
Review Article
Austin J Earth Sci. 2015;2(2): 1011.
Integrated Evaluation Model of Local Climate Policies and Regional Characteristics
Satoshi Watanabe¹* and Yukiko Yoshida²
¹Faculty of International Human Science, Suzuka International University, Japan
²Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Japan
*Corresponding author: : Satoshi Watanabe, Faculty of International Human Science, Suzuka International University, Mie Prefecture, Japan
Received: February 19, 2015; Accepted: April 10, 2015; Published: April 12, 2015
Abstract
This paper analyzed the effects of the local climate policies with “3E (Economy-Energy-Environment) model”. This model is to analyze the effects to the local economies, energy demands, and CO2 emissions by introducing the policies for anti-global warming in the local area. The 3E model of Tokai region (Aichi, Gifu, and Mie Prefecture) of this paper consists of the local macro econometric model, the local input-output model, and the local energy demandsupply model. The findings of this paper are that the production spillover effect of introducing CO2 reduction policies was larger by 0.2-0.7% than the BAU effect of BAU case. And the effect of employment was greater by about 1000- 4000 employments.
Keywords: Local climate policy; 3-E model; Economic effect
Introduction
To advance the local climate policies such as reduction of CO2 emission, it is important to make a choice about policies. The effects of local climate policies depend on the difference of regional characteristics such as economic and social structure, or geographic situations of each region. It is necessary to introduce more effective policy package matching with each regional characteristic.
To analyze the CO2 emission and economic effects of local climate policies, the integrated model for analyzing the economic, energy and environment (CO2 emissions) effect is necessary. This paper calls this model to “3-E (economy-energy-environment) model”. This study such as analyzing the economic, energy and environment effects by introducing the local climate policies was little. Matsumoto et al. [1] analyzed the employment effect of solar and wind power industries with the expanded Japanese Input-Output table in 2005. Engel et al. [2] estimated the employment creation effect of each energy sector, and showed the greater employments by renewable energy industries than nuclear power industries. Furthermore, Federal Ministry of Environment [3] showed the simulated results of employment creation effects in Germany. Sugiyama et al. [4] simulated the economic effects of two type policies (national-based policies or localbased policies) in Aichi prefecture of Japan.
This paper analyzed the effects of the local climate policies with “3-Emodel” in Tokai region (Aichi, Gifu and Mie prefecture). The analysis compared the results between BAU (business as usual) case which take a current local situation as given and another case that the local climate policies were introduced.
Estimating “3-E Model”
The data to analysis used economic indicators (consumption, investment, GRP, income and employment), social indicators (population), energy consumption, and input-output (I-O) table in Tokai region (Aichi, Gifu, and Mie prefecture) within 1990 to 2010. This model consists of regional econometric model, I-O model and energy model.
Figure 1 showed the structure of model and steps of simulation. In the first step, regional macro econometric model and I-O model were constructed to understand the structure of regional economic structure. In the second, I construct the energy model based on the results of regional macro econometric model and I-O model for understanding energy demand and supply within region. In the third step, BAU (business as usual) case was estimated which keeps the current trends on future. In the fourth step, the case of introducing CO2 reduction policies was formulated, and in the fifth step, the economic effects of macro-economic indicator (GRP, industry activities, employments and so on) were estimated with regional macro econometric and I-O model.
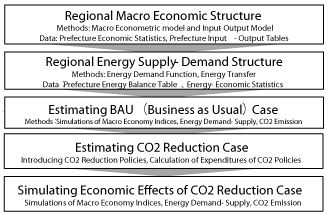
Figure 1: Structure and Methodologies of “3-E model”.
Regional macro econometric model explains the interaction between economic activities. This model is the type of demand determinant. In this model, the demand within region determines the quantities of industry activities, income distributions, and local government expenditure. And, price and wage level within region determine nominal expenditures and employments. Besides estimating these endogenous variables, this model uses the data of Japan and international level such as GDP, interest, and population as exogenous variable. The estimation of this model analyzed with multiple regression and definitional equations. The numbers of endogenous variables in Aichi prefecture are 51, those in Gifu prefecture are 56, and in Mie prefecture are 53. The numbers of exogenous variable in three prefectures are 23.
