Abstract
Marine cloud brightening with a sub-micron spray of filtered sea water can exploit the Twomey effect to enhance planetary cooling. Several previous climate model results show that it can also affect precipitation in both directions in different places. Modulating the climate model settings for the concentration of cloud condensation nuclei with separate coded sequences in a number of spray regions round the world and correlating each sequence with the resulting weather patterns in observing stations round the world can give an everywhereto- everywhere transfer function of spray from each region to each observing station. The short life of spray allows the best choices of spray regions and seasons. Spray patterns can be modified tactically to suit real-time weather observations.
Keywords: Climate model; Cloud condensation nuclei; Pseudo-random sequence; Marine cloud brightening; Twomey effect; Albedo; Solar radiation management; Stratospheric Sulphur; GeoMIP
Background
Most readers of this special issue will already be aware of the progress of our world leaders in the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, the rate of Arctic ice loss and the resulting possibility of increased methane emissions. Many will be familiar with the physics of the Twomey effect on cloud brightness [1,2] and the proposal by Latham [3,4] for its exploitation to reduce the effects of global warming.
A key feature of marine cloud brightening is that it allows control of the magnitude, place and time of the spraying. Plans can be quickly adjusted with information from real-time observations giving the option of a tactical response. This paper suggests a way to use climate models to identify and quantify both beneficial and adverse side-effects of marine cloud brightening. We want to produce an everywhere-to-everywhere transfer-function of the relationship between spray quantity, place and time as they affect temperature, precipitation, polar ice, snow cover and vegetation, using several leading climate models in parallel. This should especially show the times and places at which spraying should NOT be done.
The technique involves changing model settings for the concentration of condensation nuclei at many spray regions round the world according to separate, individual coded sequences unique to each region and correlating each of these sequences with model results at observing stations anywhere.
A first test on a set of 16 artificial changes with different magnitudes to a real 20-year temperature record showed that the magnitude of each change could be detected to 1% or 2% of the standard deviation. This is better than many thermometers. Confidence has been increased by a PhD project carried out by Ben Parkes at Leeds, who has shown that the effects of marine cloud brightening on precipitation are bidirectional.
The technique may let us steer towards beneficial climate patterns if only the world community can agree what these are. The differences between climate models may point to general model improvements, for which there is plenty of room. As well as humanitarian benefits the project may lead to better understanding of atmospheric physics and teleconnections.
Previous Work on Side Effects
Elementary physics would predict that, because of the increase in vapour pressure of warmer sea surfaces, global warming would also increase evaporation and subsequent precipitation. Caldeira and Wood [5] showed that if geoengineering with tropospheric sulphur was used to cancel a thermal increase it would over-compensate the increase in precipitation.
The immediate effect of marine cloud brightening is the reduction of sea-surface temperatures and in turn a reduction in the rate of evaporation and an increase in condensation from vapour to liquid. However marine cloud brightening also reduces the size of drops of marine clouds. The production of rain is complicated but one of the requirements is large drops falling through and coalescing with smaller ones. If we reduce drop size the immediate effect is to reduce rainfall over the sea which would leave more to fall over land. Furthermore the higher temperature difference between land and sea will mean stronger monsoon winds to transport the air mass ashore. Stronger winds mean more spray from breaking waves and more air bubbles in foam.
Bala and Caldeira [6] studied the effect of widespread and continuous marine cloud brightening in the Indian sub-continent where changed precipitation can be a matter of life and death [7]. They found that it produced a smaller reduction in precipitation effect than stratospheric sulphur and that this was more than offset by a lower evaporation rate leaving an increase of river run-off.
One of the early attempts at the identification of side effects of marine cloud brightening was in 2009 by Jones, Haywood and Boucher of the Hadley Centre [7]. They picked three regions representing only 3.3% of the world ocean area and raised the concentration of cloud condensation nuclei to 375 per cubic centimeter from initial values of 50 to 300. The regions were off California, off Peru and off Angola/ Namibia. In Figure 1 top left these are labelled NP for North Pacific, SP for South Pacific and SA for South Atlantic. These areas usually have good conditions for cloud cover and solar input. Parts close to the coast have rather high nuclei concentrations. They are good but by no means the only suitable sites for cloud spraying. The increased nuclei concentration was held steady regardless of summer/winter, monsoons or the phase of the el Niño Southern oscillation. The resulting global cooling for the separate regions was 0.45, 0.52 and 0.34 watts per square meter giving a mean annual total of 1.31 watts per square meter. However if all of the regions were sprayed together all of the time the 3.3% of ocean area would cool a little less, 0.97 watts per square meter. Even the lower amount of cooling would be a substantial fraction of the widely-accepted increase of 1.6 watts per square meter since preindustrial times.
