Abstract
The contamination of soil by anthropogenic activities has raised many concerns in scientific community. There is an urgent need of reliable and nature friendly techniques for addressing these concerns. Vermiremediation and phytoremediation are two such dependable techniques. Vermiremediation involves earthworms to convert solid organic materials and wastes into vermicompost which acts as a soil conditioner and nutrient-rich manure. The contaminants in organic wastes which could pollute the soil can be significantly reduced using earthworms. The vermicompost generated from earthworms increases soil fertility (physical, chemical, biological). In vermicompost nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, sodium, magnesium and calcium are in plant available forms. Vermicompost is increasingly considered in agriculture and horticulture as a promising alternative to chemical fertilizers. Phytoremediation involves plants and soil microbes to minimize the amount of contaminants (such as heavy metals) in the environment. Plants have capacity to uptake contaminants from the soil and execute their detoxification by various mechanisms (phytoaccumulation, phytostabilization, phytofiltration, phytodegradation, phytovolatilization). Plants store these contaminants in there tissues from where these can be harvested or dumped in safe sites. This study is aimed to document the various techniques and their role, with commercial examples, benefits, and drawbacks etc of phytoremediation and also effects of vermicompost on the soil fertility, physicochemical and biological properties of soil.
Keywords: Earthworms; Heavy metals; Microbes; Nutrients; Organic fertilizer; Vermicompost
Introduction
Excessive use of chemical fertilizers deteriorates the soil properties (physical and chemical) and also contaminates the surrounding environment [1]. According to Chaoui et al [2]. excessive leaching of nutrients and salinity-induced plant stress can be caused by the excessive use of inorganic fertilizers. The joint application of organic and chemical fertilizers maintains the Soil Quality Index (SQI) [3]. The excessive use of chemical fertilizers without organic fertilizers can deteriorate the soil properties [1]. The physico-chemical characteristics of agricultural soils can be modified directly by the application of vermicompost which acts as a soil conditioner and nutrient-rich manure [4]. Vermicomposting involves joint interaction between earthworms and microorganisms to generate a homogeneous, stable and nutrient rich product called as vermicompost [5-8]. The final vermicompost is nutritionally improved as compared to traditional compost [9-11]. Vermicomposting process increases the rate of mineralization of organic substrates and enhances higher degree of humification [12]. Soil fertility can be enhanced by the application of vermicompost through physically (aeration, porosity, water retention, bulk density), chemically (pH, electrical conductivity, organic matter content) and biologically (microbial biomass, enzymes, micro and micro nutrients) [13-15]. Vermicompost is increasingly considered in agriculture and horticulture as a promising alternative to chemical fertilizers. Vermicompost is rich source of macro and micro nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, sodium, magnesium and calcium [11,16] and can play a major role in soil nutrient management. The use of vermicompost can enhance the physiochemical properties of soil, which can increase the plant growth [17]. Phytoremediation involves plants and soil microorganisms to minimize the toxic effects of pollutants in the environment [18,19]. This technique is used to remove toxic metals and other organic pollutants. According to Mench et al. [20] plants amend soil fertility with application of organic materials. The present review article is aimed to document the effects of vermicompost on the soil fertility, plant growth, physicochemical and biological properties of soil and various techniques of phytoremediation and their role in soil stabilization.
Vermicomposting
The process of vermicomposting involves earthworms to convert organic materials into vermicompost which acts as a soil conditioner and nutrient-rich manure. Vermicomposting technology is costeffective and eco-friendly technique that plays an important role in minimizing environmental pollution. The final vermicompost can be applied for agricultural purposes which provide maximum microbial activity to the soil [21]. Through vermicomposting, many researchers have successfully converted various types of industrial wastes into nutrient rich manure [22-24].
Nutrient content in vermicompost
Vermicompost produced from organic sources can play a major role in soil fertility and also in organic farming. The final vermicompost has higher macro and micro nutrients as compared to traditional compost [10]. Vermicompost is granular, with large surface area due to mineralization and degradation by earthworms [7,25]. The nutrient content in vermicompost (prepared from cattle dung) and traditional compost is shown in Table 1.
Nutrient content
Vermicompost
Traditional compost
pH
8.92±0.09
8.40±0.10
EC (mS/cm)
2.82±0.03
3.22±0.02
TKN (%)
2.40±1.20
1.03±0.24
TOC (%)
37.12±0.11
45.40±1.01
C:N ratio
15.46±0.57
44.30±1.62
TAP (%)
1.49±0.81
0.92±0.30
TK (%)
1.90±2.08
4.01±1.20
TNa (%)
1.41±0.38
0.71±0.20
Zna
11.54±0.37
9.85±0.37
Cua
9.0 3±0.20
8.04±0.23
Fea
590.04±1.52
620.04±1.60
Mna
38.0 1±0.88
13.02±1.77
Weight in mg/Kg. Source: Bhat et al., [10].
Table 1: Nutrient content of vermicompost and traditional compost.
Effect of vermicompost on soil quality, physico-chemical and biological properties
Vermicompost increases the soil microbial population and acts as a rich source of nutrients. It increases the availability of nutrients (potassium and nitrogen) through improving phosphorus solubilization and nitrogen fixation [17]. Application of vermicompost can directly enhance the physiochemical and biological properties of soil. Vermicompost increases soil porosity, aeration, water holding capacity and infiltration [13]. According to Kale and Karmegam [26] earthworms in the soil add mucus secretion which enhances the soil stability. The combination of earthworms and microbes decreases the particle and bulk densities of soil which increases the porosity and aggregate formation of the soil [1]. Soil treated with vermicompost increases the available (N, K, P) and total (Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Mn, Na, Zn) macro and micro-nutrients in the soil [1]. Leaching problem of nutrients in soil can be reduced by the application of vermicompost. Bhattacharjee et al. [27] observed that the nutrient leaching from the soil is greatly reduced by the application of vermicompost which changes the physico-chemical characteristics of the soil. Vermicompost can also be used in acid and alkaline soils, due to its near neutral to alkaline nature of pH. According to Manivannan et al. [1] pH between 6-7 ranges increases the availability of nutrient content to the plants. Many researchers have observed that the soil pH increases in acidic soils and reduces in alkaline soils with the application of vermicompost [28,29]. In vermicomposting process, Electrical Conductivity (EC) of final vermicompost depends on initial raw material used [30]. Addition of vermicompost lowers the EC of soil due to increase in the exchangeable Ca2+ concentration, which allows higher leaching of exchanged Na+ and lowers the soil EC [31]. Vermicompost improves soil porosity and infiltration rate, which enhances salt leaching leading to decrease in EC of soil [32]. Vermicompost with EC value lower than 4.0 ds m-1 are ideal for organic soil amendments [33]. Application of vermicompost in soil increases the organic matter and biomass of soil microbes [1]. According to Atiyeh et al. [34] dehydrogenase enzyme activity was higher in vermicompost as compared to commercial medium. Application of organic fertilizers (vermicompost, neem cake, farmyard manure and ash) and biofertilizers to soil increases the enzyme activities (dehydrogenase, acid phosphatase and β-glucosidase [35]. Vermicompost increases the surface area for microbial activities and retention of nutrients [36,37]. Application of vermicompost increases the biomass of soil microbes, which increases the plant growth and fruit yield [38]. The scientific research on the plant growth by the application of vermicompost are still sparse.
