
Research Article
Austin J Endocrinol Diabetes. 2015; 2(1): 1035.
SNP (rs1570360) in Transcriptional Factor Binding Sites of the VEGFA Promoter is Associated with Hypertensive Nephropathy and Diabetic Retinopathy
Norman E. Buroker*
Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle, USA
*Corresponding author: Norman E. Buroker, Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA
Received: April 17, 2015; Accepted: June 08, 2015; Published: June 12, 2015
Abstract
The Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA) gene SNP (rs1570360) (G/A) alters the potential TFBS in the promoter which may be associated with the hypertensive nephropathy and diabetic retinopathy reported in humans. The SNP VEGFA-G allele creates four unique TFBS for the EGR1, KLF4, MZF1-5- 13 and SP2 TFs while the A-allele creates six unique TFBS for the EGR2, EHF, FOXH1, MAFK, SPIB and THAP1 TFs. These TFBS changes created by the SNP are discussed with regard to possible causes of the two diseases.
Abbreviations
SNP: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism; VEGFA: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A; TFs: transcriptional factors; TFBS: Transcription Factor Binding Sites; HD: Human disease
Introduction
The human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A gene is encoded at chromosome 6p21.1 and the transcribed protein is usually expressed as a disulfide-linked homodimer, but can also be expressed as a heterodimer with placental growth factor (PGF). VEGFA is a signaling protein involved in the regulation of angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth. It induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1570360 (A/G) in the promoter region located at -1154bp from the transcriptional start site (TSS) of the VEGFA gene has been associated with many disease conditions in humans [1-9]. A SNP in a gene’s regulatory region involving a TFBS can change a TFs ability to bind DNA [10-13] in which case TFs would be unable to effectively regulate their target genes [14-18]. This concept is examined for the rs1570360 SNP in the VEGFA promoter [6,19,20] and its implications are discussed with relation to the human diseases Hypertensive Nephropathy (HN) and Diabetic Retinopathy (DR). HN is a common cause of end-stage renal disease or hypertensive kidney disease in the United States [21]. The pathological features of the disease are vascular wall thickening with arteriolar hyaline deposits, intimal fibrosis and glomerular ischemic changes [22]. In a recent study it was shown that the G-to-A allele mutation of the VEGFA rs1570360 SNP (A/G) was associated with a significant increased risk of HN in a Hispanic population [1]. DR is a prominent pathologic vascular complication in diabetes. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) an advanced stage is reached when abnormal growth of retinal vessels leads to neovascularization with the retina and vitreous gel which is often accompanied by extensive hemorrhage and fibrosis [9]. VEGF is up-regulated in DR patients and promotes neovascularization and migration as well as vascular permeability and leakage [9]. It has been reported that the AA genotype of the VEGFA rs1570360 SNP (A/G) is significantly associated with PDR [9]. In this report the presence of the rs1570360 SNP A-allele in TFBS of the VEGFA promoter are discussed in association with these diseases.
Materials and Method
Identifying TFBS
Potential TFBS were identified for the rs1570360 VEGFA SNP using the Jaspar Core [23,24] and the ConSite databases [25]. JASPAR is a collection of transcription factor DNA-binding motifs used for scanning genomic sequences and ConSite is a web-based tool for finding cis-regulatory elements in genomic sequences. The TFBS motifs and allele locations are listed in (Table 1). The Vector NTI Advance 11 computer program (Invitrogen, Life Technologies) was used to locate the TFBS in the VEGFA gene (NCBI Ref Seq NM_001171626) which represents a scan from 2.2 kb upstream of exon one to 1.7 Kb past the 3’UTR involving a total of 19.6 Kbp.
