Abstract
WEEE management has evolved as a major policy issue for eco-innovation in Pakistan. Existing research in the domain established that there is a persistent problem of WEEE management and it has deleterious effect on the environment of the country. The paper concluded that the major issues of policy failure occurred in the management of WEEE in developing countries are; lack of inventory system, trans boundary movement, inadequate legislation, role of informal sector and most important knowledge and awareness in handling the WEEE issue. The WEEE audit of Pakistan show that more than 343062 tons of WEEE was imported between 2007-2015 years, the share of computers and computer related accessories is more than 76%. The paper focuses different management options for the strategic direction in policy formation especially useful in developing countries.
Keywords: WEEE; E-waste; Polices, Pakistan; Sustainable development; Environmental challenges; Waste management
Introduction to EEE and WEEE
Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) is one of the fastest growing waste streams in the world. With the growth of information and communication technology industries have enhanced the usage of the electric and electronic equipment exponentially. A precise definition of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE) is “those equipments which consume electric charge or electromagnetic fields for its operational procedures” [1]. After the completion of useful life; these equipments are known as Waste Electric and Electronic Equipments or WEEE. Alternative terminologies used synonymously for WEEE are e-scrap, e-junk and e-trash, End-of-Life (EoL), and e-waste. The usage of the term WEEE differs from country to country depending upon the indigenous legal system [2]. Commonly used definitions in international scenario are given in Table-1.
Definition in European Union Directive
“Waste electrical and electronic equipment, including all components, subassemblies and consumables which are part of the product at the time of discarding” [3,4].
Definition from OECD
“Any household appliance consuming electricity and reaching its life cycle end” [3,4].
Definition by Researcher
“Those electrical and electronic equipment/devices/products that connect with power plugs or use batteries which have become outdated/obsolete due to advances in technology or changes in fashion, style, and status and are nearing the end of their useful life” [5].
Table 1: WEEE Definitions.
The general perception for the use of the term WEEE is discarded old computers or computer’s networking equipments, which is a misconception. There are more than sixteen hundred items enlist in the category of WEEE. These include equipments such as computers, monitors, CPUs, servers, CD Rom, printers, speakers, CDs, scanners, photocopiers, calculators, fax machines, battery cells, cellular phones, video game consoles, transceivers, TVs, tape recorders, Decks, VCRs, medical devices etc.. WEEE can be categorized into three main sections white, brown and grey goods. The equipments falls under white goods comprises of household appliances like coolers, fridges, washing machines, air-conditioners, and dishwashers. Entertainments products likes small screen, digital cameras, television sets etc. lie in brown goods category. Computers, computer related equipments, laser or inkjet printers and facsimile machines etc. falls in grey goods category. The recycling processes for grey goods are complex due to their toxic ingredients composition [6,7].
The WEEE Issue
Modern technologies have manufactured different type of new apparatuses that bring improvement in the life style of human, but at the same time these modern technologies also creates new environmental disruption in the world [8]. A range of environmental problems that have arisen in recent decades, majority of them are linked to modern development. Waste of Electric and Electronic Equipment (WEEE); a non-biodegradable waste, is one of the such type of problem that is generated from the mismanagement of new technology. The harmful effects produced due the WEEE were previously unknown. Major factors that contribute toward the generation of WEEE are the uncontrolled growth of the electronic/ IT industry products during the last few decades. Other main reasons for production of WEEE are improvement in technology, decrease in the products lifespan, affordable prices and product design that discourage upgrading and repairs. Due to these reasons WEEE is becoming one of the fastest growing municipal waste streams in the world [9,10].
WEEE have multi-facet characterized and two of its properties are of main significance: it is hazardous, due to its content of toxic substances and at the same time it is valuable, due to the various precious metals which are equipped during manufacturing processing. These devices contain significant proportions of substances that pose threats to human health; if not dispose-off properly [11-13]. In addition to its effects on health, environmental contamination it also have social and economy effects also [14].
