
Research Article
J Dis Markers. 2022; 7(1): 1047.
Phytochemicals as Potential Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents- An In-Silico Evidence
Pandey D, Pal T and Sharma A*
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Raebareli, India
*Corresponding author: Abha Sharma, Department of Medicinal Chemistry, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Raebareli, India
Received: August 11, 2022; Accepted: September 09, 2022; Published: September 16, 2022
Abstract
Alzheimer’s Disease is a prominent neurodegenerative disorder affecting the age group 60 and above. Cholinergic hypothesis, amyloid β cascade, oxidative stress is some of the known etiologies of marked importance to name a few. We have undertaken a computational analysis where fifteen phytochemicals were selected. These natural molecules were studied and analysed against acetylcholinesterase, butyrlcholinesterase, BACE and amyloid β monomer and protofibril. The binding affinities of Genistein, Huperzine A, kaempferol, Methyl quercetin, Paclitaxel and Withinolide A against AChE and BuChE enzymes were found to be -7.7 to -8.6 Kcal/mol, respectively. Various phytochemicals like Genistein, kaempferol, Piceatannol, Ginkgolide B, Methyl quercetin and Withinolide A were found to bind the BACE-1 enzyme with the binding affinities of -6.7 to -7.9 Kcal/mol. All the phytochemicals experienced efficient binding towards Aβ monomer and Aβ protofibril. Withinolide A was found to bind all the PDB’s efficiently with binding affinity of -8.4, -8.9, -7.7, -6.6 and -6.8 Kcal/mol against AChE enzyme, BuChE enzyme, BACE-1 enzyme, Aβ monomer and Aβ protofibril, respectively as a result it can be carried forward for the further preclinical and clinical studies.
Introduction
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease affecting mostly the aged above 60 years of age marked by cognitive decline. Accumulating evidence suggests that presence of both environmental factors and genetic factors are responsible for various pathophysiological pathways of AD. Deposition of extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular hyperphosphorylated, characterize the neuropathological hallmarks of AD. Environmental factors include chronic accumulation of aluminium in brain due drinking water and genetic factors comprised mutation of APP gene and Presenilins leading to accumulation of neurotoxic amyloid-β (Aβ) in the brain.
There is a plethora of phytochemicals available which has it’s own therapeutic property in it’s own right. Various phytochemicals have been known to show potential activity against AD, flavonoids and alkaloids are amongst the most important ones to make a mention about [1]. Since time immemorial, alkaloids have been known to be beneficial in therapeutics. Alkaloids are nitrogen containing heterocycles; galantamine and rivastigmine (a synthetic analogue of physostigmine) being USFDA approved for AD [2].
Computational studies incorporated in phytochemical screening have been beneficial for determining various phytochemicals. Traditional approach towards phytochemical research has evolved with fusion of computational approach. In this study, we selected few phytochemicals and did computational studies against the prominent targets known as hallmark proteins responsible for the pathophysiological conditions of the AD patients. Fifteen phytochemicals, majority of then broadly falls in the alkaloidal group and few comprised of flavonoids and terpenoids. We did a multitarget docking study to find out the potential targets against which the chemicals showed binding affinity. We selected a acetylcholinesterase protein the principle protein which caused cholinergic crisis in AD affected brains, a butyrlcholinesterase protein which is also responsible for the cholinergic etiology. A BACE or β-secretase is an enzyme which is very crucial protein for formation of neurotoxic Aβ plaques. We have also included Aβ monomer and oligomer in this computational study as proteins against the phytochemicals of our interest.
Results and Discussion
Rationale of Selection of Phytochemicals
The current AD treatment functions to alleviate mental, behavioural and cognitive symptoms. The existing treatments relay on Donepazil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine and Tacrine that are Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors (AChEI’s) and Memantine that blocks N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptors (Figure 1). Further some antidepressants and antipsychotic treatment can be employed to improve the behavioural symptoms.
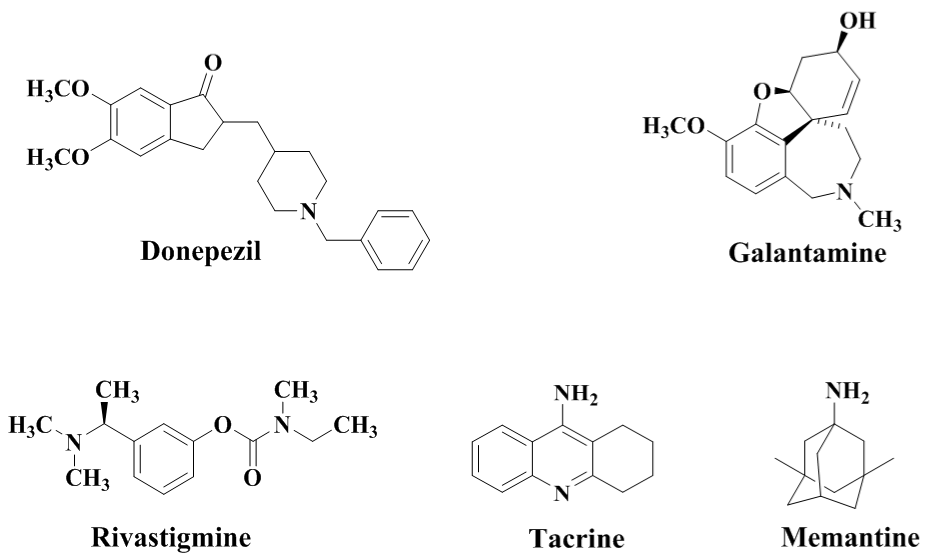
Figure 1: Traditional drugs used for treatment of AD.
