Abstract
Nanotechnology is a rapidly growing science of producing and utilizing nano sized silver particles. Nano particles compared to bulk materials exhibit improved characteristics due to their size, distribution and morphology and are used in various scientific fields. Now, engineers are studying ways that it can be made beneficial to the environment. There are general perceptions that nanotechnology will have a significant impact on developing “clean” and “green” technologies with considerable environmental benefits and this has been branded as “Green Technology”. Meaning of green technology is the technology which is environmental friendly developed in such a way that it doesn’t disturb our environment and conserves natural resources. The objectives of nanotechnology are to create eco-friendly processes and products. Conflicting with this positive message is the growing body of research that raises questions about the potentially negative effects of engineered nanoparticles on human health and environment. The main aim of this review is to give about an overview on green technology in association with nanotechnology and its complications and benefits.
Keywords: Fossil fuels; Nano silver particles; Nano fibers; Electro winning
Introduction
Nanotechnology
“It is manipulation of matter on an atomic, molecular and supramolecular scale. Nano scale is the scale of things between 1 to 100 nanometers”. It is the engineering of functional systems at molecular scale. This covers both current work and concepts that are more advanced. In its original sense, nanotechnology refers to the projected ability to construct items from the bottom up, using techniques and tools being developed today to make complete, high performance products [1]. It sometimes referred to as general purpose technology, that’s because in its advanced form it will have significant impact on almost all industries and all areas of society. The concepts that seeded nanotechnology were first discussed in 1959 by renowned physicist Richard Feynman in his talk “there is plenty of room at the bottom” in which he described the possibility of synthesis via direct manipulation of atoms. The term nanotechnology was first used by “Norio Taniguchi” in 1974 [2].
The ability to see the nanosized particles has opened up a world of possibilities in a variety of industries and scientific industries. Because it is essentially a set of techniques that allow manipulation of properties at a very small scale, it can have many applications. It has many advantages in various fields, like medical (nano medicine), clothing (fabric), and environmental (eg. Water purification systems), privacy and security (nano electronics), food industries (for better food productions), fuel cells, solar cells, fuels, sporting goods, etc. So it has this much of advantageous it is picking up the pace and has got a lot of people talking [3]. It is true that nanotechnology have helped us achieve many great things for the world but at the same time; there are certain disadvantages of this technology as well. The presence of nanomaterials is not in itself a threat; it is only certain aspects that can make them risky, in particular their mobility and their increased reactivity. Only certain properties of certain nano particles were harmful to living beings or the environment would be faced with a genuine hazard. In this case it can be called nano pollution. This only proves the fact that nothing is perfect and each thing has its positives and negatives.
Now, researchers are studying ways that it can be made beneficial to environment. This has been branded as Green Technology since it focuses on the nano scale that needed to be overcome to ensure and produce ecofriendly processes. Green technology acts to reduce contaminants and harmful processes through directly counteracting them or through altering the conditions that create them. It is the technology which environmental friendly, developed and used in such a way that, it doesn’t disturb our environment conserves natural resources [4].
Green technology
“It is a continuously evolving group of methods and materials, from techniques for generating energy to non toxic cleaning products”. Due to rapid industrialization and urbanization toxic elements are released into environment resulting global warming. Over the past 50 years, the average global temperature has increased at the fastest rate in recorded history. Global warming occurs when carbon dioxide (CO2) and other air pollutants and greenhouse gasses collect in the atmosphere and absorb sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface. Normally, this radiation would escape into space, but these pollutants, which can last for years to centuries in the atmosphere, trap the heat and cause the planet to get hotter. That’s what’s known as the greenhouse effect [5]. Combustion of fossil fuels generates sulfuric, carbonic, and nitric acids, which fall to Earth as acid rain, impacting both natural areas and the built environment. Monuments and sculptures made from marble and limestone are particularly vulnerable, as the acids dissolve calcium carbonate. Fossil fuels also contain radioactive materials, mainly uranium and thorium, which are released into the atmosphere. Moreover, these environmental pollutions impacts on the human beings because its particles of the fossil fuel on the air cause negative health effects when inhaled by people. These health effects include premature death, acute respiratory illness, aggravated asthma, chronic bronchitis and decreased lung function [6]. One of the best examples of green technology would be the solar cell. A solar cell directly converts the energy in light into electrical energy through the process of photovoltaics. Generating electricity from solar energy means less consumption of fossil fuels, reducing pollution and green house gas emissions. It is a relatively young market place but investor interest runs a very high response to global warming fears and increasing scarcity of many natural resources. It uses renewable natural resources that never depletes, so future generation can also benefit from it. It can effectively change waste pattern and production in a way that it won’t harm the planet [7].