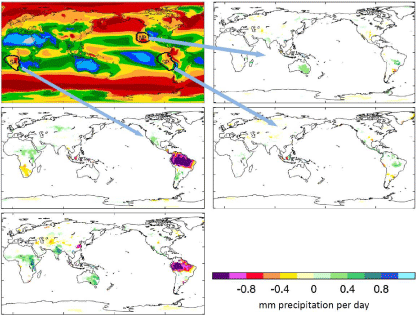
Figure 1: The separate effects of the spray regions in Jones Haywood and Boucher 2009 reference [7].
Present global climate models are less accurate for precipitation, ice and snow than for temperature. They cannot predict cloud cover, hurricanes or flood events for more than a few days ahead. Climate change with no geo-engineering is already producing extreme floods in Pakistan and Queensland with droughts in South Australia, the Horn of Africa and the United States.
The Jones, Hayward and Boucher results show that albedo control can both increase and reduce precipitation far from the spray source, even in the opposite hemisphere. Spray from California (NP) shown in the top right of Figure 1 can nearly double rainfall in South Australia. Spray off Peru give a small increase in Brazil. Spray off Angola/Namibia (SA), lower left gives a useful increase in Ethiopia, Sudan, Oman and the Horn of Africa. But most attention was given to the 15% reduction of precipitation over the Amazon.
Perhaps Brazilians watching recent television footage of dying children in Ethiopia and Sudan would be glad to have their own rainfall reduced to 2000mm a year when necessary. If all three regions in Figure 1 spray simultaneously and continuously we get the result at the lower left. The combination is less than the sum of the parts. The reduction in the Amazon is there but less marked. There are useful increases in Australia and in the Horn of Africa. The reduction in precipitation in South West Africa caused by the South Atlantic spray region has vanished. Jones et al. did not test seasonal variations, adjustment relative to the monsoons or the phase of the el Niño/la Niña cycle.
As part of the GeoMIP experiment Niemeier et al. [8] compared the effects on precipitation of three distinct methods of solar radiation management. The methods were attenuation of the solar energy flux in space, stratospheric sulphur and marine cloud brightening. Salt was injected continuously into the troposphere but only between latitudes +30 and -30 degrees regardless of cloud or clear sky conditions. All methods were applied at a rate to offset the increasing thermal effects of the RCP 4.5 rise in greenhouse gases (Figure 2).
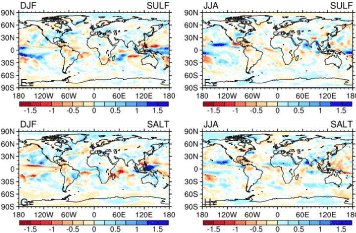
Figure 2: From Neimeier et al. [8]. Marine cloud brightening reduces precipitation, shown in red, most strongly over the sea but also gives useful increases, blue,
in dry regions on land.
Results of marine cloud brightening on precipitation, Figure 3, differed from the other two methods. While there were global reductions in precipitation they were strongest over the sea while there were useful increases in June, July and August over the Sahel and in Australia in December, January and February.
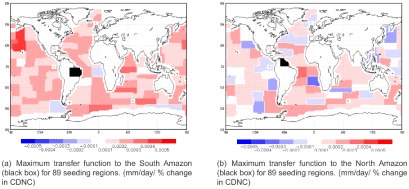
Figure 3: An example of the effect of all spray regions on two places in the Amazon. Drying from spray in the South Atlantic as predicted by the Hadley Centre
is evident but could easily be countered by spray from many other regions, especially from south of the Aleutians. Indeed, notwithstanding Figure 1, drying in the
Amazon seems to be an atypical result of marine cloud brightening.
More recent work by Gadian and Parkes at Leeds used the coded modulation of the nuclei concentration of 89 spray sources of roughly equal area round all the oceans. They then correlated the individual sequences with the resulting weather records round the world. The modulation was done by multiplying or dividing initial nuclei concentration values by a factor chosen initially as 1.5. Because of the logarithmic behaviour of the Twomey equation this alternation should have had a low overall effect.