Being synthetic molecules the above mentioned treatment may lead to various side effects and toxicity, even Tacrine has been withdrawn from market due to hepatotoxicity. Various dietary supplements such as Ginkgo biloba, Ashwagandha, Blueberries and Huperzia serrata have been reported to provide symptomatic relief from AD and other neurological disorders. The idea underlying to select these phytochemicals for our studies arise due to the risk of side effects and toxicity caused due to the use of traditional synthetic molecules. The molecules depicted in the study are the active constituents available in various dietary supplements reported to be beneficial in combating AD and hence can be isolated from the natural sources. Hence, all the Phytochemicals for the study were selected irrespective of their pharmacognostic classification. The molecules selected for this study belong to varying pharmacognostic class such as alkaloids, stilbenoids, flavanoids and diterpenoid etc. as depicted in (Table 1).
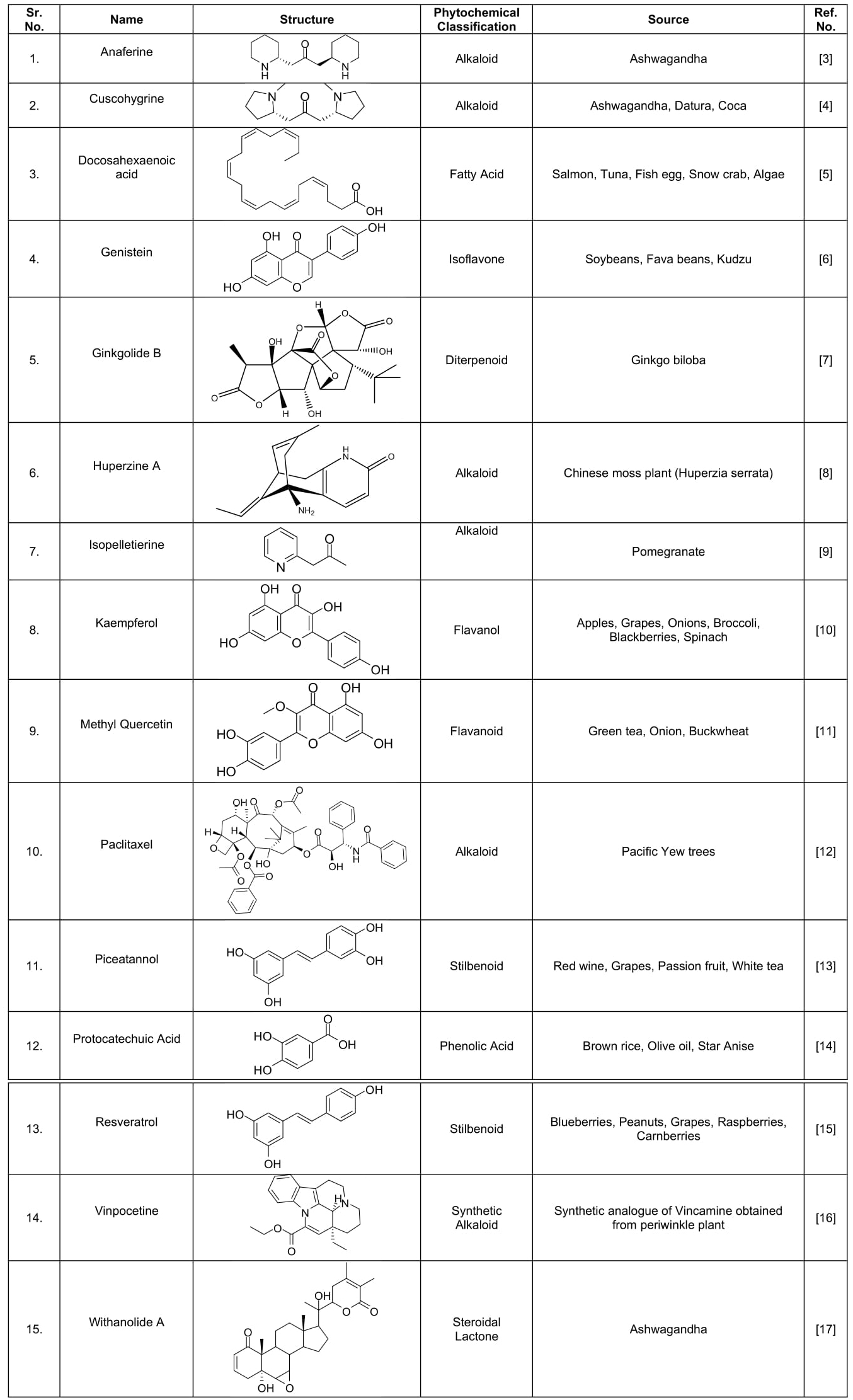
Table 1: Classification of selected Molecules.