By applying green technology leads to:
• Reduce the usage of non-renewable resource-We can minimize the usage of non-renewable energy and conserve it for the future.
• Reduce energy usage-Leading to long term cost saving.
• Life time and property value-With proper maintenance green technologies can have long life times. A small wind system can last up to 20 years.
• Increase human quality in life-We are able to live in a world there are less pollution and healthier environment.
The aim is green approach taken when constructing structures to promote healthier, better and conductive to both the internal patrons as well as the environmental as whole.
Goals of green technology
Goals of green technology are many. To meet the needs of society in ways without damaging or depleting natural resources on earth is the main Goal of green technology. A few of them are:
1) Sustainability-Meeting the present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
2) Source Reduction-Reducing waste and production by changing patterns of production and consumption.
3) Innovation-Developing alternatives to technologieswhether fossil fuel or chemical intensive agriculture-that have been demonstrated to damage health and environment.
4) Energy-May be the most urgent issue for green technology, this includes the development of alternative fuels, new means of generating energy and energy efficiencies.
5) Green Building-It encompasses everything from the choice of building materials to where a building is located.
6) Green Chemistry-The invention, design, and application of chemical products and processes to reduce or to eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances.
Types of green technology
Listed below are some popular examples of the types of green technologies and practices we’re interested in.
1) Green Chemistry-It is philosophy of chemical research and engineering that enocourages the design of products and processes that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances.
2) Green Nano Technology-Producing nano materials and products without harming the environment and human health.
3) Green Building-It refers to a structure using a process that is environmentally responsible and eco friendly too. It involves building’s life cycle; from design, construction and maintenance, renovation and demolition.
4) Green Information Technology-Aims to reduce the carbon footprint generated by the information systems. This designs which can reduce the negative effects of human activity.
5) Green Energy-Is the energy produced by natural resources, i.e., sunlight, wind, rain, tides, plants, algae and geothermal heat which put very small impact on the environment than fossil fuels i.e., oil, gas, coal etc.
Green Nanotechnology or Green biotechnology
Nanoparticles are viewed by many as fundamental building blocks of nanotechnology. They can be synthesized using a variety of methods including physical, chemical, and biological and hybrid techniques. They are the starting point for many ‘bottom-up’ approaches for preparing nano structured materials and devices. As such, their synthesis is an important component of rapidly growing research efforts in nano scale science and engineering. Nanoparticles of a wide range of materials can be prepared by a variety of methods. An attempt to describe advances in a wide range of synthesis methods has been made, at the expense of detailed coverage of any particular technique [8].
The synthesis of metallic nanoparticles involves top-down and bottom-up approaches by chemical, physical, and biological means as shown in Figure 1. Biogenic syntheses of silver nanoparticles are classified under bottom up approach. Several methods have been employed to synthesize silver nanoparticles, including chemical reduction, microwave-assisted synthesis, ultrasonic-assisted reduction, electrochemical reduction, template method, photo induced or photo catalytic reduction, irradiation reduction, micro emulsion method, and biochemical reduction.
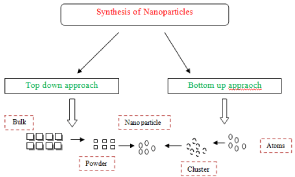
Figure 1: Flow chart for Synthesis of Silver Nano particles Using Top down and Bottom up Approach.
