Abstract
The robustness factor ƒ of the coal is a comprehensive indicator of the ability of the external coal to determine the resistance to external forces. The robustness factor is listed in the Chinese coal industry as one of the individual indicators for judging the dangers of coal and gas outbursts. It is a very important basic indicator. At present, the robustness factor can only be measured in the laboratory after the coal sample is collected on the working surface and cannot be directly measured underground. The method is troublesome to operate, and the purpose of quickly predicting the outstanding danger cannot be achieved. Therefore, a method for rapidly determining the enthalpy of the consistent coefficient of coal based on the pulverization method is proposed. The principle of measurement is described, and the specific determination steps and calculation methods are given. The optimal pulverization scheme of the coal sample pulverization experiment is established by the orthogonal test, and the optimal value of the pulverization parameters is determined as follows: the initial particle size of the coal sample is 6~7 mm, the pulverizer speed is 8000 r/min, the coal sample quality is 150 g, and the pulverization time is 10 s. The corresponding relationship between the mass fraction of coal particles with different particle sizes after pulverization of coal samples and the ƒ value is further analyzed. The relationship model between the mass fraction of coal quality x and the ƒ value of particle size below 0.5 mm after coal sample pulverization is established: ƒ = -0.454*ln(x)-0.0564. The experimental results show that the method is feasible, simple and fast, and the calculation model has strong accuracy, versatility and representativeness to meet the test requirements. This is a new method for direct and rapid determination of coal in the consistent coefficient of coal.
Keywords: Consistent coefficient ƒ; Coal sample crushing; Orthogonal test; Crushing parameter; Rapid determination
Introduction
Every mining worker cares about the ruggedness of the coal rock [1-2]. The coal rock robustness factor ƒ (also known as the Platts coefficient) was first proposed by the Russian scholar M.M. Protochi Yakonov in 1909 [3]. In 1926, the concept of classification of rocks according to their robustness was systematically and completely presented. After many evolutions, in 1950, M.M. Protochi Yakonov (who was the son of the elder Platts scholar) proposed the “mashing method” [4-6]. This method was used only to determine the consistent coefficient of the coal. The method was later widely used by many researchers to determine the firmness coefficient of rock. Its basic principle is based on the Li hypothesis, i.e., the work consumed by the destruction of brittle materials is proportional to the surface area that is reformed [7]. In 1975, the Soviet Union used the “crushing method” as a national standard to determine the rock consistent coefficient [8-9]. After continuous research and improvement and supplementation, the current “mashing method” has been widely used in the mining industry and exploration and excavation in various countries. In China, the corresponding national standard GB/23561.12-2010 “Methods for determination of physical and mechanical properties of coal and rock - Part 12: Method for determination of firmness of coal” was also formed.
The consistent coefficient ƒ of coal is a comprehensive index of the ability to resist external forces determined by various properties of coal and is a physical indicator of the strength of the coal. The consistent coefficient of coal is listed as one of the four individual indicators for judging the danger of the coal and gas outburst in China’s coal mining industry [10-12]. Studies have shown that the smaller the consistent coefficient of coal, the greater the risk of coal seam emergence [13-14].
The consistent coefficient ƒ of coal should be measured frequently, and it should be measured synchronously with the coal and gas outburst risk prediction index (gas desorption index of drill cuttings (including K1, ΔH2, etc.)). If the test results of a past location are changed to replace the inaccurate practices used in some areas, then the comprehensive prediction of the outburst risk of the working face can therefore be achieved by combining the gas desorption index, which is mainly used to reflect the coal seam gas pressure and gas desorption rate of the drill cuttings with the consistent coefficient of the coal reflecting the physical and mechanical properties of the coal. For example, the Chongqing Branch of the Coal Research Institute has proposed a comprehensive indicator Kf that reflects the magnitude of the hazard. The indicator Kf has been proved by field tests [15-16].
In summary, the determination of the consistent coefficient of coal is a very important basic effort. In the Chinese national standard GB/23561.12-2010, the laboratory uses the “crushing method” to determine the ƒ value [17]. The measurement process can be summarized as follows: the value is calculated based on the amount of the coal sample of a given mass broken to a particle size of 0.5 mm or less under a certain impact force. In the process of determining the consistent coefficient of coal, the “crushing method” must ensure that the weight is freely dropped after raising the weight to 600 mm every time. Due to objective factors, such as the instability of human operation, during the coal sample process, there may be cases where the weight is not in place, and the wall of the hammer is encountered during the process of the weight falling. The measurement result is greatly affected by the artificial factor, and the measurement process is cumbersome, which consumes the energy and strength of the experimenter. These factors may lead to the diversity of the results of the same coal sample depreciation [18-20]. Moreover, rapid down hole measurement cannot be achieved, and the purpose of quickly predicting the outstanding danger cannot be achieved.