Next, the future I-O table was forecasted in 3 prefectures with the growth rates of expenditures which were estimated on regional macro econometric model. Constructing the future I-O tables forecast the trends of input coefficients based on actual tables, and simultaneously estimate import coefficients and converters. The data sources of this model are three actual I-O tables of each prefecture in 1995, 2000 and 2005.
Energy model explains to the determinants of primary energy supply, energy conversion and energy demand within regions. The energy demands of manufacturing industries were calculated by multiplying the specific energy consumptions by estimated product values in each industry. The energy demands of other sectors (agriculture, construction, service industries, household, public sector, transportation, and so on) were estimated by energy demand functions. The data of this model were energy consumptions in each prefecture within 1990 to 2010. The data source is Agency for Natural Resources and Energy [5].
Simulation of BAU Case in 2030
Table 1 shows the results of simulation analysis of BAU case in 2030. Compared with actual values in 2005, the average rate of change of gross regional products (GRP) was increased by 0.0-1.0% in each prefecture.
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
2005
2030
2005
2030
2005
2030
GRP (1billion JY)
38,716
42,139
7,856
7,774
8,315
10,733
Income (1billion JY)
25,172
23,291
5,994
5,056
5,820
6,344
Employment
3,426
2,061
928
839
824
791
Tax revenue (1billion JY)
1,089
847
223
152
228
277
Products of manufacturing (1billion JY)
4,440
4,377
572
501
1,063
1,498
Table 1: Comparison of actual values and the results of BAU case (summary).
Table 2 shows the result of BAU case estimation with forecast I-O table of 3 prefectures in 2030. The forecast products of each industry was 0.1% growth per year in Aichi and Mie, and was -0.5% declining in Gifu from 2005 to 2030. The results of each industry show that most of industries in Aichi and Mie were grown up, in contrast those in Gifu were declined such as steel, other manufacturing, commerce and finance, public service and customer service.
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
Agriculture
282
(-1.3%)
119
(1.2%)
182
(-0.8%)
Construction
21
(-0.1%)
696
(-1.4%)
542
(-0.7%)
Chemistry
1,325
(-0.4%)
389
(-0.6%)
1,427
(0.0%)
Steel
4,939
(1.5%)
406
(-0.7%)
804
(0.1%)
Machine
22,169
(-0.4%)
2,227
(-0.6%)
5,248
(0.1%)
Other manufacturing
11,968
(0.1%)
1,522
(-0.7%)
3,132
(0.0%)
Water, Waste
533
(0.0%)
161
(1.2%)
163
(0.3%)
Commerce, Finance
15,880
(0.2%)
2,249
(-0.6%)
2,266
(0.1%)
Public service
7,413
(0.1%)
1,865
(-0.3%)
1,789
(0.6%)
Business services
4,595
(0.6%)
665
(1.0%)
350
(-0.8%)
Customer services
3,138
(0.1%)
619
(-0.6%)
767
(0.5%)
Other services
8,765
(0.7%)
1,369
(0.0%)
1,434
(0.0%)
Total
81,029
(0.1%)
12,287
(-0.5%)
18,104
(0.1%)
Note: Percent figure in this table is the average change rate per year in 2030 below 2005.
Table 2: Products values of each industry in 2030 (BAU case, unit: 1billionJY).
Energy model used the forecast values which were estimated in macro econometric and I-O model, and in addition, energy prices which was estimated in International Energy Agency [6] as exogenous variable. Table 3 shows the results of forecasting energy demands on 3 prefectures in 2030 compared with the actual values in 2005.