WEEE in Global Context
WEEE has the highest growth rate in the world; estimate shows that every year approximately 20-50 million tons of WEEE is generated worldwide [15] which is equal to 2% of the total quantity of solid waste produced in the world [16]. The noteworthy effect of WEEE is noted in countries of European Union where 5 to 7 million tons of WEEE is produced each year. The data indicated that in European Union the WEEE is increasing at a rate of 16% -28 % which is equal to three times of the municipal waste generated every year [17,18]. Situation in the United States are also worsening, the number of obsolete products stored or discarded is currently growing at frightening ratio. Out of the 3 million WEEE products that is currently owned in America, only 18% were recycled while the rest 82% were disposed in landfills or transported / exported to developing countries [19,20]. Reports by Basel Action Network [21] shows second hand electronic equipments especially computer’s accessories are widely trade in Asian and African countries, the report further indicates that the graph of export of disposal electronic equipments from developed countries towards developing countries is rising exponentially [22].
In developed republics they have imposed strict laws, high environmental standards, awareness of environmental issues in general public, high economical cost for recycling for WEEE disposal, as well as the scarcity of land for landfills sites are some of the factors that compel the developed republics to dispose their WEEE to rest of the under developed world [23]. In under developed nation’s they do not have any technology or management knowhow to handle the WEEE issue in an eco-friendly manner. Major reasons for exports are low wages, cheap labor, lax laws, little awareness by the general public and lack of environmental and occupational standards in under developing world [24,25]. Therefore the bulk of toxic effluent in the shape of WEEE is dumped in developing countries in up hazard manner without any planning or management [26].
Due to advancement and revolution in technology, developing countries like Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, China, Bangladesh, etc. are facing forthcoming danger in the management of WEEE. Favorite destinations of WEEE dumping are Pakistan, India, Philippines, China, Sri-lanka and Bangladesh [26]. A report by SACEP indicates that from 1991 the dumping in these countries had increased by 125% in Pakistan, 97.3% in India and 37% in Bangladesh [27]. Investigation on WEEE shows that most of the WEEE consignments from European and American countries end up in Asia where they are dispose-off or recycled without considering any environmental or worker health and safety requirements [28]. As the rate of WEEE transferred is so fast toward developing nations that within few years it will became only the problem of these developing nations; therefore the need of the time for the developing nations to gain knowledge, awareness about environmental issues and equip with technology to cope with the WEEE management problem.
WEEE Audit of Pakistan
Pakistan, with a population of about 160 million, is facing different types of environmental problems such as growing water shortages, air pollution problems, solid waste management, deforestation and degradation of rangelands etc. and now with the immense import of second hand electronic products, the new threat to Pakistan in the line of environmental problem is through WEEE- another environmental problem that country deals with its meagre resources. The country’s growing mounds of WEEE are cause for concern both from a health and environmental perspective. The WEEE problem is one of the important issues that need to be addressed immediately in Pakistan and also in developing nations.
Methods and Results
In this study “Mix Method” research methodology was adopted because it helps to analyze the qualitative and quantitative approaches simultaneously [29,30]. The research work was broken down into various steps, the first step deals with multidisciplinary literature review of the theoretical aspects of WEEE management. The second stage was to collect, compile, and compare data for import of WEEE in Pakistan. Most of the information gathered for the study is from official documents of Pakistan’s Customs Department. Unstructured interviews were conducted to the various stakeholders (dealers in WEEE, custom officers; field staff of custom appointed on the check posts) involved in servicing and the trading of WEEE.
The raw data on WEEE imports is obtained from Pakistan customs. The data collected for the last nine year period, i.e., from 2007 to 2015. The imported WEEE items that are consider for calculation are computer sets (in working condition), computer system incomplete (CPU along with monitor broken or missing parts, these are not in working conditions), computer printers, laptops, refrigerators, television, audio / video devices. These products are taken because they constitute 90% of the entire volume of the WEEE import in Pakistan. The results of WEEE import are summarized in Table-2.
