
Review Article
J Dis Markers. 2014;1(3): 1013.
Predictive Role of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-1 in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases
Alexander E Berezin*
Department of Internal Medicine, State Medical University of Zaporozhye, Ukraine
*Corresponding author: Alexander E Berezin, Department of Internal Medicine, State Medical University of Zaporozhye, Ukraine
Received: October 05, 2014; Accepted: October 13, 2014; Published: October 14, 2014
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor-1 (VEGF-1) is a glycoprotein that belongs super family of vascular endothelial factors with sufficient capacity to stimulation of angiogenesis in vivo. VEGF-1 is widely expressed in various tissues and over expressed due to hypoxia and inflammation by different spectrum of the cells. A regulation of the VEGF-1 synthesis is mediated by paracrine mechanisms with involvement of specific solubilized receptor VEGFR that plays a pivotal role in a reduction of ischemic tissue injury through modulation of target organ protection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. The clinical correlations of circulating levels of VEGF-1 in subjects with cardiovascular diseases are still unclear. It has been suggested exaggerated concentration of VEGF-1 might refer a better prognosis in CAD patients, while a negative effect of neovascularization in plaque region supporting by VEGF-1 is defined. The negative effect of VEGF-1 on progression in age-related diseases, such as early diabetic retinopathy, has been reported. This review is dedicated the discussion of controversial role of the VEGF-1 among cardiovascular disease patients and assay to predictive value of VEGF- 1 as biomarker at risk stratification.
Keywords: Vascular endothelial growth factor; Angiogenesis; Neovascularization; Cardiovascular diseases; Age-related diseases; Metabolic comorbidities
Introduction
Angiogenesis and neovascularization might have a controversial role in pathogenesis of several cardiovascular diseases [1]. On the one hand, generating new blood vessels mediated is considered a powerful mechanism that leads to attenuation of ischemic damage and restore of tissue perfusion [2]. On the other hand, new vessel formation plays a critical role in the progression of atherosclerotic lesions and appearance of vulnerability [3-5]. It is known that neovascularization may distribute to the plaque throughout vessel wall resulting induce of instability, mechanical plaque' cap disorders and rupture [4]. Vascular endothelial growth factor-1 (VEGF-1) appears to be a glycoprotein that belongs super family of vascular endothelial factors that are synthesized by a wide spectrum of cells and possessed a sufficient angiopoetic activity [6]. VEGF-1 is a main player in processing of revascularization, neoangiogenesis, reperfusion, as well as neuro protection and cardio protection. This review is dedicated the consideration of controversial role of the VEGF-1 among cardiovascular disease patients and assay to predictive value of VEGF-1 as biomarker at risk stratification.
Biological Role of VEGF-1
Vascular endothelial growth factor-1 (VEGF-1) is synthesized by a cells different origin and produces sufficient angiopoetic activity in vivo [6]. Recent investigations have shown VEGF-1 appears to be stimulated angiogenesis in several settings by an association with the tyrosine kinas receptors VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) located on the endothelial cells surface [7, 8]. Binding of VEGF-1 with VEGFR-2 causes cell growth, proliferation, and migration, neovascularization and angiogenesis [9, 10]. Therefore, VEGF-1 as a ligand for alpha-5 / beta-1 integrin may activate the migration of progenitor cells, endothelial cells and mononuclear's that leads to potentiate vasodilatation and to increase an inflammation [11, 12]. Figure presents a key mechanisms that are involved VEGF-1 in pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease.
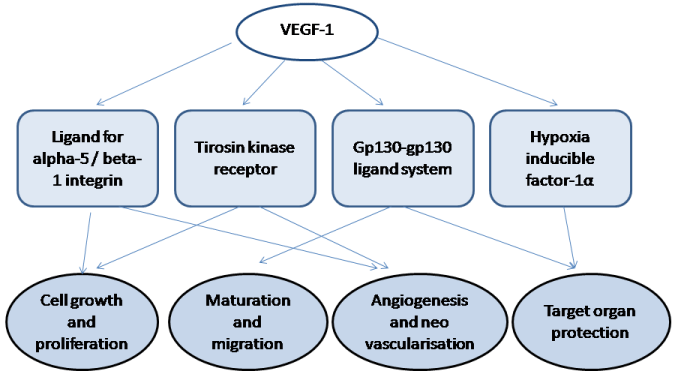
Figure 1: The key mechanisms that are involved VEGF-1 in pathogenesis of
cardiovascular disease.