Docking Studies
To brief about our computational study design against the selected molecules, we targeted the cholinergic hypothesis and following it, we selected hallmark proteins for Aβ cascade hypothesis.
Docking studies with acetylcholinesterase enzyme: Taking human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzyme (PDB ID 5HF6), we docked the fifteen phytochemicals of our interest against the aforesaid enzyme. The AChE is responsible for the cholinergic crisis leading to the pathophysiological conditions. The catalytic anionic site or the CAS site is formed of the amino acids Ser 203, His 447 and Glu 334. The peripheral anionic site or PAS site is formed of the principle amino acid Trp 86. It also comprises Tyr 72, Asp 74, Tyr 124, Trp 286 and Tyr 341. The hydrophobic interactions include the PAS site of the enzyme, whereas the CAS is responsible for the hydrophilic interactions of the ligand with the enzyme. Out of the 15 phytochemicals screened, few showed excellent binding affinity within the range of -7.7 to -8.5 Kcal/mol as shown in (Table 2).
Sl. No.
Molecule
Binding Affinity (Kcal/mol)
PAS/CAS
Amino acid Residues with interactions
1.
Anaferine
-6.5
CAS & PAS
Tyr-124(H-bonding); His-447, Val-294(Carbon H-bond); Tyr-337, Tyr-341(Pi-alkyl bond); Trp-86(Pi-sigma bond).
2.
Cuscohygrine
-5.4
Not identified
His-381(H-bonding); His-381, Tyr-382(Carbon H-bond); His-381, Tyr-382(Pi-alkyl bond)
3.
Docosahexaenoic acid
-4.3
PAS
Asp-74, Thr-75, Leu-76, Trp-286, Glu-292, Ser293, Arg-296, Tyr-341(Van der waal’s interaction)
4.
Genistein
-7.7
Not identified
Thr-383(H-bonding); His-381(Pi-Pi interaction); Ala-397(Pi-alkyl bond)
5.
Ginkgolide B
-6.7
Not identified
Tyr-382, Arg-525, Gln-527(H-bonding); Ala-397(Alkyl interaction)
6.
Huperzine A
-8.5
Not identified
Gln-291, Gln-369(H-bonding);Arg-247(Pi-cation); Phe-295, Val-239, Pro-368(Alkyl interaction); Pro-368, Leu-289, Pro-290(Pi-alkyl bond)
7.
Isopelletierine
-5.4
Not identified
Asn-186(H-bonding); Arg-13(Pi-alkyl bond); Trp-182(Carbon H-bond).
8.
Kaempferol
-8.6
Not identified
His-381, Arg-525(H-bonding); His-381(Carbon H-bond); His-381(Pi-Pi stacking).
9.
Methyl Quercetin
-7.9
PAS
Arg-296(pi-alkyl); Tyr-124, Tyr-341(Pi-Pi T shaped); Trp-286(Pi-Pi stacking).
10.
Paclitaxel
-8.3
Not identified
No interaction
11.
Piceatannol
-7.4
PAS
Asp-74, Gln-291, Ser-293(H-bonding); Arg-296(Pi-cation interaction); Arg-296(Pi-alkyl interaction); Trp-286(Pi-Pi T shaped)
12.
Protocatechuic Acid
-6.1
Not identified
His-381, Gln-527(H-bonding); His-381(Carbon H-bond)( Pi-Pi T shaped)(Pi-cation)
13.
Resveratrol
-6.6
Not identified
His-381(Pi-cation)
14.
Vinpocetine
-7.1
Not identified
Pro-235, Trp-532(Carbon H-bond); Pro-410, Pro-537(Pi-alkyl); His-405(Alkyl interaction)
15.
Withanolide A
-8.4
Not identified
Leu-214(Carbon H-bond); Arg-219(H-bonding)(Pi-alkyl) Phe-321, Arg-219(Alkyl interaction).
Table 2: Analysis of Docking results of AChE enzyme (PDB ID- 5HF6) [18] against the selected molecules.