Year
Computer Sets
Computer Systems incomplete
Computer
Printers
laptop
Fridge
Television
Audio video device
Total Units imported
2007
1092224
127769
936322
38734
80078
56544
553722
2,885,393
2008
749097
91206
265851
129572
80116
43302
258049
1,617,193
2009
600622
114355
578195
174626
89396
109986
154582
1,821,762
2010
656338
177875
375988
72012
46992
77180
137901
1,544,286
2011
704724
170076
451086
132294
54374
87431
165622
1765607
2012
725463
89456
786209
128671
66733
56739
135678
1988949
2013
716766
90567
659821
99856
76289
73728
265781
1982808
2014
678653
96142
715630
77562
45782
67328
145333
1826430
2015
653622
87501
683960
108223
50982
70982
137280
1792550
Total
5,921,171
1,044,947
5,453,062
961,550
590,742
575,892
1,953,948
17,224,978
Grand Total Units 17224978
Table 2: Import of WEEE assessment for the years 2007-2015 in quantity. Source: Custom Department, Government of Pakistan, 2016.
The statistics compiled for the quantities (in tons) of WEEE, are manipulated in Table-3. The average weight calculated for computer sets (CPU along with screen, key board, mouse) is 23 kg, incomplete computer system is 21 kg, computer printer as 15 and laptop is 04 kg, refrigerator (two doors to three doors) as 35 kg, television set (21 inches to 86 inches) is 38 kg, and audio/ video devices as 20 kg. The Table-3 shows the details for WEEE for each year below:
Year
Computer Sets
Computer Accessories
Computer
Printers
Laptop
Fridge
Television
Audio Video Device
Total in tons
2007
25121
2683
14045
155
2803
2149
11074
58,030
2008
17229
1915
3988
518
2804
1645
5161
33,260
2009
13814
2402
8673
698
3129
4179
3092
35,987
2010
15096
3735
5640
288
1645
2933
2758
32,095
2011
16209
3572
6766
529
1903
3322
3312
35,613
2012
16685
1879
11793
515
2336
2156
2714
38,078
2013
16485
1902
9897
399
2670
2802
5316
39,471
2014
15609
2019
10734
310
1602
2558
2907
35,739
2015
15033
1837
10259
433
1784
2697
2746
34,789
Total
151,281
21,944
81,795
3,845
20,676
24,441
39,080
343,062
Grand total 343062 tons
Table 3: Import of WEEE assessment for the years 2007-2015 in tons. Source: Custom Department, Government of Pakistan, 2016.
The analysis shows that computers and computers related accessories account for most WEEE imports. Out of 343,062 tons of trade in WEEE, the cumulative weight of computer related accessories is 258865 tons. It accounts for 76 % total share of total WEEE imports during the nine years. Audio video devices have the second largest share in WEEE scrap, 39080 tons which makes up 11 % of the junk. Refrigerators and television sets contribute the rest of WEEE scrap at about 6 % and 7 % respectively. A ratio of WEEE import is presented by pie chart via Figure-1.
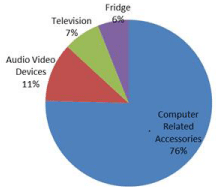
Figure 1: WEEE import data for Pakistan from 2007-2015, Source compiled.
Discussion WEEE Audit of Pakistan
In developing countries and especially in Pakistan the progress of Information and Telecommunications Technology (ICT) depends more on second hand or refurbished Electric and Electronic Equipments (EEEs). The second hand items are easily affordable and infiltrated every segments of life; effecting every field such as trade, commerce, education, health, welfare institutions, and households; especially its effects had been noted in far flung rural areas where it provides luxury, education, awareness, health, security and technological knowhow to the people [31]. The rapid growth of these products has led to an improvement in the buying capacity of public especially towards computers and other electric equipments. Therefore demands of WEEE in developing countries are increasing at an alarming rate but due to short useful life of these equipments they become junk in very short span of time and as a result increase the volume of WEEE in developing countries [32].