A regulation of the VEGF-1 synthesis is mediated by paracrine mechanisms with involvement of VEGFR that plays a pivotal role in a reduction of ischemic tissue injury through modulation of target organ protection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis [13]. It is well known that the initial stimuli for over expression of VEGF-1 are active forms of oxygen in the tissue that may modulate the expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1a (HIF-1a) [1]. Both growth factors are controlled by prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins (PHD), which is considered a potential cardio protective and neuro protective factor, as well as certain angiopoetic modulator [14]. As known, VEGF-1 increases the permeability of the layer of endothelial cells, leads to plasma proteins to extravasate and lay down a provisional extracellular matrix scaffold and, thereby, promote sufficient pro-angiogenic effect [1]. Therefore, it is suggested that the glycoprotein 130- glycoprotein 130 ligand systems may involve in VEGF-related regulation in human cardiac myocytes [15]. Indeed, increased VEGF-1 expression was found in myocardial tissue obtained from a patient with acute myocarditis and a selective stimulation of VEGF by gp130 ligand was reflected by a specific receptor expression on cardiac myocytes [15]. Because glycoprotein 130 is a common receptor subunit for several inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukins (IL) -6, IL-11, cardiotrophin-1 etc, the ability of glycoprotein 130-glycoprotein 130 ligand system to up-regulate VEGF expression in the myocardium is crucial for maintenance of cardiac function in myocarditis and ischemic cardiomyopathies [1, 15].
In fact, several pathological processes, such as hypoxia and inflammation via induction of VEGF through auto- and paracrine mechanisms may play a pivotal role in myocardial revascularization. Exaggerated production of VEGF-1 may depend on over expression micro RNAs (miRNAs) that involved in the modulation of various angiopoetic factors. It has been found that miR-181a, miR-106a and miR-20b may regulate various biological processes independently associated with angiogenesis, such as cell migration, cell growth and proliferation through modulation of VEGF-1 over-expression [16]. VEGF-1 may improve survival of endothelial cells through an activation of intracellular regulating enzymes, such as PI3-kinase, Akt and Src [17]. Overall, VEGF-1 promotes proliferative changes by two ways: a classical promotion of endothelial cell layer and a non canonical ability to engage platelet-derived growth factor receptor a and gp130-gp130 ligand system [18]. We do not know whether one of these mechanisms is key player in cardiovascular remodeling in patients with various settings and what is the predictive role of circulating VEGF-1 in different clinical settings.
VEGF-1 in Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease
The clinical correlations of circulating levels of VEGF-1 in asymptomatic atherosclerosis and symptomatic coronary artery disease (CAD), including unstable CAD subjects who are required PCI are largely unclear. For acute and stable CAD, asymptomatic atherosclerosis and planned or post pounded revascularization procedures (CABG, PCI) VEGF-1 may produce multi-directed effects [19].
It is well known that formation of new vessels from vasa origin characterized severely stenotic lesions and correlated well with the extent of inflammatory cell infiltration of lipid core and lipid core size [20]. VEGF-1 produced by peripheral blood mononuclear cells, which are accumulated in the rupture plaque. Interestingly, new vessels from lumen origin were found in plaques with 40% and 50% artery stenosis and were associated frequently with hemorrhage in the plaque [21]. On the one hand, there is closely interrelationship between neovascularization and plaque instability that is considered a potentially unfavorable condition for survival of the patients [22]. On the other hand, the extent of ischemic myocardial damage and appearance of acute myocardial infarction (MI) contributes to the elevation of serum VEGF-1 levels that allows VEGF-1 to improve left ventricular function by promoting angiogenesis and re endothelialization after MI [23]. Indeed, there are evidences that the patients with acute MI have elevated circulating VEGF-1 levels when compared with healthy subjects [24]. After reperfusion, the serum VEGF-1 levels rapidly returned almost completely to the normal control range. These data allowed authors to strongly suggest that the serum level of VEGF-1 is one of the most sensitive indicators of myocardial ischemia. Kranz et al [25] have been measured the levels of VEGF-1 in the serum and in the coronary sinus of the patients after acute MI. Surprisingly, accordingly data obtained the main source for VEGF-1 in the blood stream is not the infarcted myocardium, while concentration of VEGF-1 in coronary sinus was higher compared with peripheral blood stream. Authors concluded that the most likely source of the elevated VEGF-1 in acute MI patients is circulating platelets, rather than the infracted myocardium. However, obtained data of the investigation have suggested that VEGF-1 is key player in endogenous activation of coronary collateral formation in the human heart. This suggesting is confirmed the results obtained by Ramos et al [26]. Authors examined the longitudinal changes of VEGF-1 concentrations after PCI for predicting major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in CAD patients. The VEGF-1 concentration showed a positive evolution through one year in 84% of patients enrolled in the study. The longitudinal changes of circulating VEGF-1 levels in the patients significantly increased to one month and remainedrelatively steady to one year approaching the VEGF-1 levels of healthy volunteers. Low baseline VEGF concentration (<40.8 pg/ mL) conveyed increased risk for recurrent hospitalization and MACE in a 5-year follow-up after PCI with drug eluting stent placement. According opinion of investigators the results reflect a positive role of elevated VEGF-1 in serum in recovery and support its importance in CAD prognosis. It is needed to take into consideration that VEGF- 1 levels were below detection limit in almost 50% of the acute MIor acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and non-ACS patients at the baseline in majority investigations dedicated this issue. Noted the data obtained from the patients with acute MI, who were not candidates for PCI, indicated a sufficient predictive role of circulating VEGF- 1 too [27, 28]. However, exaggerated VEGF-1 level would confer a better prognosis in CAD patients undergoing PCI or without it as its actions may contribute to ameliorate the damaged endothelium and promote rapid recovery after stinting and reperfusion due to thrombolysis.