With the improvement of mine intelligence and mechanization, the importance of mine safety work and the demand for advanced technology and equipment are also increasing. By studying new methods, new technologies and new equipment for depreciation, the devaluation is accurate. Rapid measurement is the need to improve the prediction of coal mine and gas outbursts, impact ground pressure and other special coal-rock dynamic disaster predictions and noncontact continuous monitoring and early warning. The existing research results show that [21-22] the particle size of coal pulverization obeys a certain distribution law, and the mechanical pulverization process can ensure the stability of the crushing work during the determination of coal sample enthalpy. Moreover, numerous coal samples of different particle sizes can quickly be obtained during the drilling process of the mine working face, and the coal sample required for determining the consistent coefficient of the coal can reduce the special and large-scale on-site sampling work performed during the ƒ value determination process, reduce measurement time and improve measurement efficiency.
Therefore, a method for rapid determination of the consistent coefficient of coal based on the pulverization method is proposed, and relevant experimental schemes are designed. The key technical parameters in the method are determined according to the determination. The calculation model of the consistent coefficient of coal is established, and the feasibility and accuracy of the method are verified by experiments.
Method for Determining the Firmness Coefficient of Coal-Pulverization Method
Measurement principle
The consistent coefficient ƒ of coal is a comprehensive index to characterize the anti-destructive ability of coal. The consistent coefficient reflects the mechanical strength, hardness and development degree of cracks of coal, and under the influence of a certain impact force, the coal body crushing work is proportional to the increased surface area of the crushed material [23-25]. Under the action of certain crushing work, the larger the consistent coefficient, the larger the average particle size of the coal sample after crushing. Similarly, under the condition that the average particle size of the coal body before or after pulverization is the same or similar, the pulverization work required for the coal body with the larger firmness coefficient is larger. Therefore, the devaluation reflects the amount of work required to break the coal. Furthermore, we can indirectly reflect the ƒ magnitude by analyzing the extent to which the coal sample is destroyed. The damage degree of the coal sample can be reflected by the proportion of different particle size distribution after the coal sample is crushed and destroyed [26-29]. Therefore, the relationship between the consistent coefficient of the coal and the proportion of the distribution of a certain specific particle size after the coal sample is crushed and destroyed can be further established.
Based on the above analysis, the principle of determining the enthalpy of the consistent coefficient of coal based on the pulverization method can be expressed as: the coal sample of a specific particle size and specific mass is pulverized under the specific conditions of the same pulverization time and pulverization power. The ƒ value is indirectly calculated by establishing a relationship model between the mass fraction of a certain size of coal particles in the newly formed coal smash and the consistent coefficient of the coal.
Coal sample collection
In the freshly exposed position of the coal seam to be tested, sampling can be carried out by using the groove method or the drilling sample collection.
After taking the coal sample, use the coal sample standard sieve to select, select a certain quality coal sample of a certain size, and then put the coal sample into the Ziplock bag, and attach the coal sample information label (including the coal mine name, coal seam number, sampling location, etc.). Then, bring the coal sample back to the laboratory, paying attention to the fact that it should not be bumped during the carrying and transportation of the coal sample.
Measuring device
By consulting a large amount of literature, as well as the market research of the current miniaturized pulverizer, and fully considering the size of the coal sample required to be pulverized to a certain particle size requirement, it can be determined that there are high requirements for the key parameters such as the power and speed of the pulverizer. Therefore, the mature Chinese medicine high-speed pulverizer (Figure 1) is used to pulverize the collected coal samples to be tested. The specific parameters are shown in (Table 1).
Numbering
Parameter name
Numerical value
1
Numerical value
220 V
2
Rated power
1200 W
3
Motor speed
28000 Transfers/ minute
4
Capacity
300 g
5
Degree of crushing
60~300 items
Table 1: pecific parameters of the crusher.
Determination steps
The procedure for determining the firmness factor of coal by the pulverization method is as follows:
(1) Coal sample collection: collect freshly exposed coal samples of the coal seam to be tested, and use a coal sample standard sieve to separate 150 g coal samples with a particle size of 6~7 mm.
(2) Coal sample pulverization: the coal sample is placed in the pulverizing device shown in (Figure 1) for pulverization, wherein the pulverization time is set to 10 s, and the pulverizer rotation speed is 8000 r/min.

Figure 1: Smashing device diagram.
(3) Screening of coal particles: screen the coal samples after crushing, measuring the mass of the coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less after pulverization, and determine the mass ratio x of the coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less.
(4) Model establishment: According to the steps of (1), (2), and (3), the typical coal samples collected from different coal seams in different mining areas in China are subjected to crushing experiments, and the mass proportion of coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less after pulverization of different coal samples is obtained (i = 1, 2, 3,..., n).
At the same time, the typical coal samples collected from different coal seams in different mining areas are determined by the “crushing method” for the consistent coefficient ƒ value, and the consistent coefficient ƒi of different coal samples is obtained. Then, through a large amount of experimental data for fitting analysis, a relationship model between ƒi and xi is established.
(5) Laboratory and on-site application: for the coal seam to be tested, according to the steps of (1), (2), (3), determine the mass proportion x of coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less. Bring the relationship model between ƒi and xi established in (4), and calculate the firmness coefficient ƒ value of the coal seam to be tested.