Results
The rs1570360 SNP and TFBS
This SNP is located in the promoter region of the VEGFA gene at -614 base pairs (bps) from the beginning of exon 1 [19] or -1154 bps from the TSS in exon 1 [26,27]. The major G- allele frequency of the SNP (A/G) ranges from 0.61 in Northern Han Chinese [28] to 0.94 in a black ethnic group [27]. The G-allele creates four unique potential TFBS for the EGR1, KLF4, MZF1-5-13 and SP2 TFs (Table 1, Supplement) while the A-allele creates six unique potential TFBS for the EGR2, EHF, FOXH1, MAFK, SPIB and THAP1 TFs. The two alleles create five common potential TFBS for the KLF5, SP1, SREBF1, TFAP2C and ZNF354C TFs (Table 1, Supplement). The G-allele [G (+ strand) or C (- strand)] located in the potential EGR1, KLF4, MZF1_5-13, and SP2 TFBS have a 97%, 98% 69% and 71% occurrence, respectively and consequently have been reasonably well conserved in human evolution (Table 1, Figure 1). As can be seen from (Table 1), each of these potential TFBS occur only once in the gene except for the KLF4 TFBS which also appears in intron six, and consequently, this SNP would probably have a great impact on these four TFs regulating the gene. The A-allele [A (+ strand) or T (- strand)] located in the potential EGR2, EHF, FOXH1, MAFK, SPIB and THAP1 TFBS have 16%, 100%, 5%, 47%, 96% and 29% occurrence, respectively and have not been well conserved in human evolution except for the EHF and SPIB TFBS (Table 1). The EHF TFBS occurs two other times in the gene (introns 5 & 6) while the SPIB site occurs only the one time and consequently, the SNP should have an impact on regulating the SPIB site.
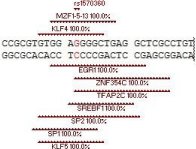
Figure 1: Double stranded DNA from the VEGFA promoter showing the
potential TFBS for nine different TFs which can bind their respective DNA
sequence either above (+) or below (-) the duplex (cf. Table1). The rs1570360
common VEGFA-G allele is found in each of these TFBS. As shown, this
rSNP is located -1154bp from the TSS in the promoter of the VEGFA gene.
Also included with the potential TFBS is their 100% sequence homology to
the duplex.
The rs1570360 SNP and disease associations
Presently there are two human diseases of interest that have been associated with this SNP (Table 2). They are hypertensive nephropathy in a Hispanic population [1] and diabetic retinopathy in a Caucasian population [9]. For the hypertensive nephropathy disease the G-allele frequency changes from 0.76 in the control group to 0.58 in the affected group while for the diabetic retinopathy disease the G-allele frequency changes from 0.62 in the control group to 0.26 in the affected group. In both studies, the A-allele frequency increased significantly [1,9] in the affected group at the expense of the G-allele (Table 2).
Sample size
Genotypes Percent
Allele Frequencies
Ethnic group
Patients
Reference
N
AA
AG
GG
A
G
86
18.6
47.7
33.7
0.42
0.58
Hispanic
HN
1
155
6.5
34.2
47.7
0.24
0.76
Hispanic
Control
45
57.8
33.3
8.9
0.74
0.26
Caucasian
PDR
9
61
34.4
47.5
18
0.38
0.62
Caucasian
Control
Table 2: The rs1570360 SNP (G/A) genotype and allele frequencies for hypertensive nephropathy (HN) and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) patients and controls from two studies. Also listed is the sample size of each ethnic group.
Discussion
The rs1570360 SNP VEGFA-G allele which generates the potential early growth response-1 (EGR1) TFBS has been found to be associated with hypertensive nephropathy [29] and proliferative diabetic retinopathy [30]. In addition, the VEGFA-G allele which also generates the Kruppel-like factor-4 (KLF4) TFBS has been found to be associated with nephropathy [31,32]. Consequently the loss of those TFBS in the VEGFA promoter created by the alternate VEGFA-A allele should have an impact on the regulation of the gene by the EGR1 and KLF4 TFs (Table 1, Figure 1). EGR1 belongs to a family of four zinc finger DNA-binding proteins which is induced by many stimuli, including hypoxia, shear stress, injury, growth factors and cytokines [32,33]. EGR1 plays a key role in orchestrating tissue response to acute injury by activating the transcription of many proliferation-associated genes such as VEGFA [33]. From (Table 1), it can be seen that the VEGFA-G allele [C (- strand)] in the potential EGR1 TFBS has been extremely well conserved in human evolution with a 97% occurrence which means that individuals carrying the VEGFA-G allele would have an EGR1 TFBS 97% of the time. This becomes especially important since this binding site only occurs only in the VEGFA promoter. From the Table, it can