Nevertheless, this issue seems to be not obviously, because there are evidences for negative effects of VEGF-1 toward atherothrombosis. There are at least two facts that are confirmed a negative effect of neovascularization in plaque region [4]. The recent human researches have been shown reducing micro vessel formation in fibrocalcific plaques when compared with vulnerable ruptured and lipid-rich plaques that are considered a life-threatening finding [2]. Therefore, second fact relating neo vessels to plaque regression is the impressive 85% and 70% reduction of atherosclerosis in apo-E knockout mice treated with the angiogenic inhibitors endostatin and TNP-470 respectively [29]. Moreover, over expression of VEGF-1 in endothelial cells and circulating mononuclear's may contribute in thrombosis and thrombus remodeling [2]. Because VEGF-1 is considered a key pro-angiogenic factor in atherosclerotic plaques, which is expressed in the necrotic nucleus of the atheroma, the final result of the expression will define plaque evolution and small vessel growth around ischemic or necrotic zone [3]. Probably, VEGF-1 may involve in the cardiovascular remodeling through ST2/IL33 pathway that is activated by biomechanical stress or as result in ischemia injury [30]. However, it is reported that tumor necrosis factor alpha may enhance transcription of ST2 on surface of the endothelial cells and thereby modulate revascularization [30]. On the other hand, interleukin-33 as a functional ligand of ST2 ligand activates mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK)-kinases on surface of circulating inflammatory cells that leads to inhibition of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) kinase complex and suppression of the production cytokines and activation of inflammatory cells. In fact, over expression of VEGF- 1 and ST2/IL33 pathway in endothelial cells may be two faces of one process aimed neovascularization that is enhanced by inflammatory stimuli. Overall, a dual role of VEGF-1 in cardiovascular disease is presented in Table.
Positive effects
Negative effects
Target organ protection followed by a potentially pathogenic induction of vascular remodeling.
Neovascularization of plaque region with increased vulnerability of patients
Attenuation of endothelial lesion
Stimulation of instability of plaque
Supporting of cardiac pump and diastolic function
Increased tissue and vascular remodeling
Stimulation of collateral blood flow
Pro-apoptotic effect in nitric oxide dependent manner
Increasing vasa permeability
Regulation of systemic blood pressure
Stimulation of natriuresis
Low-intensive anti-inflammatory effect
Table 1: The dual role of VEGF-1 in cardiovascular diseases.
Thus, the role of the VEGF-1 in CAD patients may depend on clinical settings, requirement of reperfusion procedures, and, probably, type and generation of the stent. This issue is required more detail investigations with higher statistical power, while preliminary reports regarding predictive role of exaggerated VEGF-1 levels, seems to be optimistic.
The Role of VEGF-1 in Age-related Diseases
The role of VEGF-1 in age-related diseases is still under discussion and appears to be very controversial. The negative effect of VEGF-1 on disease progression in age-related diseases, such as early diabetic retinopathy, has been defined very well in animal model and in the clinical studies [31, 32]. Overall, for diabetic patients with retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, the final result of stimulation of angiogenesis is certainly negative, on the other hand, for subjects with obesity, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease [7, 33, 34]. Probably the role of VEGF-1 over expression is defined uncertain or harm [34, 35]. In fact, suppression of angiogenesis might be favorable in diabetic population [36, 37]. Indeed, using anti-VEGF drugs has been shown that there is a positive responses affected metabolic faces of age-related diseases [38]. However, these suggestions are not obviously [40]. Surprisingly, anti-VEGF treatment increased insulin sensitivity in young and old mice but had no effects in the mid-aged group. Therefore, anti-VEGF remedies significantly improved insulin sensitivity in mid-aged obese mice fed a high-fat diet [40].
