Abstract
Limited domestic resources, high fuel imports and finite access to modern fuel resulting in economic burden has led to increase in energy poverty in Pakistan. Moreover, waste management is the burning issue in the context of agricultural residue which is burned by farmers causing soil deterioration and air pollution. These significant and interconnected issues of the Pakistan that have far-reaching economic, environmental, and social implications. The primary goal of sustainable fuel production is to reduce the environmental and social harm associated with traditional fossil fuel extraction and production methods. Bio-crude is a liquid biofuel produced by thermochemical conversion of wide variety of biomass. Fast pyrolysis considered as an efficient and the most economical technique of valorization is used for the production of bio-crude from wheat straw. Catalytic upgrading methods like hydro-processing are then employed to upgrade biocrude to a variety of fuels including diesel and gasoline. In present work, techno-economic and environmental assessment is made for the process. Moreover, a complete process route is developed with detailed economic analysis to determine its feasibility. The process was also subjected to an economic study, and the results indicate that the project is fiscally feasible. With a 3.9 - year payback period and a positive present worth value, this project is the best investment. With pyrolysis being the most inexpensive route towards biofuels, the developed process can serve as a solution towards energy crisis issues of Pakistan.
Keywords: Pyrolysis; Wheat Straw; Bio-diesel, Circular Economy; Energy Crisis; Fuels
Introduction
The utilization of renewable energy sources, particularly biodiesel, for power generation, has garnered significant attention on a global scale. In the context of Pakistan, this approach holds promise in alleviating the current and anticipated energy challenges the nation faces [31]. Pakistan has a severe economic crisis stemming from a persistent disparity between energy demand and supply (Okopi et al., 2023). The power and gas supply shortage has already resulted in the stagnation of numerous industrial sectors, including textiles, small and medium enterprises, and local transportation. There is a prevalent concern in today's world regarding the depletion of fossil fuels, coupled with the relentless escalation of energy costs, which are projected to peak by 2050. The diminishing fossil fuel reserves within Pakistan have necessitated the annual importation of approximately 8.1 million tons at a cost of around US$ 9.4 billion [5]. Therefore, the sustainable maintenance of renewable energy resources, such as biodiesel, is imperative to attain a sustainable energy mix and ensure energy security. In light of this imperative, the extensive integration of various biodiesel sources holds the potential to effectively address the energy shortfall and ensure energy security in Pakistan. In this context, the advancements in biodiesel related research within Pakistan are evaluated and presented, emphasizing strategies to fulfil the objectives outlined by the government. This comprehensive study deliberates on biodiesel as a renewable energy source, aiming to mitigate energy crises, foster a pollution-free environment, drive economic growth, and notably increase farmers' income.
Bio-Diesel
Biodiesel, a renewable and biodegradable fuel, is obtained from various natural sources, including vegetable oils (e.g. canola and soybean etc.), animal fats, recycled cooking grease, and lignocellulosic biomass like wheat straw. Biodiesel can either be used in its pure form, or blended with fossil fuel derived diesel in varying concentrations, such as B20 (20% bio-diesel, 80% conventional diesel), to power diesel engines [12]. The benefits of biodiesel are significant, including a substantial reduction in GHG emissions compared to conventional fossil-derived fuels, which helps combat climate change. It also decreases dependence on finite fossil fuel sources, fostering energy security. Biodiesel has superior lubricating properties that can enhance engine performance and longevity. Moreover, the use of biodiesel supports local agriculture and economies, providing farmers with additional revenue streams and promoting rural development. Biodiesel production from waste materials, such as used cooking oil and wheat straw, contributes to waste reduction and promotes a circular economy. Overall, biodiesel represents a versatile and environmentally friendly substitute to traditional fossil-based diesel, with multiple production routes and numerous environmental and economic benefits.
Global Market of Bio-Diesel: The United States remains at the forefront of biodiesel production, generating approximately 2.5 billion gallons of biodiesel in 2022. The country's biodiesel industry relies heavily on agricultural outputs such as soybean oil, animal fats, and recycled cooking oil, with considerable production facilities in states like Iowa, Texas, and Illinois. With an annual production of around 1.3 billion gallons (about 4.9 billion liters) in 2022, Brazil is another significant contributor to the biodiesel market (Hargreaves, 2017). The country's biodiesel production predominantly relies on soybean oil, benefiting from its extensive farming. In 2022, the European Union collectively produced about 3.2 billion gallons (approximately 12 billion liters) of biodiesel, with leading countries in biodiesel production including Germany, France, and Spain. The EU's biodiesel production is sustained by rapeseed oil, used cooking oil, and animal fats, driven by renewable energy directives and environmental policies.
Production, Consumption and Import of Crude Oil in Pakistan: Pakistan's domestic crude oil production remains relatively modest compared to its consumption needs. As of 2022, the country's crude oil production stood at approximately 88,000 barrels per day (bpd). The oil fields are predominantly situated in the southern and central regions, encompassing the Sindh and Punjab provinces.
Despite continuous exploration and development endeavours, domestic production only satisfies a small fraction of the national demand. Pakistan's consumption of crude oil surpasses its production significantly. In 2022, the country consumed about 450,000 barrels per day (bpd) of crude oil. Various sectors drive this substantial consumption, including transportation, power generation, and industrial uses. Notably, the transportation sector emerges as a significant consumer of oil products, primarily relying on diesel and gasoline as the principal fuels. Due to the notable disparity between production and consumption, Pakistan relies heavily on imports to fulfil its crude oil requirements. In 2022, the country imported approximately 362k BPD of crude oil to bridge the gap between domestic production and demand (Hargreaves, 2017). Pakistan sources its crude oil imports from various international suppliers, including critical sources from Middle Eastern countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Kuwait. These imports are critical in meeting the country's energy needs and ensuring a consistent supply of refined petroleum products.