WEEE has also a powerful economic and social driver; it improves job prospects and lifts people out of poverty. In many developing countries for example in African country-Ghana, 20300 – 33600 people work are involved in WEEE recycling and refurbishing industries [33]. Over 1 million poor people are engage in India in the manual recycling operations [34]. In USA disposing a computer can cost up to USD 20 [22], while a recycling worker in Pakistan takes less than two dollars for this job. A WEEE labourer in Pakistan can earn a handsome amount (Rs. 1000/ 10 $ to Rs. 9000/ 90 $ per day); more than a white color job in Pakistan. That why economic factor also plays a significant role in forcing government to turn a blind eye to WEEE issue. The vested interests of unskilled labor to earn income through reusing or recycling the WEEE items are one of the primary factors driving the uncontrolled transboundry movement of WEEE towards the third world countries [35].The WEEE import businesses in Pakistan are booming especially the computer market in Pakistan is enormous. Different electronic imported products are 04 to 30 years old. The sorting of these electronic items are done manually and only 15 to 40 per cent of these items are found working conditions, the remaining is junk. Besides operational computers systems the computer’s old versions and obsolete models like XT, AT, 286, 386, 486, etc. are still imported in Pakistan. The use of these old and obsolete models is the extraction of precious metals because these computers models contain higher contents of gold, silver and other expensive metals. Extraction of these computers indicates that a PC of 23 Kg can yield gold up to 0.0016 kg, copper up to 6.93 kg, plastics up to 23 kg and glass (silica) up to 2.49 kg, along with the materials [36].
In practice, after removing the working machines and usable parts the bulk of the consignment is utilized by unorganised informal recycling industry. The conditions of recyclable work places are terrible. The operations of recycling are basically perform manually in family recycling workshops, where large number of children are also engaged in disassembling. The treatment methods adopted for the extraction are rudimentary and dangerous. For example in extraction of gold, first the hardware is burned and then a strong acid is used to extract gold. The workers involve in extraction process do not take any precautionary measures and are often exposed to toxic fumes or burn from acids. The residue of the burned hardware is thrown in the sewage system of the city or cultivated agriculture land, polluting the water bodies or made agriculture land degraded. WEEE disposal in Pakistan is a severe issue because unregulated and unsafe waste management practices let hazardous materials to disseminate into the environmental resources. Over time, these toxic heavy metals leech into the ground and contaminate the soil and ground water causing serious health infections; for example the recycling processes in Karachi, take place at the bank of Lyari River; the effluents ultimately flow into the Arabian Sea polluting the marine ecosystem.
In Pakistan the computers and other obsolete electronic goods are imported under the pretext of ‘second-hand equipment’ or ‘metal scrap’. According to Pakistani Laws these products are not consider waste or hazardous. Beside that Pakistan’s neighbour Afghanistan is a land lock country having no seaport of its own, it uses Pakistani ports and transport systems (Railways and Roads) for its trade under an accord signed by the two countries (Afghanistan and Pakistan). Since smuggling of goods are also common practices between two countries, the goods imported for Afghanistan are illegally brought back to Pakistan that increases the volume of WEEE in Pakistan.
Researches on electronic waste basically deal on WEEE recycling processes and depend on traditional methods [37]. These traditional methods for recycling depends on single material basically used in house hold they are not so complex in structure and are made from malleable, aluminum, paper, wood, vulcanized rubber, etc. these product are easier, and less costly to recycle rather than complicated WEEE goods [18,38-40]. The complicated structure of WEEE recycling processes are still in its initial stages and it will take time.
Policy is the instrument of change. It will push more products to be treated in an environmentally friendly ways. The WEEE issue has received little attention from government and non-governmental environmental bodies in the developing countries. The management problems to handle environmental issues are similar in developing countries due to their meager resources. Therefore the developing countries joint hands in overcoming the WEEE issue and developed long term strategies for the management of WEEE. In this regards all signatories of Basel convention, with the joint collaboration program enforcement law to control WEEE movement from one country to other and work for the betterment of the society.
Policy Directions for WEEE Management
The WEEE management is one the vital issue at global scale. The WEEE issue is getting bad to worse in recent times, if the world will give a blind eye on WEEE issue than unfortunate severe contamination effects are recorded on worldwide. The study proposes policy directions for the WEEE management that will be useful in designing the future environmental policies in Pakistan that are also equally useful for developing countries.
The standard definition is a vital step in designing WEEE policy that is necessary for sustainable development. In Pakistan no standard definition of WEEE exists; therefore Pakistan needs a comprehensive definition of WEEE for policy making.
In framing the WEEE policy, the parameter of cross boarder illegal trade should also be incorporated. Existing policies are not very useful in controlling the transboundry illegal trade. Emphases in policies are given on stoppage of cross boarder illegal dumping of WEEE in underdeveloped countries. Regional pacts between countries are very helpful in controlling the cross boarder movement of WEEE.