The innate exact mechanisms affected VEGF and their role in metabolism is not still understood. Because levels of VEGF expression in various white adipose tissues may change uninterruptedly in various age populations, it has been suggested adipose vasculature sufficiently modulates fat mass, adipocyte functions, blood lipid composition, as wells as insulin sensitivity [41]. By now it is known that the pro angiogenic mononuclear phagocytes are able selectively recruited to sites of pathological neovascularization in response to locally produced semaphoring 3A as well as VEGF-1 that is essential for disease progression [32]. Therefore, hyperglycemia may increase VEGF-1 and VEGFR mRNA without changing their intracellular protein levels in neurons different origin, such as dorsal root ganglion that may leads to early affected neurite outgrowth through the impairment of VEGF/VEGFR signaling [41-43].
Thus, VEGF-1-related pathological neovascularization is defined a pivotal mechanism of negative evolution of age-related diseases, such as diabetes, obesity and insulin resistance [40]. More evidences for predictive role of VEGF-1 in the diabetes and other metabolic comorbidities in patients with cardiovascular diseases are required. Recent clinical studies have shown that serum VEGF increases in diabetic poly neuropathy [39], particularly in the neurologically active symptomatic stage [42, 45].
The Role of VEGF-1 in Systemic Hypertension
By now it is known that hypertension is common complication of the anti-VEGF signaling pathway therapy. Therefore, the incidence and severity of hypertension are dependent mainly on the type and the dose of the anti-VEGF drugs. But exact mechanisms that are lead to hypertension in subjects treated with anti-VEGF are still unclear. Results of recent studies have been allowed to suggest that the therapeutic use of the VEGF antagonist sunitinib is able to induced hypertension through Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibition in nephron that leads to increasing of renal vascular resistance (RVR) and renal sodium re-absorption [46]. Overall, VEGFR may regulate renal sodium absorption and attenuate vasomotion. In this context, anti- VEGF- drug induced hypertension is considered a model of primary sodium retention deterioration associated with increased RVR. Therefore, anti-VEGF drugs may suppress metabolism of podocites and thereby lead to their dysregulation, proteinuria and hypertension [47]. Thus, blocking of VEGF signaling pathway is key mechanism of hypertension in patients with advanced or recurrent malignancy underwent chemotherapy.
There are attempts to use circulating VEGF-1 level as biomarker of clinical evolution of hypertension in small patient cohorts. Although circulating level of VEGF-1 in hypertensive patients is low, there are evidences that increased VEGF levels in pregnant women with severe hypertension may be discussed a risk of preeclampsia and predictor of impaired fetal growth [48, 49]. Some pregnancyrelated antihypertensive drugs (methyldopa) may affect placental vascularization and prevent gestosis by increased VEGF concentration [50]. Lacchini et al. [51] reported that VEGF-1 polymorphisms is associated well with cardiac remodeling and left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients. Moreover, genotypes for VEGF-1 polymorphisms can be useful to help to identify hypertensive patients at greater intrinsic risk for heart failure. Probably we need novel investigations to be understanding of the predictive role of the VEGF-1 in pre hypertension and hypertensive state.
VEGF-1 and Cardiac Dysfunction in Myocarditis
The exact innate molecular mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in myocarditis have not been understood. Given data obtained in recent clinical studies it remains controversial whether angiogenesis is beneficial or harmful in inflammatory disease, because there are evidences that sufficient vascular lesions is able possibly to impair global cardiac pump function in myocarditis [52, 53]. It has been suggested that neovascularization supporting by over expression of VEGF-1 is able to improve contractility function in myocarditis through suppression of oxidative stress [54]. These are data indicated that over expression of VEGF-1 appears not only the ability to regulate cardiac remodeling, as well as contribute to prevent the development of post myocarditis dilated cardio myopathy [55]. Although recent studies have shown that the increased level of VEGF-1 mRNA has been detected after transient inflammatory and ischemic injury [23, 56], the predictive role of circulating VEGF-1 mRNA in myocardities and dilated cardiomyopathies is still not clear.