Effect of vermicompost on productivity and growth of plants
Many researchers studied the effect of vermicompost on productivity and growth of plants [39-42]. Vermicompost contains high levels of soil enzymes and plant growth hormones and also retains nutrients in soils for longer duration without affecting the environment [17,36]. Vermicompost can be used as a soil additive and plant container media for overall growth and development of plants [43]. According to Roy et al. [44] vermicompost increases the root and shoot weight and plant height as compared to traditional compost. Earthworms in the soil may impact the physico-chemical characteristics of the soil and other organisms (nematodes, collembolans) living within the soil [45]. Application of vermicompost accelerates the growth of crops and plants. Vermicompost contains enzymes and hormones that stimulate plant growth and makes it pathogen free [46]. Plant growth promoting substances and plant growth hormones (auxin, cytokinins, humic substances) produced by microbes have been reported from vermicompost by many researchers [47,48]. The final vermicompost is considered an excellent material of homogenous nature as it has reduced level of contaminants and holds more nutrients over a longer time without affecting the environment [49]. Many researchers [50-53] have reported that the vermicompost produced from animal dung, sewage and paper industry sludge contains higher amounts of humic substances, which have important role in growth and productivity of plants. So vermicomposting and vermiculture technology is economically sound, environmentally safe technology for organic waste degradation and can create employment opportunities for all weaker sections of the society. India, were a large amount of organic waste is available could produce million tons of vermicompost and will reduce the use of toxic chemical fertilizers. Hidalgo et al. [54] observed that the addition of vermicompost to a greenhouse potting medium (mixture of sand, pine bark and peat) showed a significant increase in water holding capacity and total porosity. Ferreras et al. [55] reported that addition of 20 ton ha-1 of vermicompost in two consecutive years to an agricultural soil significantly improved soil porosity and fertility. Marinari et al. [56] reported that the elongated soil Macropores number increased significantly in corn field after a single vermicompost application equal to 200 kg ha-1 of N. Gopinath et al. [57] observed increase in total organic carbon and soil pH and decrease in bulk density of soil after application at a rate equal to 60 kg ha-1 of N of vermicompost in two consecutive growing seasons. Vermicompost is increasingly considered in agriculture and horticulture as a promising alternative to chemical fertilizers. Vermicompost not only produces yield with all nutrients but also at the same time increases the soil fertility and nutrient availability to the crops. Thus it is a double edged technology which plays a major role in sustainable development.
Limitations of Vermicomposting
While vermicomposting offers substantial environmental benefits, it also is associated with a number of limitations as given below:
- Earthworms require neutral pH, mesophilic temperature and maintenance of 60-70% moisture level.
- Vermicomposting unit is more expensive to set up than compost piles.
- Earthworms should be protected from direct light. Shade is required for maintaining moisture temperature and faster rate of degradation.
- Worms needs to be separated from vermicompost and do require some attention and proper care (Protection from other predators).
Heavy Metal Contamination of Soil
With the advent of industrialization life has certainly become easy and human living conditions have improved vastly. But it has also brought with it the menace of environmental pollution which has become a severe cause of concern and existential threat for life on earth. Among different forms of pollution, soil heavy metal contamination is most dangerous because it affects the sources of food and thus poses severe risk to life on earth.
Heavy metals are the metals having atomic mass greater than 20 and are transition metals, metalloids, actinides and lanthanides [58]. Heavy metals in biological processes are classified into two classes: Essential heavy metals and Non-essential heavy metals. Those heavy metals which are required by organisms for their physiological processes are essential metals such as Copper (Cu), Cobalt (Co), Iron (Fe) etc. Non-essential metals are not required by organisms or sometimes are toxic even in small amounts such as Arsenic (As), Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr), Lead (Pb) etc. [19]. The essential elements above maximum permissible limits can pose severe risks to organisms. The main concern regarding the heavy metals is their long term persistence in environment, such as 150 – 5000 years for Pb, 18 years for Cd etc. [59-61]. Considering such long persistence and toxic effects of heavy metals, their management and removal from soil becomes mandatory. There are several physical and chemical techniques available for remediation of heavy metals such as electrophoresis, soil washing, vitrification, pneumatic fracturing, chemical reduction etc. [62]. But these techniques have “pump and trial” and “dig and dump” approach. Also these techniques have very high cost, require huge setup, disturb the native soil micro flora and even generate secondary pollutants. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a cost effective, eco friendly and sustainable technique which can solve the problem of heavy metal contamination of soil.
from soil becomes mandatory. There are several physical and chemical techniques available for remediation of heavy metals such as electrophoresis, soil washing, vitrification, pneumatic fracturing, chemical reduction etc. [62]. But these techniques have “pump and trial” and “dig and dump” approach. Also these techniques have very high cost, require huge setup, disturb the native soil micro flora and even generate secondary pollutants. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a cost effective, eco friendly and sustainable technique which can solve the problem of heavy metal contamination of soil.
In recent times, “phytoremediation” has emerged as a very effective tool for decontamination of heavy metal polluted soils.
Phytoremediation
Phytoremediation is a technique that involves growing heavy metal tolerant plants having metal accumulating potential to clean the contaminated site. These plants can absorb, accumulate and detoxify pollutants from the site through their metabolic processes. Many studies have been conducted throughout the world on accumulation and phytoremediation of heavy metals from soil [63-76,107-120] (Table 2).
