
Research Article
Austin J Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017; 4(1): 1055.
Pretreatment with the Combination of Drugs Protects against Cognitive Impairment in Diabetic Rats
Tenzin Tender* and Rema Razdan
Department of Pharmacology, Al-Ameen College of Pharmacy, India
*Corresponding author: Tenzin Tender, Department of Pharmacology, Al-Ameen College of Pharmacy, Bangalore-560027, Karnataka, India
Received: February 23, 2017; Accepted: March 30, 2017; Published: April 21, 2017
Abstract
Objectives: The World Health Organization has foreseen that 35.6 million people suffer from dementia is due diabetes and this number might be doubled by 2030 and unlike other complications due to diabetes, cognitive impairment occur early in patients. Pharmacological treatments cannot cure or stop the progression of cognitive impairment due to diabetes. Hence, in current study the attempt has made to prevent or delay the cognitive impairment in diabetic rats using combination of drugs.
Methodology: Diabetes was induced in male Wistar rats by administrating streptozotocin (52mg/kg,i.p). Diabetic rats were treated with combination of gamma linolenic acid (30mg/kg,p.o), alpha lipoic acid (30mg/kg,p.o), phloroglucinol (250mg/kg,p.o), benfotiamine (100mg/kg,p.o), in one group and gamma linolenic acid (30mg/kg,p.o), alpha lipoic acid (30mg/kg,p.o), allantoin (200mg/kg,p.o), benfotiamine (100mg/kg,p.o), in other group for eight weeks. The degree of protection was determined by measuring motor co-ordination, Barne maze, Glycosylated Haemoglobin (GHb) and transmitter like dopamine, nor-adrenaline, serotonin, gamma amino butyric acid and acetyl cholinesterase.
Results: Administration of combination of drugs significantly reduced glycated haemoglobin,dopamine,serotonin, latency to enter escape cage and significantly elevated the body weight, motor co-ordination, nor-adrelanine, gamma amino butyric acid, acetylcholinesterase levels compared to diabetic control rats.
Conclusion: Supplementation of combination treatment showed improved glycemic and neurotransmitters control in diabetic rats. Hence, the pretreatment with combination of drugs may be a way to delay cognitive impairment resulting from hyperglycemia and distortion of neurotransmitters.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Dementia; Streptozotocin; Gamma linolenic acid; Alpha lipoic acid; Benfotiamine; Phlorogluci-nol; Allantoin
Introduction
It has reported that diabetes mellitus can cause serious neuronal impairment and cognitive deficits [1,2]. The effect of diabetes mellitus on cognitive functions have been found to occur early in patients unlike other complications due to diabetes which usually requires years of diabetes before becoming clinical apparent. The most common cognitive deficits identified in patients with type 1 diabetes are slowing of information processing speed [3-6] and worsening psychomotor efficiency [3,4,7]. However, other deficits like attention, memory, motor strength and executive function have also been reported. Although much research has been done, the pathophysiology of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes is not well understood but it is likely that hyperglycemia, vascular disease, hypoglycaemia and insulin resistance play significant roles. The World Health Organization has foreseen that 35.6 million people suffer from dementia and this number might be doubled by 2030. One study suggested that over 80% of cases of Alzheimer Disease (AD) had either type 2 diabetes or impaired fasting glucose [8]. Furthermore, diabetes patients have a 50% - 75% increased risk of developing AD compared to nondiabetes patients [9]. Pharmacological treatments cannot cure or stop the progression of cognitive impairment due to diabetes. Hence, in current study the attempt has made to prevent or delay the cognitive impairment in diabetic rats using combination of drugs. Addressing these deficits by single drug has yet to produce effective treatment for diabetic induced cognitive impairments. The current study addresses the treatment for diabetic induced cognitive impairment by using a combination of drugs targeted at various mechanisms underlying the progression of diabetic induced cognitive impairments.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Experimental animals, adult male Wistar rats (n=5) weighing between 200-250 g were included for the study. All rats were maintained under standard housing condition at controlled temperature at 25°C ± 2°C with 12 hr light/dark cycle with food and water provided standard rat diet and water ad labitum. Animals which did not comply with above criteria, and which were found to be diseased were excluded from the study. After one-week adaptation period, the healthy animals were used for the study. All the protocols were approved by Institutional Animal Ethical Committee. IAEC NO: AACP/P-48, India.