In developing the WEEE policy special role of municipalities are to be assigned. Municipalities should deal with all the process for WEEE management that include sorting, collection, recycling, recovery, dumping etc. and trained people for safe extraction of precious elements present in WEEE products.
A data recording system should be developed in Pakistan. Besides imported WEEE, the domestic generation of WEEE also added a significant role in total inventory of the WEEE. The recording system includes WEEE inland production, import and export, sales of each product, recycle and reuse within country.
The government gives incentives for informal sector because livelihood of millions of people is engaged in this sector. The incentive includes tax reduction plans for WEEE recycling; government should give the status of WEEE recycling as home industries and gave training and awareness to the participants for the management of home recycling industry.
For goods fabricated in country, the manufactures and producers are made responsible to take back their goods after their useful life is over. In this regard tax rebate and incentive based offers should be given to the manufactures and producers by the government.
The policy should also contain knowledge and awareness program in his chapter. The chapter also involves the general public for WEEE management. The program also developed the capacity building of the stakeholders in planning business and WEEE management.
Conclusion
The problem of WEEE is gaining momentum in Pakistan and it is feared that Pakistan will become one of the topmost hit country for WEEE dumping station in Asia. At present there is no law or regulation imposed in Pakistan to control this situation. Therefore necessitates expedites prompt measures and framing of WEEE Policy for the management of WEEE in Pakistan and steps should be taken to avoid transforming the cities of Pakistan into dumping station of WEEE of the World. Further the developed and developing countries should not have a blind eye on WEEE issue. As the management of WEEE is a global problem and it needs a global solution therefore cooperation at all levels between different stakes holders of developed and developing nations is essential to solve the WEEE problem. Ultimately in developing countries with the lapse of time, the WEEE flow will becomes exponentially large and unable to manage with meagre resources and the effects of the WEEE’s effluents and contamination will destroyed the environmental resources in developed or developing countries.
References
- Chancerel P, Rotter S. Recycling-oriented characterization of small waste electrical and electronic equipment. Waste Manag. 2009; 8: 2336-2352.
- Adediran YA, Abdulkarim A. Challenges of Electronic Waste Management in Nigeria. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology. 2012; 4: 640-648.
- Gaidajis G, Angelakoglou K, Aktsoglou D. E-waste: Environmental Problems and Current Management. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review. 2010; 3: 193-199.
- Wath SB, Vaidya AN, Chkrabarti T. A roadmap for the development of sustainable E-waste management system in India. Sci Total Environ. 2010; 409: 19-32.
- Widmer R, Oswald- Krapf H, Sinha-Khetriwal D, Schnellmann M, B¨oni H. Global perspectives on e-waste. Environmental Impact Assessment Review. 2005; 25: 436-458.
- Sinha S. Downside of the Digital Revolution. Toxics Link. 2007.
- Chalwla P, Jain N. Estimation of Wastes Generated from Obsolete Personal Computers in India. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research. 2012; 3: 1-11.
- Khan SS. Empirical Modeling of Toxic and other Airborne Matter: A Case Study of Quetta Valley, Pakistan. VDM Verlag Dr. Muller. 2011.
- Asase M, Yanful EK, Mensah M, Stanford J, Amponsah S. Comparison of municipal solid waste management systems in Canada and Ghana: A case study of the cities of London, Ontario, and Kumasi, Ghana. Waste Manag. 2009; 29: 2779-2786.
- Dodson JR, Hunt AJ, Parker HL, Yang Y, Clark JH. Elemental sustainability: Towards the total recovery of scare metals. Chem Eng Process. 2012; 51: 69-78.
- Scheutz C, Mosbaek H, Kjeldsen P. Attenuation of methane and volatile organic compounds in landfill soil covers. J Environ Qual. 2004; 33: 61-71.
- Deng WJ, Zheng JS, Bi XH, Fu JM, Wong MH. Distribution of PBDEs in air particles from an electronic waste recycling site compared with Guangzhou and Hong Kong, South China. Environ Int. 2007; 33: 1063-1069.
- Bigum M, Peterson C, Christensen TH, Scheutz C. WEEE and the portable batteries in residual household waste: quantification and characterisation of misplaced waste. Waste Manag. 2013; 33: 2372-2380.