Docking studies with butyrlcholinesterase enzyme: To elucidate the role of butyrlcholinesterase (BuChE) enzyme, it has been found that in absence of AChE, BuChE can also hydrolyze acetylcholine. Therefore, for potentially targeting cholinergic hypothesis, where AChE crisis becomes a major concern, BuChE inhibition also gains subtle importance in this pathway of cholinergic crisis in AD brains. Therefore, we subjected all the molecules of our interest to docking study against BuChE and it’s further analysis has been tabulated in (Table 3). To lay a comparison between Table 2 and 3, the molecules which showed a fairly high binding affinity within the range -7.7 to -8.5 Kcal/mol showed consistently high binding affinity for BuChE enzyme also. A single molecule showing affinity to both the enzymes can prove very beneficial for the treatment of AD,
Sl. No.
Molecule
Binding Affinity (Kcal/mol)
Amino acid Residues with interactions
1.
Anaferine
-5.4
Cys-400, Pro- 401 (alkyl interaction)
2.
Cuscohygrine
-6.3
Phe- 329, Trp-231, Trp- 82 (alkyl/pi-alkyl interaction); Ser-198,Gly-117 (H-Bonding)
3.
Docosahexaenoic acid
-4.3
Asn-57 (H-Bonding)
4.
Genistein
-8.3
Asn- 228 (H-Bonding); Asp-304 (pi-anion interaction); Pro-401 (pi-alkyl interaction)
5.
Ginkgolide B
-8.3
Asn-289, Gln- 71 (H-Bonding); Ala-277 (alkyl interaction)
6.
Huperzine A
-8.3
Trp-82 (pi-sigma interaction); Leu-125 (alkyl/pi-alkyl interaction)
7.
Isopelletierine
-5.6
Tyr-440, Trp- 430, Trp-82 (H-Bonding); His-438, Trp- 82 (pi-pi stacking)
8.
Kaempferol
-9.1
Trp- 82 (pi-pi stacking); Asp-70 (pi-anion interaction); Gly-439 (pi-donor H-Bonding)
9.
Methyl Quercetin
-7.8
Asp-304, Thr-523(H-Bonding); Trp-522(amide pi-stacking); Pro- 401(pi-alkyl interaction); Asp-304 (pi-anion interaction)
10.
Paclitaxel
-10.3
No interaction
11.
Piceatannol
-7.8
Tyr- 128, Glu-197, Ser-198 (H-Bonding); Trp-82(pi-pi stacking)
12.
Protocatechuic Acid
-5.0
His-372,Asp-375 ,Asp-391 (H-Bonding); Ala-388(pi-alkyl interaction)
13.
Resveratrol
-6.6
Pro-230 (H-Bonding, pi-sigma interaction, pi-alkyl interaction); Pro-401 (pi-sigma interaction); Trp-522 (amide-pi stacking)
14.
Vinpocetine
-7.8
Pro-230,Pro-527, Pro-401 (alkyl/pi-alkyl interactions), Trp-522 (amide pi-stacking)
15.
Withanolide A
-8.9
His-372, Phe-521, Phe-525,Phe-371 (pi-alkyl interactions); Phe-371 (pi-sigma interaction)
Table 3: Analysis of Docking results of BuChE enzyme (PDB ID- 6EP4) [19] against the selected molecules.
Docking studies with BACE-1 enzyme: The BACE or β-secretase is an aspartic protease, responsible for cleaving the amyloid precursor protein or APP. This cleavage yields neurotoxic amyloid β fibrils that get deposited into amyloid β plaques or Aβ plaques. Inhibition of this BACE enzyme is a very crucial check point for inhibition of the Aβ cascade in AD pathophysiology. Therefore, after a elaborative docking analysis on cholinergic hypothesis, where AChE and BuChE were the potential targets, we sought to put the molecules for a docking study against the BACE enzyme. All of the exhibited binding interactions, except paclitaxel as tabulated in (Table 4).
Sl. No.
Molecule
Binding Affinity (Kcal/mol)
Amino acid Residues with interactions
1.
Anaferine
-3.8
Asn-278 (unfavourable donor-donor interaction)
2.
Cuscohygrine
-4.5
Pro-24, Leu-84, Pro- 88(alkyl interaction); Ser-86 (H-Bonding)
3.
Docosahexaenoic acid
-3.0
Met-215 (H-Bonding)
4.
Genistein
-6.9
Tyr-71 (pi-pi stacking); Thr-231(H-Bonding); Ile-110 (pi-alkyl interaction)
5.
Ginkgolide B
-6.7
Trp-277, Thr-275, Tyr-320 (H-bonding); Thr- 274 (C-H Bonding)
6.
Huperzine A
-5.7
Ala-157, Gln-303 (H-Bonding); Tyr-320,Pro-308, Val-361 (alkyl interaction)
7.