Determine the Comminution Parameters Based on the Orthogonal Test
Determine the comminution parameters
From the principle of determining the consistent coefficient of coal by the pulverization method in section 2.1, there are four main pulverization parameters to be determined by the determination method: pulverization power, pulverization time, initial particle size of coal sample and quality of coal sample. Among them, the pulverizing power and the pulverizing time jointly determine the size of the pulverizing work done on the coal sample, and the two have a correlation effect on the pulverizing work.
Through the performance test of the pulverizer selected in Figure 1, the coal sample has a consistent coefficient f value of 0.5 and a particle size of 1~3 mm can be pulverized to a particle size of 0.5 mm or less in a short time. Further tests found that it is difficult to control the time error when the coal sample is pulverized within the range of 5 s. If the time is too long, it is difficult to ensure that the coal sample is in a state of incomplete pulverization (need to ensure that the coal sample is in a variety of different particle sizes after smashing for a certain period). If the state of the distribution is completely pulverized to a particle size of 0.5 mm or less, the mass ratio analysis of the coal dust of different particle sizes cannot be performed, and the calculation of ƒ cannot be performed.
Through many test statistics in the performance test process, the pulverization time can be determined as 10 s, which not only can achieve precise control of the pulverization time, effectively eliminate the influence of time error, and effectively control the degree of pulverization of the coal sample. Moreover, the factor determining the size of the pulverization work can be reduced from the two control factors of the pulverization time and the pulverization power to one of the pulverizing power.
The pulverizing power is related to the speed of the pulverizer. Therefore, by adding a frequency converter (Figure 2), to adjust the frequency of the power supply. Parameters are shown in (Table 2), the speed of the pulverizer can then be adjusted to achieve the purpose of controlling the pulverized power output.

Figure 2: Single-phase motor dedicated inverter.
Voltage level
Model
Power kW
Battery capacity kVA
Line input current A
Line output current A
Simplex 220 V
AVT10-2SR4GH-T3
0.4
0.95
4.5
2.4
Table 2: Inverter parameter table.
In summary, under the condition that the pulverization time is fixed at 10 s, the main pulverization parameters of the smashing method for determining the consistent coefficient of coal can be further determined as three: initial particle size of the coal sample, quality of the coal sample and rotation speed of the pulverizer
Orthogonal test design for determination of pulverization parameters
Initial particle size selection of coal samples: According to a large amount of on-site sampling, coal particles with a particle size of 1 to 10 mm can generally be taken at the orifice during the drilling process. Through the performance test of the pulverizer, if the coal sample with too small particle size is used for pulverization, there will be a special case where the coal particles is completely pulverized to a particle size of 0.5 mm or less within 10 s. This makes the pulverized coal sample not in a state of a common distribution of a plurality of different particle sizes, resulting in failure of the experiment [30-32]. If the coal sample size is too large, it is difficult to ensure that the quality of the required coal sample can be collected once after the collected coal sample is screened. Only by increasing the sampling time and sampling depth can the oil sample be obtained after screening. A coal sample of sufficient quality, in this case, causes a problem that the sampling position is difficult to ensure a relative fixed point, resulting in a large deviation in the measurement results. Therefore, for the initial particle size of the coal sample, this orthogonal experiment selects the coal sample with the initial particle size in the range of 4~7 mm (Figure 3) for the crushing experiment.

Figure 3: Three factors and level table of coal sample crushing experiment.
Coal sample quality selection: If there are too many coal samples, the accumulation volume of the coal sample in the pulverizer is too large, and it is difficult to ensure that all the coal samples participate in the pulverization in a short time. Too little coal sample will cause the coal sample to be completely pulverized to below 0.5 mm. Therefore, according to the crusher capacity of the crusher (maximum capacity of 300 g in Table 1) and the difficulty of sampling on site, the quantity of the coal sample is determined to be 50~150 g.
Determination of the pulverizer speed: Through the pulverization experiment of coal samples with particle size of 4~7 mm and mass of 50~150 g at different pulverizer speeds (Figure 4), when the rotation speed is greater than 10000 r/min, the pulverized coal sample is basically coal ash. When the rotation speed is less than 8000 r/min, there are still more coal samples of 4~7 mm, which indicates that the coal is not fully involved in the pulverization process when the rotation speed is too low. Therefore, the range of the pulverizer speed is set at 8000~10000 r/min.

Figure 4: Crushing effect diagram of different speed coal samples.
Orthogonal test design: Based on the above preferred determination of the range of values for each major comminution parameter, the optimal combination of the initial particle size, coal sample quality and pulverizer speed of the coal sample is determined by the orthogonal test. Therefore, this orthogonal test is to establish the optimal combination of three factors. Refer to the range of values of each pulverization parameter given above to give the three-level value of each factor and select Ln(3t) type positive. The orthogonal test was carried out in the cross-tab [33-35], and the values of different factors are shown in Table 2.