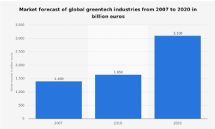
Figure 2: Market Forecast of Global Green Technology industries from 2007 -2020.Statistica 2017, Roland Burger.

Figure 3: Nano Technology for Green Cars.
Source: “Indications of socio-economic impacts of nanotechnologies”, forthcoming chapter in the edited volume of the fourth annual conference of the Society for
the study of Nanoscience and Emerging Technologies (S-NET) Adapted from Robinson DKR (2013).
Several methods are employed to synthesize silver nanoparticles. A thorough search of the literature revealed diverse methods for the production of silver nanoparticles. They are:
1) Synthesis at Room Temperature
2) Synthesis at Higher Temperature
3) Synthesis Using Microwave Irradiation
4) Light Induced Synthesis
In general green technology means synthesizing nano particles or nanomaterials using biological routes such as those involving microorganisms, plants, viruses or their byproducts such as proteins and lipids with the help of various biotechnological tools. Nanoparticles produced by green technology are far superior to those manufactured with physical and chemical methods based on several aspects. For example, green techniques eliminate the use of expensive chemicals, consume less energy, and generate environmentally benign products and by products. The principles of green chemistry have now become a reference guide for researchers, scientists, chemical technologists, and chemists around the world for developing less hazardous chemical products and by products.
Green nano technology in industries: The potential to commercialize nanotechnology for green innovation has become a particular focus of interest in recent years as nanotechnology research is beginning to be used in multiple concrete applications. Due to the rising energy scarcity as well as global warming, countries closer attention are now paying much closer attention to clean energy technologies and using green technology in industry [9]. Over the long term, a new industrial ecology might emerge if nanomaterials made by green synthesis, replaced existing materials in products, if new products were designed using green engineering principles, and if cleaner nano-based manufacturing processes were adopted [10].
Major corporations following green technology in India: Several developed countries across the world are already encouraging the green technology in industry, as shown in Table 1. Billions are being invested in Green wind projects, and biomass plant. Stateowned enterprises and private sectors are motivated to develop the green technology industry [11].
Industry
Number of establishments reporting atleast one green technology or practice
Total, all industries
4,933,500
Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing and hunting
64,600
Mining, quarrying , oil and gas extraction
13,400
Utilities
16,900
Construction
4,03,200
Manufacturing
2,21,700
Wholesale trade
302,400
Retail Trade
712,900
Transportation and warehousing
120,800
Information
94,600
Finance and Insurance
2,94,600
Real estate, Rental or leasing
2,06,700
Professional, scientific and Technical Services
5,40,200
Management of companies and Enterprises
29,500
Administrative and waste services
252,100
Educational Services
114,300
Healthcare and Social services
560,800
Arts and Entertainment
80,200
(Source: Green Technology for Sustainable Development, Prem Kumar. U)
Table 1: Number of Industrial Establishments practicing Green Technology.
Some of them are: ITC Limited, Tata Metallics Limited (TML), Tamil Nadu News Print and Papers Limited, Wipro Technologies, HCL technologies, ONGC, IndusInd Bank, Idea Cellular, Hero Honda Motors and Suzlon Energy, PNB and Reliance Industries etc.
Some of the international industries are: Nokia, Intel, Cisco, Dell etc.
Green nano manufacturing: It emphasizes the production of nanomaterials with a reduced carbon foot print, low toxicity and little to no impact on the environment and human health. “Nano fibers” made from starches and proteins could be manufactured using electro spinning technology. This technique offers the prospect of recycling, huge amounts of biopolymer wastes from the chemical good and pharmaceutical industries turning them into useful biodegradable nanofibres [12].