Energy
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
Sector
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
Coal
0.993
0.909
1.579
Agriculture
0.915
0.689
0.953
Coal products
0.953
0.963
1.516
Construction
0.972
0.869
1.157
Light oil
0.975
0.833
0.954
Chemistry
0.960
0.923
1.080
Heavy oil
0.917
0.925
1.043
Steel
1.031
0.892
1.335
LPG
1.011
0.988
1.044
Machine
0.915
1.468
1.321
LNG
1.281
1.213
1.163
Other manufacturing
0.847
0.944
0.988
City gas
1.030
0.987
1.108
Shipping
0.972
0.748
0.935
Renewable
1.021
1.016
1.033
Car
0.865
0.658
0.822
Electricity
0.940
0.949
1.075
Office
1.008
0.942
1.095
Heat
0.934
0.958
1.072
Household
0.986
1.017
1.066
Total
0.964
0.924
1.055
Total
0.964
0.924
1.055
Note: Values in table means Energy Demand in 2030/Energy Demand in 2005.
Table 3: Forecast values of energy demands in 2030.
Table 4 shows the results of forecasting emission based on estimated energy demands in 2030, and of actual emissions in 1990 and 2005.
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
Emissions in 1990(10 thousands ton unit CO2)
7,112
1,298
2,489
Emissions in 2005(10 thousands ton unit CO2)
8,038
1,341
2,733
Forecast emissions of BAU case in 1990(10 thousands ton unit CO2)
7,564
1,314
2,697
Table 4: Forecasting emission in 2030(BAU case) and actual emission of CO2.
Simulation of Introducing Local Climate Policies
Table 5 shows the policy package to achieve CO2 reduction and its expenditures within each prefecture. Based on these expenditures to introduce the policy package, the economic effects of introducing CO2 reduction policies was simulated with macro econometric and I-O model.
CO2 reduction
policies
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
Expenditure
Reduction
Expenditure
Reduction
Expenditure
Reduction
Electric car
5,263
19.0
526
2.0
1,053
3.0
Photovoltaic
27,368
26.0
8,211
8.0
8,211
6.0
Wind power
3,158
13.0
1,053
4.0
10,526
34.0
Gasoline vehicle
mileage
29,974
38.0
29,974
15.0
29,974
24.0
Light oil vehicle
Mileage
2,240
25.0
2,240
5.0
2,240
3.0
Green home electronics
8,960
15.0
8,960
6.0
8,960
4.0
Green OA equipment
1,680
14.0
1,680
4.0
1,680
4.0
Middle or small hydroelectric generation
9,316
40.0
24,842
265.0
62,105
82.0
Geothermal energy
6,211
8.0
24,842
77.0
62,105
31.0
Combined heat and power
98,684
323.0
13,158
43.0
19,737
65.0
Gas conversion in plants
974
48.4
105
4.0
385
19.0
Community bicycle
5,920
8.0
296
0.0
1,480
2.0
Biomass Methane
157,895
141.0
15,789
14.0
39,474
35.0
Woody biomass
610
4.0
4,880
28.0
49
0.0
Green reforming of
House
38,737
108.0
7,747
21.6
3,874
10.8
Fuel change in generations
16,500
165.0
0
0.0
330
2.0
RPF
3,126
7.0
0
0.0
2,084
5.0
Greening in urban area
15,789
0.0
15,789
0.0
15,789
0.0
Total
432,405
1,002.4
234,620
496.6
195,530
329.8
Table 5: CO2 Reduction Policies and the Quantities of CO2 Reduction in Tokai region. (Expenditure: 10 thousands JY, Reduction:10 thousands ton of CO2, Accumulated total within 2011-2030)
Table 6 shows the result of simulation with macro econometric model. The change of GRP by introducing CO2 reduction policies was larger by 0.2-0.7% than BAU case. Similarly, that of income by doing their policies was greater by 0.5-2% than BAU case.