Isopelletierine
-4.0
Pro- 308, Val- 361(pi-alkyl interaction)
8.
Kaempferol
-6.7
Gln-303,Tyr-320, Asp-318 (H-Bonding); Val-361,Pro-308 (pi-alkyl interaction); Trp-277 (pi-pi interaction)
9.
Methyl Quercetin
-7.0
Arg-235, Gln-73 (H-Bonding)
10.
Paclitaxel
-5.9
No interaction
11.
Piceatannol
-7.9
Asp-228 (H-Bonding); Tyr-71 (pi-pi stacking); Leu-30 (pi-alkyl interaction)
12.
Protocatechuic Acid
-5.7
Asp- 228( H-Bonding); Tyr-71 (pi-pi stacking)
13.
Resveratrol
-5.6
Asp-378, Asp-212, Tyr-220, Met- 215 (H-Bonding); Arg-205( pi-cation/anion interaction); Cys-217 (pi-alkyl interaction)
14.
Vinpocetine
-5.7
Lys-214, Arg-205, Cys-217 (alkyl/pi-alkyl interaction); Cys-217 (pi-sulfur interaction)
15.
Withanolide A
-7.7
Val-141,Lys-142,Tyr-123, Ala-124 (alkyl/pi-alkyl interaction); Arg-347,Asn-148, Glu-125 (H-Bonding)
Table 4: Analysis of Docking results of BACE-1 enzyme (PDB ID- 1W51) [20] against the selected molecules.
Docking studies with Aβ monomer and protofibril: As described in the section 2.2.3, the amyloidogenic pathway is responsible for the formation of the intracellular Aβ plaques which are ultimately neurotoxic for the brain, and therefore is responsible for the pathophysiological scenario of the AD. We have taken both the monomer and the protofibril in consideration for the docking analysis of the molecules of interest. The exhibited significant interaction gives us an idea about the probable aggregation and disaggregation inhibitory properties. High binding affinity of the Aβ monomer can halt the aggregatory process to form plaques, while high affinity for the protofibrils can pose a probability that the molecule can be able to demonstrate disaggregatory property against the already formed Aβ plaques. Table 5 and 6 shows the docking analysis of the molecules of interest against the Aβ monomer and Aβ protofibrils. Withanolide A showed consistently high binding affinity with both Aβ monomer and Aβ protofibril proteins.
Sl. No.
Molecule
Binding Affinity (Kcal/mol)
Amino acid Residues with interactions
1.
Anaferine
-3.1
Ala-30 (H-Bonding); Ile-31( alkyl interaction)
2.
Cuscohygrine
-3.9
Gln-15, Lys-16( H-Bonding), Phe-19 (pi-alkyl interaction);Val-12(alkyl interaction)
3.
Docosahexaenoic acid
-3.3
Lys-16 (H-Bonding)
4.
Genistein
-5.3
Glu-11, Gln-15 (H-Bonding); Val-12,Lys-16 (pi-alkyl interactions)
5.
Ginkgolide B
-5.3
His-13, His-13( H-Bonding); Leu-17, Tyr-10 (pi-alkyl interaction)
6.
Huperzine A
-4.9
Tyr-10 (pi-alkyl, pi-sigma interactions); Glu-11 (H-Bonding)
7.
Isopelletierine
-3.0
Tyr-10 (pi-sigma interaction)
8.
Kaempferol
-5.2
Val-12 (pi-alkyl interaction); Lys-16 (H-bonding, pi-sigma interactions)
9.
Methyl Quercetin
-5.2
Val-12, Ser-8 (pi-sigma interactions); Gln-15 (H-Bonding)
10.
Paclitaxel
-5.2
No interaction
11.
Piceatannol
-4.8
Asp-23, Gly-33 ( H-Bonding); Ile- 31(pi-sigma interaction); Leu-34 (pi-alkyl interaction)
12.
Protocatechuic Acid
-3.6
Asp-7, Glu-3 (H-bonding interactions)
13.
Resveratrol
-4.4
Tyr-10 (pi-pi stacking interaction)
14.
Vinpocetine
-4.9
Gln-15 (H-Bonding); Val-12,Phe-19 (pi-sigma interactions); Lys-16 (pi-alkyl interactions)
15.
Withanolide A
-6.6
Ser-8 (C-H bonding); Phe-19, Val-12 (pi-alkyl interactions)
Table 5: Analysis of Docking results of Aβ monomer (PDB ID- 1LYT) [21] against the selected molecules.
Sl. No.
Molecule
Binding Affinity (Kcal/mol)
Chain
Amino acid Residues with interactions
1.
Anaferine
-3.5
B
Met-35(alkyl interaction)
2.
Cuscohygrine
-4.0
B
Met-35 (alkyl interaction); Gly- 33 (H-Bonding)
3.