Determination of pulverization parameters
According to the orthogonal test scheme of (Table 3), the coal samples were taken from the 15 coal seams of Pingdingshan No. 8 Mine in Henan Province in northern China. A total of 9 coal samples were collected at the same location according to the design parameters of (Tables 1 and 3). Samples collected at the same site of the same coal seam were subjected to crushing experiments under different initial particle sizes, pulverizer speeds and coal sample quantities, and the mass ratio of coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less after the coal sample is pulverized was recorded. At the same time, the smashing value of the coal sample at the same place of the same coal seam was measured by the “crushing method” (the f value of the coal sample was determined to be 0.48), and the mass proportion of coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less after the coal sample was broken was recorded. The results of the orthogonal test are shown in (Table 4).
Factor
Factor interval (horizontal) range division or value
1
2
3
Initial particle size of coal sample A
4 mm~5 mm (A1)
5 mm~6 mm (A2)
6 mm~7 mm (A3)
Crusher speed B
8000 r/min (B1)
9000 r/min (B2)
10000 r/min (B3)
Coal sample quantity C
50 g (C1)
100 g (C2)
150 g (C3)
Table 3: Three factors and level table of coal sample crushing experiment.
A
B
C
1
2
3
4
1
A1
B1
C1
1
2
A1
B2
C2
2
3
A1
B3
C3
3
4
A2
B1
C2
3
5
A2
B2
C3
1
6
A2
B3
C1
2
7
A3
B1
C3
2
8
A3
B2
C1
3
9
A3
B3
C2
1
Table 4: Crushing effect diagram of different speed coal samples.
The orthogonal test judgment index ei is the absolute value of the difference in the mass ratio of coal samples with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less after completion of the two “crushing” methods. The symbol Kij is introduced to represent the sum of the test results of the level i on the jth column.
Table 4 shows that K3A‹K2A‹K1A, K1B‹K2B‹K3B, K3C‹K2C‹K1C. According to the orthogonal test principle, the parameter combination (A3, B1, C3) of experiment No. 7 has the best effect, and A3, B1 and C3 are the most influential factors among the factors. Therefore, the optimal combination of each factor combination in this orthogonal test is A3, B1, C3, which is the optimal smashing scheme sought by the experiment. Therefore, the optimal values of the three pulverization parameters can be determined as follows: the initial particle size of the coal sample is 6~7 mm, the pulverizer speed is 8000 r/min, and the coal sample quantity is 150 g.
Investigation of pulverization effect under optimal pulverization parameters
To investigate the pulverization stability and versatility under the optimal pulverization parameters determined by the orthogonal test, the pulverization experiment was carried out on the coal sample of the No. 1 coal seam of the faer coal mine in Guizhou Province in southwest China. According to the initial particle size (6~7 mm) and coal sample quantity (150 g) determined in 3.3, the coal sample was divided into 4 groups, the speed of the crusher was adjusted to 8000 r/min, and then the 4 sets of coal samples were separately crushed. The post-screening coal samples are shown in (Figure 5) (exemplified by one set of coal samples). Figure 6 shows that the four curves are basically coincident, indicating that the coal samples collected at the same location of the same coal seam were pulverized several times under the same pulverization conditions, and the proportion of coal samples distributed in each grain size interval is not much different. After the pulverization, the particle size distribution of the coal sample is basically the same. Moreover, the coal sample with a particle size distribution below 0.5 mm has the smallest difference in mass ratio, indicating that the coal sample distribution and mass ratio of the particle size below 0.5 mm after pulverization are the most stable, further illustrating that in the section 3.3, we use the two methods of “crushing method” and “mashing method” to determine the absolute value of the difference in the mass ratio of coal samples with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less. The judgment indicators of the test are reasonable. The value of the pulverization parameters established by the orthogonal test is reasonable. The pulverization process of the coal sample under the optimal pulverization parameters established by the orthogonal test is stable and reliable [36-37]. Moreover, the pulverization effect was investigated in the coal samples used in the experiment, and the coal samples used in the orthogonal test were collected from coal seams in different parts of northern and southwestern China. The consistency law of different coal samples under the same conditions of pulverization experiments shows that the optimal pulverization parameters determined by orthogonal test have good versatility.
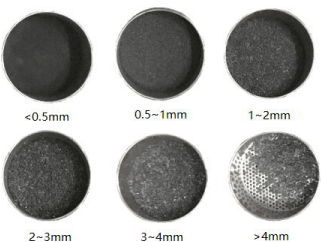
Figure 5: Selection of a set of coal samples after crushing.
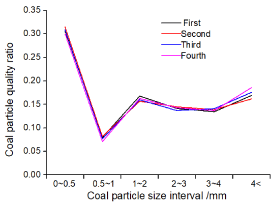
Figure 1: The proportion of coal samples with different particle sizes after
pulverization.