S. No.
Plant species
Metals accumulated
References
1
Acorus calamus, Cyperus malaccensis, Eleocharis valleculosa, Equisetum ramosisti, Juncus effuses, Leersia hexandra, Neyraudia reynaudiana, Phragmites australis, Phalaris arundinacea, Polypogon fugax, Typha latifolia, and Typha angustifolia
Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn
Deng et al., [64]
2
Brassica napus and Raphanus sativus
Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn
Marchiol et al., [107]
3
Paspalum notatum, Pennisetum glaucum × P. purpureum, Stenotaphrum secundatum and Vetiveria zizanioides
Pb and Cd
Xia, [108]
4
Achnatherum chingii, Adiantun capillus-veneris L., Arundinella yunnanensis, Artemisia lancangensis, Carpinus wangii, Fargesia dura, Juncus effuses, Lithocarpus dealbatus, Llex plyneura, Pinus yunnanensis Tranch, Populus yunnanensis, Polystichum disjurctam, Rhododendron decorum, Rhododendron annae, Rhododendron decorum, Rhododendron annae, Salix cathayana, Sambucus chinensis, and Trifdium repensl
Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn
Yanqun et al., [63]
5
Carthamus tinctorius L., Cannabis sativa L., Malva verticillata L., Melilotus alba L., and Trifolium pratense L.,
As, Cd, Pb, and Zn
Tlustoš et al., [109]
6
Bidens alba var. radiate, Cyperus esculentus L., Gentiana pennelliana Fern., Plantago major L., Phyla nodiflora L., Rubus fruticosus L., Sesbania herbacea and Stenotaphrum secundatum
Cu, Pb and Zn
Yoon et al., [65]
7
Aeschynomene indica L., Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb, Aster subulatus Michx, Cyperus iria L., Cyperus difformis L., Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop, Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn, Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv, Echinochloa caudata Roshev, Echinochloa oryzicola (Ard.) Fritsch, Eclipta prostrata L., Fimbristylis miliacea (L.) Vahl, Isachne globosa (Thunb.) Kuntze , Monochoria vaginalis (Burm. f.) Presl, Oryza sativa L., Phragmites communis Trin., Polygonum lapathifolium L., Polygonum hydropiper L. and Zizania latifolia (Griseb.) Stapf
Cd, Pb and Zn
Liu et al., [110]
8
Dianthus chinensis, Rumex crispus, Rumex K-1, Rumex acetosa DSL, Rumex acetosa JQW, Sedum alfredii, Vertiveria zizanioides and Viola baoshanensis
Cd, Pb and Zn
Zhuang et al., [111]
9
Artemisia lactiflora Wall, Aster subulatus Michx, Bauhinia variegate, Buddleia officinalis Maxim, Colocasia esculenta, Conyza canadensia (L.) Cronq., Debregeasia orientalis, Polygonum chinense, Polygonum rude, Pteris ensiformis, Pteridium var, Pteris fauriei Hieron, Osyris wightiana, Ricinus communis L., Rumex hastatus, Smilax china L. and Tephrosia candida
Cu, Pb and Zn
Xiaohai et al., [67]
10
Lobelia chinensis and Solanum nigrum
Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn
Peng et al., [112]
11
Helianthus annuus and Tithonia diversifolia
Pb and Zn
Adesodun et al., [68]
12
Amaranthus viridis L., Brachiaria reptans (L.) Gard. & Hubb.,
Cr, Cu, Co, Ni, Pb and Zn
Malik et al., [113]
Cannabis sativa L., Cenchrus pennisetiformis Hochst. and Steud. ex Steud., Chenopodium
album L., Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Cyprus rotundus L., Dactyloctenium aegyptium (L.)
P. Beauv., Elusine indica (L.) Gaerth., Ipomoea hederacea Jacq., Malvastrum
coromandelianum (Linn.) Garcke., Parthenium hysterophoirus L., Partulaca oleracea L., Ricinus communis L., Solanum nigrum L., and Xanthium stromarium L.
13
Beta vulgaris var. canditiva L., Brassica oleracea var. capitata L., Cucurbita pepo L. convar. giromontiana Greb., Cichorium intybus var. foliosum Hegi, Hordeum vulgare L., Medicago sativa L., Pastinaca sativa L., Phaseolus vulgaris L., and Zea mays L. convar. saccharata Koern.
Cd, Pb and Zn
Poniedzialek et al., [114]
14
Brassica campestries, Croton bonplandianum, Datura stramonium, Dolichos lablab, Lycopersicum esculentum, Parthenium hysterophorus, Ricinus communi, Solanum nigrum, Solanum xanthocarpum, Triticum aestivum and Typha spp (weed)
Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn
Singh et al., [115]
15
Solanum nigrum L.
Cd
Ji et al., [70]
16
Argemone mexicana, Cassia italic, Calotropis procera, Citrullus colocynthis, Cyperus laevigatus, Phragmite australis, and Rhazya stricta
Cd, Cr, Co, Cu, Fe, Pb, Ni and Zn
Badr et al., [116]
17
Arrhenatherum album, Corrigiola telephiifolia, Cynosorus echinatus, Digitalis thapsi, Holcus mollis, Jasione montana, Plantago lanceolata, Rumex acetosella, Thymus zygis, and Trisetum ovatum
Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn
García-Salgado et al., [117]
18
Alternanthera Philoxeroides, Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) and Pistia stratiotes L.
Cu, Fe, Mg, Mn and Zn
Hua et al., [71]
19
Medicago sativa
Fe, Al, Ni, Zn, Cr, Co, Cu and Pb
Al-Rashdi and Sulaiman, [118]
20
Sargassum hemiphyllum and Sargassum henslowianum
Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn
Yu et al., [119]
21
Plantago major L.
Al, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sr, V and Zn
Galal and Shehata, [72]
22
Trifolium respinatum L.
Ni
Rad and Ghasemi et al., [120]
23
Trifolium alexandrinum
Cr, Cu, Cd, Co and Pb
Bhatti et al., [74] 2016
24
Pennisetum sinese Roxb
As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn
Ma et al., [73]
Table 2: Various studies conducted on metal accumulation and phytoremediation potential of plants.
Different types of phytoremediation processes (Figure 1) are discussed here.
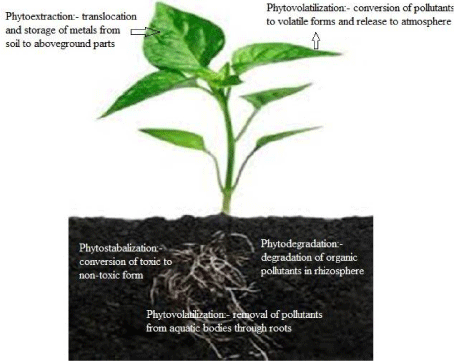
Figure 1: Various types of Phytoremediation.
Phytostabilization
In this process plants block the mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals in soil by converting the toxic metals to less toxic forms, thus stabilizing these metals in soils [75]. In this way metals are locked up in soil and do not pollute the groundwater, food chain, wind etc. [76]. Significant amounts of heavy metals can be stored at root level, especially in polyannual plant species, which contributes to long term stabilization of heavy metals [77]. The concept of phytostabalization lies in the variation in toxicity of different metal species. For example, Cr (VI) is highly toxic and readily bioavailable in comparison to Cr (III) [78]. But by excreting special redox enzymes in rhizosphere plants efficiently converts Cr (VI) to Cr (III) thus reducing its mobility and toxicity [79]. But phytostabilization is not an ultimate solution because the heavy metals will remain in soil can get converted back to their toxic form with changing conditions.
Phytodegradation (Phytotransformation)
In phytodegradation plants degrade the organic pollutants in soil by enzymatic activity in rhizosphere [80]. Plants release enzymes like dehalogenase, nitroreductase, peroxidase, laccase and nitrilase to degrade organic pollutants [62, 81].
Phytovolatilization
It is a technique in which plants absorb pollutants from soil and converts them to their volatile form, which is released into the atmosphere. It is specifically used for organic contaminants and metals like Mercury (Hg). However it is a controversial technique since it removes metal from soil but releases it into atmosphere from where it can be redeposited into soil [19].