also be seen that the EGR homologue EGR2 TFBS is created by the VEGFA-A allele [T (- strand)] and the T-nucleotide in this motif has not been well conserved in human evolution with a 16% occurrence which means that individuals carrying the A-allele would have a EGR2 TFBS 16% of the time. The EGR2 TFBS also only occurs once at this location in the VEGFA gene. Consequently, if the EGR TF is required to active the VEGFA gene, then individuals carrying the VEGFA-A allele might be at a disadvantage. Similar logic can be used to evaluate the other TFBS in (Table 1). EGR1 is up-regulated in the kidney in response to renal artery occlusion [34]. The Transcription Factor (TF) Stimulating Protein-1 (SP1) is involved with the transcription regulation of the Kruppel-like factor-4 (KLF4) gene which encodes a zinc finger- containing TF. The two proteins are part of a (SP/ KLF) family of TFs that are involved with diverse cellular processes, such as vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation, cell differentiation, apoptosis, oncogenesis [35,36], pluripotent stem cells [37] and gene transcription [38-41]. There have been 20 KLFs identified in mammals that participate in one of the above biological functions [40] in addition to blood vessel, hematopoiesis and epidermal development [42]. KLF4 plays a key role in pathological vascular processes and acts as a molecular switch in regulating VSMC function [40]. KLF4 and SP1 physically interact in a co-operative manner when occupying the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) promoter inducing transcription in VSMCs under basal conditions [43]. KLF4 and SP1 also have TFBSs in VEGFA promoter and the SP1 TF has been shown to bind its TFBS and regulate the gene [44]. The KLF4 TF is expressed in kidney podocytes [45] and acts as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma [31]. From (Figure 1) and (Table 1), it can be seen for the rs1570360 SNP that the KLF4 TF binds the duplex DNA on the plus strand while SP1 binds the DNA on the minus strand suggesting that these two TFs may be involved in duplex strand separation at this location [46,47] during transcription. Since KLF4/SP1 bind the DNA at the same location, a nucleotide change in their TFBS could affect the regulation of the VEGFA gene. With a 98% and 77% nucleotide occurrence of the G-allele in vertebrates, respectively, in the KLF4 and SP1 TFBS (Table 1), individuals with the rs1570360 A-allele may not experience effective SP1/KLF4 regulation of the VEGFA gene. As an example, a significantly higher incidence of the VEGFA rs1570360 A-allele has been found in HN [1] and PDR [9] patients compared to their respective control groups (Table 2). In fact, the AA-genotypes change from 6.5% in the control group to 18.6% in the HN patients while the AG-genotypes change from 34.2% to 47.7%, respectively. This indicates that even individuals with an AG heterozygous genotype succumb to the disease at a higher incidence than their control. Evidently, individuals with the VEGFA rs1570360 A-allele may be at risk for HP in the Hispanic population. Among PDR patients, the AA-genotypes change from 34.4% in the control group to 57.8% in disease patients while the AG-genotypes change from 47.5% to 33.3%, respectively. This indicates that Caucasians with an AG heterozygous genotype may be somewhat protected from the disease when carrying a VEGFA rs1570360 G-allele which is contrary to what was observed with HN patients. This may be due to the nature of each disease, the TFs regulating the VEGFA gene and the ethnic group studied. As an example, in a Brazilian study it has been reported that in a systemic hypertension group of patients compared to a control group, the rs1570360 SNP VEGFA-A allele reduces the VEGFA promoter activity by 25% compared to the VEGFA-G allele; however, there was no significant difference between the alleles or genotypes of the disease patients and the control group in this report [48]. Single nucleotide changes in TF motifs have the ability to alter gene regulation and thereby result in disease. There are many reports appearing in the literature describing human disease and the association with SNPs [49], however, few of these reports are examining the SNP location for accompanying changes in potential TFBS that would affect gene regulation [50]. The present report illustrates how a SNP in the regulatory region can change the DNA landscape and alter the potential TFBS for the TFs to regulate a gene; however, further binding assays and gene activation studies are required for verification.