Predictive Role of VEGF-1 in Acute Stroke
Inflammation appears to be a key mechanism in the pathogenesis of acute stroke [57, 58]. Given data of recent clinical studies, which demonstrated an indirect interrelation between level of proinflammatory cytokines in serum and a cardiovascular risk in acute ischemic stroke subjects [59-61], the effect of low intensity proinflammatory activation on modulation of recurrent cardiovascular events is still understood and remains controversial [62, 63]. Proinflammatory cytokines were postulated to be able to modulate the activity of endothelial cells via induction of synthesis of VEGF [6].
It has been known that VEGF-1 improved blood-brain barrier integrity [9]. While an induction of VEGF-1 on endogenous neurogenesis and angiogenesis is known, the innate mechanisms of atherothrombosis-related evolution of brain injury and activated endogenous repair mechanisms are not fully understood. The production of VEGF-1 due to focal brain ischemia was found to be able to create a neuro protection, to improve neoangiogenesis and neurogenesis [5, 64]. Therefore, VEGF-1 is able to induce postischemic neurovascular remodeling and apoptosis [65]. Probably, these mechanisms underlie the derangement of progressive three-dimensional per vascular cytoarchitectonics, expanding the penumbra zone and worsening cerebral ischemia [66]. Since the angiopoetic VEGF-1 effect is systemic, it might be assumed that neovascularization in the vulnerable atheroma site should promote progressive worsening of the mechanical capacity of the atheroma cap, the formation of the phenomenon of "fatigue" cap, the appearance of endothelial dysfunction and deregulation of vascular tone, which ultimately leads to a corresponding atherothrombosis events in any vascular territories [22, 67]. It has been supposed that immediate VEGF-1 effects are probably adaptive in nature in hypertensive patients after ischemic stroke, while delayed VEGF-1 effects may be associated with recurrent clinical events, in particular, mediated by atherothrombosis [62, 63].
In this context, clinical studies are required, probably, using comparison various biologic markers, including VEGF-1. Really, recent investigations have revealed that some biological markers of endothelial dysfunction, such as VEGF-1, and some indicators of proinflammatory activation had a predictive value for clinical outcomes in patients at high cardiovascular risk only [68-72]. It has been hypothesized that the predictive value of the repeatedly measured circulating VEGF-1 level will be better than single peak VEGF-1 level for predicting of recurrent cardiovascular events in patients with acute ischemic stroke [62]. There are the preliminary results of the small studies that appear to be optimistic for use of VEGF-1 monitoring in acute stroke patient with further risk stratification [63]. Thus, VEGF-1 level in acute ischemic stroke patients might be have a value for at risk stratification. On the other hand, data regarding VEGF-1 in patients with other types of stroke, including intracranial hemorrhage, is very limited.
Conclusions
Although there are not sufficient evidences that the clinical correlations of circulating levels of VEGF-1 in subjects with cardiovascular diseases might have predictive value, it has been suggested exaggerated VEGF-1 level would confer a better prognosis in CAD patients, especially those who are underwent revascularization procedures or have acute / acutely decompensate heart failure due to ischemic and inflammatory reasons. By now it has data for potentially negative effect of VEGF-1-related neovascularization in plaque region that might be considered a mechanism of vulnerability of patient. Therefore, the negative effect of VEGF-1 on progression in agerelated diseases, such as early diabetic retinopathy, has been reported. Although currently the continued monitoring for changes in VEGF-1 level is not recommended, but vulnerable patient populations at high cardiovascular risk, probably, may have some benefit in prediction of clinical outcomes based on circulating VEGF-1 measurement.
List of all Abbreviation
ACS - acute coronary syndrome
CABG - coronary artery bypass grafting
HIF-1a - hypoxia inducible factor-1a
MACE - major adverse cardiac events
MAPK - mitogen-activated protein kinase
MI - myocardial infarction
NF-κB - nuclear factor-κB
PHD - prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein
PCI - percutaneous transluminal coronary intervention
ROCK - Rho kinase
RVR - renal vascular resistance
VEGF - vascular endothelial growth factor
VEGFR - receptor-2 for vascular endothelial growth factor
References
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK . Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. 2011; 473: 298-307.
- Hansson GK . Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352: 1685-1695.
- Al-Rasheed NM, Attia HA, Mohamed RA, Al-Rasheed NM, Al-Amin MA. Preventive effects of selenium yeast, chromium picolinate, zinc sulfate and their combination on oxidative stress, inflammation, impaired angiogenesis and atherogenesis in myocardial infarction in rats. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2013; 16: 848-867.