Phytofiltration
Phytofiltration is a process where plants are used to remove pollutants especially heavy metals from aqueous environments such as surface waters, waste water, nutrient recycling systems [82,83]. The ideal plants for phytofiltration should have extensive root biomass and root surface area, which should be able to accumulate and tolerate high levels of pollutants and have minimum handling requirements [84]. Various researchers have documented the metal uptake capabilities of aquatic plants, such as Water hyacinth, Water lettuce and Siligator alternenthera [85-87].
Phytoextraction
Among all the techniques of phytoremediation, phytoextraction is most efficient and useful technique for removal of heavy metals from soil [88]. Phytoextraction is the main technique of phytoremediation from commercial point of view also. This technique involves heavy metal uptake from contaminated soils in huge amounts and their translocation to aboveground aerial parts of plants [58]. These aerial parts sometimes accumulate higher concentration of pollutants than the soil and thus are highly desirable. This contaminated aerial biomass can be used for incineration purposes, thus fulfilling the much needed energy requirements. The ashes and remains after incineration can be dumped, included in construction materials or subjected to metal extraction [89]. The most important characteristics required for phytoextraction of metals by plants are shoot metal content and shoot biomass [90]. In order to quantify the phytoextraction capability of a plant two factors are calculated:
a) Bioconcentration Factor (BCF): It is expressed as ratio of heavy metal content in harvestable plant tissues to soil [91]
BCF = Charvested tissue/Csoil
where Charvested tissue is the metal concentration in harvested tissue and Csoil is the metal concentration in soil.
b) Translocation Factor (TF): It is a ratio of heavy metal contents in shoots to roots [92]
TF = Cshoot/Croot
Where Cshoot and Croot are metal concentration in shoots and roots, respectively
Both BCF and TF are required to assess the phytoextraction potential of a plant. Plants having both BCF and TF greater than 1 are excellent for phytoextraction; plants having BCF >1 and TF <1 are suitable for phytostabalisation [65].
Hyperaccumulators
Hyperaccumulators are the plants which have unusual capacity of accumulating and tolerating very high content of heavy metals. This concept was firstly given by Brooks et al [93]. To explain the plants which can accumulate >1000 mg/kg of Ni while growing in their natural habitat. In 1989, Bakers and Brooks gave criteria for hyperaccumulation, according to which plants capable of accumulating >100 mg/kg of Cd, 1000 mg/kg Ni, Cu, Co and Pb and 10,000 mg/kg of Zn and Mn in their shoots are hyperaccumulators. A second criterion which can be used to identify hyperaccumulators is based on BCF and TF. Plants having both BCF and TF values >1 can be considered for hyperaccumulation [65]. This criterion is highly useful in areas having low heavy metal contents. Throughout the world 400-500 plant species belonging to families Brassicaceae, Asteraceae, Caryophyllaceae, Fabaceae, Cyperaceae etc. have been identified as hyperaccumulators [94]. Plants like Thlaspi caerulescens, Alyssum bertolonii, Arabidopsis halleri etc. are known hyperaccumulators of Cd, Co, Ni, Pb, Zn etc. Table 3 represents some of the most prominent hyperaccumulator plants. Usually the metal uptake in plants depends on metal bioavailability to plants. But hyperaccumulation of metals by plants is achieved by over expression of transport systems required for enhanced sequestration, tissue-specific expressions of proteins and high metal chelator concentration in soil [95].
S.No.
Metals
Hyperaccumulator plant species
1
As
Pteris vittata L., Piricum sativum L., Pteris biaurita, Pteris cretica, Pteris quadriaurita and Pteris ryukyuensis
2
B
Gypophila sphaerocephala Fenzel
3
Cd
Azolla pinnata, Eleocharis acicularis, Lemna minor L., Oryza sativa L., Rorippa globosa, Solanum photeinocarpum, Thlaspi caerulescens, Thlaspi caerulescens J. & C. Presl. and Vettiveria zizanioides L.,
4
Cr
Brassica juncea L.,Pteris vittata L. and Vallisneria americana
5
Co
Berkheya coddii Roessler and Haumaniastrum robertii (Robyns) P .A. Duvign. & Plancke
6
Cu
Brassica juncea (L.) Czern., Eleocharis acicularis, Elsholtzia splendens Nakai ex Maekawa, Festuca rubra L., Lemna minor L., and Vallisneria americana Michx.
7
Pb
Alyssum wulfenienum Bernh., Arrhenatherum elatius (L.) Beauv., Chenopodium album L., Cepaefolium (Wulfen) Rouy & Fouc, Euphorbia cheiradenia, Festuca ovina L., Hemidesmus indicus L., Thlaspi rotundifolium (L.) Gaudin ssp. Thlaspi caerulescens J. & C. Presl., and Vetiveria zizanioides L.
8
Mn
Agrostis castellana Boiss. & Reuter, Phytolacca americana L., and Schima superb
9
Hg
Marrubium vulgare L. and Pistia stratiotes L.
10
Ni
Alyssum bertolonii, Alyssum caricum, Alyssum corsicum, Alyssum heldreichii, Alyssum markgrafii, Alyssum murale, Alyssum pterocarpum, Alyssum serpyllifolium, Alyssum lesbiacum (Candargy) Rech. f., Agropyron elongatum (Host.)P. Beauv., Berkheya coddii, Isatis pinnatiloba, Lemna minor L. and Thlaspi spp.
11
Se
Brassica rapa L., Brassica spp (Wild type) and Lemna minor L.
12
U
Chenopodium amaranticolor H.J.Coste & Reyn and Lolium perenne L.
13
Zn
Brassica juncea L., Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers., Cardaminopsis spp., Eleocharis acicularis, and Thlaspi spp.
Sources: Jabeen et al., [62]; Vamerali et al., [76]; Ali et al., [19].
Table 3: List of hyperaccumulator species.
The heavy metals once up taken by roots is either stored in roots or translocated to the shoots [62]. The heavy metal tolerance in plant tissues is governed by inter-related network of physiological and molecular mechanisms which includes processes such as metal exclusion, vacuolar compartmentalization, phytochelatin production, metallothioneins secretion for metal chelation etc [96].
Although the natural metal absorption by plants is always preferable, but it has some hurdles such as significant reduction of plant biomass while metal accumulation and inability of natural mechanism to absorb insoluble fraction of metals in soil. Therefore, to overcome these drawbacks different chelators such as EDTA, citric acid, EDDS etc. are used, which increases the metal solubility so that leaching of metals can occur [97]. But some of these metal chelators are non-biodegradable and can pollute the groundwater and soil.
Use of Metal Accumulating Plants
The plants that are used for phytoremediation can be used for several purposes such as construction, incineration and Phytomining. Phytomining is a process of extracting metals from hyperaccumulator plants [19, 98]. In this process plant biomass which has accumulated heavy metals is first incinerated and the metals can be extracted from ashes which are considered as bio-ore. The incineration process can provide energy for vital functions.