Allele
TFs
Protein Name
TFBS
Strand
# of Sites
G
EGR1
Early growth response 1
gcctCagCccCtcc
minus
1
C=97%
KLF4
Kruppel-like factor 4
gtGGaGgGGc
plus
2
G=98%
KLF5
Kruppel-like factor 5
gCCcCtCCac
minus
1
C=100%
MZF1_5-13
Myeloid zinc finger 1
ggAgGGGctg
plus
1
g=69%
SP1
Specificity Protein 1
CCCcTCCACA
minus
1
c=77%
SP2
Specificity Protein 2
cctCagCCcctccac
minus
1
c=71%
SREBF1
Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1
cTCAgcccct
minus
1
c=1%
TFAP2C
Transcription factor AP-2 γ
gcgagCctcAGcccc
minus
1
c=18%
ZNF354C
Zinc finger protein 354C
ctCCAC
minus
27
c=38%
A
EGR2
Early growth response 2
agccCttCCaCacgc
minus
1
t=16%
EHF
Ets homologous factor
cCTTCCAc
minus
3
T=100%
FOXH1
Fork head box H1
gccctTccACa
minus
1
t=5%
KLF5
Kruppel-like factor 5
cCtcagCCCt
minus
1
t=30%
MAFK
v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibro sarcoma oncogene homolog K
gagccTCAGCccttc
minus
1
t=47%
SP1
Specificity Protein 1
cctCagCCctt
minus
1
t=15%
SPIB
Transcription factor Spi-B
tgtGGAA
plus
1
A=96%
SREBF1
Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1
cTCAgcccTt
minus
1
T=99%
TFAP2C
Transcription factor AP-2 γ
gcgagCctcAGccct
minus
1
t=20%
THAP1
THAP domain containing, apoptosis associated protein 1 protein 1
cagCCcttc
minus
3
t=29%
ZNF354C
Zinc finger protein 354C
ttCCAC
minus
9
t=6%
Table 1: The VEGFA rs1570360 SNP (G/A) alleles. Listed are the transcriptional factors (TFs), protein name, the TFBS containing the SNP allele, DNA strand orientation and number of times the TFBS occurs in the gene. TFs in bold only occur with the given allele. Upper case nucleotides are conserved (>90%) in the TFBS region and bold is the SNP location of each allele. Below the TFBS is the nucleotide occurrence (%) obtained from the Jaspar core database.
Conclusion
A single nucleotide substitution in the promoter of the VEGFA gene created by the rs1570360 SNP (A/G) results a change in TFs binding motifs which are associated with the human diseases hypertensive nephropathy and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. The VEGFA-G allele creates four unique potential TFBS for the EGR1, KLF4, MZF1_5-13, and SP2 TFs while the VEGFA-A allele creates six unique potential TFBS for the EGR2, EHF, FOXH1, MAFK, SPIB and THAP1 TFs. The EGR1 TF is involved with renal artery occlusion while the KLF4TF is involved with pathological vascular processes making the VEGFA-G allele favorable over the A allele in avoiding these human diseases. Therefore, SNP related changes in TFBS for TFs that regulate genes can lead to human disease or sickness.
References
- Yang JW, Hutchinson IV, Shah T, Fang J, Min DI. Gene polymorphism of vascular endothelial growth factor -1154 G>A is associated with hypertensive nephropathy in a Hispanic population. Mol Biol Rep. 2011; 38: 2417-2425.
- Hong TT, Zhang RX, Wu XH, Hua D. Polymorphism of vascular endothelial growth factor -1154G>A (rs1570360) with cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 16 case-control studies. Mol Biol Rep. 2012; 39: 5283-5289.
- Supic G, Jovic N, Zeljic K, Kozomara R, Magic Z. Association of VEGF-A genetic polymorphisms with cancer risk and survival in advanced-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oral Oncol. 2012; 48: 1171-1177.
- Al-Habboubi HH, Mahdi N, Abu-Hijleh TM, Abu-Hijleh FM, Sater MS, Almawi WY. The relation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene polymorphisms on VEGF levels and the risk of vasoocclusive crisis in sickle cell disease. Eur J Haematol. 2012; 89: 403-409.
- Wu X, Xin Z, Zhang W, Wu J, Chen K, Wang H, et al. Polymorphisms in the VEGFA promoter are associated with susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma by altering promoter activity. Int J Cancer. 2013; 133: 1085-1093.
- Buroker NE, Ning XH, Zhou ZN, Li K, Cen WJ, Wu XF, et al. VEGFA SNPs and transcriptional factor binding sites associated with high altitude sickness in Han and Tibetan Chinese at the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Physiological Sciences. 2013; 63:183-193.
- Chen Y, Li T, Yu X2, Xu J3, Li J4, Luo D5,et al. The RTK/ERK pathway is associated with prostate cancer risk on the SNP level: a pooled analysis of 41 sets of data from case-control studies. Gene. 2014; 534: 286-297.
- Qi M, Huang X, Zhou L, Zhang J. Four polymorphisms of VEGF (+405C>G, -460T>C, -2578C>A, and -1154G>A) in susceptibility to psoriasis: a meta-analysis. DNA Cell Biol. 2014; 33: 234-244.