The results in Figure 3 show that, as well as the spray sources used by Jones et al., there are many other spray sources which will either increase or reduce precipitation in the Amazon. The two regions in the Amazon basin are shown black. Red shows sites which would increase precipitation at the black site and blue shows a reduction. The Amazon increases from the red spray sources off California and Peru are in agreement with the 2009 Hadley Centre result. The strongest blue in (b) off Namibia and the weaker blue off Angola in (a) are also in agreement. But the great majority of spray sites, particularly the one in (a) south of the Aleutians and (b) off Recife, show increases in the Amazon precipitation. The results of this project will be maps like these for every observing station of interest. This could amount to many hundreds of maps depending on the resolving power of the climate models.
The black circles in Figure 4 show the scatter of precipitation results from 8 runs with different coded sequences from 89 spray sites on one place. Blue bars show standard deviations. A low scatter implies reliable operation of the technique but is not universal. While the general trend is towards slightly more precipitation, there are changes in both directions with less scatter in the wetter direction.
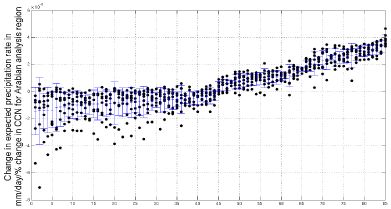
Figure 4: If the results of perturbations from separate runs with different code sequences show a large scatter we can deduce that the technique is not working
well for that source and observing station.
It is also possible to show the transfer function of each spray site on target regions on land all round the world. Figure 5 shows a sweep of spray sources along the east sides of the North and South Atlantic. There are alternating effects in South America and Australia. Spraying between the English Channel and Labrador has little effect in the Amazon or Australia but the next region south increases rain in both. The Atlantic coast off Mauritania further increases Amazon precipitation, gives weaker precipitation in eastern Australia but dries the west. A block from Liberia to Nigeria has little effect on either the Amazon or Australia but is close to where hurricanes begin. Angola confirms the Hadley center drying of the south Amazon but not the north. Namibia reverses this. Spray off the Cape of Good Hope increases rainfall in both regions of the Amazon but the effect fades as we spray from further south. Spray further south increases rain in the Indian sub-continent and Japan.
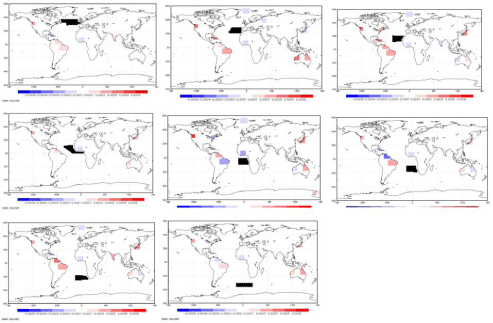
Figure 5: A sweep of spray regions along the east side of North and South Atlantic show cyclical effects on precipitation in South America and Australia. Ben Parkes’
work provides 89 such maps.
The maximum swings are 0.0006mm per day for each percentage variation of the initial nuclei concentration. This means that for the 100% nuclei increase needed to give a reflectivity increase of 0.057, the annual precipitation change would be 0.0006 x 365 x 100 mm = 21.9mm per year. This is much smaller than precipitation changes indicated by the Hadley Centre but the size of individual spray regions is about one third. The Hadley Centre increase from their lowest concentration of 50 per cubic centimeter in a clean spray region raised to 375 is a much stronger stimulus by a factor of 15 and, according to Twomey, would give a reflectivity increase of 0.168. The offshore edge of the Hadley test regions would have presented an impossibly high slope of nuclei concentration. Perhaps climate systems react just as badly to sharp changes as engineering components under stress. The full Parkes thesis can be downloaded from [9].
Suggestions for Future Work
Because of the poor representation of precipitation in global climate models and in the absence of any better prediction method, we want to use a multiple approach with at least five different climate models driven by different research groups attempting the same jointly agreed objectives but with some freedom to follow interesting results. Suggestions for the central questions which should be tackled by all groups are as follows. They must be debated and approved but then adhered to.
Run duration
This project will be greedy for computer time. Statistical theory suggests that the scatter of model predictions will fall with the square root of the run-time of an experiment. We have to decide the difficult balance between computer cost and precision of results. It might help to look at initial results and then take a decision about whether a run should be extended. It may be possible to use idle computer time using the methods developed for the search for extra-terrestrial intelligence, SETI.