Advantages of Phytoremediation
The concept of phytoremediation was first given by Chaney [99] and today this technique has gained acceptance worldwide. It is a green and eco approach which overall improves the environment. No secondary pollutants are generated in phytoremediation as plants have highly efficient systems. This process is highly cost effective. For example, Salt et al [100]. suggested that in order to clean up one acre of soil (depth 50 cm) soil excavation USD 4,000,000 was required, whereas phytoremediation only required USD 60,000 – 1,000,000. Plants having high biomass and fast growth such as Jatropha, grasses, willow etc. can be further used for economic purposes such as construction, incineration etc. [101]. Therefore, phytoremediation is a durable and effective method for soil cleanup.
Limitations of Phytoremediation
Although phytoremediation is a very sustainable and advantageous technology for decontamination of soil, there are certain limitations to it also. First of all, this technology is highly dependent on environmental conditions [58]. Plants which are considered hyperaccumulators may only grow in certain environmental conditions and certain seasons only. In that case rigorous research is required to identify the plants which could accumulate metals in different types of conditions. Secondly, phytoremediation is a very slow process in comparison to other metal decontamination methods [19]. Thirdly, this technology is more suitable in case of high biomass producing plants and does not work very well with low biomass plants [102]. Another major setback is the root system of plants. Plants having extensive and spread root system (as in grasses) are more capable in extracting metals from soil. On the contrary plants having limited roots are not capable for metal uptake and accumulation [103, 104]. There is also a high risk of food chain contamination, if proper care is not taken [105].
Future Prospects
Phytoremediation is a reliable and environment friendly technique for cleaning up of soil. Although recently most of the research on phytoremediation is focused on laboratory based experiments, but more emphasis should be given to plants growing in wild and natural conditions which may provide better understanding of metal accumulating plants [70]. Extensive research should be focused on improving the metal uptake capabilities of weeds and other plants growing in wild by application of various genetic and biotechnological tools [106]. Lastly research must be focused on utilizing the plant material used for phytoremediation in profitable process in order to make this technique a commercial success [19].
Combined Application of Vermiremediation and Phytoremediation: Boost to Soil Management
Although both Vermiremediation and Phytoremediation are distinct and very effective techniques for soil management, but if used in combination these techniques can bring marvelous results. In various contaminated environments (e.g. municipal dumpsites, industrially polluted lands, agro-chemically contaminated soils etc.) where soil is already affected by various pollutants, phytoremediation provides a sustainable solution for extracting out the pollutants and cleaning up the environment [19,62,76]. On the other hand vermiremediation provides an instrumental solution for managing the waste which can further contaminate that environment. Vermiremediation also generates very useful products such as vermicast and vermiwash [2,24]. These products further supplement phytoremediation by providing non-polluting nutrient source for plants used in phytoremediation. It will enhance the growth rate of plants and thus their phytoremediation potential. Also the vermicast and vermiwash are very efficient alternatives for polluting agrochemicals used in agriculture. Thus while decontaminating the agricultural soil using plants, vermicast and vermiwash can be used to enhance and maintain the soil nutrient pool. Thus, phenomenal results can be achieved by using vermiremediation and phytoremediation in tandem.
Conclusions
The rising levels of pollutants (especially heavy metals) in soils pose severe risks to future generations. To fulfill the requirements of increasing human population many adverse and environmentally dangerous methods are being used in every field. Undoubtedly, these unsustainable methods have increased human capacity to extract more from nature, but this has also led to deterioration of nature. Therefore, there is urgent need for environment friendly techniques such as Vermiremediation and Phytoremediation. Vermiremediaiton is a very efficient technique of waste management and reduction. The use of earthworms significantly reduces the toxic substances from the waste and decontaminates them. It also provides us manures and vermiwash which are very good alternatives of chemical fertilizers. The vermicompost generated during the process is a highly nutritious product for plants which increases the fertility of soil and also enhances microbial biomass in soil. On the other hand, phytoremediation provides us a green solution for already contaminated soils. The use of hyperaccumulating plants to extract metals from contaminated soils is the best eco-friendly remedy available. The use of plants for metal accumulation from soils is a highly efficient and cost effective system in comparison to other methods of decontamination. The metals stored in these plants can further be extracted out by phytomining processes. The efficiency of these metal accumulating plants can be increased using various genetic tools also. Thus, these two techniques i.e. vermiremediation and phytoremediation are best tools for waste management, soil fertility enhancement and decontamination of already contaminated sites. Further research must be carried out to improve and explore these techniques, as they hold the key to sustainable development.
Acknowledgement
Sartaj Ahmad Bhat is thankful to the UGC, New Delhi for UGCBSR Fellowship and Department of Botanical and Environmental Sciences, Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar, Punjab, India for providing research facility.
References
- Manivannan S, Balamurugan M, Parthasarathi K, Gunasekaran G and Ranganathan LS. Effect of vermicompost on soil fertility and crop productivity – beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Environ Biol. 2009; 30: 275–281.
- Chaoui HI, Zibilske LM and Ohno T. Effects of earthworm casts and compost on soil microbial activity and plant nutrient availability. Soil Biol Biochem. 2003; 35: 295–302.
- Sharma KL, Sharma SC, Bawa SS, Singh S, Chandrika DS, Sharma V et al. Combined effect of tillage and organic fertilization on soil quality key indicators and indices in alluvial soils of Indo-Gangetic Plains under rainfed maize–wheat system. Arch Agron Soil Sci. 2015; 61: 313-327.
- Nagavallemma KP, Wani SP, Lacroix S, Padmaja VV, Vineela C, Rao MB et al. Vermicomposting: recycling wastes into valuable organic fertilizer. J SAT Agric Res. 2006; 2: 20–37.
- Sim EYS, Wu TY. The potential reuse of biodegradable municipal solid wastes (MSW) as feedstocks in vermicomposting. J Sci Food Agric. 2010; 90: 2153–2162.
- Lim SL, Wu TY, Sim EYS, Lim PN, Clarke C. Biotransformation of rice husk into organic fertilizer through vermicomposting. Ecol Eng. 2012; 41: 60–64.
- Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP. Potential utilization of bagasse as feed material for earthworm Eisenia fetida and production of vermicompost. Springerplus. 2015; 4: 11.
- Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP. Vermistabilization of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L) waste produced from sugar factory using earthworm Eisenia fetida: Genotoxic assessment by Allium cepa test. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2015; 22: 11236-11254.
- Pramanik P, Ghosh GK, Ghosal PK, Banik P. Changes in organic –C, N, P and K and enzyme activities in vermicompost of biodegradable organic wastes under limiting and microbial inoculants. Bioresour Technol. 2007; 98: 2485-2494.
- Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP. Vermiremediation of dyeing sludge from textile mill with the help of exotic earthworm Eisenia fetida Savigny. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2013; 20: 5975-5982.
- Bhat SA, Singh J, Vig AP. Genotoxic Assessment and Optimization of Pressmud with the help of Exotic Earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2014; 21: 8112-8123.
- Garg VK, Gupta R. Optimization of cow dung spiked pre-consumer processing vegetable waste for vermicomposting using Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2011; 74: 19–24.
- Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Babenko A, Cannon J, Galvis P, Metzger JD. Influences of vermicomposts, produced by earthworms and microorganisms from cattle manure, food waste and paper waste, on the germination, growth and flowering of petunias in the greenhouse. Appl Soil Ecol. 2008; 39: 91–99.
- Gupta R, Garg VK. Stabilization of primary sewage sludge during vermicomposting. J HazardMater. 2008; 153: 1023–1030.
- Prabha ML. Waste management by vermitechnology. Ind J Env Prot. 2009; 29: 795–800.
- Pattnaik S, Reddy MV. Nutrient status of vermicompost of urban green waste processed by three earthworm species: Eisenia fetida, Eudrilus eugeniae, and Perionyx excavates. Appl Environ Soil Sci. 2010.
- Padmavathiamma PK, Li LY, Kumari UR. An experimental study of vermi-biowaste composting for agricultural soil improvement. Bioresour Technol. 2008; 99: 1672–1681.
- Greipsson S. Phytoremediation. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2011; 2: 7.
- Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere. 2013; 91: 869–881.
- Mench M, Schwitzguebel JP, Schroeder P, Bert V, Gawronski S, Gupta S. Assessment of successful experiments and limitations of phytotechnologies: contaminant uptake, detoxification and sequestration, and consequences for food safety. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2009; 16: 876–900.
- Lim SL, Wu TY. Characterization of matured vermicompost derived from valorization of palm oil mill byproduct. J Agric Food Chem. 2016; 64: 1761-1769.
- Vig AP, Singh J, Wani SH, Dhaliwal SS. Vermicomposting of tannery sludge mixed with cattle dung into valuable manure using earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Bioresour Technol. 2011; 102: 7941-7945.
- Singh J, Kaur A, Vig AP. Bioremediation of Distillery sludge into soil-enriching material through vermicomposting with the help of Eisenia fetida. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014; 174: 1403-1419.
- Bhat S, Singh J, Vig AP. Management of sugar industrial wastes through vermitechnology. Int Lett Nat Sci. 2016; 55: 35-43.
- Lim SL, Wu TY, Clarke C. Treatment and biotransformation of highly polluted agro-industrial wastewater from palm oil mill into vermicompost using earthworms. J Agric Food Chem. 2014; 62: 691-698.
- Kale RD, Karmegam N. The role of earthworms in Tropics with emphasis on Indian ecosystems. Appl Env Soil Sci. 2010.
- Bhattacharjee G, Chaudhuri PS, Datta M. Response of paddy (Var. Trc-87-251) crop on amendment of the field with different levels of vermicomposts. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci. 2001; 3: 191–196.
- Fernandez-Bayo JD, Nogales R, Romero E. Assessment of three vermicomposts as organic amendments used to enhance diuron sorption in soils with low organic carbon content. Eur J Soil Sci. 2009; 60: 935–944.
- Valdez-Perez MA, Fernandez-Luqueno F, Franco-Hernandez O, Flores Cotera LB, Dendooven L. Cultivation of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in limed or unlimed wastewater sludge, vermicompost of inorganic amended soil. Sci Hortic. 2011; 128: 380–387.
- Gutierrez-Miceli FA, Santiago-Borraz J, Molina JAM, Nafate CC, Abud-Archila M, Llaven MAO et al. Vermicompost as a soil supplement to improve growth, yield and fruit quality of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum). Bioresour Technol. 2007; 98: 2781–2786.
- Oo AN, Iwai CB, Saenjan P. Soil properties and maize growth in saline and nonsaline soils using cassava–industrial waste compost and vermicompost with or without earthworms. Land Degrad Dev. 2015; 26: 300-310.
- Srivastava PK, Gupta M, Shikha, Singh N, Tewari SK. Amelioration of sodic soil for wheat cultivation using bioaugmented organic soil amendment. Land Degrad Dev. 2016; 27: 1245-1254.
- Fernandez-GomezMJ, Diaz-Ravina M, Romero E, Nogales R. Recycling of environmentally problematic plant wastes generated from greenhouse tomato crops through vermicomposting. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 2013; 10: 697–708.
- Atiyeh RM, Edwards CA, Subler S, Metzger JD. Pig manure vermicompost as a component of a horticultural bedding plant medium: effects on physiochemical properties and plant growth. Bioresour Technol. 2001; 78: 11–20.
- Dinesh R, Srinivasan V, Hamza S, Manjusha A, Kumar PS. Short-term effects of nutrient management regimes on biochemical and microbial properties in soils under rainfed ginger (Zingibe officinale Rosc.). Geoderma. 2012; 173–174: 192–198.
- Sharma S, Pradhan K, Satya S, Vasudevan P. Potentiality of earthworms for waste management and in other uses: a review. J Am Sci. 2005; 1: 4–16.
- Singh R, Sharma RR, Kumar S, Gupta RK, Patil RT. Vermicompost substitution influences growth, physiological disorders, fruit yield and quality of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.). Bioresour Technol. 2008; 99: 8507–8511.
- Arancon NQ, Edwards CA, Bierman P, Metzger JD, Lee S, Welch C. Effects of vermicomposts on growth and marketable fruits of field-grown tomatoes, peppers and strawberries. Pedobiologia. 2003; 47: 731–735.
- Bachman GR, Metzger JD. Growth of bedding plants in commercial potting substrate amended with vermicomposts. Bioresour Technol. 2008; 99: 3155– 3161.
- Lazcano C, Revilla P, Malvar RA, Dominguez J. Yield and fruit quality of four sweet corn hybrids (Zea mays) under conventional and integrated fertilization with vermicompost. J Sci Food Agric. 2011; 91: 1244–1253.
- Shahi SK. Effect of organic manures, inorganic fertilizers and biofertilizers addition on soil properties and productivity under onion (Allium cepa L.). Plant Arch. 2013; 13: 381–387.
- Singh M, Wasnik K. Effect of vermicompost and chemical fertilizer on growth, herb, oil yield, nutrient uptake, soil fertility, and oil quality of rosemary. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2013; 44: 2691–2700.
- Kalantari S, Ardalan MM, Alikhani HA, Shorafa M, Comparison of compost and vermicompost of yard leaf manure and inorganic fertilizer on yield of corn. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2011; 42: 123–131.
- Roy S, Arunachalam K, Dutta BK, Arunachalam A. Effect of organic amendments of soil on growth and productivity of three common crops viz. Zeamays, Phaseolus vulgaris and Abelmonchus esculentus. Appl Soil Ecol. 2010; 45: 78–84.
- Bartlett MD, Briones MJI, Neilson R, Schmidt O, Spurgeon D, Creamer RE. A critical review of current methods in earthworm ecology: from individuals to populations. Eur J Soil Biol. 2010; 46: 67–73.
- Abbasi SA, Ramasamy EV. Biotechnological methods of pollution control. Orient Longman, Universities Press India Ltd., Hyderabad. 1999; 168.