Experimental design
Thirty two rats were randomly divided into four groups. Group I served as normal control group. Group II, Group III and IV were induced diabetic rats and included in the study as experimental rats. Group II served as diabetic control group whereas Group III received gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine and Group IV received gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, allantoin, benfotiamine daily for eight weeks. Treatment was started after diabetes was confirmed in rats. Rats were also administered insulin (3IU/day, s.c.) [10] for the complete period of the study. After 8 weeks initial and terminal body weight, behavioural and biochemical parameters were determined to evaluate the severity of diabetes induced cognitive impairment in treated group as compare to normal and diabetic control group.
Assessment of body weight
To assess the general condition of animals, they were examined daily for clinical signs such as alopecia, piloerection or hind limb weakness and mortality. Body weight was measured using digital balance (Essae® DS-252). Loss of body weight was compared between body weight measured at the beginning and at the end of the study.
Behavioural parameters
Motor co-ordination test and Barnes maze test were done according to published papers [11,12].
Biochemical parameters
Measurement of Glycosylated Hemoglobin (GHb) [13], brain neurotransmitters like dopamine, noradrenaline, serotonin. Gamma amino butyric acid, and acetyl cholinesterase were done according to published papers [14,15,16,17,18,19].
Statistical analysis
Statistical evaluations were done by ANOVA, expressed as mean ± S.E.M. followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test using Graph Pad Prism 5 computer program. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Assessment of body weight
The percentage change in body weight of normal and diabetic rats at 8th week was found to be 17.72±1.66g and -24.53±2.706g. The body weight of diabetic rats was significantly reduced (P<0.001) as compared to normal control, similarly the change of body weight of diabetic treated with comb.1 and comd.2 was found to be ‑12.49±0.93g and -12.30±2.457g which significantly improved as compared to diabetic control rats (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on %
body weight change in diabetic rats. Values are represented as mean ± SEM
(n=5). One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test.
***P<0.001, *P<0.05 Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1, gamma linolenic
acid, alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma
linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Behavioural studies
Measurement of motor coordination using rota rod: Fall of time at 15 rpm of normal and diabetic rats was found to be 235.3±1.753 and 37.58±2.343secs respectively, and the latency of diabetic rats was significantly reduced (P<0.001) as compared to normal control. Latency in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 81.56±1.90 secs and 76.93±0.865secs and same was significantly P<0.001 improved when compared to diabetic control rats (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on
muscle incordination by rota rod performance in diabetic rats. Values are
represented as mean ± SEM (n=5). One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s
Multiple Comparison Test. ***P<0.001 Vs diabetic control group.Comb.1,
gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2,
gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Measurement of spatial memory and learning using barnes maze: Time taken to enter escape cage by normal and diabetes rats was found to be 15.59 ±0.51and 52.20±1.58secs respectively, and the latency of diabetes
rats was significantly increased (P<0.001) as compared to normal control. Latency in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 25.29±2.066secs and 21.22±0.70secs and same was significantly P<0.001 improved when compared to diabetic control rats (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on
spatial learning and memory by Barne maze in diabetic rats. Values are
represented as mean ± SEM (n=5). One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s
Multiple Comparison Test. ***P<0.001 Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1,
gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2,
gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Biochemical studies
Estimation of GHb: The percentage GHb of normal and diabetes rats was found to be 1.667±0.1476 and 13.43±1.198and same was significantly increased (P<0.001) as compared to normal control. The percentage GHb of diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 6.150±0.3510 and 5.117±0.407 and same were significantly improved. P<0.001 when compared with diabetic control rats (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on
%GHB in diabetic rats. Values are represented as mean ± SEM (n=5). One
Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. ***P<0.001
Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1, gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid,
phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic
acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Estimation of dopamine: The dopamine content in brain of normal and diabetic rats was found to be 46.9±1.005ng/dl and 71.7±0.88ng/dl respectively and the dopamine level of diabetic rats was significantly increased (P<0.001) as compared to normal control rats. Dopamine level in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 64.94±0.33ng/dl and 63.10±0.64ng/dl and same was significantly increased (P<0.001) when compared to diabetes control rats (Figure 5).