Current Bio-Diesel Market: The current biodiesel market in Pakistan is at a nascent stage of development, with a noticeable shift towards adopting renewable energy and a focus on environmental sustainability. Although biodiesel production and consumption levels are currently modest compared to traditional fossil fuels, this sector has a growing interest and influx of investments. Government-led initiatives promoting renewable energy, including mandates for biodiesel blending and tax incentives, are significant market expansion drivers. Nonetheless, challenges persist, such as limited infrastructure, technological constraints, and competition from conventional fuels [27]. As awareness of the environmental advantages of biodiesel expands and technological advancements enhance production efficiency, the biodiesel market in Pakistan is poised for substantial growth, presenting opportunities for investment, innovation, and the advancement of sustainable energy.
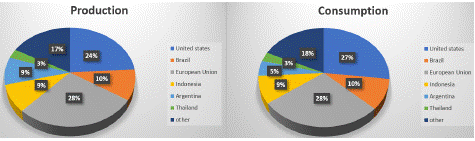
Figure 1: Production and Consumption of Bio-diesel in the world.
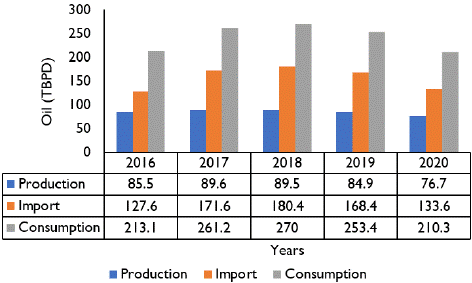
Figure 2: Production, Consumption and Import of Crude oil in Pakistan.
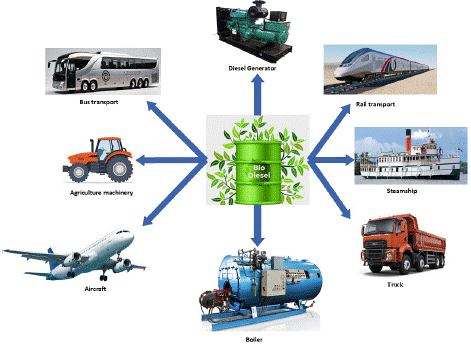
Figure 3: Applications of Bio-diesel.
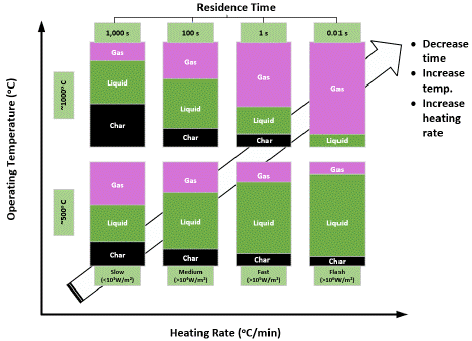
Figure 4: Types of Pyrolysis Processes.
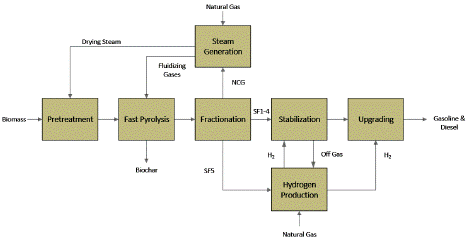
Figure 5: BFD proposed for the Process.
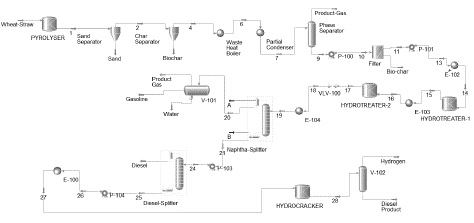
Figure 6: Simulated Flowsheet of Proposed Plant.
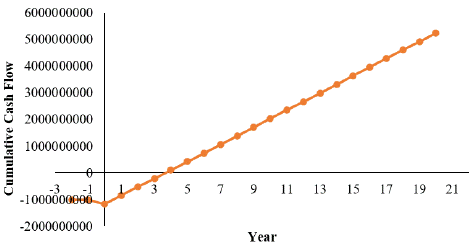
Figure 7: Cumulative Cash Flow Diagram.
Applications of Bio-Diesel: Biodiesel exhibits diverse applications across multiple sectors due to its renewable nature and environmental advantages (Hobbie et al., 2022). The primary applications of biodiesel encompass: [15,19].
• Biodiesel is a widely used fuel for diesel engines in various modes of transportation, including cars, trucks, buses, and other vehicles.
• Biodiesel is commonly used in farm equipment and machinery, such as tractors and harvesters, supporting a sustainable agricultural cycle by enabling farmers to utilize biofuel produced from their crops.
• Biodiesel is employed in marine vessels, including boats and ships. It offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional marine fuels and contributes to reducing water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
• Biodiesel is employed in diesel generators to produce electricity, particularly in remote or off-grid locations. This thereby mitigates dependence on fossil fuels and fosters the utilization of renewable energy sources.