- Muscolo A, Bovolo F, Gionfriddo F, Nardi S. Earthworm humic matter produces auxins-like effect on Daucus carota cell growth and nitrate metabolism. Soil Biol Biochem. 1999; 31: 1303-1311.
- Atiyeh RM, Subler S, Edwards CA, Bachman G. Metzger JD, Shuster W. Effect of vermicompost and compost on plant growth in horticulture container media and soil. Pedobiologia. 2000; 44: 579-590.
- Ndegwa PM, Thompson SA. Integrating composting and vermicomposting in the treatment of bioconversion of biosolids. Bioresour Technol. 2001; 76: 107–112.
- Senesi S, Saiz JC, Miano TM. Spectroscopic characterization of metal humic acid like complexes of earthworms composed organic wastes. Sci Total Environ. 1992; 117: 111-120.
- Garcia C, Ceccanti B, Masciandaro G, Hernandez T. Phosphatase and β-glucosidase activities in humic substances from animal wastes. Bioresour Technol. 1995; 53: 79-87.
- Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B, Garcia C. Soil agro-ecological management: fertirrigation and vermicompost treatments. Bioresour Technol. 1997; 59: 199-206.
- Elvira C, Sampedro L, Benitez E, Nogales R. Vermicomposting of sludges from paper mill and dairy industries with Eisenia andrei: a pilot scale study. Bioresour Technol. 1998; 63: 205– 211.
- Hadilgo PR, Matta FB, Harkess RL. Physical and chemical properties of substrates containing earthworm castings and effects on marigold growth. HortiScience. 2006; 41: 1474-1476.
- Ferreras L, Gomez E, Toresani S, Firpo I, Rotondo R. Effect of organic amendments on some physical, chemical and biological properties in a horticultural soil. Bioresour Technol. 2006; 97: 635-640.
- Marinari S, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B, Grego S. Influence of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil biological and physical properties. Bioresour Technol. 2000; 72: 9–17.
- Gopinath KA, Supradip S, Mina BL, Pande H, Kundu S, Gupta HS. Influence of organic amendments on growth, yield and quality of wheat and on soil properties during transition to organic production. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys. 2008; 82: 51-60.
- Ghori Z, Iftikhar H, Bhatti MF, Nasar-um-Minullah, Sharma I, Kazi AG, et al. Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soil. Ahmad P, editor. In: Plant Metal Interaction, Emerging Remediation Techniques. Elsevier. 2016; 385-409.
- Forstner U. Land contamination by metals: global scope and magnitude of problem. Allen HE, Huang CP, Bailey GW, Bowers AR, editors. In: Metal speciation and contamination of soil. CRC Press, Boca Raton. 1995; 1-33.
- Kumar PB, Dushenkov V, Motto H, Raskin I. Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environ Sci Technol. 1995; 29: 1232-1238.
- Gisbert C, Ros R, de Haro A, Walker DJ, Bernal MP, Serrano R, et al. A plant genetically modified that accumulates Pb is especially promising for phytoremediation. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2003; 303: 440-445.
- Jabeen R, Ahmad A, Iqbal M. Phytoremediation of heavy metals: Physiological and molecular mechanisms. Bot Rev. 2009; 75: 339-364.
- Yanqun Z, Yuan L, Schvartz C, Langlade L, Fan L. Accumulation of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in plants and hyperaccumulator choice in Lanping lead–zinc mine area, China. Environ Int. 2004; 30: 567-576.
- Deng H, Ye ZH, Wong MH. Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environ Pollut. 2004; 132: 29-40.
- Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma LQ. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci Total Environ. 2006; 368: 456-464.
- Liu W, Shu W, Lan C. Viola baoshanensis, a plant that hyperaccumulates cadmium. Chinese Sci Bull. 2004; 49: 29-32.
- Xiaohai L, Yuntao G, Khan S, Gang D, Aikui C, Li L, et al. Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on contaminated sites and their potential accumulation capacity in Heqing, Yunnan. J Environ Sci. 2008; 20: 1469-1474.
- Adesodun JK, Atayese MO, Agbaje T, Osadiaye BA, Mafe O, Soretire AA. Phytoremediation potentials of sunflowers (Tithonia diversifolia and Helianthus annuus) for metals in soils contaminated with zinc and lead nitrates. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010; 207: 195-201.
- Ramamurthy AS, Memarian R. Phytoremediation of mixed soil contaminants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012; 223: 511-518.
- Ji P, Sun T, Song Y, Ackland ML, Liu Y. Strategies for enhancing the phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated agricultural soils by Solanum nigrum L. Environ Pollut. 2011; 159: 762-768.
- Hua J, Zhang C, Yin Y, Chen R, Wang X. Phytoremediation potential of three aquatic macrophytes in manganese-contaminated water. Water Environ. J. 2012; 26: 335-342.
- Galal TM, Shehata HS. Bioaccumulation and translocation of heavy metals by Plantago major L. grown in contaminated soils under the effect of traffic pollution. Ecol Indicat. 2015; 48: 244-251.
- Ma C, Ming H, Lina C, Naidu R, Bolan N. Phytoextraction of heavy metal from tailing waste using Napier grass. Catena. 2016; 136: 74–83.
- Bhatti SS, Sambyal V, Nagpal AK. Heavy metals bioaccumulation in Berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) cultivated in areas under intensive agriculture, Punjab, India. Springerplus. 2016.
- Eapen S, Dsouza SF. Prospects of genetic engineering of plants for phytoremediation of toxic metals. Biotech Adv. 2005; 23: 97-114.
- Vamerali T, Bandiera M, Mosca G. Field crops for phytoremediation of metal-contaminated land. A review. Environ Chem Lett. 2010; 8: 1-17.
- Vamerali T, Bandiera M, Coletto L, Zanetti F, Dickinson NM, Mosca G. Phytoremediation trials on metal- and arsenic-contaminated pyrite wastes (Torviscosa, Italy). Environ Pollut. 2009; 157: 887-894.
- Wu G, Kang H, Zhang X, Shao H, Chu L, Ruan C. A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. J Hazard Mater. 2010; 174: 1-8.
- James BR. Remediation-by- reduction strategies for chromate-contaminated soils. Environ Geochem Health. 2001; 23: 175-189.
- Vishnoi SR, Srivastava PN. Phytoremediation-green for environmental clean. In: The 12th World Lake Conference. 2008; 1016-1021.
- Schnoor JL, Light LA, McCutcheon SC, Wolfe NL, Carreira LH. Phytoremediation of organic and nutrient contaminants. Environ Sci Technol. 1995; 29: 318-323.
- Maine MA, Duarte MV, Sune NL. Cadmium Uptake by Floating Macrophytes. Water Res. 2001; 35: 2629-2634.
- Mukhopadhyay S, Maiti SK. Phytoremediation of metal enriched mine waste: a review. Global J Environ Res. 2010; 4: 135-150.
- Dushenkov D, Kapulnik Y. Phytofiltration of metals. Raskin I, Ensley BD, editors. In: Phytoremediation of toxic metals-using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York. 2000; 89-106.