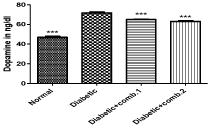
Figure 5: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on brain
dopamine level in diabetic rats.Values are represented as mean ± SEM (n=5).
One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. ***P<0.001
Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1, gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid,
phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic
acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Estimation of nor-adrenaline: The nor-adrenaline level in brain of normal and diabetic rats was found to be 17.30±0.66ng/dl and 5.060±0.31ng/dl respectively and the nor-adrenaline level of diabetic rats was significantly reduced (P<0.001) as compared to normal control rats. Nor-adrenaline level in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 12.14±0.66ng/dl and 9.8±0.74ng/dl and same was significantly increased when compared to diabetes control rats (Figure 6).

Figure 6: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on brain
nor-adrenaline level in diabetic rats.Values are represented as mean ± SEM
(n=5). One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test.
***P<0.001, **P<0.01 Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1, gamma linolenic
acid, alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma
linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Estimation of serotonin: The serotonin content in brain of normal and diabetic rats was found to be 2.64±0.19ng/dl and 8.02±0.33ng/dl respectively and the serotonin level of diabetic rats was significantly increased (P<0.001) as compared to normal control rats. Serotonin level in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 4.5±0.2ng/dl and 6.310±0.64ng/dl and same was significantly reduced /(P<0.001) when compared to diabetes control rats (Figure 7).

Figure 7: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on brain
serotonin level in diabetic rats.Values are represented as mean ± SEM (n=5).
One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. ***P<0.001
Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1,gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid,
phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic
acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Estimation of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA)
The GABA level in brain of normal and diabetic rats was found to be 7.94±0.37ng/dl and 2.84±0.143ng/dl respectively and the GABA level of diabetic rats was significantly reduced (P<0.001) as compared to normal control rats. GABA level in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 4.78±0.19ng/dl and 5.74±0.172ng/dl and same was significantly increased when compared to diabetes control rats (Figure 8).

Figure 8: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on brain
GABA level in diabetic rats. Values are represented as mean ± SEM (n=5).
One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test. ***P<0.001
Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1,gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid,
phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic
acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Estimation of acetylcholinesterase (AchE)
The Ache level in brain of normal and diabetic rats was found to be 3.920±0.086 μmoles/min/mg and 2.38±0.1 μmoles/min/mg respectively and the AchE level of diabetic rats was significantly reduced (P<0.001) as compared to normal control rats. AchE level in diabetic rats treated with comb.1 and comb.2 was found to be 3.14±0.103 μmoles/min/mg and 2.8±0.070 μmoles/min/mg and same was significantly increased when compared to diabetes control rats (Figure 9).

Figure 9: Effect of treatment of combination of drugs for eight weeks on
brain AchE level in diabetic rats. Values are represented as mean ± SEM
(n=5). One Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Test.
***P<0.001, P<0.05Vs diabetic control group. Comb.1, gamma linolenic acid,
alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine; Comb.2, gamma linolenic
acid, alpha lipoic acid, allantoin, benfotiamine.
Discussion
The current study has used comb.1 containing gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid, phloroglucinol, benfotiamine and Comb.2 containing gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid,allantoin, benfotiamine to alleviate the persistence of cognitive impairment in diabetic rats.
The metabolised product of gamma linolenic acid undergoes oxidative metabolism by cyclooxygna- ses and lipoxygenases to produce anti-inflammat- ory eicosanoids (prostaglandins of series 1 and leukotrienes of series 3). Gamma linolenic acid and its metabolites also affect expression of various genes where by regulating the levels of gene products including matrix proteins. These gene products play a significant role in immune functions and also in cell death [20]. Lipoic acid is a cofactor essential in mitochondrial metabolism with anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. The mechanisms of action of alpha lipoic acid in experimental diabetic rats include reduction of oxidative stress along with improvement in nerve blood flow, nerve conduction velocity and several other measures of nerve functions [21]. Benfotiamine has been shown to prevents the progession of diabetic complications probably by increasing tissue levels of thiamine diphosphate and so enchancing transketolase activity and it is also found to inhibit Advance Glycation Endproducts [22]. It was shown that benfotiamine (S-benzoylthiamine O-mono phosphate) possesses anti-inflammatory effects [23]. Phloroglucinol has been reported to have inhibitory activity in the formation of Advanced Glycation Endproducts (ADEs) and also provides antihyperglycemia and good anti-oxidant activity [24,25], Allantoin shows anti-diabetic effects by modulating antioxidant activities,lipid profile and by promoting release of Glucagon Like Peptide (GLP- 1), thereby improving the function of β- cells maintaining normal insulin and glucose level. Allantoin has also been found to increase Nitric Oxide (NO) level [26].