- Subbotin VM. Neovascularization of coronary tunica intima (DIT) is the cause of coronary atherosclerosis. Lipoproteins invade coronary intima via neovascularization from adventitial vasa vasorum, but not from the arterial lumen: a hypothesis. Theor Biol Med Model. 2012; 9: 11.
- Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, et al . VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111: 1843-1851.
- Ferrara N1, Gerber HP, LeCouter J . The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003; 9: 669-676.
- Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM, Cross MJ. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: structure, function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell Signal. 2007; 19: 2003-2012.
- Howangyin KY, Silvestre JS . Diabetes mellitus and ischemic diseases: molecular mechanisms of vascular repair dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014; 34: 1126-1135.
- Shen F, Walker EJ, Jiang L, Degos V, Li J, Sun B, Heriyanto F . Coexpression of angiopoietin-1 with VEGF increases the structural integrity of the blood-brain barrier and reduces atrophy volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011; 31: 2343-2351.
- Takahashi H, Shibuya M . The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond). 2005; 109: 227-241.
- Luque A, Carpizo DR, Iruela-Arispe ML . ADAMTS1/METH1 inhibits endothelial cell proliferation by direct binding and sequestration of VEGF165. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278: 23656-23665.
- Orecchia A., Lacal P.M., Schietroma C., Morea V., Zambruno G., Failla C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is deposited in the extracellular matrix by endothelial cells and is a ligand for the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Sci. 2003; 116: 3479-3489.
- Siow RC, Churchman AT . Adventitial growth factor signalling and vascular remodelling: potential of perivascular gene transfer from the outside-in. Cardiovasc Res. 2007; 75: 659-668.
- Reischl S, Li L1, Walkinshaw G2, Flippin LA2, Marti HH1, Kunze R1 . Inhibition of HIF prolyl-4-hydroxylases by FG-4497 reduces brain tissue injury and edema formation during ischemic stroke. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e84767.
- Weiss TW1, Speidl WS, Kaun C, Rega G, Springer C, Macfelda K, et al . Glycoprotein 130 ligand oncostatin-M induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human adult cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2003; 59: 628-638.
- Cuevas A, Saavedra N1, Cavalcante MF2, Salazar LA1, Abdalla DS3 . Identification of microRNAs involved in the modulation of pro-angiogenic factors in atherosclerosis by a polyphenol-rich extract from propolis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014; 557: 28-35.
- Tsurumi Y, Murohara T, Krasinski K, Chen D, Witzenbichler B, Kearney M, et al . Reciprocal relation between VEGF and NO in the regulation of endothelial integrity. Nat Med. 1997; 3: 879-886.
- Pennock S, Haddock LJ, Mukai S, Kazlauskas A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Acts Primarily via Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor a to Promote Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy. Am J Pathol. 2014 Sep 24. pii: S0002-9440(14)00496-9.
- D'Amario D, Leone AM, Iaconelli A, Luciani N, Gaudino M, Kannappan R, et al . Growth properties of cardiac stem cells are a novel biomarker of patients' outcome after coronary bypass surgery. Circulation. 2014; 129: 157-172.
- Scicchitano P, Marzullo A, Ciccone MM. The Role of Intimal Arterial Calcification in the Context of Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability. J Cytol Histol 2014; 5: 111.
- Kumamoto M, Nakashima Y, Sueishi K . Intimal neovascularization in human coronary atherosclerosis: its origin and pathophysiological significance. Hum Pathol. 1995; 26: 450-456.
- Niccoli Asabella A, Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Scicchitano P, Gesualdo M, Zito A, et al. Higher reliability of 18F-FDG target background ratio compared to standardized uptake value in vulnerable carotid plaque detection: a pilot study. Ann Nucl Med. 2014; 28: 571-9.
- Hojo Y, Ikeda U, Zhu Y, Okada M, Ueno S, Arakawa H, et al . Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 35: 968-973.
- Seko Y, Imai Y, Suzuki S, Kamijukkoku S, Hayasaki K, Sakomura Y, et al . Serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing reperfusion therapy. Clin Sci (Lond). 1997; 92: 453-454.
- Kranz A, Rau C, Kochs M, Waltenberger J. Elevation of vascular endothelial growth factor-A serum levels following acute myocardial infarction. Evidence for its origin and functional significance. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2000; 32: 65-72.
- Ramos C, Napoleão P2, Selas M3, Freixo C3, Viegas Crespo AM4, Mota Carmo M5, et al . Prognostic value of VEGF in patients submitted to percutaneous coronary intervention. Dis Markers. 2014; 2014: 135357.