Green synthesis of nanomaterials: A green method for making water-soluble carbon nano-tubes which have promising application in, thin films, electronics, composite materials and drug delivery. Environment factors are not only the reason biological synthesis is also preferred also because it can be used to produce large quantities of nano particles that are free of contamination and have a well defined size and morphology. By using micro organisms, plants, viruses, proteins and lipids using various biotechnological tools we can synthesize green nano particles [13].
Green nanotechnology in automobiles: With automotive manufacturers striving to match stricter emission norms set by regulatory authorities, they have begun considering nanotechnology as a necessity. With precise structuring and exceptional physical and mechanical properties, nanomaterials-based products have the potential to redefine energy and materials applications. “Their ability to replace expensive platinum in fuel cells that are more environment-friendly than regular gasoline cars, are expected to act in their favour,” said a study from Frost and Sullivan. Take for instance NanoLub, a lubricant developed based on compounds discovered at the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, had nano-spheres and nanotubes of inorganic compounds. The particles have a unique structure of nested spheres that lubricate by a special mechanism greatly reducing friction and wear [14].
Green machines like hybrids and hydrogen vehicles stand to benefit even more. Engineers are already developing fuel cells packed with carbon nano tubes to store hydrogen and increase reactivity.
For example green cars, are complex products which incorporates green technology in several different ways being present in the tyres, in the chassis, and in the wind screen. It also enables components of the green car and its production for example, through the use of to reduce energy waste, and to monitor and reduce energy waste [13].
Nano-enhanced green technologies: Until recently, electronic devices are not considered as major consumers of energy, compared with engines or heating systems. New Zero power systems are being developed in which low energy electronics use energy harvesters to convert ambient energy into electrical energy (Photovoltaics, piezoelectronics, thermic etc).
Nano-enhanced cleanup technologies: This include with the environmental cleaning and remediation (water and air purification, sewage treatment, environmental remediation and waste management). Currently, a number of green technology methods are tested and used for waste water treatment either alone or combine with other traditional methods. Some of them are bioreactors, biofiltration, bioremediation, electro winning and electro coagulation [15].
Green nano electronics: The ultimate goal of this research is to create paths for the production of human and environmentally friendly electronics in general and integration of such electronic circuits with living tissue in particular. Green materials and ‘‘green’’ technologies are carving avenues towards achieving the ambitious goal of sustainability in the field of electronics, by identifying (i) economically feasible-high throughput synthetic routes that avoid the usage of toxic solvents for the fabrication of electronic grade materials and do not generate toxic waste requiring expensive handling and disposal and should ensure (ii) low cost processing routes in practical devices, (iii) render electronics that feature biodegradability in mild degradation conditions at the end of their life cycle and/or electronics that are suitable for performing complex biological functions (e.g. transduction, sensing, recognition, event triggering, etc.) as a tool for interfacing electronics with various forms of life [16].
Green investments
When people talk about “green investments” they’re speaking generally of investing in activities that, in a popular context, can be good for the environment in a direct or indirect manner. If investors find protecting the environment by encouraging the eco-friendly business to be important to them green investing can be attractive way to put their money to work. Some of the options an investor has if they want to build a portfolio including securities mutual funds and ETF’s and bonds. Some of the green mutual funds that are available include: The TIAA-CREF, Social Charity Equality Fund. Green bonds can sometimes be offered by governments, and generate revenue for funding projects or businesses – these can sometimes be tax-free [17].
One of the most fundamental challenges particular to green technology is that, the science, the testing, the regulatory strategy and even the processes need for commercial production are all being developed and deployed at the same time [18].
Barriers to develop and commercialization of green nano technology [18]:
1) There are no clear design guidelines for researchers in initial discovery phases of green nano sciences.
2) Many green nano materials require new commercial production techniques, which increases need for basic research, engineering research and coordination of the two between the industrial and research communities.
3) The lack of a deep bench of scientists and engineers with experience developing in green nanotechnology.
4) Toxicology and analysis protocols need to developed and constantly updated to reflect advances in science.
5) Regulatory uncertainty persists, and green technologies often face higher regulatory barriers than existing or conventional chemicals.