Crushing Method Measurement Model
Establish the crushing method measurement model
The principle of determining the consistent coefficient enthalpy of coal is based on the pulverization method described in Section 2.1 and ensures the broad representativeness, applicability and versatility of the “crushing method” for determining the ƒ value model. We collected 30 coal samples from 30 coal mines in 11 major coal- producing areas. (each group collected 2 samples at the same location, a total of 60 coal samples, the sampling method of coal samples was carried out in accordance with Section 2.2, and the same sampling method was adopted for the same group of coal samples at the same location) The coal sample collection information is shown in (Table 5). For each group of 2 coal samples, one coal sample was crushed by the “crushing method”, and the other coal sample was subjected to the “fracturing method” for the ƒ determination experiment.
A
B
C
Index
1
2
3
4
ei
1
A1
B1
C1
1
0.518
2
A1
B2
C2
2
0.447
3
A1
B3
C3
3
0.356
4
A2
B1
C2
3
0.331
5
A2
B2
C3
1
0.247
6
A2
B3
C1
2
0.598
7
A3
B1
C3
2
0.078
8
A3
B2
C1
3
0.526
9
A3
B3
C2
1
0.512
1.321
0.927
1.642
1.277
1.176
1.22
1.29
1.123
1.116
1.466
0.681
1.213
Preferred solution
A3 B1 C3
Table 5: Orthogonal test results of coal sample pulverization.
Select 1~20 sets of coal samples in Table 5, respectively, to determine the smashing value of the smashing method and the pulverizing coal sample by the “crushing method”. The relationship between the particle size distribution of the coal sample after the “crushing method” and the firmness coefficient was analyzed. According to the optimum pulverization parameters determined by the orthogonal test in Section 3.2, the pulverization of 20 coal samples was carried out, and the proportion of coal particles below 0.5 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm and 3 mm after pulverization of different coal samples was measured and recorded. According to the enthalpy of the coal sample consistent coefficient measured by the “crushing method”, the relationship between the mass ratio of different sizes of coal dust and the coal sample enthalpy after the above 20 sets of coal sample pulverizations is analyzed is shown in Figure 7.
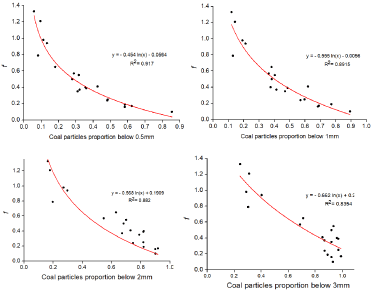
Figure 7: The fitting line of the coal particles quality fraction at different particle size. (a) below 0.5 mm; (b) below 1 mm; (c) below 2 mm; (d) below 3 mm.
Figure 7 shows that 20 pieces of coal samples are pulverized under the optimal pulverization scheme, and the mass fraction of the coal particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm and 3 mm is determined by the corresponding “crushing method”. The logarithmic fitting relationship is shown between the ƒ values. Among them, the correlation between the mass fraction of coal dust with the particle size below 0.5 mm and the ƒ value is the highest, and the correlation coefficient R2 is 91.7%. With the increase in the coal particle size, the degree of data fitting gradually decreases.
The selected 20 sets of coal samples are from the main coal producing areas of Guizhou, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Henan, Xinjiang, Yunnan, etc. and have strong representativeness. Table 5 shows that the f value distributes at 0.1 ~1.33, the span is larger, and the distribution is more uniform. Therefore, the selected coal samples can reflect the characteristics of coal seams in China’s major coal-producing areas. Experiments based on this law are also highly representative and versatile.
Therefore, under the premise of the determined pulverization measuring device and the optimal pulverization parameters established by the orthogonal test, the relationship model between the mass fraction of the coal particles and the ƒ value of particle size below 0.5 mm after coal sample pulverization can be established as follows:
ƒ = -0.454*ln(x)-0.0564 (1) In the formula, x is the mass fraction of coal dust with a particle size of 0.5 mm or less after pulverization of the coal sample, %.
Model verification
To examine the applicability, versatility and accuracy of the enthalpy determination model (1) determined in section 4, for the remaining 10 sets of coal samples from the 21st to the 30th groups in (Table 5), the coal sample pulverization and the “crushing method” ƒ value are determined according to the same pulverization experimental conditions determined in sections 3.3 and 3.4. The results of the calculation of the formula (1) are compared with the results of the “crushing method” enthalpy measurement, as shown in (Table 6), and the comparison curve is shown in (Figure 8). f value curve of the pulverization method and the “crushing method”
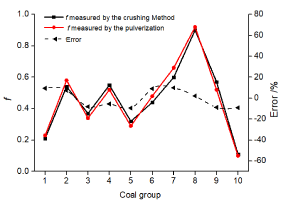
Figure 8: ƒ value curve of the pulverization method and the “crushing
method”.