Docosahexaenoic acid
-3.7
A
Leu-34, Val-36 (alkyl interactions)
4.
Genistein
-5.6
A
Asp- 23( H-Bonding); Gly-25 (pi-sigma interaction); Leu-34 (pi-alkyl interaction)
5.
Ginkgolide B
-6.1
D
Val-39 (alkyl interaction)
6.
Huperzine A
-5.5
E
Phe-19, Leu-34, Val-36 (alkyl and pi-alkyl interactions); Ala-21 (pi-sigma interaction); Glu-22 (H-Bonding)
7.
Isopelletierine
-4.2
A
Phe-19 (pi-sigma interaction); Ala-21 (pi-alkyl interaction)
8.
Kaempferol
-5.6
A,B
Gly-25 (H-Bonding,pi-sigma interaction); Ile-32 (pi-alkyl interaction); Lys-28 :B (pi-cation interaction); Leu-34 (pi-sigma interaction)
9.
Methyl Quercetin
-5.7
A, B
Asp-23, Gly-29 (H-Bonding); Ile-32 (pi-alkyl interaction); Leu-34(pi-sigma interaction); Gly-25 (pi-sigma interaction); Lys-28:B( pi-cation interaction)
10.
Paclitaxel
-6.5
No Interaction
11.
Piceatannol
-5.4
A
Asp-23(H-Bonding); Ala-21(amide-pi stacking); Leu-34 (pi-sigma interaction); Val-36,Ile-32 (pi-alkyl interaction)
12.
Protocatechuic Acid
-4.4
A
Ala-21,Gly-37 (H-Bonding); Phe-19 (pi-pi stacking); Ala-21 (pi-alkyl interaction)
13.
Resveratrol
-5.9
A,B
Ala-21,Val-36, Val-40, Val-40:B( pi-alkyl interactions); Phe-20 (H-Bonding, pi-pi stacking)
14.
Vinpocetine
-5.3
B,C
Met-35:B, Met:35:C (alkyl interactions); Ile-31 (pi-sigma interaction)
15.
Withanolide A
-6.8
C,D,E
Val-36:C (H-Bonding); Val-39:D,Val-39:E, Ile-41:D, Ile-41:E (alkyl interactions)
Table 6: Analysis of Docking results of Aβ protofibril (PDB ID- 2BEG) [21] against the selected molecules.
Materials and Methods
Molecular Docking studies
Preparation of protein: The 3D structure of all the proteins human AChE enzyme (PDB ID- 5HF6), BChE enzyme (PDB ID- 6EP4), BACE1 enzyme (PDB ID- 1W51), Aβ monomer (PDB ID- 1LYT) and Aβ protofibril (PDB ID- 2BEG) were downloaded in .pdb format from the Protein Data Bank (https://www.rcsb.org/).
Preparation of ligands structure: The ligands ie. All the phytochemicals were selected from various dietary supplements and the structures were drawn by ChemDraw14.0 tool. The Chem Draw 3D tool was then used for conversion of the structures to 3D. Vega ZZ program was used to fix the charges of the ligands as gasteiger. The energy of the ligands was minimized using Vega ZZ program and the ligands were saved in .pdb format.
Docking studies: AutoDock Tools (ADT v1.5.6) and AutoDock Vina, developed by the Scripps Research Institute (http://www. scripps.edu/downloads) has been used to perform the docking studies of selected molecules against all the targets of interest. The AutoDock Tools program consists of Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm search engine [22]. The docking study was performed by following the standard docking protocol, grids of 126, 126, and 126 points in x, y, and z directions were built for the protein preparation and the grid spacing was set to 0.375Å. The exhaustiveness was set to default. AutoDock Tools (ADT v1.5.6) was used to save the proteins and ligands as .pdbqt format. The docking of selected phytochemicals was performed by using Auto Dock Tools program. Docking output and log file for the docking study was generated once the docking was completed. The docking output was optimized with the minimum energy. The visualization of docking output and generation of 2Ddiagram for the docking studies were done using Discovery Studio 2017 R2 tool. The binding interactions were observed for almost all the selected phytoconstituests towards the targets of interest.