• Biodiesel can be utilized in residential and commercial heating systems as a substitute for heating oil, requiring minimal or no modifications to existing oil furnaces and boilers.
• Although still in the experimental phase, biodiesel is being subjected to trials as a potential Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) to aid in curbing the aviation industry's carbon footprint.
• Biodiesel is applied in various industrial settings, including as a solvent for cleaning and degreasing and in the production of lubricants and other chemicals.
Wheat Straw Availability
Wheat straw, the fibrous byproduct remaining after wheat grain harvest, is primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. This agricultural residue holds significant potential for sustainable energy production, particularly in the form of biodiesel. Its significance in biodiesel production lies in its role as a lignocellulosic biomass, which can be converted into biodiesel through thermochemical processes e.g. pyrolysis and gasification, followed by upgrading methods such as Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. It is estimated that Pakistan produces around 25 million metric ton of wheat straw on yearly basis, and the major provinces for this production includes Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Balochistan [4]. About 50% of this straw is consumed by animals for food, and around 20% is utilized in activities like mulching, bedding, and composting. A small proportion goes to industrial uses like production of paper and other related products. But it is alarming that around 30% of straw is left unutilized and is mostly burnt or lacking proper handling facilities [31]. This has a negative impact on the environment and the wastage of good organic matter that can be of great benefit to human beings [7].
Utilizing wheat straw for biodiesel production offers various environmental and economic benefits:
• It helps reduce waste by providing a productive use for agricultural residues that might otherwise be burned or left to decompose, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
• The use of wheat straw as a feedstock for biodiesel can reduce the reliance on food crops like soybean or canola, thus avoiding the food-versus-fuel conflict and enhancing food security.
• Converting wheat straw into biodiesel contributes to a circular economy by turning agricultural waste into valuable energy resources, supporting rural economies, and creating new revenue streams for farmers.
• Biodiesel produced from lignocellulosic biomass like wheat straw has a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels, thus contributing to climate change mitigation.
Routes to Bio-Diesel: Converting wheat straw into biodiesel can be achieved through two major thermochemical processes:
• Pyrolysis
• Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL)
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process of biomass material in the presence of heat and absence of oxygen to produce bio-oil/bio-crude, syngas and char [8]. This process normally occurs at the temperature of about 400-600°C and can be classified as slow, fast and flash pyrolysis [3]. Fast pyrolysis is preferable for bio-oil production because of higher liquid yield and higher yield of bio-oil compared to slow pyrolysis which yields more char and flash pyrolysis which may produce unstable bio-oil at 450-500°C and high heating rates (Kataria et al., 2022). On the other hand, Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL) utilizes H2O at high temperatures (250-374°C) and pressures (4-22 MPa) to convert biomass into bio-crude oil which has higher energy density and similar to conventional fossil fuels [21]. HTL typically produces better quality of bio-oil and is capable of processing wet biomass directly, which offers feedstock flexibility and superior product quality on one hand, but it is complex and pricey due to the need for high pressure equipment on the other hand [8]. As for the two methods, fast pyrosoysis is more commercializable on a large scale because of its lower operational intensity and cost, thus considered suitable for the conversion of wheat straw to biodiesel (Johannes et al., 2024).
Process Description
The process of producing biodiesel from wheat straw via pyrolysis involves several vital stages: pretreatment, pyrolysis, upgrading of bio-oil through hydrotreating and hydrocracking, separation of diesel and gasoline fractions through distillation, and final storage [18]. Each stage is crucial for efficiently converting wheat straw into high-quality biodiesel. Pretreatment begins with size reduction, where wheat straw is mechanically processed through shredding or milling. This reduces the particle size, enhancing heat transfer and increasing the efficiency of the pyrolysis process [21]. Additionally, impurities such as stones, metals, and other contaminants are removed to prevent pyrolysis equipment damage and to enhance the quality of the resulting bio-crude. The pyrolysis process is conducted at temperatures between 500°C in an O2-free atmosphere to prevent combustion. The heating rate is rapid, ensuring quick decomposition of the biomass (Jin et al., 2022). The resulting products include bio-oil, syngas, and char. Bio-oil, the primary product, is a complex mix of organic compounds, while syngas and char are indispensable byproducts. Bio-oil serves as the feedstock for further upgrading into biodiesel (Theristis et al., 2018). Hydrotreating involves adding hydrogen to remove oxygen from the bio-oil, using catalysts under high pressure and moderate temperatures [22]. Following hydrotreating, hydrocracking further breaks down the large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more desirable ones, such as diesel and gasoline fractions [21]. This process occurs under high pressure and temperature in the presence of catalysts, resulting in a mixture of hydrocarbons suitable for use as fuels (Peng et al., 2013). The upgraded bio-oil undergoes distillation to separate the mixture on the basis of the boiling points of its constituents [14]. The mix is heated during distillation, causing the different hydrocarbons to vaporize at their respective boiling points. These vapours are then condensed into liquid form and collected in separate fractions. Diesel and gasoline are two primary fractions obtained, each with distinct properties and uses [9].