CO2 reduction(A)
BAU(B)
(A)-(B)
2020
2030
2020
2030
2020
2030
GRP
(1billion JY)
Aichi
41,673
42,409
41,402
42,139
271
270
Gifu
7,642
7,789
7,630
7,774
12
15
Mie
9,926
10,736
9,911
10,733
15
3
Income (1billion JY)
Aichi
24,880
23,418
24,746
23,291
134
127
Gifu
5,555
5,195
5,417
5,056
138
138
Mie
6,529
6,468
6,379
6,344
150
124
Employment
Aichi
3,028
2,065
3,020
2,061
7.9
3.8
Gifu
885
840
884
839
0.6
0.7
Mie
813
791
813
791
0
0
Tax revenue
(1billion JY)
Aichi
1,043
864
1,027
847
16
17
Gifu
187
162
177
152
10
10
Mie
285
284
275
277
10
7
Products of
manufacturing (1billion JY)
Aichi
4,628
4,436
4,569
4,377
59.2
59.2
Gifu
521
506
517
501
3.8
4.8
Mie
1,370
1,505
1,368
1,498
1.4
6.2
Table 6: Economic Effects of Introducing CO2 Reduction Policies with Estimating Macro Econometrics Model (summary).
Table 7 shows the result of simulation with I-O model (forecasting I-O table in 2030). This result means that the spillover effect to production by introducing CO2 reduction policies was larger by 0.5-1.3% than that of BAU case in each prefecture. According to the results of each industry productions of agriculture and construction industries increased by 4-9% more than those of BAU case. The share of the spillover effects in each industry was about 20-30% in each prefecture. Employment creation effect within each industry was that machine, public service and business service industries were greater than other industries in each prefecture. But, the second-largest share of industry about employment creation effect was service industries such as commerce and customer service industries in Aichi and Mie prefecture, whereas that was agriculture and construction industries in Gifu prefecture.
Aichi
Gifu
Mie
Production
Employment
Production
Employment
Production
Employment
Agriculture
18
255
11
186
8
46
Construction
2
191
51
185
22
88
Chemistry
1
58
0
10
1
14
Steel
22
219
4
60
1
29
Machine
124
955
40
492
28
246
Other manufacturing
19
161
6
132
6
90
Water, Waste
35
79
4
96
10
32
Commerce, Finance
412
443
22
127
11
152
Public service
9
511
6
201
2
119
Business services
41
857
8
371
6
175
Customer services
13
401
3
93
1
90
Other services
23
278
8
71
4
30
Total
719
4,408
162
2,024
99
1,109
Table 7: Production Spillover Effect and Employment Creation Effect (Summary, unit: Production: 1 Brillion JY).
Conclusion
This paper used “3E model” and analyzed the economic effect in case of introduction of the local climate policies on Tokai region. As the result of the simulations, the production spillover effect of introducing CO2 reduction policies was larger by 0.2-0.7% than the BAU effect of BAU case. The effect of employment was greater by about 1000-4000 employments. Furthermore, the result with forecasted I-O table is that the effect of the production spillover and employment creation in the machine industry was largest within all industries. The result shows that the effect was different in 3 prefectures; in one hand the effect to machine industry was larger in Aichi; on the other hand, the same to agriculture and construction industries were greater in Gifu and Mie prefecture. The future researches should be undertaken to improve the simulation model for utilizing the endogenous technological changes to CO2 reduction policies, and to measure the feasibilities of CO2reduction policies within regions.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (2RF-1303) of the Ministry of the Environment, Japan.
References
- Matsumoto N, Honto Y. “Analysis on employment effects of the introduction of renewable energy technologies using an extended input-output table”. Journal of the Japan Institute of Energy. 2011; 90: 258-267.
- Engel D, Kammen DM, Patadia S, Wei M, Januario CS. “Green Jobs and the Clean Energy Economy” World Business Summit on Climate Change. 2009.
- Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety. “Renewably employed: Short and long term impacts of the expansion of renewable energy on the German labor market” Federal Ministry for the Environment, the Nature Conservation, and Nuclear Safety website. 2011.
- Sugiyama N, Watanabe S, Takeuchi T. “A Case Study in Revitalizing Local Economies through Regionally-based CO2 Reduction Measures”. Environmental science. 2012; 25: 391-396.
- Agency for Natural Resources and Energy. “Energy Consumption Statistics by Prefecture”. Agency for Natural Resources and Energy website. 2012.
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2010. IEA website. 2010.