- Churchill AJ, Carter JG, Ramsden C, Turner SJ, Yeung A, Brenchley PE, et al. VEGF polymorphisms are associated with severity of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49: 3611-3616.
- Claessens F, Verrijdt G, Schoenmakers E, Haelens A, Peeters B, Verhoeven G, et al. Selective DNA binding by the androgen receptor as a mechanism for hormone-specific gene regulation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2001; 76: 23-30.
- Hsu MH, Savas U, Griffin KJ, Johnson EF. Regulation of human cytochrome P450 4F2 expression by sterol regulatory element-binding protein and lovastatin. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282: 5225-5236.
- Takai H, Araki S, Mezawa M, Kim DS, Li X, Yang L, et al. AP1 binding site is another target of FGF2 regulation of bone sialoprotein gene transcription. Gene. 2008; 410: 97-104.
- Buroker NE, Huang JY, Barboza J, Ledee DR, Eastman RJ, Reinecke H, et al.The adaptor-related protein complex 2, alpha 2 subunit (AP2alpha2) gene is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor cardiac target gene. Protein. J. 2012; 31:75-83.
- Buroker NE, Huang JY, Barboza J, Ledee DR, Eastman RJ Jr, Reinecke H et al. Genetic polymorphisms in oestrogen receptor-binding sites affect clinical outcomes in patients with prostate cancer receiving androgen- deprivation therapy. J Intern Med 2012; 271:499-509.
- Huang CN, Huang SP, Pao JB, Chang TY, Lan YH, Lu TL, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in androgen receptor-binding sites predict survival in prostate cancer patients receiving androgen-deprivation therapy. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:707-713.
- Yu B, Lin H, Yang L, Chen K, Luo H, Liu J, et al. Genetic variation in the Nrf2 promoter associates with defective spermatogenesis in humans. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012; 90: 1333-1342.
- Wu J, Richards MH, Huang J, Al-Harthi L, Xu X, Lin R, et al. Human FasL gene is a target of β-catenin/T-cell factor pathway and complex FasL haplotypes alter promoter functions. PLoS One. 2011; 6: e26143.
- Alam M, Pravica V, Fryer AA, Hawkins CP, Hutchinson IV. Novel polymorphism in the promoter region of the human nerve growth-factor gene. Int J Immunogenet. 2005; 32: 379-382.
- Buroker NE, Ning XH, Zhou ZN, Li K, Cen WJ, Wu XF, et al. AKT3, ANGPTL4, eNOS3, and VEGFA associations with high altitude sickness in Han and Tibetan Chinese at the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int J Hematol. 2012; 96: 200-213.
- Buroker NE: ADRBD1 (GRK2), TBXA2R and VEGFA rSNPs in KLF4 and SP1 TFBS Exhibit Linkage Disequilibrium. Open Journal of Genetics. 2014; 4.
- Hirth RA1. The organization and financing of kidney dialysis and transplant care in the United States of America. Int J Health Care Finance Econ. 2007; 7: 301-318.
- Meyrier A, Simon P. Nephroangiosclerosis and hypertension: things are not as simple as you might think. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996; 11: 2116-2120.
- Bryne JC, Valen E, Tang MH, Marstrand T, Winther O, da Piedade I, et al. JASPAR, the open access database of transcription factor-binding profiles: new content and tools in the 2008 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008; 36: D102-106.
- Sandelin A, Alkema W, Engström P, Wasserman WW, Lenhard B. JASPAR: an open-access database for eukaryotic transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32: D91-94.
- Sandelin A, Wasserman WW, Lenhard B. ConSite: web-based prediction of regulatory elements using cross-species comparison. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32: W249-252.
- Awata T, Inoue K, Kurihara S, Ohkubo T, Watanabe M, Inukai K, et al. A common polymorphism in the 5'-untranslated region of the VEGF gene is associated with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002; 51: 1635-1639.
- Prior SJ, Hagberg JM, Paton CM, Douglass LW, Brown MD, McLenithan JC, et al. DNA sequence variation in the promoter region of the VEGF gene impacts VEGF gene expression and maximal oxygen consumption. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006; 290: H1848-1855.
- Yuan Q, Zuo X, Jia J. Association between promoter polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor gene and sporadic Alzheimer's disease among Northern Chinese Han. Neurosci Lett. 2009; 457: 133-136.