Plant Specifications:
• Plant Capacity = 2000 tons/day of Biodiesel
• Raw Material Supplied = 23870 tons/day of Wheat Straw
• Bio-oil Yield = 42%
• Bio-oil Production rate = 10025.4 tons/day
• Plant commences operation in 4-7 years
• Plant life is 20 – 22 yrs
• Plant operation is 300 days/yr
Conventional VS Wheat Straw Derived Diesel: Biodiesel derived from pyrolysis of wheat straw is a viable substitute for regular diesel as it has similar energy density, cetane number, viscosity, density and distillation characteristics [25]. For instance, this other diesel has lower levels of sulfur and aromatic hydrocarbons, resulting in lower sulfur oxides and particulate emissions [11]. Interestingly (Wu et al., 2020), these similarities suggest that the diesel produced from pyrolysis of wheat straw can easily be used in the existing diesel engines and dissemination channels, [20] thus making it easier to substitute the current unsustainable fuel [17,42].
Economic Analysis
The economic feasibility of producing diesel from wheat straw pyrolysis is evident from the economic analysis of the process and the benefits of using the produced diesel over the conventional diesel. It also efficiently employs an agricultural waste product which is available in large quantities and hence cuts down the costs of feedstock (Inayat et al., 2022). The investment and maintenance costs of pyrolysis plants especially the fast pyrolysis are relatively low compared to the other advanced biofuel technologies making them financially feasible. In addition, byproducts like biochar and syngas can be sold to create more income streams for the business. The reduction in the sulfur content and the ability of pyrolysis derived diesel to emit fewer pollutants can reduce costs by avoiding penalties and meeting set regulations. Therefore, the economic and environmental impacts and the fact that few changes to the infrastructure make this process crucial to the progress of energy security and sustainability.
Capital Investment
Before commencing operations, an industrial plant requires substantial financial resources to procure and install essential equipment and machinery. Furthermore, acquiring land and service facilities, as well as complete plant construction with all necessary pipe controls and services, is imperative. Moreover, it is crucial to have funds available to cover the plant's operational expenses. The capital required for procuring the essential manufacturing and plant facilities is represented as fixed capital investment, whilst the funds essential for the plant's operation are called working capital investment.
Fixed Capital Investment: The capital needed to supply fixed plant facilities is called fixed capital investment. It is categorized in to two sub classifications,
• Direct Cost
• Indirect Cost
Working Capital Investment: The capital that is essential for the operation of the plant is known as working capital investment.
WCI = Working Capital Investment = 15% of FCI = $ 151357134
Total Capital Investment = FCI + WCI = $ 1160404697
Variable Costs
The variable cost of a plant includes costs that fluctuate with the output of the plant. These costs include the cost of the materials used in the production process, wages and salaries of employees, and energy costs, which can fluctuate depending on the amount of products or services produced.
Raw Material Cost
Total wheat straw production = 25 million tons per annum
Animal Fodder
50%
Pulp & Paper Industry
5%
Domestic use
2%
Export
5%
As a fuel
10%
Available wheat straw
28%
Table 1: Availability of Raw Material in Pakistan.
Properties
% Content
Cellulose
33.19
Hemi-cellulose
25.20
Lignin
15.27
Carbon
48.93
Hydrogen
6.52
Nitrogen
1.11
Oxygen
42.56
HHV (MJ/Kg)
18.01
Moisture Content
6.5
Ash Content
5.45
Fixed Carbon
13.35
Table 2: Physio-Chemical Properties of Wheat Straw.
Parameter
Pyrolysis
Hydrothermal Liquefaction
Feedstock
dry
Wet
Particle Size
1 – 20 mm
< 1mm
Temperature
~500 °C
200 – 350 °C
Pressure
1 bar
50 – 200 bar
Oil Yield (wt%)
80
20 – 60
Present Status
Commercialised
Underdeveloped
Bio-oil viscosity mPa.s
13 – 70
67000
Relative capital cost
low
high
Table 3: Difference between Pyrolysis and Hydrothermal Liquefaction.
Property
Fossil Fuel Diesel
Biodiesel
Gasoline / Diesel Equivalent
1 gallon = 1.12 GGE
1 gallon = 1.00 DGE1 gallon = 1.05 GGE
1 gallon = 0.93 DGELHV
128,488 Btu/gal
119,550 Btu/gal
Cetane Number
40 – 56
48 – 65
Flash Point
165°F
212° to 338°F
Cloud Point
-3
-3 to 15
Pour Point
-13
-5 to 10
Specific Gravity
0.843
0.88
Table 4: Conventional VS Bio-diesel Properties.
Item
% of Purchased Cost
%
cost ($)
Purchased Equipment
100
206602695
Installation
25 – 55
40
82641078
Instrumentation and control
6 – 30
18
37188485
Piping
40 – 80
60
123961617
Electricity
10 – 15
13
25825337
Building
15
15
30990404
Land
4 – 8
7
12396162
Service facility
30 – 80
56
113631482
Yard Improvement
10 – 20
14.5
30990404
Insulation Cost
8 – 9
9
17561229
TOTAL
681788894
Table 5: Calculations on the basis of Purchased Equipment cost.
Item
% of Direct Cost
%
Cost ($)
Engineering and supervision
25
25
170447223.4
Contractor fees
2 – 8
5
34089444.68
Construction expenses
10
10
68178889.35
Contingencies
8
8
54543111.48
TOTAL
327258668.9
Direct Cost = $ 681788894
Indirect Cost = $ 327258668.9
FCI = Fixed Capital Investment = DC + IDC = $1009047562
Table 6: Indirect Cost on the basis of Direct cost.
Table 7
Item
$ per kg
Flowrate (kg/yr)
Total $/yr
Wheat Straw
0.1
8712547080
871254708
Hydrogen
2
143716560
287433120
TOTAL
1158687828
Table 7: Raw Material Cost.