Correlation lag
The changes to weather are not immediate so we should include a time lag between spray release and the autocorrelation period. There may also be several time lags with different durations. We can make good estimates by choosing a plausible guess for the response period, driving all or a subset of spray sources in unison to add a sinusoidal component at that period to the nuclei concentration, running the climate model, subtracting the mean offset at each observing station round the world and multiplying the mean response by the sine and cosine of the nuclei variation signal. This will produce two offset means. The tangent of the phase lag of the response at each observing station will be the cosine offset divided by the sine offset. Repeating the process for various periods will allow the choice of correlation lag for each observing station. The amplitude and phase of the response as a function of period will give an interesting insight into important climate system processes but does not allow the separation of effects from individual spray sources as is possible with coded modulation.
Coded modulation sequences
Random number generators can, by chance, sometimes produce short groups with abnormal auto-correlation. Andrew Jarvis at Lancaster can give ‘ultra-random’ sequences without these. When God made random sequences He made a great many so we can all use different ones but it will be interesting to compare results of exactly the same sets of sequences in different models.
Change-over period
The encoding sequence can be seen as a series of coin tosses. Each toss decides whether the spray/not spray mode should be reversed or left alone. If the coin is tossed too frequently then the weather system will not have time to respond. But, if the intervals are too long, the length of the computer run needed to get a reasonably low scatter will be expensive. Perhaps initially the very shortest change-over period should be about the time for which reliable forecasts can be made, perhaps ten days. At each possible change-over period there will be a 50% chance of no change and a 25% chance of getting three ‘no-change’ events in a row and so on. Carbon emissions vary over a weekly cycle and the release of decay gases and di-methyl sulphide from seaweed can be related to the 28 day tidal cycle so we must avoid being phase-locked to these periods. Parkes used a change-over period of 10 days for computational efficiency and a case can be made for 20 days. We should later extend the changeover period but not to the point where too many changes spread across a monsoon period.
Monsoon season
All the climate model work so far has used continuous spray through the year. It might occur even to a naïve engineering person that the monsoon seasons could possibly have an effect on patterns of precipitation and evaporation. This means that we should do separate correlations and calculate separate transfer functions according to the monsoon phase. If the technique shows promise and computing time is available we may be able to resolve transfer functions down to monthly levels provided that we can get resources to allow the use of high resolution models.
Spray amplitude
The susceptibility of an ocean spray region, defined as albedo change per drop number, is a function of low cloud, clean air, incoming solar energy and perhaps wind to drive spray vessels and disperse spray. Large spray volumes in what initially appear to be regions of high susceptibility will reduce that susceptibility. A lower dose over a wider region will be more effective. Multiplying and dividing the initial nuclei concentration value by 1.5 was quite small but we do not know that it is the best choice. A sweep over multiplying and dividing amplitudes from 1.25, 1.5, 2, 3 and 4.5 will help us choose the best spray amplitude(s) for later work.
Spray asymmetry
The Twomey results can be condensed into an equation which says that the change in reflectivity is 1/12 of the natural log of the ratio of nuclei concentration. The long term led to the decision to multiply and divide initial nuclei concentration values by a constant rather than by the addition of some chosen amount. It was intended to cancel the mean thermal effects in other regions. However it may be that the multiplier should not be exactly equal to the divider. We need to establish the best numbers to use for the lowest external interference so as to minimize interference between regions. A possible method might be to use results of the sinusoidal modulation. Any departure from a sinusoidal wave form produces harmonics which can be detected by multiplying the signal minus its mean by the sine and cosine of 2, 3, 4 etc. times the fundamental.
Spray concentration profile
While time constraints forced Parkes to use blocks of spray with sharp edges is would be more realistic to have smoother variations of nuclei concentration, perhaps with the bell-shaped Gaussian concentration.
Number and position of spray sources
The Parkes choice of 89 spray regions was not made with any great confidence. We wanted at least two across the narrow section of the Atlantic. Parkes started with equal areas but then divided them round the Caribbean and either side of Iceland because of the current patterns. Some climate models show strange alterations either side of the equator in the Pacific. There is no need for spray regions to have equal areas provided that we can give each an appropriate weighting. There is no need for everyone to use the same regions provided that research result maps (discussed later) can give a common presentation. Individual selections should be encouraged and results merged to avoid blocky results.
The production of seasonal and monthly susceptibility maps
Regions might be merged if there is little difference between their susceptibilities or divided if differences between adjacent neighbours are large provided that the spray regions are large enough to produce a consistent forcing over several grid points.