- Hasan SH, Talat M, Rai S. Sorption of Cadmium and Zinc from aqueous solutions by Water Hyacinth (Eichchornia crassipes). Bioresour Technol. 2007; 98: 918-928.
- Alvarado S, Guedez M, Lue-Meru MP, Nelson G, Alvaro A, Jesus AC et al. Arsenic removal from waters by bioremediation with the aquatic plants Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and Lesser Duckweed (Lemna minor). Bioresour Technol. 2008; 99: 8436-8440.
- Hua JF, Hu LJ, Zhang CS, Yin YL, Wang XX. Phytoremediation of manganese-contaminated water by three aquatic macrophytes. Ecol Environ Sci. 2011; 19: 2160-2165.
- Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xu Y, Wang L, Liang X. The role of EDTA on cadmium phytoextraction in a cadmium-hyperaccumulator Rorippa globosa. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol. 2011; 3: 45-51.
- Vamerali T, Bandiera M, Mosca G. Field crops for phytoremediation of metal-contaminated land. A review. Environ Chem Lett. 2010; 8: 1-17.
- Li JT, Liao B, Lan CY, Ye ZH, Baker AJM, Shu WS. Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in cultivars of a high-biomass tropical tree (Averrhoa carambola) and its potential for phytoextraction. J Environ Qual. 2010; 39: 1262-1268.
- Blaylock MJ, Salt DE, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y et al. Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Tech. 1997; 31: 860-865.
- Zu YQ, Li Y, Chen JJ, Chen HY, Qin L, Christian S. Hyperaccumulation of Pb, Zn and Cd in herbaceous grown on lead-zinc mining area in Yunnan, China. Environ Int. 2005; 31: 755-762.
- Brooks RR, Lee J, Reeves RD, Jaffrre T. Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants. J Geochem Explor. 1977; 7: 49-57.
- Padmavathiamma PK, Li LY. Phytoremediation technology: hyperaccumulation metals in plants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007; 184: 105-126.
- Viehweger K. How plants cope with heavy metals. Botanical Studies. 2014; 55: 35.
- Singh OV, Labana S, Pandey G, Budhiraja R, Jain RK. Phytoremediation: an overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003; 61: 405-412.
- Romkens P, Bouwman L, Japenga J, Draaisma C. Potentials and drawbacks of chelate-enhanced phytoremediation of soils. Environ Pollut. 2002; 116: 109-121.
- Salt DE, Smith RD, Raskin I. Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Phys Plant Molec Biol. 1998; 49: 643-668.
- Chaney RL. Plant uptake of inorganic waste constituents. Parr JF, Marsh PB, Kla JM, editors. In: Land Treatment of Hazardous Wastes. Noyes Data Corp., Park Ridge, NJ.1983; 50-76.
- Salt DE, Blaylock M, Kumar NPBA, Dushenkov V, Ensley D, Chet I et al. Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology. 1995; 13: 468-474.
- Abhilash PC, Powell JR, Singh HB, Singh BK. Plant-microbe interactions: novel applications for exploitation in multipurpose remediation technologies. Trends Biotechnol. 2012; 30: 416-420.
- Tong YP, Kneer R, Zhu YG. Vacuolar compartmentalization: a second generation approach to engineering plants for phytoremediation. Trends Plant Sci. 2004; 9: 7-9.
- Clemens S. Developing tools for phytoremediation: towards a molecular understanding of plant metal tolerance and accumulation. Int. J Occup Med Environ Health. 2001; 14: 235-239.
- Oh K, Cao T, Li T, Cheng H. Study on application of phytoremediation technology in management and remediation of contaminated soils. J Clean Energy Technol. 2014; 2: 216-220.
- Naees M, Ali Q, Shahbaz M, Ali F. Role of rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metals: an overview. Int Res J Plant Sci. 2011; 2: 220-232.
- Ruiz ON, Hussein HS, Terry N, Danniell H. Phytoremediation of organomercurial compounds via chloroplast genetic engineering. Plant Physiol. 2003; 132: 1344-1352.
- Marchiol L, Assolari S, Sacco P, Zerbi G. Phytoextraction of heavy metals by canola (Brassica napus) and radish (Raphanus sativus) grown on multicontaminated soil. Environ Pollut. 2004; 132: 21-27.
- Xia HP. Ecological rehabilitation and phytoremediation with four grasses in oil shale mined land. Chemosphere. 2004; 54: 345-353.
- Tlustos P, Szakova J, Hruby J, Hartman I, Najmanova J, Nedelnik J, et al. Removal of As, Cd, Pb, and Zn from contaminated soil by high biomass producing plants. Plant Soil Environ. 2006; 52: 413-423.
- Liu J, Dong Y, Xu H, Wang D, Xu J. Accumulation of Cd, Pb and Zn by 19 wetland plant species in constructed wetland. J Hazard Mat. 2007; 147: 947-953.
- Zhuang P, Yang QW, Wang HB, Shu WS. Phytoextraction of heavy metals by eight plant species in the field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007; 184: 235-242.
- Peng KJ, Luo CL, Chen YH, Wang GP, Li XD, Shen ZG. Cadmium and other metal uptake by Lobelia chinensis and Solanum nigrum from contaminated soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2009; 83: 260-264.
- Malik RN, Husain SZ, Nazir I. Heavy metal contamination and accumulation in soil and wild plant species from industrial area of Islamabad, Pakistan. Pak J Bot. 2010; 42: 291-301.
- Poniedzialek M, Sekara A, Jedrszczyk E, Ciura J. Phytoremediation efficiency of crop plants in removing cadmium, lead and zinc from soil. Folia Horticulturae Ann. 2010; 22: 25-31.
- Singh R, Singh DP, Kumar N, Bhargava SK, Barman SC. Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals in soil and plants from fly ash contaminated area. J. Environ Biol. 2010; 31: 421-430.
- Badr N, Fawzy M, Al-Qahtani KM. Phytoremediation: An ecological solution to heavy-metal-polluted soil and evaluation of plant removal ability. World App Sci J. 2012; 16: 1292-1301.
- Garcia-Salgado S, Garcia-Casillas D, Quijano-Nieto MA, Bonilla-Simon MM. Arsenic and heavy metal uptake and accumulation in native plant species from soils polluted by mining activities. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012; 223: 559-572.
- Al-Rashdia TT, Sulaiman H. Bioconcentration of heavy metals in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) from farm soils around Sohar industrial area in Oman. APCBEE Procedia. 2013; 5: 271-278.
- Yu Z, Zhu X, Jiang Y, Luo P, Hu C. Bioremediation and fodder potentials of two Sargassum spp. in coastal waters of Shenzhen, South China. Marine Pollut Bull. 2014; 85: 797-802.
- Rad MY, Ghasemi H. Phytoremediation ability and oxidative enzymes activity of Persian clover (Trifolium resupinatum L.) in the presence of nickel. Iranian J Plant Physiol. 2015; 5: 1511-1520.