Utilities Cost
Table 8
Item
$ per kg
Flowrate (kg/yr)
Total $/yr
Steam
0
8500000000
170000000
Cooling Water
0
200000000000
3600000
TOTAL
173600000
Table 8: Utilities Cost.
Catalyst Cost
Table 9
Catalyst cost ($/kg)
7.5
catalyst weight(kg)
5043
Total catalyst cost ($/yr)
37822.5
Table 9: Catalyst Cost.
Miscellaneous Cost
Table 10
Maintenance cost
7% of FCI
70633329.37
Miscellaneous material
10% of maintenance cost
7063332.937
Table 10: Miscellaneous Cost.
Fixed Operating Cost
Other costs that are related to operating costs and are also known as ‘fixed costs’ or ‘overhead costs’ are costs that stay unvarying regardless of the level of production. These costs do not alter according to the level of activity of the facility for a particular period of time. Examples include rental or lease expenses for facilities, salary for permanent employees, insurance charges, and depreciation of equipment [23]. Fixed operating costs provide stability in the financial projections since they are predictable; however, they also contribute to the firm’s obligations that have to be met regardless of low production or sales.
Total Production Cost
Direct Production Cost: Direct Production Cost= Variable Cost + Fixed Operating Cost
DPC = $ 2509884156
Overhead Charges = 30% DPC
Overhead Charges = 752965246.7
Manufacturing Cost = Overhead + DPC
Manufacturing Cost = 3262849403
General Expenses
Table 12
Item
% of FCI
Cost ($)
Maintenance cost
7
70633329
Operating cost of labour
10
100904756
Laboratory cost
20
201809512
Supervision cost
15
151357134
Plant overhead
50
504523781
Capital Charges
10
100904756
Insurance
1
10090476
Local Taxes
2
20180951
Royalties
1
10090476
TOTAL
1170495172
Table 11: Fixed Operating Cost.
Item
% of Manufacturing Cost
Cost ($)
Administration
2
65256988.05
Distribution and marketing
2
65256988.05
Research and development
5
163142470.1
Total
293656446.2
Total Production Cost = Manufacturing Cost + General Expenses
Total Production Cost = $ 3556505849
Table 12: General Expenses.
PRODUCTION COST
Total Production rate
3650000000
Kg/yr
Production cost
0.974385164
$/kg
PRODUCT SELLING PRICE
Price of bio-diesel in Market
2.085
$/kg
Selling price of the product
1.2
$/kg
PROFIT PER YEAR
Selling price - production cost
0.225614836
$/kg
profit per year
823494151.2
$/yr
TOTAL INCOME
Selling price
1.2
$/kg
Total production rate
3650000000
Kg/yr
Total Income
4380000000
$/yr
GROSS PROFIT ATTAINED
Total Income - Total Production Cost
823494151.2
$/yr
Table 13: Profitability Analysis.
DEPRECIATION
Machinery and equipment
20% of FCI
201809512.5
$/yr
Building
4% of Building cost
1239616.17
$/yr
Total Depreciation
Machinery and equipment + Building
203049128.6
$/yr
TAXES
Let the tax rate is 40%
Taxes
0.4×Gross Profit
329397660.5
$/yr
NET PROFIT
Net Profit before Taxation
Gross profit – Depreciation
620445022.6
$/yr
Net Profit
Net Profit before Taxation – Taxes
291047362.1
$/yr
ANNUAL RATE OF RETURN
Rate Of Return
net profit/tci *100
25.08153948
%
PAYBACK PERIOD
Payback Period
1/rate of return
3.986996097
yrs
Table 14: Depreciation and Payback.
Profitability Analysis
Total Income and Gross Profit: Evaluating the profitability of a plant requires a careful analysis of the plant’s financial status using measures like the total income and the gross profit. Total income refers to the money that the plant makes through its operation and is inclusive of all sales of products or services. Gross profit on the other hand is derived by subtracting the cost of sales which include direct cost such as raw materials and direct labour from the total revenue. This calculation gives a clue of the degree to which the plant is able to convert its sales into profit once the costs of production have been factored in. These metrics can be used by analysts to assess the efficiency of the plant, the success of the pricing strategy, and the overall profitability. The analysis provided here is quite useful in understanding the financial health of the plant and its competitiveness in the market.
Depreciation and Payback: Depreciation is an accounting term that describes a method of diffusing the cost of a physical item over the passage of its useful life. The term "depreciation" refers to the amount of an asset's worth that has been used up. It allows companies to acquire assets over time and create income from them. If depreciation is not taken into account, it could significantly affect a company's profitability. For tax and accounting reasons, long-term investments might also be written off as expenses.
Cumulative Cash Flow: The net cash flow calculations made for the pyrolysis plant that converts wheat straw into diesel reveals that payback period is 3. 9 years. On the horizontal axis of the graph, the time is represented in years. The values below this axis are negative, which indicates the initial investment phase and early years of operation, where the total cash flow may be negative due to capital expenditure and operating costs being higher than revenues.
On the other hand negative values on the horizontal axis refer to subsequent years where the cumulative cash flow becomes positive since the amount of money that is generated from the sale of diesel is greater than the ongoing expenses. The vertical axis depicts the cumulative cash flow in monetary units, using negative values for the investment and the startup phase and positive values for the profitable phase. This paper is a financial tool of great importance as it presents the plant’s performance and its path to profitability to help the potential investors and stakeholders in making sound decisions.