Region grouping
It is well known that climate patterns all over the world are affected by the cycle of el Niño/la Niña temperature differences across the South Pacific, sometimes with disastrous outcomes. It will be interesting to drive the cloud nuclei concentration differentially either side of the Pacific with code sequences of each side in unison in a number of coherent ways. Two obvious ones are first an equal 50/50 east/west split with a sharp divide, secondly a linear ramp with concentration depending on distance either side of the midline and thirdly a blend of positive and negative Gaussian distributions. Other Boolean combinations of spray regions can be chosen but with the risk that this could lead to a combinatorial explosion of possibilities and so we need careful planning.
Tactical spraying in response to observations
There is no need for spray rates to be preordained and fixed for a whole experiment lasting many years. For example if we see that surface temperatures in the Pacific are forming an el Niño or la Niña pattern and we know the cooling power of world spray sites, even ones far from the Pacific, we can drive them so as to increase or reduce the Southern Oscillation. The spray can be in phase with the temperature anomaly or its rate of change or even at some other phase angle.
A force opposing change of position of a system, i.e. a spring, will increase its oscillation frequency. Control engineers know that very small amounts of damping (a force opposing velocity) or its opposite, can have very large effects on the growth or decay of oscillations. We like error sensors and actuators with a high frequency-response and low phase-shift. Tropospheric cloud albedo control has an attractively rapid response - a few days compared with stratospheric sulphur at low latitudes which is about two years. With sufficiently high resolution we may also detect early signs of hurricane formation. The Francis temperature gradient between equator and poles and the orientation and position of the jet-stream waves might be a powerful indicator.
Map projections
The site http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/MapProjections/ projections.html gives a useful selection and explanation of map projections. All projections of a solid globe to a flat plane involve some distortions but we can choose between distorting area, direction, shape or distances at various places in the map. The Mercator projection is very common but produces gross distortion of east/west distances and areas at the high latitudes which are now seen to be of very great importance to climate change. For polar areas the Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection looks best. We can tilt this projection in other directions so that several images can show the whole world with acceptably low distortion. The obvious starting one would be six Lambert azimuthal views, two from the poles and four from the equator at longitudes of 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees and an option to set any other latitude and longitude for any other view. It can be very useful to have a transparent layer of one parameter laid over another but this will need coordination of page layout. Six 90mm diameter circles on a 100mm pitch can fit neatly on one page of A4 or letter page with room for arrows to adjacent balloons. If necessary we can fit 12 on an A3. A single 180 mm circle can be used to show finer detail. The modelling teams must consider the question carefully, come to a joint view and then stick to the common decision and page scale. We can then combine results and plot contradictions between them.
Solid modelling packages (e.g. SolidWorks) are increasingly common for engineering design and several offer free viewing software to let customers spin images of engineering components about any axis. A spinning image can give a good presentation of complex three-dimensional shapes. It should be possible to modify software to give surface colours with 10 saturation levels and text to regions of a spinning sphere.
Naming of sea areas
We must make it easy for people to know which of many possible spray regions are being discussed even if they are not the same as the original Parkes 89. One way is to pick an agreed spot at the centroid of an ocean and then give the bearing and distance of the centroid of the spray region under discussion in terms of the bearing and distance from the ocean centroid. Two digits are enough to identify runways at airports and most regions will be larger than 100 kilometers or a few model grid points so, for example, we could use a description such as South Pacific 18, 30 for a spray region 3000 kilometers due south of the ocean centroid.
Mapping contours
Result maps need to show the magnitude and slope of at least temperature, precipitation, evaporation ice and snow cover. While a continuous rainbow spectrum looks beautiful and gives a superficial impression of work done it is almost useless at providing any numerical information beyond the position of a peak and the direction of a gradient. There are some meteorological result maps which have colour allocations that are particularly unhelpful, for example the one in Figure 6.
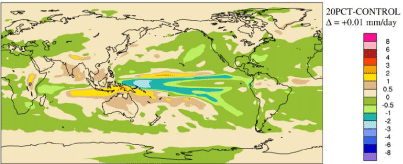
Figure 6: How not to display the results of a climate model. No names no pack-drill. The lead author of the paper from which this figure was taken agrees with me
but was unable to challenge official policy. Result format for this project may be dictatorial but will be more intelligent.