We have observed a significant reduction in the body weight of the diabetic rats as compare to the normal control group. Oxidative degradation of amino acids causes loss of tissue proteins and lipolysis which can cause reduction in body weight in diabetes .Improvement in the weight loss may be due to increase in the rate of metabolism in cell by combination treatment and decrease in the oxidative stress causing preservation of tissue protein by decreasing the muscle wasting contributing to the recovery of body weight.
In the present study diabetic control rats showed a significant reduction in falling latency on rota rod apparatus. The severity of diabetic neuropathy has been associated with decreased muscle strength in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and weak grip strength in grip strength meter indicating poor motor/muscle activity [27]. Recently researcher have elucidate the influence of glial activation leading to cellular degradation and glutamate toxicity on altered behavioral activity in STZ induced diabetic rats. Time taken by diabetic rats to enter escape cage of Barne maze apparatus was significantly higher when compared with normal and treated rats. The decline in spatial navigational learning and memory in diabetes rats can be due to hyperglycemia which causes distortion in neurotransmitters level. In Type 1 diabetes mellitus an elevation in the glucose level is directly proportional to the rate of glycosylation of hemoglobin causing the formation of GHb (glycosylated hemoglobin) over previous four weeks to three months. Marked increase in percentage of GHb has been reported in previous studies in diabetic rats [28]. GHb has been implicated in various diabetic microvascular complications like cognitive impairment, neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy etc. Glycosylation may lead to the formation of oxygen-derived free radicals in diabetes mellitus and its level can be considered as one of the important marker of oxidative stress. Therefore, in the present study we have measured the level of GHb as a marker of diabetes induced oxidative stress. Our results showed that the level of GHb in diabetic rats was significantly higher as compared to the normal rats. Treatment with the combination drugs significantly reduced HBA1c suggesting an improvement in glycaemic control.
Diabetes mellitus causes distortion in neurotransmitters level in brain which are responsible for learning,memory and many other activities. Dysfunction of neurotransmitters can be due to hyperglycemia,various vascular diseases and insulin resistance. In current study we found that the level of dopamine and serotonin in diabetic rats were significantly increased when compared to normal control rats whereas the level of nor-adrenaline, GABA and AchE were significantly decreased in diabetic rats when compared to normal rats.Treatment with combination restored the altered transmitter levels.
Conclusion
The combination contains drug acting by multiple mechanisms like gamma linolenic acid, alpha lipoic acid and benfotiamine which have been used since long. Addition of allantoin or phloroglucinol drug with good safety profile can be a safe for long term administration in diabetics to successfully delay the developments of cognitive impairment.
References
- Biessels GJ, Deary IJ, Ryan CM. Cognition and diabetes: A lifespan perspective. Lancet Neurol. 2008; 7: 184–190.
- Wrighten SA, Piroli GG, Grillo CA, Reagan LP. A look inside the diabetic brain: Contributors to diabetes-induced brain aging. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1792: 444–453.
- Brands AM, Kessels RP, Hoogma RP, Henselmans JM, van der Beek Boter JW, Kappelle LJ, et al. Cognitive performance, psychological well-being, and brain magnetic resonance imaging in older patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006; 55: 1800–1806.
- Ryan CM, Geckle MO, Orchard TJ. Cognitive efficiency declines over time in adults with type 1 diabetes: effects of micro- and macrovascular complications. Diabetologia. 2003; 46: 940–948.
- Ryan CM, Williams TM, Finegold DN, Orchard TJ. Cognitive dysfunction in adults with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus of long duration: effects of recurrent hypoglycaemia and other chronic complications. Diabetologia. 1993; 36: 329–334.
- Wessels AM, Rombouts SA, Remijnse PL, Boom Y, Scheltens P, Barkhof F, et al. Cognitive performance in type 1 diabetes patients is associated with cerebral white matter volume. Diabetologia. 2007; 20: 1763–1769.