Net Present Worth: Minimum Acceptable Rate of Return (MARR) = 15%
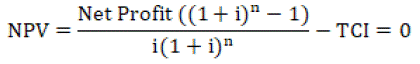
By performing iterations,
IRR = 24.45%
NPV = $ 29973061
IRR > MARR
24.45% > 15%
The Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) are critical fiscal measures when assessing the economic viability of the pyrolysis plant. The project's IRR of 24.45% indicates that the expected returns surpass the cost of capital, signifying its financial attractiveness. NPV, which accounts for the time value of money and initial investment by omitting future cash flows to current value, reflects the project's cost-effectiveness today. A positive NPV indicates that the project produces added profit than its costs, further bolstering its potential as a sustainable and profitable venture in converting wheat straw into diesel. These metrics affirm the plant's capacity to yield substantial returns throughout its operational lifespan, positioning it as an enticing investment opportunity in the renewable energy sector.
Environmental Assessment
The primary objective of this assessment is to analyze the potential environmental impacts linked to biodiesel production from wheat straw pyrolysis [1]. By methodically evaluating the environmental problems, this assessment contributes to making well-informed decisions that balance economic development and environmental protection [6].
Air Quality
The production of biodiesel from wheat straw using pyrolysis and hydroprocessing plays a substantial role in reducing GHG emissions when contrasted to typical fossil fuels [11]. This in turn positively impacts efforts to combat climate change by lowering the lifecycle emissions of biodiesel.
Moreover, biodiesel contains minimal sulfur content, stemming in lower emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) [24], a key donor to air pollution and acid rain when used as a fuel. Conversely, it is imperative to note that the pyrolysis process can release Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), Carbon monoxide (CO), Nitrogen oxides (NOx), and Particulate Matter (PM), all of which can have adverse effects on air quality if not properly managed (Aprovitola et al., 2021). Similarly, hydro-processing, particularly when reliant on hydrogen produced from non-renewable sources, can result in emissions of CO2 and other pollutants. Additionally, the process itself may emit small amounts of VOCs and NOx, necessitating the use of effective emission control technologies (Luo et al., 2020).
Water Quality
On the water quality front, one notable advantage of the pyrolysis process is the production of biochar, which can be used to improve soil structure and water retention, thereby reducing the need for chemical fertilizers that contribute to water contamination through agricultural runoff. This can have a positive impact on both soil and water quality by reducing the potential for nutrient leaching into water bodies (Y. Xu et al., 2014). However, it's worth mentioning that both the pyrolysis and hydro processing processes are water-intensive, requiring substantial amounts of water for cooling and hydrogen production, which can deplete local water resources. Furthermore, hydro processing may generate wastewater containing contaminants such as residual hydrocarbons, catalysts, and other chemicals, posing the risk of significant water pollution if not properly treated.
Soil Quality
Concerning soil quality, the use of biochar, a by-product of the pyrolysis technique, offers numerous benefits. Biochar can appreciably enhance soil potency, nutrient retention, and soil organic carbon content, ultimately leading to better crop yields and reducing the dependency on chemical fertilizers [16]. Additionally, biochar helps sequester carbon in the soil, contributing to the reduction of atmospheric CO2 levels and assisting in mitigating climate change (Ndlovu et al., 2022). Nonetheless, it's important to note the potential negative effects on soil quality, such as soil contamination if bio-oil or residual chemicals from the production process are not properly managed (Pennington, 2015). Also, the transportation and storage of these materials pose risks that must be carefully managed. Moreover, an overreliance on agricultural residues like wheat straw for biofuel production can lead to soil degradation over time if not appropriately compensated with other organic inputs [1].
Sustainable Development Goals
The process of producing biodiesel from wheat straw pyrolysis is closely linked to a few Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These include SDG 1 (No Poverty), SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 13 (Climate Action). This project has the potential to make a difference in various ways – it could help reduce poverty by creating employment opportunities and generating income, contribute to the renewable energy sector, foster technological and industrial innovation, and play a role in combating climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using wheat straw to produce biodiesel through pyrolysis offers a promising solution to Pakistan's escalating energy requirements and waste management issues. Circulating fluidized beds and multi-tubular reactors are employed for wheat straw pyrolysis and bio-oil upgrading. An in-depth technical evaluation and economic analysis of the pyrolysis plant have been conducted. The initial assessment indicates high feasibility, reasonable conversion rates, and yields. The economic analysis reveals that the total capital investment needed for a pyrolysis plant is estimated at $1.1 billion, with an annual production cost of approximately $3.5 billion and potential revenue generation of $800 million per year. The anticipated net profit from the plant is $291 million annually, with a 25.08% rate of return and an estimated payback period of 3.9 years. By addressing both agricultural waste management and Pakistan's energy crisis, wheat straw pyrolysis holds the potential to solve two significant challenges. With an annual production of 25 million tons of wheat straw in Pakistan, primarily burnt in rural areas, converting this abundant resource into biodiesel presents an opportunity to mitigate waste management issues and address the country's energy shortages, particularly for electricity generation. This initiative tackles environmental concerns related to straw burning. It contributes to sustainable energy production, fostering energy security and effective waste utilization in line with Pakistan's objectives for renewable energy development and environmental sustainability.