- Sun S, Ning X, Zhai Y, Du R, Lu Y, He L, et al. Egr-1 mediates chronic hypoxia-induced renal interstitial fibrosis via the PKC/ERK pathway. Am J Nephrol. 2014; 39: 436-448.
- Lin CY, Lin TY, Lee MC, Chen SC, Chang JS. Hyperglycemia: GDNF-EGR1 pathway target renal epithelial cell migration and apoptosis in diabetic renal embryopathy. PLoS One. 2013; 8: e56731.
- Li H, Wang J2, Xiao W, Xia D, Lang B3, Wang T, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of KLF4 is associated with urothelial cancer progression and early recurrence. J Urol. 2014; 191: 493-501.
- Ritchie MF, Zhou Y, Soboloff J. WT1/EGR1-mediated control of STIM1 expression and function in cancer cells. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011; 16: 2402-2415.
- El-Asrar AM, Missotten L, Geboes K. Expression of high-mobility groups box-1/receptor for advanced glycation end products/osteopontin/early growth response-1 pathway in proliferative vitreoretinal epiretinal membranes. Mol Vis. 2011; 17: 508-518.
- Ouellette AJ, Malt RA, Sukhatme VP, Bonventre JV. Expression of two "immediate early" genes, Egr-1 and c-fos, in response to renal ischemia and during compensatory renal hypertrophy in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990; 85: 766-771.
- Nemer M, Horb ME. The KLF family of transcriptional regulators in cardiomyocyte proliferation and differentiation. Cell Cycle. 2007; 6: 117-121.
- Liu Y, Zhang C, Fan J, Xiao L, Yin B, Zhou L, et al. Comprehensive analysis of clinical significance of stem-cell related factors in renal cell cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2011; 9: 121.
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007; 131: 861-872.
- Suzuki T, Aizawa K, Matsumura T, Nagai R. Vascular implications of the Krüppel-like family of transcription factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005; 25: 1135-1141.
- Kalra IS, Alam MM, Choudhary PK, Pace BS. Krüppel-like Factor 4 activates HBG gene expression in primary erythroid cells. Br J Haematol. 2011; 154: 248-259.
- Shi JH, Zheng B, Chen S, Ma GY, Wen JK. Retinoic acid receptor α mediates all-trans-retinoic acid-induced Klf4 gene expression by regulating Klf4 promoter activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287: 10799-10811.
- Evans PM, Liu C. Roles of Krüpel-like factor 4 in normal homeostasis, cancer and stem cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008; 40: 554-564.
- Oates AC, Pratt SJ, Vail B, Yan Y, Ho RK, Johnson SL, et al. The zebrafish klf gene family. Blood. 2001; 98: 1792-1801.
- Zhang XH, Zheng B, Gu C, Fu JR, Wen JK. TGF-β1 downregulates AT1 receptor expression via PKC-δ-mediated Sp1 dissociation from KLF4 and Smad-mediated PPAR-γ association with KLF4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012; 32: 1015-1023.
- Abdelrahim M, Smith R 3rd, Burghardt R, Safe S. Role of Sp proteins in regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004; 64: 6740-6749.
- Hayashi K, Sasamura H, Nakamura M, Azegami T, Oguchi H, Sakamaki Y, et al. KLF4-dependent epigenetic remodeling modulates podocyte phenotypes and attenuates proteinuria. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124: 2523-2537.
- Gaudreault I, Guay D, Lebel M. YB-1 promotes strand separation in vitro of duplex DNA containing either mispaired bases or cisplatin modifications, exhibits endonucleolytic activities and binds several DNA repair proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32: 316-327.
- Joel P, Shao W, Pratt K. A nuclear protein with enhanced binding to methylated Sp1 sites in the AIDS virus promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993; 21: 5786-5793.
- Lacchini R, Luizon MR, Gasparini S, Ferreira-Sae MC, Schreiber R, Nadruz W, et al. Tanus-Santos JE: Effect of genetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2014;113: 491-496.
- Shastry BS1. SNPs: impact on gene function and phenotype. Methods Mol Biol. 2009; 578: 3-22.
- Teng M, Ichikawa S, Padgett LR, Wang Y, Mort M, Cooper DN, et al. regSNPs: a strategy for prioritizing regulatory single nucleotide substitutions. Bioinformatics. 2012; 28: 1879-1886.