- Heeschen C, Dimmeler S, Hamm CW, Boersma E, Zeiher AM, Simoons ML; CAPTURE (c7E3 Anti-Platelet Therapy in Unstable REfractory angina) Investigators . Prognostic significance of angiogenic growth factor serum levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2003; 107: 524-530.
- Korybalska K, Pyda M, Kawka E, Grajek S, Bręborowicz A, Witowski J . Interpretation of elevated serum VEGF concentrations in patients with myocardial infarction. Cytokine. 2011; 54: 74-78.
- Moreno PR, Purushothaman KR, Sirol M, Levy AP, Fuster V . Neovascularization in human atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2006; 113: 2245-2252.
- Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Gesualdo M, Riccardi R, Di Nunzio D, Moncelli M, et al . A novel cardiac bio-marker: ST2: a review. Molecules. 2013; 18: 15314-15328.
- Abu El-Asrar AM, Nawaz MI, Kangave D, Mairaj Siddiquei M, Geboes K. Angiogenic and vasculogenic factors in the vitreous from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Res 2013; 2013: 539658.
- Yan HT, Su GF2 . Expression and significance of HIF-1 α and VEGF in rats with diabetic retinopathy. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014; 7: 237-240.
- Dejda A, Mawambo G, Cerani A, Miloudi K, Shao Z, Daudelin JF, et al. Neuropilin-1 mediates myeloid cell chemoattraction and influences retinal neuroimmune crosstalk. J Clin Invest. 2014; .
- Taiana MM, Lombardi R1, Porretta-Serapiglia C1, Ciusani E2, Oggioni N3, Sassone J1, et al . Neutralization of schwann cell-secreted VEGF is protective to in vitro and in vivo experimental diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e108403.
- Tufro A, Veron D . VEGF and podocytes in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2012; 32: 385-393.
- Mitry D, Bunce C, Charteris D . Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for macular oedema secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013; 1: CD009510.
- Nicholson BP, Schachat AP . A review of clinical trials of anti-VEGF agents for diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010; 248: 915-930.
- Badros A, Porter N, Zimrin A . Bevacizumab therapy for POEMS syndrome. Blood. 2005; 106: 1135.
- Schratzberger P, Walter DH, Rittig K, Bahlmann FH, Pola R, Curry C, et al . Reversal of experimental diabetic neuropathy by VEGF gene transfer. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107: 1083-1092.
- Honek J, Seki T1, Iwamoto H1, Fischer C1, Li J2, Lim S1, et al . Modulation of age-related insulin sensitivity by VEGF-dependent vascular plasticity in adipose tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; .
- Kennedy JM, Zochodne DW . Impaired peripheral nerve regeneration in diabetes mellitus. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2005; 10: 144-157.
- Leinninger GM, Vincent AM, Feldman EL . The role of growth factors in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2004; 9: 26-53.
- Zochodne DW, Verge VM, Cheng C, Sun H, Johnston J . Does diabetes target ganglion neurones? Progressive sensory neurone involvement in long-term experimental diabetes. Brain. 2001; 124: 2319-2334.
- Deguchi T, Hashiguchi T, Horinouchi S, Uto T, Oku H, Kimura K, et al . Serum VEGF increases in diabetic polyneuropathy, particularly in the neurologically active symptomatic stage. Diabet Med. 2009; 26: 247-252.
- Mironidou-Tzouveleki M, Tsartsalis S, Tomos C . Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr Drug Targets. 2011; 12: 107-114.
- Grisk O, Koenen A, Meissner T, Donner A, Braun D, Steinbach A, et al . Rho kinase inhibition mitigates sunitinib-induced rise in arterial pressure and renal vascular resistance but not increased renal sodium reabsorption. J Hypertens. 2014; 32: 2199-2210.
- Hayman SRn, and renal toxicity. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012; 14: 285-294.
- Zawiejska A, Wender-Ozegowska E, Iciek R, Brazert J. Concentrations of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, angiotensin-converting enzyme, vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor in maternal blood and maternal metabolic status in pregnancy complicated by hypertensive disorders. J Hum Hypertens. 2014 Sep 4; 28: 670-676
- Wender-Ozegowska E, Zawiejska A, Iciek R, BrÄ…zert J . Concentrations of eNOS, VEGF, ACE and PlGF in maternal blood as predictors of impaired fetal growth in pregnancy complicated by gestational hypertension/preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2014; .
- Xu B, Charlton F, Makris A, Hennessy A. Antihypertensive drugs methyldopa, labetalol, hydralazine, and clonidine improve trophoblast interaction with endothelial cellular networks in vitro. J Hypertens. 2014; 32: 1075-83.