Future aspects
The potential for biodiesel production from wheat straw pyrolysis in Pakistan is substantial and presents various promising aspects from an academic perspective:
Investment in research and development can potentially enhance pyrolysis technologies, leading to increased bio-oil yield and improved quality. Innovations in catalytic pyrolysis and reactor designs promise to enhance the efficiency and economic viability of the entire process.
Pakistan's significant wheat production produces abundant wheat straw, a readily available feedstock. Utilizing this agricultural residue for biodiesel production can reduce waste and create a sustainable energy source.
Developing a biodiesel industry could introduce new economic opportunities, particularly in rural areas. This can stimulate local economies, create jobs, and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, thus contributing to energy security.
Biodiesel production from wheat straw has the potential to contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. This provides a cleaner alternative to conventional fossil fuels and aligns with Pakistan's commitments to international climate agreements.
Government incentives and policies promoting renewable energy and using waste biomass are essential for driving investment in biodiesel production. Supportive frameworks, including subsidies, tax breaks, and research grants, can expedite industry growth.
Establishing integrated biorefineries for producing biodiesel and other valuable by-products such as biochar, syngas, and chemicals could significantly enhance process economics and sustainability. This approach maximizes the value derived from wheat straw.
Collaborating with international research institutions and industries promises to bring advanced technologies and best practices to Pakistan, thereby facilitating the development of a robust biodiesel sector.
Increasing awareness about the benefits of biodiesel and educating farmers and stakeholders about the potential of wheat straw as a feedstock is critical in driving acceptance and participation in the biodiesel supply chain.
References
- Ali F, Solangi BK, Bazai MJK, Lahri SM, Shahzad F, Ullah A, et al. Effect of different planting dates on the growth and flower production of gladiolus under the agro-climatic conditions of Sohbat pur Balochistan. Pure and Applied Biology. 2023; 12: 862-873.
- Pires APP, Arauzo J, Fonts IE, Domine M, Arroyo AF, Garcia-Perez ME, et al. Challenges and Opportunities for Bio-oil Refining: A Review. Energy & Fuels. 2019; 33: 4683-4720.
- Ansari KB, Arora JS, Chew JW, Dauenhauer PJ, Mushrif SH. Fast pyrolysis of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin: Effect of operating temperature on bio-oil yield and composition and insights into the intrinsic pyrolysis chemistry. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 2019; 58: 15838–15852.
- Auersvald M, Shumeiko B, Vrtiška D, Straka P, Staš M, šimáček P, et al. Hydrotreatment of straw bio-oil from ablative fast pyrolysis to produce suitable refinery intermediates. Fuel. 2019; 238: 98-110.
- Awan A, Bilgili F, Rahut DB. Energy poverty trends and determinants in Pakistan: Empirical evidence from eight waves of HIES 1998–2019. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2022; 158: 112157.
- Belinskaya NS, Afanaseva DA, Bykova VV, Kosten MS. Studying the regularities and development of a model of the vacuum gas oil hydrocracking process. Oil and Gas Technologies. 2021; 135: 10-15.
- Biomass to Biofuels: Strategies for global industries. Focus on Catalysts. 2010; 2010: 8.
- Bridgwater A, Peacocke GVC. Fast pyrolysis processes for biomass. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2000; 4: 1-73.
- Chen D, Shuang E, Liu L. Analysis of pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of sweet sorghum bagasse and cotton stalk. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 2017; 131: 1899-1909.
- Gollakota ARK, Kishore N, Gu S. A review on hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2018; 81: 1378-1392.
- Crippa M, Guizzardi D, Banja M, Solazzo E, Muntean M, Schaaf E, et al. CO2 emissions of all world countries – JRC/IEA/PBL 2022 Report, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg. 2022.
- Danso-Boateng E, Achaw OW. Bioenergy and biofuel production from biomass using thermochemical conversions technologies—a review. AIMS Energy. 2022; 10: 585–647.
- Dennis Pennington. Chapter 7 - Bioenergy Crops, Bioenergy, Academic Press. 2017; 111-134.
- Dietrich Meier, Bert van de Beld, Anthony V Bridgwater, Douglas C Elliott, Anja Oasmaa, Fernando Preto. State-of-the-art of fast pyrolysis in IEA bioenergy member countries, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2013; 20: 619-641.
- Elhenawy Y, Fouad K, Bassyouni M, Gadalla M, Ashour FH, Majozi T. A Comprehensive Review of Biomass Pyrolysis to Produce Sustainable Alternative Biofuel. In: Negm, A.M., Rizk, R.Y., Abdel-Kader, R.F., Ahmed, A. (eds) Engineering Solutions Toward Sustainable Development. IWBBIO 2023. Earth and Environmental Sciences Library. Springer, Cham. 2024: 19-30.
- Eschenbacher A, Saraeian A, Shanks BH, Jensen PA, Li C, Duus JØ, et al. Enhancing bio-oil quality and energy recovery by atmospheric hydrodeoxygenation of wheat straw pyrolysis vapors using pt and mo-based catalysts. Sustainable Energy & Fuels. 2020; 4: 1991–2008.
- Ferreira AD, Ferreira SD, Rodrigues de Farias Neto S. Study of the influence of operational parameters on biomass conversion in a pyrolysis reactor via CFD. Korean J Chem Eng. 2023; 40: 2787–2799.
- Green DW. Perry’s chemical engineer’s handbook 8/E section 19 reactors (Pod). McGraw Hill Professional. 2007.