Coal sample number
Mine name
Province
Coal seam number
f value
Quality ratio of coal particles under 0.5 mm /%
1
Xin yuan
Yunnan
C9
0.19
58.27
2
Gao Po
Guizhou
M5
0.17
62.20
3
San Sheng Si
Sichuan
K1
0.25
48.40
4
Xu Sheng
Shanxi
4#
0.24
48.13
5
Fa Er
Guizhou
1#
0.37
32.13
6
Xin Yuan
Shanxi
9#
0.41
42.47
7
Xin Jing
Shanxi
6#
0.39
35.93
8
Gu Qiao
Anhui
13-1#
0.55
31.67
9
Xing Long
Guizhou
M16
0.50
27.87
10
Hong Si
Ningxia
4#
0.57
28.80
11
Bai Tuyao
Xinjiang
B1
0.79
8.13
12
Zhong Fu
Xinjiang
B4
1.33
5.80
13
Liu Jiaba
Guizhou
M30
1.21
9.50
14
Hong Ling
Henan
21
0.16
58.17
15
Datong first
Chongqing
M8
0.40
35.44
16
Xin Feng
Henan
15
0.35
31.00
17
Hong Si
Xinjiang
9-2#
0.65
18.00
18
Jin Jitan
Shanxi
2-2#
0.94
13.32
19
Fu Quan
Inner Mongolia
3#
0.10
85.43
20
Xin Yuan
Yunnan
C5
0.98
11.20
21
Tian Chi
Shanxi
15#
0.21
53.73
22
Xin Qian
Henan
22
0.54
24.80
23
Tian Chi
Shanxi
15#
0.37
41.50
24
Ying Jiao
Guizhou
M16
0.55
27.90
25
Tong Hua
Chongqing
K3
0.32
46.30
26
Tong De
Shanxi
5#
0.44
30.60
27
Jian Ye
Henan
21
0.60
20.45
28
Xinji Second
Anhui
8#
0.90
11.60
29
Da Tianba
Guizhou
C8
0.57
27.80
30
Ping Yu
Henan
21
0.11
70.90
Table 6: Coal sample collection information and experimental data list.
Number
Quality proportion of coal particles below 0.5 mm/%
ƒ value calculated by equation (1)
ƒ value calculated by mashing
Deviation
%
1
53.73
0.23
0.21
9.52
2
24.80
0.58
0.54
7.41
3
41.50
0.34
0.37
-8.11
4
27.90
0.52
0.55
-5.45
5
46.30
0.29
0.32
-9.38
6
30.60
0.48
0.44
9.09
7
20.45
0.66
0.60
10
8
11.60
0.92
0.90
2.22
9
27.80
0.52
0.57
-8.77
10
70.90
0.10
0.11
-9.09
Table 7: Comparison of the f value between the pulverization method relation model and the “crushing method”.
Table 6 and Figure 8 show that the calculated value of the consistent coefficient based on the pulverization method is very close to the ƒ value measured by the “crushing method”, and the absolute value of the difference is controlled within the range of 0 ~ 0.06. The absolute value of the error is controlled within 0~10%, and the average error is 7.9%, which can meet the needs of engineering measurement. Moreover, the 10 sets of coal samples used in the verification experiment were collected in 10 coal mines in 6 different coal-producing areas such as Yunnan, Shanxi, Henan, Guizhou, Chongqing and Anhui province, which are regional and representative. Therefore, the applicability and versatility of the enthalpy measurement model (1) are also explained [38-39]. From the above analysis, we can see that the model of the relationship between the mass fraction of coal particles and the f value of the particle size below 0.5 mm after the pulverization of the coal sample is reasonable and accurate and has strong versatility and representativeness. At the same time, it is feasible to quickly determine the consistent coefficient of coal samples based on the pulverization method, which can meet the actual measurement needs.
Application prospects
This experiment was carried out in the laboratory, which provided a new method for the rapid determination of the consistent coefficient f of coal, which laid the experimental foundation for the realization and application of the rapid determination of the ƒ value in a coal mine. On this basis, the relevant design of the measuring device can be carried out, and the down hole rapid measurement of the ƒ value can be realized. For example, the pulverization measuring device (Figure 1) is designed for explosion protection in accordance with the relevant requirements for the use of underground coal mines. Or change the power supply mode to mechanical drive mode, such as replacing the motor in the pulverizing device with a pneumatic motor and use the mine pressure to provide drive energy. As shown in (Figure 9), the measurement of the ƒ value in the underground coal mine environment can be achieved.
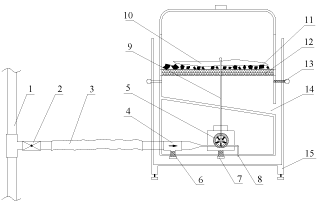
Figure 9: Schematic diagram of the pulverization measuring device (1. air
duct; 2. ball valve; 3. hose; 4. voltage regulator; 5. air motor; 6. regulator valve
adjustment knob; 7. pneumatic motor speed control knob; 8. exhaust port; 9.
motor shaft; 10. crushing blade; 11. coal sample to be crushed; 12. 35 mesh
screen; 13. tank tilt adjuster; 14. drainage port; 15. adjustable base).