ADME Prediction by Using Swiss-ADME Tool
The bioavailability potential of the selected molecules can be detected through absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME). Computational prediction using ADME software is an in silico method, suitable due to quick screening, financially affordable, no animal testing, etc. Swiss ADME online tool (freely accessible at http://www.swissadme.ch) was used for the prediction of in silico studies, especially pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, drug likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness. The tool presents an early estimation of these ADME parameters (for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion) and provides sufficient information about the physicochemical parameters which is needed to be improved during formulation [23]. Human gastrointestinal absorption (HIA) and Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) permeation is represented as Boiled Egg model provided by this tool [24]. The Boiled egg representation of the selected phytochemicals is depicted in (Figure 2). In this model some the molecules were found to be permeable through the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) that is very essential in the treatment of AD and most of the molecules were found to be absorbed through gastrointestinal tract and Ginkgolide B was found out of range. The tool also gives the idea about the details of chemistry information of the molecules such as molecular weight, Molecular formula, hydrogen-bond donor, hydrogen-bond acceptor etc. The tool also provides detailed information on the inhibitory action of the molecules towards the enzyme of cytochrome enzyme series. The chemistry information of the molecules is described in (Table S1; See supplementary information) while Pharmacokinetics prediction, Bioavailability prediction, Druglikeness prediction and Medicinal chemistry prediction are depicted in (Table S2, Table S3, S4 & S5; See supplementary information) respectively. All the tabular information relating to Swiss ADME prediction are provided in supporting information. The Swiss ADME data reviles that most of the phytochemicals are water soluble, highly GI absorbable and some are even permeable through BBB. Most of the phytochemicals follow the rules of Drug likeness and have a good synthetic accessibility score.
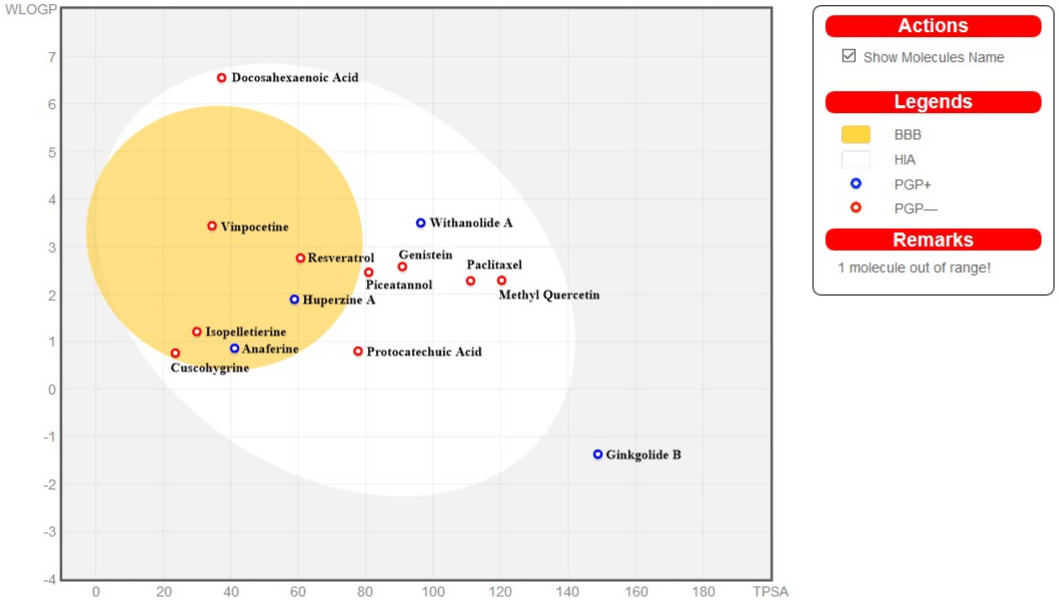
Figure 2: BOILED EGG representation of the selected phytochemicals where the yolk denotes the molecules that are blood-brain-barrier permeable, while the
white portion denotes the molecules that can be absorbed through gastrointestinal tract. The graph is plotted against WLogP [a log P (n-octanol/water partition
coefficient) method developed by Wildman and Crippen] versus TPSA or Topological Polar Surface Area.
Conclusion
The study initiated with the selection of phytochemicals that are the main constituents of dietary supplements used in AD. The study was designed to evaluate the phytochemicals against multiple targets involved in AD. The initial phase of the study revolves around the cholinergic hypothesis and the binding of phytochemicals with the AChE and BuChE enzymes were evaluated using docking studies. The binding affinities of Genistein, Huperzine A, kaempferol, Methyl quercetin, Paclitaxel and Withinolide A against both the enzymes were found to be -7.7 to -8.6 Kcal/mol respectively. The second hypothesis of concern was Aβ aggregation and the main factor for the aggregation is BACE-1 enzyme. Various phytochemicals like Genistein, kaempferol, Piceatannol, Ginkgolide B, Methyl quercetin and Withinolide A were found to bind the BACE-1 enzyme with the binding affinities of -6.7 to -7.9 Kcal/mol. Further the binding of the phytochemicals to Aβ monomer and Aβ protofibril was evaluated and all the molecules bind efficiently with both the PDB’s. Withinolide A was found to bind all the PDB’s efficiently with binding affinity of -8.4, -8.9, -7.7, -6.6 and -6.8 Kcal/mol against AChE enzyme, BuChE enzyme, BACE-1 enzyme, Aβ monomer and Aβ protofibril respectively as a result it can be carried forward for the further preclinical and clinical studies.