- GREEN. Perry’s chemical engineer’s handbook 8/E section 5 heat & mass transfer (Pod). McGraw Hill Professional. 2007.
- Haarlemmer G, Guizani C, Anouti S, Déniel M, Roubaud A, Valin S. Analysis and comparison of bio-oils obtained by hydrothermal liquefaction and fast pyrolysis of beech wood. Fuel. 2016; 174: 180-188.
- Han Y, Gholizadeh M, Tran C, Kaliaguine S, Li C, Olarte M, et al. Hydrotreatment of pyrolysis bio-oil: A review. Fuel Processing Technology. 2019; 195: 106140.
- Heat transfer. Process Engineering and Design Using Visual Basic®, Second Edition. 2013: 141-234.
- Inayat A, Ahmed A, Tariq R, Waris A, Jamil F, Ahmed SF, et al. Techno-economical evaluation of bio-oil production via biomass fast pyrolysis process: A review. Frontiers in Energy Research. 2022: 9.
- Introduction: Perry’s background information. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, Eighth Edition. 2015: 19-34.
- Jamil F, Shahbaz M, Tarar ZH, Rehan M, Yusup S. Development of mathematical models for bio-oil production via fast pyrolysis of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum). Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery. 2020; 12: 1469-1477.
- Jiang J, Zhang W, Bai Y. Research on the pyrolysis of cotton stalk in a fixed-bed reactor. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects. 2017; 39: 1911-1917.
- L Wu, G Sui, D Zhang, C Wang, T Zhang, Y Tang. Thermal-Conversion Characteristics and Chemical Kinetics of Chlorinated Polypropylene and Polyethylene: A Mechanistic Perspective. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 2022; 61: 4453-4467.
- Li S, Kim J. Industrial utilization of microalgae for biofuels and co-products: Recent developments and emerging opportunities. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2022; 158: 112163.
- M Rehan, F Al-Sulaiman, S Nizami, LA Naz, IA Rafique. Advances in biofuel production from municipal solid waste in conjunction with other waste streams: A case study of Saudi Arabia. Energy Conversion and Management. 2020; 221: 113145.
- M Zeynali, MA Sadrameli. Chapter 16 - Thermal Cracking Processes for the Production of Light Olefins from Hydrocarbons. In: Sadrameli, S.M. (ed.) Thermal and Catalytic Processes in Petroleum Refining, Academic Press. 2018.
- Maria A Pinheiro, Jesus Arauzo, Isabel Fonts, Marcelo E Domine, Alberto F Arroyo, Marta E Garcia-Perez, et al. Review of recent developments in fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic materials and thermochemical reactions of bio-oil components. Energy & Fuels. 2019; 33: 4683-4720.
- Myllyoja J, Visuri A, Salo S, Tynjälä T. Catalytic pyrolysis and char upgrading for bio-oil and biochar production from lignin. Frontiers in Energy Research. 2020; 8.
- Nizami AS, Rehan M, Al-Salem SM, Özcan HK, Khalid M, Siddiqui FA, et al. Recent advances in gasification of waste plastics: A critical overview. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2015; 50: 201-233.
- Ong YK, Nguyen NT, Shanmugam S, Phan TT, Kai TW. A study on catalytic and non-catalytic microwave pyrolysis of palm kernel shell for bio-oil production. Energy Conversion and Management. 2018; 156: 294-302.
- Orozco E, Veizaga JE. Pyrolysis of tropical biomass in Bolivia: Characterization and product distribution. Renewable Energy. 2023; 207: 1021-1031.
- Pan J, Han L, Wu Q, Shi F, Zhang D. Bio-oil stabilization by blending with diesel and residual oil: A review. Fuel. 2022; 319: 123795.
- Raja MM, Mujeebu MA, Abdullah MZ. Optimization of palm oil waste-based biodiesel production using artificial neural network integrated harmony search algorithms. Renewable Energy. 2013; 55: 490-495.
- Shahbaz M, Rehan M, Yusup S, Dittmar A, Fialkovskaia I. The Effect of Biomass Blending on Physico-chemical Properties and Thermal Degradation Kinetics. BioEnergy Research. 2021; 15: 160–173.
- Song H, Lv G, Yu X, Cheng Y, Li D, Qiu, J. Co-pyrolysis characteristics of walnut shell and low-density polyethylene: Kinetic analysis using a distributed activation energy model. Renewable Energy. 2020; 147: 2111-2119.
- Wang L, Li J, Zhang S, Cui X. Pyrolysis and catalytic pyrolysis of octanol lignin to obtain aromatics using ZSM-5, H-beta, H-USY, and Silica-alumina as catalysts. Catalysis Today. 2017; 298: 1-9.
- Yoshio Nagai, Ido H. Calculation of Reaction-Equilibria and Distribution Coefficients for the Estimation of Liquid-Liquid Phase Equilibria in Ionic Liquid Systems Containing Biomass and Water Components by Using Flory–Huggins, Wilson and NRTL Equations. Energies. 2021; 14: 6615.
- Zhang H, Sun Z, Pan SY, Xu G. A critical review of biomass fast pyrolysis. Fuel. 2023; 350: 128819.
- Zhang Y, Xue Y, Liu J, Yin Y, Zhou X, Ren H, et al. Application of ZSM-5 as catalyst in hydrothermal liquefaction of Chlorella Pyrenoidosa to produce bio-oil. Frontiers in Energy Research. 2021: 8.