Figure 9 Schematic diagram of the pulverization measuring device (1. air duct; 2. ball valve; 3. hose; 4. voltage regulator; 5. air motor; 6. regulator valve adjustment knob; 7. pneumatic motor speed control knob; 8. exhaust port; 9. motor shaft; 10. crushing blade; 11. coal sample to be crushed; 12. 35 mesh screen; 13. tank tilt adjuster; 14. drainage port; 15. adjustable base)
The rapid measurement of the f-value down hole can not only quickly grasp the ƒ value as one of the four individual indicators for judging the outstanding risk of the coal seam but also has other engineering significance. For example, in the application of noncontact dynamic disaster acoustic emission prediction technology, Wen et al. [40] found the attenuation coefficient a of the acoustic emission signal in the coal-rock medium is exponentially related to the value of the ƒ. The larger the ƒ, the smaller the attenuation of the acoustic emission signal propagation and the farther the propagation. Therefore, if the rapid determination of the ƒ value can be achieved, the physical and mechanical properties of the coal-rock layer in the area to be monitored can be preliminarily grasped, and the reasonable installation of the acoustic emission sensor and the effective identification of the signal can be guided to improve the prediction accuracy of the coal-rock dynamic disaster.
Conclusion
The accurate and rapid determination of the consistent coefficient of coal plays an important role in the prevention of coal and gas outbursts. According to the actual needs, this paper proposes a new method for determining the firmness coefficient, which is verified, and the main conclusions are as follows:
(1) A method for rapid determination of the coal consistent coefficient ƒ based on the pulverization method is proposed. The feasibility of the determination principle is verified by experimental research. The specific determination steps and calculation methods are given. The method is simple and fast. The characteristics simplify the measurement process of determining the ƒ by the current “crushing method” and provide a new method for realizing the direct and rapid determination of the coal robustness coefficient.
(2) The optimal pulverization scheme of the coal sample pulverization experiment is preferably established by the orthogonal test method, and the optimal value of the pulverization parameters is determined: the initial particle size of the coal sample is 6~7 mm, the pulverizer speed is 8000 r/min, and the coal sample mass is 150 g, the pulverization time is 10 s, and the stability of the coal sample pulverization process under this pulverization scheme was verified by experiments.
(3) By studying the correspondence between the mass fraction of coal particles with different particle sizes after pulverization of coal samples and the ƒ value, the relationship model between the mass fraction x and the ƒ value of coal particles with a particle size below 0.5 mm after coal sample pulverization is established: ƒ = -0.454*ln(x)- 0.0564, and the accuracy, versatility and representativeness of the computational model were verified experimentally.
References
- Wei Y, Wang K, Li H. Prediction of the coal and gas outburst by neural network// International Symposium on Computational Intelligence & Design. 2009.
- Zhao FJ, Li XB. Theoretical analysis and experiments of rock fragmentation under coupling dynamic and static loads. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering. 2005; 24(8):1315-1320.
- Cai CG, Xiong YX. Theoretical and experimental study on crushing energy of outburst-proneness coal. Journal of China Coal Society. 2005; 30(1): 63-69.
- Tang SH, Zhu BC, Yan ZF. Effect of crustal stress on hydraulic fracturing in coalbed methane wells. Journal of China Coal Society. 2011; 36(1): 65-69.
- Guo CY, Xian XF, Wu XH. The relationship among rock crushing energy, the protodyakonov coefficient and rock strength. 2008; 30(6): 28-31.
- Bi WQ, Jiang CL, Wang ZL. Accuracy and stability study of determining firmness coefficient of coal (rocks). 2012; 43: (8): 41-44.
- Luo J, Huang G, Zhang L. Micro shape of coal particle and crushing energy. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology. 2018; 28(6): 1009- 1014.
- Wang B, Sun FJ, Tang DZ. Hydrological control rule on coalbed methane enrichment and high yield in FZ Block of Qinshui Basin. Fuel. 2015; 140: 568-577.
- Li JG, Liu H. Application conditions on acoustic emission (AE) technique monitoring coal and rock dynamic disasters in mines. Advanced Materials Research. 2012; 413(9): 6.
- Hord S M, Roy P. Rrock resistant coefficient in tunnel based on Lade-Duncan failure criterion. Journal of China Coal Society. 2013; 38(6): 982-986.
- Fan L, Liu S. A conceptual model to characterize and model compaction behavior and permeability evolution of broken rock mass in coal mine gobs. International Journal of Coal Geology. 2017; 172: 60-70.
- Mokhov A V. A rock mass permeability model within the subsidence zone in workings of coal fields. Doklady Earth Sciences. 2017; 473(2): 390-393.
- Dong Y, Zhao Y, Hu Y. The constitute law of gas seepage in rock fractures undergoing three-dimensional stress. Transport in Porous Media. 2006; 63(3): 463-472.
- Whittles DN, Kingman S, Lowndes I. Laboratory and numerical investigation into the characteristics of rock fragmentation. Miner Eng. 2006; 19(14): 1418- 29.