Communication Number
NIPER-R/
Availability of Data and Material
Data is given in article and supplementary information.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Authors’ Contributions
All authors designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data and wrote the paper.
References
- Essa MM, Vijayan RK, Braidy N, Guillemin GJ, Berry B. Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Products Against Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res. 2012; 37: 1829–1842.
- Ng YP, Cho T, Or T, Ip PNY. Plant Alkaloids as Drug Leads for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Int. 2015; 89: 260-270.
- Rao RV, Descamps O, John V, Bredesen DE. Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Alzheimer’s Res Ther. 2012; 4: 1–9.
- Rubio NC, Thurmann D, Krumbiegel F, Pragst F. Behaviour of hygrine and cuscohygrine in illicit cocaine production establishes their use as markers for chewing coca leaves in contrast with cocaine abuse. Drug testing and analysis. 2017; 9: 323-326.
- Calder PC. Docosahexaenoic Acid. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016; 69: 8–21.
- Tuli HS, Tuorkey MJ, Thakral F, Sak K, Kumar M, Sharma AK, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Genistein in Cancer: Recent Advances. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2019; 10.
- Feng Z, Sun Q, Chen W, Bai Y, Hu D, Xie X. The neuroprotective mechanisms of ginkgolides and bilobalide in cerebral ischemic injury: a literature review. Molecular Medicine. 2019; 25.
- Qian ZM, Ke Y. Huperzine A: Is It an Effective Disease-Modifying Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014; 6: 1–6.
- Ramawat KG, Mérillon JM. Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes. 2013.
- Imran M, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, Saeed F, Imran A, et al. Kaempferol : A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules. 2019: 24.
- Kumar ADN, Bevara GB, Kaja LK, Badana AK, Malla RR. Protective effect of 3-O-methyl quercetin and kaempferol from Semecarpus anacardium against H2O2 induced cytotoxicity in lung and liver cells. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016; 16.
- Baas PW, Ahmad FJ. Beyond taxol: microtubule-based treatment of disease and injury of the nervous system. Brain : a journal of neurology. 2013; 136: 2937-2951.
- Dai Y, Lim JX, Yeo SCM, Xiang X, Tan KS, Fu JH, et al. Biotransformation of Piceatannol, a Dietary Resveratrol Derivative: Promises to Human Health. Molecular nutrition & food research. 2019; 64: 1900905.
- Semaming Y, Pannengpetch P, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N. Pharmacological Properties of Protocatechuic Acid and Its Potential Roles as Complementary Medicine. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM. 2015; 2015: 1-11.
- Berman AY, Motechin RA, Wiesenfeld MY, Holz MK. The therapeutic potential of resveratrol: a review of clinical trials. NPJ Precision Oncology. 2017; 1.
- Billakota S, Andresen JM, Gay BC, Stewart GR, Fedorov NB, Gerlach AC, et al. Personalized medicine: Vinpocetine to reverse effects of GABRB3 mutation. Epilepsia. 2019; 60: 2459-2465.
- Chen LX, He H, Qiu F. Natural Withanolides: An Overview. 2011; 28: 705-40.
- Franklin MC, Rudolph MJ, Ginter C, Cassidy MS, Cheung J. Structures of paraoxon-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase reveal perturbations of the acyl loop and the dimer interface. Proteins: Structure. 2016; 84: 1246-1256.
- Rosenberry TL, Id XB, Macdonald IR, Wandhammer M, Trovaslet-leroy M, et al. Human Butyrylcholinesterase and Acetylcholinesterase : 2017; 22: 1–21.
- Patel S, Vuillard L, Cleasby A, Murray CW, Yon J, Technology, A. Apo and Inhibitor Complex Structures of BACE ( b -Secretase ). 2004; 343: 407–416.
- Kaur A, Narang SS, Kaur A, Mann S, Priyadarshi N, Goyal B, et al. Multifunctional mono-triazole derivatives inhibit Aβ42 aggregation, Cu2+ mediated Aβ42 aggregation and protect against Aβ42 induced cytotoxicity. Chemical research in toxicology. 2019; 32: 1824-1839.
- Nisha CM, Kumar A, Vimal A, Bai BM, Pal D, Kumar A. Docking and ADMET prediction of few GSK-3 inhibitors divulges 6-bromoindirubin-3-oxime as a potential inhibitor. Journal of molecular graphics & modelling. 2016; 65: 100- 107.
- Puja Tripathi, Subhasis Ghosh, Soumendra Nath Talapatra. Bioavailability Prediction of Phytochemicals Present in Calotropis Procera (Aiton) R. Br. by Using Swiss-ADME Tool. Wsn. 2019; 131; 147–163.
- Daina A, Zoete V. A Boiled-Egg To Predict Gastrointestinal Absorption and Brain Penetration of Small Molecules. Chemmedchem. 2016; 11: 1117-1121.