The area of ‘no change’ is between the lighter buff colour and the darker green. It covers a large fraction of the map. The polarity of the contour gradient is not obvious where light green moves to cyan or the darker buff moves to orange. Light green is a stronger effect than dark green. Numbers on the colour code bar refer to the borders not the middle of contours. Readers may confuse this map for precipitation with another map for temperature which uses the same colour set.
The right presentation of results can reveal the reasons for the most peculiar phenomena. We must make it as quick and as easy as possible for lazy, tired, non-technical readers to see effects with the minimum of mental decoding effort even when they are looking at a great many different maps for different teams.
The first requirement is that areas with effects that are below the level of statistical significance or the middle of the range should be white. Either side of this region there should be just two colours with increasing saturation. Red and blue would be intuitive for temperature with green and brown for river runoff. The male human eye can reliably distinguish 10 saturation levels provided regions are in contact with sharp edges. (Females have higher discrimination.) This gives a range of 20 steps (more than most result maps) plus a white central zero for the mean or the anomaly reference. The steps give an obvious direction of gradients. Adults, babies, birds and many animals can count up to five in an instant ‘analogue’ way. If we have thin black contour lines between the lowest five saturation steps and thin white lines between each of the top five colours we can avoid getting lost. We can also include black or white text numbers to show the contour value and total area of the contour region. An example is shown in Figure 7.
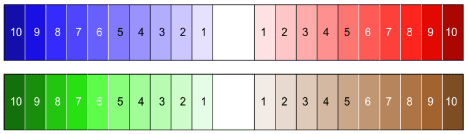
Figure 7: Suggested colour contours and boundary makings.
Astronomers developed a very powerful technique to detect changes in the position or brightness of astronomical objects. Two images of star fields containing thousands of objects, taken at different times but with exactly the same magnification, would be shown alternately at intervals of about one second.
A change in any one of them would be immediately apparent. We can adapt this for use with PowerPoint images to detect small differences in maps of model results provided that we can standardize the presentation format across all groups. We can also flicker through a sweep of many small changes in time or nuclei concentration.
Reports should have verbose comments and complete meta-data close to each map with minimum risk of confusion between them. This means frequent repetition and no jumps to other pages, or even other journals as is sometimes done. The clarity of caption wording should be tested by naive readers from outside the field, rather than the intimidatory, in-group style of many journals. The tendency of ingroups to defend their territory against outside incursions by means of obscure abbreviations to save tiny amounts of page space must be avoided.
Results can be presented as absolute values or as anomalies from some agreed reference baseline. We must agree on a small selection of base lines such as preindustrial, 1960-90, present, x2 preindustrial CO2 or one of the IPCC scenarios. We must also be able to show instantly the differences between sets of results from different baselines, modelling codes or institutions. We must be able to combine results with various weightings from different teams. This will require an agreement between the teams of what the format should be, followed by their obedience to the agreement. It will be important to get advice from good information technology experts. There are large quantities of historic data using quite different colour codes for the presentation of results. This makes it very hard to see similarities and differences. It should be possible to write colour conversion software to give an agreed colour coding so that old results can be used.
Blockiness
Because of pressure of time, the Parkes thesis results were presented as blocks with sharp edges which are unusual in meteorology except for either sides of mountain ranges or places like the Cape of Good Hope. We should agree on a method to produce smoothly blended curves for both spray concentration regions and results.
Ganging up
We may learn something about the climate system by using independent spray patterns to identify all the spray regions which have the same effect on one observation station, such as drying Queensland, and then driving them in unison with both increases and reductions. We then reverse the selection to all the spray regions which increase Queensland precipitation.
Numerical data
If we want daily results of 4 parameters affected by 100 spray regions for 500 different observing stations over 20 years with twobyte precision we will have to access nearly a Terabyte of information. Requirements are unlikely to shrink. We want this to be made freely accessible to anyone. We need verbose and intuitive labels and selection filters with same look and feel from all modelling groups. Subsets should be available in a widely used format, agreed by all teams such as netCDF and GrADS. People should normally supply numerical results in a common, agreed and widely-used format. If other formats have to be used then the teams should provide conversion software or do the conversions themselves on request.
Carbon dioxide variation
We should first test the technique with one agreed level of atmospheric greenhouse gases. If we can establish confidence in the coded modulation technique we can later experiment with changes to gas concentrations. Obvious ones are pre-industrial, double preindustrial, ramped rises at various rates, methane burps and even the effects of plausible rates of CO2 removal. The study of the results for very large CO2 concentrations, favoured by workers hostile to geoengineering, is of less importance because we have to get through the lower concentrations to get there. However access to present real observations will be useful and so there is a strong case for using present day gas concentrations unless there is a sudden need for work on methane burps.