- Sun R, Liu G, Zheng L. Characteristics of coal quality and their relationship with coal-forming environment: A case study from the Zhuji exploration area, Huainan coalfield, Anhui, China. Energy. 2010; 35(1): 423-435.
- Yao Y, Liu D, Huang W. Influences of igneous intrusions on coal rank, coal quality and adsorption capacity in Hongyang, Handan and Huaibei coalfields, North China. International Journal of Coal Geology. 2011; 88(2): 135-146.
- Magnus Bengtsson C, Evertsson Magnus. Measuring characteristics of aggregate material from vertical shaft impact crushers. Miner Eng. 2006; 19(15): 1479-1486.
- Chen Z, Liu J, Pan Z. Influence of the effective stress coefficient and sorptioninduced strain on the evolution of coal permeability: Model development and analysis. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control. 2012; 8(5): 101- 110.
- Devi KS, Roy B, Patra P. Combined effects of directional compaction, non- Darcy flow and anisotropic swelling on coal seam gas extraction. International Journal of Coal Geology. 2013; 109(2): 1-14.
- Ward CR, Crouch A, Cohen DR. Identification of potential for methane ignition by rock friction in Australian coal mines. International Journal of Coal Geology. 2001; 45(2): 91-103.
- Zhao T, Yin Y, Xiao F. Rockburst disaster prediction of isolated coal pillar by electromagnetic radiation based on frictional effect. The Scientific World Journal. 2014; (3): 814050.
- Bai XF, Wang ZW, Liu KM. Effect of coal size and different size grade coal petrographtic feature on coking coal property. Clean Coal Technology. 1999; 5(4): 47–51.
- Liu S, Shen J, Zhou HM. Study on occurrence status characteristics of trace elements in imported indonesia coals of shanghai port using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Rock & Mineral Analysis. 2015(4): 436–441.
- Zhou XH, Xu K, Qi QJ. Fuzzy clustering analysis and application of the degree of difficulty of coal seam water injection. Advanced Materials Research. 2014; (45): 939–945.
- Yao X, Cheng G, Shi B. Analysis on gas extraction drilling instability and control method of pore–forming in deep surrounding–rock with weak structure. Journal of China Coal Society. 2010; 35(12): 2073–2081.
- Yang Z, Dai S, Li X. Stress–electricity–thermal coupled model of composite coal–rock in deformation and fracture under load. Journal of China Coal Society. 2016; 41(11): 2764–2772.
- Zhang C, Li XH, Yao Q. Orthogonal experimental research on instability factor of roadway with coal–rock interbeded roof. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology. 2015; 44(2): 220–226.
- Ward CR, Crouch A, Cohen DR. Identification of potential for methane ignition by rock friction in Australian coal mines. International Journal of Coal Geology. 2001; 45(2): 91–103.
- Wilk R, Zielinski Z, Kòlarz W. Determination of overall burning rate coefficient of coal–oil droplet mixtures. Fuel. 1990; 69(1): 110–116.
- Aboyade AO, Gorgens JF, Carrier M. Thermogravimetric study of the pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of coal blends with corn and sugarcane residues. Fuel Processing Technology. 2013, 106(2): 310–320.
- Yu S, Wei YM, Guo H. Carbon emission coefficient measurement of the coalto– power energy chain in China. Applied Energy. 2014; 114(2): 290–300.
- Lu J, Meng X, Wang Y. Prediction of coal seam details and mining safety using multicomponent seismic data: A case history from China. Geophysics. 2016; 81(5): B149–B165.
- Wu X. Study on the influence of crack anti–friction mechanism of coal containing gas on the process of disaster–causing fracture. Applied Mechanics & Materials. 2014; 6: 501–504.
- Hu GZ, Zhu YR, Li ZQ. Experimental study on desorption enhancing of methane in coal mass using a controlled microwave field. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering. 2017; 36(4): 874–880.
- Zhao LJ, Liu XN, Ma LW. Optimization research on shearer’s kinematic parameters based on economical cutting. Journal of China Coal Society. 2013; 38(8): 1490–1495.
- Gao F, Xu AB, Zhou FB. Research on the coal and rock damage and gas permeability in the protective seams mining. Journal of China Coal Society. 2011; 36(12): 1979–1984.
- Zhang Z, Guo R, Lin W. A Classification model for rock mass quality of the roof and floor of productive coal seams during coal geological exploration. Journal of Basic Science & Engineering. 2016.
- Moldowan JM, Dahl JE, Chen Z. Burgeoning technologies contribute to understanding of oil and gas habitat. Geochmica Et Cosmochimica Acta. 2005; 69(10).
- Yi X, Feng G, Teng T. Effect of Gas Pressure on Rock Burst Proneness Indexes and Energy Dissipation of Coal Samples[J]. Geotechnical & Geological Engineering. 2016; 34(6): 1–12.
- Preliminary study on the application conditions of acoustic emission monitoring dynamic disasters in coal and rock. Journal of China Coal Society. 2011; 36(2): 278–282.