- Gullett BK, Linak WP, Touati A, Wasson SJ, Gatica S, King CJ. Characterization of air emissions and residual ash from open burning of electronic wastes during simulated rudimentary recycling operations. Journal of Material Cycle Waste Management. 2007; 10: 32-37.
- USEPA Report. Municipal Solid Waste Generation, Recycling, and Disposal in the United States: Facts and Figures for 2008. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2009.
- Ciocoiu N, Stefan B, Valentina T. The WEEE Management System in Romania. Dimension, Strengths and Weaknesses. Theoretical and Empirical Researches in Urban Management. 2011; 5: 5-22.
- Steubing B, Böni H, Schluep M, Silva U, Ludwig C. Assessing computer waste generation in Chile using material flow analysis. Waste Manag. 2010; 30: 473-482.
- United Nations University. Review of Directive 2002/96 on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment. 2008.
- Luther L. Managing Electronic Waste: Issues with Exporting E-Waste. Congressional Research Service. 2010.
- European Union. Directives 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 04 July 2012 on waste electric and electronic equipment (WEEE) Text with EEA relevance. Official Journal of the European Union. 2012.
- BAN. Basel Conference Addresses Electronic Wastes Challenge, United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). 2004.
- UNEP BAN. Basel Conference Addresses Electronic Wastes Challenge. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). 2006.
- Bret HR. E-Waste: an assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci Total Environ. 2009; 408: 183-191.
- Nnorom IC, Osibanjo O. Overview of electronic waste (e-waste) management practices and legislations, and their poor applications in the developing countries. Resources, Conservation and Recycling. 2008; 52: 843-858.
- Lee S, Na S. E-Waste Recycling Systems and Sound Circulative Economies in East Asia: A Comparative Analysis of Systems in Japan, South Korea, China and Taiwan. Sustainability. 2010; 2: 1632-1644.
- Khan SS, Lodhi SA, Akhtar F, Khokar I. Challenges of Waste of Electric and Electronic Equipment (WEEE): Toward a Better Management in a Global Scenario. Management of Environmental Quality. 2014; 25: 166-185.
- SACEP. Scoping Exercise on E-waste Management in South Asia. Position paper on e-waste management in south Asia. 2007.
- Kesselman R. Intel Brief: E-waste hazards. ISN Security Watch. 2008.
- Jonson RB, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Mixed Methods Research: A Research Paradigm Whose Time Has Come. Educational Researcher. 2004; 33: 14-26.
- Jonson RB, Onwuegbuzie AJ, Turner LA. Toward a Definition of Mixed Methods Research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 2007; 1: 112-133.
- Priyadharshini S, Meenambal T. A survey on electronic waste management in Coimbatore. International Journal of Engineering science and technology. 2011; 3: 2099-2104.
- Herat S, Aqamuthu P. E-waste: a problem or an opportunity? Review of issues, challenges and solutions in Asian countries. Waste Manag Res. 2012; 30: 1113-29.
- Khan SS, Lodhi SA, Akhtar F. Sustainable WEEE management solution for developing countries applying human activity system modeling. Management of Environmental Quality. 2015; 26: 84-102.
- Toxics Link Report. Scrapping the hi-tech myth: Computer waste in India. Toxics Link. 2008.
- Chi X, Streicher-Porte M, Wang MY, Reuter MA. Informal electronic waste recycling: a sector review with special focus on China. Waste Manag. 2011; 31: 731-742.
- Liu Y. China’s E-Waste Problem: Facing Up to the Challenge. Worldwatch. 2006.
- Yoshida A, Tasaki T, Terazono A. Material flow analysis of used personal computers in Japan. Waste Manag. 2009; 29: 1602-1614.
- Savage M, Ogilvie S, Slezak J, Artim JL. Implementation of the waste electric and electronic equipment directive in the EU 25. Institute for Prospective Technological Studies. 2006.
- Bohr P. The Economics of Electronics Recycling: New Approaches to Extended Producer Responsibility. Technical University of Berlin. 2007.
- Nixon H, Ogunseitan OA, Saphores J, Shapiro AA. Electronic waste recycling of the 2007. IEEE International Symposium on Electronics and the Environment. 2007.