Specific Questions
There is a grave risk of a combinatorial explosion suppressing the detection of differences between climate models and so initially we must agree on as many test conditions as possible. The following are suggestions for debate.
What spray rates, change-over periods, concentration profiles and correlation delays should be used for commonly-agreed experiments?
What level of scatter will still allow us to draw useful conclusions?
What level of model resolution should be used?
How does the scatter of results vary with the length of run?
How does scatter vary with the size of target area?
Can scatter be low enough to allow seasonal or monthly transfer functions?
Do we need to merge target areas?
How does scatter vary with spray source and observing station?
What spray regions, spray rates and seasons will produce unacceptable changes to what observing stations?
How far does the Twomey log equation for nuclei-concentration to change-of-reflectivity hold?
What ratio of multiplier to divider will minimize interference between spray sources?
Negative modulations are easy in a computer model but less so in the real world. How does susceptibility vary if the modulation is asymmetric or is only positive?
How does the susceptibility for temperature, precipitation and ice cover vary with the amplitude of the perturbation?
Will tactical variations based on day-to-day observations be useful for hurricanes and precipitation adjustment in both directions?
Are there large winner-to-loser ratios?
Can overall winner-to-loser ratios be minimized?
What other experiments should be attempted?
What is the probability that this project would improve the reliability of climate models?
Milestones and Deliverables
Suggestions for improvements to this document.
Agreement on result presentation, data format, colour codes and low-level common analysis software packages.
Circulation and analysis of the existing Ben Parkes results.
Agreement on the rank order of target parameters such as, temperature, precipitation, evaporation, ice, snow-line, vegetation and CO2 level plus others.
Agreement between teams on timescales for deliverables.
Measurement with sinusoidal excitation of the phase and amplitude response to choose correlation lags.
The production of maps of annual spray site susceptibility, defined as the annual change of each result parameter per unit of spray volume.
Maps of quarterly and perhaps monthly spray site susceptibility in particular at high latitudes around the summer solstice.
As above with spraying adjusted with a selection of correlations linked to the monsoon seasons. Even if the computer models cannot detect the onset of a monsoon we can use historic records to pick dates.
Investigation of tactical spray rate variation.
Analysis of results for groups of spray regions working in unison or subtle harmony especially with Trans-Pacific amplification and attenuation of el Niño/la Niña oscillations.
The calculation of the economic value or penalty of climate modification. For example the cost of rainfall reduction over the sea would be low but should involve the cost of providing and operating desalination plant for every small island to restore the previous water supply. The value of removing the need for flood defenses for coastal cities could be very high.
Design of a world-wide spray plan to cool the planet with the minimum winner/loser ratio.
Identification of the strengths and weaknesses, agreements and disagreements of the various climate models leading to suggestions for improvement.
Climate Chaos
Objectors to cloud albedo control have argued that the climate system is chaotic and so nothing can be done to redirect it. But there have been a great many phenomena such as planetary motions, chemical reactions, the incidence of disease, flower colours and the motions of sea waves which were all thought to be chaotic by the leading thinkers of the day. Then Kepler showed that elliptical planetary orbits followed rules more precise than any man-made machinery. Mendeleev produced his periodic table and was able to predict the existence and properties of hitherto unknown elements. Pasteur developed germ theory. Muriel Wheldale explained the apparently random variations of snapdragon flowers. Test tanks can now produce apparently complex sea states with repeatability of a few parts per thousand. An oscilloscope signal from any backplane connector of a computer appears to be an entirely random string of zeros and ones but is in fact one of the most highly defined sequences that we can produce.
A favourite lecture demonstration of chaotic behaviour uses the fall of sheets of paper from above the demonstrator’s head. The smallest increase of the angle of incidence between the paper and the apparent airflow produces a pitching moment to increase its value up to the moment of stall. Sheets will be scattered over a wide area. But if a sheet of paper is folded in the form of a paper dart to increase stiffness, and a weight is added to the nose to bring the center of gravity forward of the center of pressure, then the area enclosing the position of impact points is greatly reduced. The scatter could be further reduced if the falling item was fitted with optical systems driving control surfaces. We could call it a GBU12 Paveway bomb which has an accuracy of about one meter despite chaotically random cross winds. Similarly we could fit video cameras and hinge actuators to the nails of Galton’s bagatelle board. Clearly the magnitude of chaos is variable and can be affected by small changes to engineering design.