6) The end market demand is unclear, especially since there are only a limited no. of commercial grade products, that can be compared to conventional materials in terms of performance.
Advantages and limitations of green nano technology: After defining the concepts of nanotechnology and green sustainable development we studied seven nano technology area applications that are pertinent to green growth and sustainability. These application areas are assessed relative to their scale and scope through market forecasts, green benefits and potential issues and limitations [19].
Advantages
- It uses renewable resources that never depletes in nature. That means, future generation can benefit from them too without harming the planet.
- Waste production management, therefore offers solution for waste disposal and recycling
- Can slow the effect of global warming by reducing CO2 emissions.
- Bring economic benefit to certain areas (Farming).
- Increase in production and productivity.
Limitations
As the technology is being developed, greater efforts are being made to find ways of assessing or tracking the impact of nanotechnology on specific policy objectives such as green growth. This is a very challenging task. The risks of using new green nanotechnologies need to be considered relative to the risks in using current technologies and valued against the human and environmental costs of not effectively addressing key global challenges [20].
Some of them are;
1) High Implementing cost.
2) Lack of Information (no clear data to what extent research organizations, universities, companies are doing on this).
3) No known alternative chemical or raw material inputs.
4) No known alternative process technology.
5) Uncertainty about performance impacts.
6) Lack of human resources and skills.
Conclusion
Green technology is a blessing to modern industrialized world. So, by adopting nanotechnological methods by using traditional methods we can reduce the scarcity of natural resources and reduce the environmental pollution. So in terms of environmental sustainability, the technology industries are embracing change. They are changing to avoid negative consequences or to meet green demand or to achieve both. Whatever their motivation, they are incontrovertibly shifting toward green. By introducing this knowledge sustainable development, preservation of nature, conservation of human population and other living beings, elimination of wastage and reusability, innovation of existing one are made possible in a more successful manner.
References
- Nanotechnology. Wikipedia.
- Ram Prasad. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Photosynthetic Plants. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Nanoparticles. 2014; 963961: 8.
- Introduction to Understanding Nano.
- K Walker. What is Green Nanotechnology? 2013.
- Global Warming 101.
- Liodakis EG. The Nuclear Alternative: Energy Production within Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. AIP Conference Proceedings 1342. 2011.
- Do We Consume Too Much?
- Patra JK, Baek KW. Green Nanobiotechnology: Factors Affecting Synthesis and Characterization Techniques. Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Nanomaterials. 2014.
- Ahuja D, Tatsutani M. Sustainable energy for developing countires; Sapiens (Surveys and Perspectives Integrating Environment and society. 2009.
- Weisner Mark. R Vicki. L.Colvin. Environmental Implications of emerging nanotechnology, Environmentalism and the technologies of tomorrow: Shaping the next industrial revolution. Washington: Island press. 2005; 41- 52.
- Golub, SS, C Kauffmann, P Yeres. Defining and Measuring Green FDI: An Exploratory Review of Existing Work and Evidence. OECD Working Papers on International Investment, 2011.
- Zhonghua Xu, Scott Lenaghan, David Gilmore, Lijin Xia, Mingjun Zhang. Automated High Throughput Scalable Green Nanomanufacturing for Naturally Occurring Nanoparticles using English Ivy. 2012.
- OECD Science, Technology and Industry Policy Papers. 2013.
- Nano Technology For Green Vehicles.
- Alex Barshai. Advanced Green Technologies for Wastewater Treatment. 2017.
- Mihai Irimia vladu. Green electronics: biodegradable and biocompatible materials and devices for sustainable future. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014; 489-736.
- Green Investing.
- Kira JM Matus, James E Hutchison, Robert Peoples, Skip Rung, Robert L Tanguy. Green Nanotechnology Challenges and Opportunities. ACS Green Chemistry. 2011.
- The Main Features and Benefits of Green Technology. 2015.
- Miguel de la Guardia. The challenges of green nanotechnology. BioImpacts, 2014; 4: 1-2.