- Weinger K, Jacobson AM, Musen G, Lyoo IK, Ryan CM, Jimerson DC, et al. The effects of type 1 diabetes on cerebral white matter. Diabetologia. 2008; 51: 417–425.
- Janson J, Laedtke T, Parisi JE, Brien PO, Petersen RC, Butler PC. Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Alzheimer Disease. Diabetes. 2004; 53: 474-481.
- Kim B, Backus C, Oh S, Hayes JM, Feldman EL. Increased Tau Phosphorylation and Cleavage in Mouse Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrinology. 2009; 150: 5294-5301.
- Federiuk IF, Casey HM, Quinn MJ, Wood MD, Ward W. Induction of type-1 diabetes mellitus in laboratory rats by use of alloxan: route of administration, pitfalls, insulin treatment. Comprehensive Medical. 2004; 54: 252-257.
- Rosenfeld CS, Ferguson SA. Barnes Maze Testing Strategies with Small and Large Rodent Models. Jove of visualized experiments. 2014; 84: e51194.
- Peeyush KT, Gireesh G, Jobin M, Paulose CS. Neuroprotective role of curcumin in the cerebellum of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Science Journal. 2009; 85: 704- 710.
- Nathan DM, Singer DE, Hurxthal K, Goodson JD. The clinical information value of the glycosylated hemoglobin assay. The England journal of Medicine. 1984; 310: 341-346.
- Pal DK. Determination of brain biogenic amines in. 2009; 1: 190-197.
- Attack CV. The determination of dopamine by a modification of the dihydroxyindole flurimetric assay. Br J Pharnacol. 1973; 48: 699-714.
- Ciarlose AE. Further modification of a Flurometric for analyzing brain amines. 1978; 23: 9-12.
- Benbow GM. Short communications. Vet Rec.1977; 101: 97.
- Saravana kumar A, Gandhimathi R. Effect of guettarda speciosa extracts on biogenic amines concentrations in rat brain after induction of seizure. Internation journal of pharma science. 2009; 1: 237-243.
- Kumar S, kessari KK, Bihari J. Evaluation of genotoxic effects in male Wistar rats following microwave exposure. Indian journal of experimental biological. 2010; 48: 586-592.
- Kapoor R, Huang YS. Gamma linolenic acid: an antiinflammatory omega-6 fatty acid. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. 2006; 7: 531-534.
- Sharma M, Gupta YK. Effect of alpha lipoic acid on Intracerebroventricular streptozot-ocin model of cognitive impairment in rat. 2003; 13: 241-247.
- Volvert ML, Seyen S, Piette M, Evrard B, Gangolf M, Plumier JC, et al. Benfotiamine, a synthetic S-acyl thiamine derivative, has different mechanisms of action and a different pharmacological profile than lipidsoluble thiamine disulfide derivatives. BMC Pharmacol. 2008; 8: 10.
- Bozicl, Savic D, Stevanol, Pekovic S, Nedeljkovic N, Lavrnja. Benfotiamine upregulates antioxidative system in activated BV-2 microglia cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015; 9: 351.
- Kyoung AK, RuiZ, Sungwood C, Su JL, Jihoon K, Jeongtae K, et al. Phloroglucinol (1,3,5-trihydroxy benzene) protects against ionising radiationinduced cell demage through inhibition of oxidative stress invitro and invivo. Chemico- Biological Interaction. 2010; 185: 215- 216.
- Ting TL, Yi SZ, Lan H, Nian SL, Jun P, Yuan JL. Protective effect of phloroglucinol against myocardial ischaemai-reperfusion injury is related to inhibition of myeloperoxidase activity and inflammatory cell infiltration. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Phyisiology. 2013; 38: 27-33.
- Go HK, Rahman MM, Kim GB, Na CS, Song CH, Kim JS, et al. Antidiabetic effects of yam (Dioscorea batatas) and Its Active Constituent, Allantoin, in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced iabetes. Nutrients. 2015; 7: 8532-8544.
- Andersen H, Nielsen S, Mogensen CE, Jakobsen J. Muscle strength in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004; 53: 1543-1548.
- Krishnamurti U, Steffes MW. Glycohemoglobin: a primary predictor of the development or reversal ofcomplications of diabetes mellitus. Clinical Chemistry. 2001; 47: 1157-1165.