: Epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020; 83: 1559-1565.
- Amer A, Fischer H. Prurigo nodularis in a 9-year-old girl. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2009; 48: 93-95.
- Jorgensen KM, Egeberg A, Gislason GH, Skov L, Thyssen JP. Anxiety, depression and suicide in patients with prurigo nodularis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017; 31: e106-e107.
- Schuhknecht B, Marziniak M, Wissel A, Phan NQ, Pappai D, et al. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fibre density in lesional and nonlesional prurigo nodularis skin as a potential sign of subclinical cutaneous neuropathy. Br J Dermatol. 2011; 165: 85-91.
- Iking A, Grundmann S, Chatzigeorgakidis E, Phan NQ, Klein D, et al. Prurigo as a symptom of atopic and non-atopic diseases: aetiological survey in a consecutive cohort of 108 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol. 2013; 27: 550-557.
- Boozalis E, Tang O, Patel S, Semenov YR, Pereira MP, et al. Ethnic differences and comorbidities of 909 prurigo nodularis patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018; 79: 714-719.
- Winhoven SM, Gawkrodger DJ. Nodular prurigo: metabolic diseases are a common association. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2007; 32: 224-225.
- Williams KA, Huang AH, Belzberg M, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: Pathogenesis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020; 83: 1567-1575.
- Labib A, Ju T, Vander Does A, Yosipovitch G. Immunotargets and Therapy for Prurigo Nodularis. Immunotargets Ther. 2022; 11: 11-21.
- Munoz-Bellido FJ, Moreno E, Davila I. Dupilumab: A Review of Present Indications and Off-Label Uses. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2022; 32: 97-115.
- Dupilumab [Prescribing Information]. June, 2022. Available at: https://www.regeneron.com/downloads/dupixent_fpi.pdf.
- Dagotto G, Yu J, Barouch DH. Approaches and Challenges in SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Development. Cell Host Microbe. 2020; 28: 364-370.
- Graham BS. Rapid COVID-19 vaccine development. Science. 2020; 368: 945-946.
- COVID-19 Vaccination Technical Guidelines. China Center for Disease Control and Prevention; March 29, 2021. Available at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/jkj/s3582/202103/c2febfd04fc5498f916b1be080905771.shtml.
- Liu T, Bai J, Wang S, Ying S, Li S, et al. Effectiveness of Dupilumab for an Elderly Patient with Prurigo Nodularis Who Was Refractory and Contradicted to Traditional Therapy. J Asthma Allergy. 2021; 14: 175-178.
- Cunha IM, Valadao I, Gomes E, Marinho A. Dupilumab: A Safe and Successful Treatment in Refractory Prurigo Nodularis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022; 10: 1365-1366.
- Ferrucci S, Tavecchio S, Berti E, Angileri L. Dupilumab and prurigo nodularis-like phenotype in atopic dermatitis: our experience of efficacy. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021; 32: 453-454.
- Husein-ElAhmed H, Steinhoff M. Dupilumab in prurigo nodularis: a systematic review of current evidence and analysis of predictive factors to response. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022; 33: 1547-1553.
- McMahon DE, Amerson E, Rosenbach M, Lipoff JB, Moustafa D, et al. Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: A registry-based study of 414 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021; 85: 46-55.
- Kreuter A, Licciardi-Fernandez MJ, Burmann SN, Burkert B, Oellig F, et al. Induction and exacerbation of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus following mRNA-based or adenoviral vector-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022; 47: 161-163.
- Kim MA, Lee YW, Kim SR, Kim JH, Min TK, et al. COVID-19 Vaccine-associated Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions: Consensus Statements of the KAAACI Urticaria/Angioedema/Anaphylaxis Working Group. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2021; 13: 526-544.