There may really be systems such as fluid turbulence and subatomic physics which are genuinely chaotic. But if we believe that all systems which we cannot at present understand are chaotic then we greatly reduce our chances of making a scientific discovery. The common factor of chaotic systems is that small changes, like the angle of incidence of a sheet of fluttering paper, are amplified. This means that a very small amount of input energy applied intelligently can produce large changes in output energy. That is just what we need to control energy in the planetary climate system. Apparent chaos could imply the possibility of successful control.
Conclusions
The first objective of this project must be to identify times and places where marine cloud brightening should NOT be done.
Correlation of coded sequences can be used to detect very small signals buried in large background noise. The magnitudes of multiple artificial changes to a 20-year temperature record can be predicted with the precision equalled only by very best thermometers. Precision should improve with the square root of computer run time.
Changes to precipitation patterns are a major concern for climate engineering but marine cloud brightening can affect it in both directions. There is a trend to make dry places a little wetter and wet places a little drier.
Reductions of precipitation over the sea are of less concern than over dry land areas.
The scatter of results for one spray source to one observing station for different sequences is a good indication of the usefulness of the technique.
The wide range of choices for colour contours at present used for result maps is a serious impediment to new discoveries.
Map projections must be chosen with care. The widely-used Mercator projection produces gross area distortions in Polar Regions which are now seen as being of major importance for climate change.
Marine cloud brightening offers a great many control knobs, few of which have, so far, been used or understood by climate modellers.
Monthly maps of susceptibility would be very valuable for planning spray patterns, especially for short periods at midsummer in high latitudes.
The short life of spray allows high-frequency, low phase-shift control and tactical variation of spray plans in the light of real-time weather observations.
It may be possible to choose times and places for spray which have win-win results for world food supplies.
Coded modulation could give valuable insights into the climate system and improve climate models.
Too rigid a belief in climate chaos might have negative career implications for rigid believers.
Tailpiece
The world can be compared to a vehicle with free-castor wheels which is rolling down a hill with increasing gradient. A few of the passengers, the more intelligent ones, are warning that there may be a cliff edge somewhere ahead. Some, perhaps even more intelligent, are suggesting that there might just be time to design and fit brakes, steering and even a reverse gear. However others advise that the slopes often vary and the one ahead might level off and so brakes and steering would be a waste of money which is badly needed for international climate conferences and their invaluable results. Some objectors complain that the passengers could never learn to drive or agree on the best direction to steer. Some argue that sudden braking can lead to dangerous skidding. Some are close to claiming that God wants humanity to drive over the cliff edge and that it is wrong to interfere with Divine Intentions.
We could also consider the climate system as a piano in which the spray regions are the keys, some black some white, on which a wide number of pleasant (or less unpleasant) tunes could be played if a pianist knew when and how hard to strike each key.
Acknowledgements
Climate engineering research at Edinburgh University is privately supported.
References
- Twomey S. Influence of pollution on the short-wave albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977; 34: 1149-1152.
- Schwartz SE & Slingo A. Enhanced shortwave radiative forcing due to anthropogenic aerosols. In Clouds Chemistry and Climate (Eds P Crutzen & V Ramanathan). 1996; 191-236. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer.
- Latham J. Control of global warming? Nature. 1990; 347: 339-340.
- Latham J, Bower K, Choularton T, Coe H, Connelly P, Cooper G, et al. Marine cloud brightening. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. A. 2012; 370: 4217-4262.
- Caldeira K, Wood L. Global and Arctic climate engineering: numerical model studies. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. A. 2008; 366: 4039-4056.
- Bala G, Caldeira K, Nemani R, Cao L, Ban-Weiss G, Shin H. Albedo enhancement of marine clouds to counteract global warming: impacts on the hydrological cycle. Climate Dynamics. 2010; 37: 915-931.
- Jones A, Haywood J, Boucher O. Climate impacts of geoengineering marine stratocumulus clouds. Journal of Geophysical Research. 2009; 114.
- Niemeier U, Schmidt H, Alterskjær K, Kristjánsson JE. Solar irradiance reduction via climate engineering: Impact of different techniques on the energy balance and the hydrological cycle. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 2013; 118: 1-13.
- Parkes B. Climate Impacts of Marine Cloud Brightening. 2012. PhD Thesis University of Leeds.