- Lacchini R, Luizon MR1, Gasparini S2, Ferreira-Sae MC2, Schreiber R2, Nadruz W Jr2, et al . Effect of genetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2014; 113: 491-496.
- Tada Y, Ogawa M, Watanabe R, Zempo H, Takamura C, Suzuki J, et al. Neovascularization induced by hypoxia inducible transcription factor is associated with the improvement of cardiac dysfunction in experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014; 23: 149-162.
- Huusko J, Merentie M, Dijkstra MH, Ryhänen MM, Karvinen H, Rissanen TT, et al . The effects of VEGF-R1 and VEGF-R2 ligands on angiogenic responses and left ventricular function in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 86: 122-130.
- Jain K, Suryakumar G, Prasad R, Ganju L . Upregulation of cytoprotective defense mechanisms and hypoxia-responsive proteins imparts tolerance to acute hypobaric hypoxia. High Alt Med Biol. 2013; 14: 65-77.
- Arumugam S, Mito S, Thandavarayan RA, Giridharan VV, Pitchaimani V, Karuppagounder V, et al. Mulberry leaf diet protects against progression of experimental autoimmune myocarditis to dilated cardiomyopathy via modulation of oxidative stress and MAPK-mediated apoptosis. Cardiovasc Ther. 2013; 31: 352-62.
- Banai S, Shweiki D, Pinson A, Chandra M, Lazarovici G, Keshet E.. Upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression induced by myocardial ischaemia: implications for coronary angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 1994; 28: 1176-1179
- Zeng L, He X, Liu J, Wang L, Weng S, Wang Y, et al . Differences of circulating inflammatory markers between large- and small vessel disease in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Med Sci. 2013; 10: 1399-1405.
- Jin R, Liu L, Zhang S, Nanda A, Li G . Role of inflammation and its mediators in acute ischemic stroke. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013; 6: 834-851.
- Arenillas JF, Alvarez-Sabín J, Molina CA, Chacón P, Montaner J, Rovira A, et al. C-reactive protein predicts further ischemic events in first-ever transient ischemic attack or stroke patients with intracranial large-artery occlusive disease. Stroke. 2003; 34: 2463-2468.
- Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Pecoraro R, Arnao V, Pinto A, Licata G . Inflammation in ischemic stroke subtypes. Curr Pharm Des. 2012; 18: 4289-4310.
- Luo Y, Wang Z, Li J, Xu Y . Serum CRP concentrations and severity of ischemic stroke subtypes. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012; 39: 69-73.
- Berezin AE, Lisovaya OA. Predictive Value of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-1 in Arterial Hypertension Patients. Internal Medicine: Open Access, 2014; 11: 006
- Berezin AE, Lisovaya OA. Predictive Value of Circulating Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-1 Level Measured Repeatedly During Long-Term Follow-Up in Patients with Arterial Hypertension after Acute Ischemic Stroke. Angiology: Open Access. 2014, 2: 119-216.
- Hayashi T, Abe K, Itoyama Y . Reduction of ischemic damage by application of vascular endothelial growth factor in rat brain after transient ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998; 18: 887-895.
- Hermann DM, Zechariah A . Implications of vascular endothelial growth factor for postischemic neurovascular remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009; 29: 1620-1643.
- Lo EH . A new penumbra: transitioning from injury into repair after stroke. Nat Med. 2008; 14: 497-500.
- Testa U, Pannitteri G, Condorelli GL . Vascular endothelial growth factors in cardiovascular medicine. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2008; 9: 1190-1221.
- Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al . Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24: 35-41
- Khurana D, Mathur D, Prabhakar S, Thakur K, Anand A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels unaltered in symptomatic atherosclerotic carotid plaque patients from north India. Front Neurol. 2013; 4: 27.
- Ridker PM, Paynter NP, Rifai N, Gaziano JM, Cook NR . C-reactive protein and parental history improve global cardiovascular risk prediction: the Reynolds Risk Score for men. Circulation. 2008; 118: 2243-2251, 4p following 2251.
- Ridker PM, Rifai N, Clearfield M, Downs JR, Weis SE, Miles JS, et al; Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study Investigators . Measurement of C-reactive protein for the targeting of statin therapy in the primary prevention of acute coronary events. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344: 1959-1965.
- Kim S, Jun JH, Kim J, Kim do W, Jang YH, Lee WJ, . HIF-1α and VEGF expression correlates with thrombus remodeling in cases of intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6: 2912-2918.