
Research Article
Austin J Environ Toxico. 2024; 10(1): 1047.
Evaluation of Radio-Diagnostic Imaging on Knee and Total Hip Spare Technique in Selected Hospitals within the Southeast and Southwest Nigeria
Linus Benedict¹*; Modesta Nneka Okeke²; Stanley Chigbo Okafor³
¹Department of Medical Radiography and Radiological Sciences, University of Nigeria.
²Enugu State Science and Technology (ESUT) Business School.
²University of Hertfordshire.
*Corresponding author: Linus Benedict Department of Medical Radiography and Radiological Sciences, University of Nigeria. Email: linusbenedict2013@gmail.com
Received: December 29, 2023 Accepted: February 03, 2024 Published: February 09, 2024
Abstract
A study of radio-diagnostic imaging in total hip and knee spare method at National Orthopaedic Hospital Enugu (NOHE) and National Orthopaedic Hospital Igbobi Lagos (NOHI) was investigated to understand the role of radio-diagnostic imaging in this aspect. A structural questionnaire of 29 items was distributed to extract information from a total of number of 38 respondents which constituted of radiographer and orthopaedic surgeons, working in the hospitals. The study reveals that radio-diagnostic imaging is used during the treatment and planning process before the surgical procedure, in the theatre and also during a follow up study post operation. From the study, it was revealed that each hospital does at least one hip and knee joint replacement every week. Also, from the study, the most used imaging modality is conventional x-ray imaging followed by C-arm fluoroscopy while other modalities are seldom used. The outcomes of the research show that the patients hardly report any complication after treatment therefore the use of the imaging modalities have great impact in the success of the procedures. From this research, it has shown clearly that radio-diagnostic imaging has a great impact in total hip and knee replacement procedure as imaging is used at each stage of the joint replacement. Summarily, the impact of radio-diagnostic imaging in the joint’s replacement procedure is such that the procedure can never be successful without the use of imaging.
Introduction
A joint is a point where two or more bones meet [1]. The lower limb of human is composed of three major joints namely: the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint from superior to inferior [1]. The knee joint is the joint between the femur and the tibia and fibula, while the hip joint is between the femur and the pelvic bones. The function of joint is mainly to ensure free movement and stability [2].
Joint replacement is a procedure whereby a deceased or injured joint is being replaced artificially in order to restore the primary function of the joint. A lot of abnormalities such as a long-term severe arthritis and a severely damaged joint caused by accident can damage a joint beyond management and therefore indicate joint replacement [3].
Joint replacement is always done when other methods to restore the normal function of the joint proves abortive [3].
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to replace the weight bearing surface of the knee joint to relief pains and disabilities [4]. It is most commonly performed for osteoarthritis, and also other knee diseases such as Rheumatoid Arthritis and psoriatic Arthritis [4]. The major cause of pain in the joint includes meniscus tears, cartilage defects, and ligament tears. Debilitating pain from osteoarthritis is much more common in the elderly [5].
Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, hip prosthesis [6]. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi replacement. A total hip replacement consists of replacement of both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty only replaces femoral head [6].
Joint replacement started very long ago around 1939 when Stephen Shudack began animal testing with artificial joints. This is to show that at the beginning animals were used to test the possibility of joint replacement on humans.
At early stage, joint replacement involves the replacement of both muscles and bones but at present joint replacement is more focused on the replacement of the bones that made up the joints. The former method is called interposition arthroplasty whereby some tissues are used to keep inflammatory surfaces separate while the other form of arthroplasty is excision arthroplasty which uses scar tissues to fill the gaps.
The methods and materials for hip and knee replacement, has evolved to a great extent ranging from using ivory to replace femoral head in 1891 to glass in 1935 and to metal in 1953. Today various prosthesis are used in the joint replacement and most importantly, the use of radio-diagnostic imaging comes into play. The role of imaging started with the conventional radiography but due to various advances in technology of imaging, more advanced imaging modalities such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are now employed in replacement of joints.
The knee joint is a synovial joint which connects the femur, our thigh bone and longest bone in the body, to the tibia, our shinbone and second longest bone [10]. There are two joints in the knee- the tibiofemoral joint, which joins the tibia to the femur and the pattello-femoral joint which joins the kneecap to the femur. These two joints work together to form a modified hinge joint that allows the knee to bend and straighten, but also to rotate slightly and from side to side.
The knee is part of a chain that includes the pelvis, hip and upper leg above, and the lower leg, ankle and foot below [11]. All these works together and depend on each other for function and movement. The joint bears most of the weight of the body. When we are sitting, the tibia and femur barely touch, standing they lock together to form a stable unit [11].
The knee does not have much protection from trauma or stress. In addition to wear and tear on the knee, sports injuries are the source of many knee problems [4].
Knee symptoms come in many varieties. Pain can be dull, sharp, constant or off and on. Pain can also be mild to agonizing [4]. The range of motion in the knee can be too much or too little. You may hear grinding or popping, the muscles may feel weak or the knee can lock. Some knee problem only needs rest and ice, others need physical therapy or even surgery [4]. The symptoms include but not limited to the following; swelling, locking, snaps, crackles and pops, pain and tenderness etc. [4].
Some pathological conditions and syndromes in the knee are osteochondritis dissecans, osteoarthritis, infectious arthritis, chondromalacia patellae, gout, plica syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, chondromalacia and osteoarthritis [9].
Traumatic knee injuries include anterior cruciate ligament injury, ligament injury, posterior cruciate ligament injury, patellar injuries etc. [9].
Repetitive knee injuries include patellofemoral syndrome (runners’ knee), tendonitis, bursitis (housemaid knee), illiotibial band syndrome and Osgood-Schlatter disease [9].
The hip joint is one of the largest joints in the body and is a major weight–bearing joint. Weight bearing stresses on the hip during walking can be 5 times a person’s body weight [12]. A healthy hip can support your weight and allow you to move without pain. Changes in the hip from disease or injury will significantly affect your gait and place abnormal stress on joints above and below the hip [12].
It takes great force to seriously damage the hip because of the strong, large muscles of the thigh that support and move the hip. Osteoarthritis affects many people, and the brittle bone from osteoporosis in the elderly can lead to life threatening fracture [6].
Common problems of the hip includes but not limited to aseptic or avascular necrosis, congenital dislocation, perthes’ disease, aplasia of the acetabulum, coca valga, coxa vara, osteoarthritis, dislocation, burstitis, legg-perthes disease, bone tumor, fracture etc [6].
Radio-diagnostic imaging involves the use of x-ray or radiochemical tracers in the diagnostic of diseases and injury. Using Radiographic technique, the images of the internal body can be produced, analyzed and accurate diagnosis made [7].
Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representation of the interior of the body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues [7]. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin in hip joint and knee joint, which will help in ensuring that accurate diagnosis and treatment are made [7]. It is also used to access the accuracy of the surgical procedures after the replacement. Medical imaging also establishes a data base of normal anatomy and physiology of the hip and knee joint to make it possible to identify abnormalities [7].
In joint replacement, x-ray images of the joint are taken before, during and after surgical processes. The joint may be replaced with a variety of materials, including metal, polyethylene and ceramic [8].
Radiography is the primary imaging method for the evaluation or assessment of hip and knee replacements, and the imaging of hip and knee arthroplasty and its complications primarily relies on the information that is obtained from routine radiography, however, there are specific roles for other imaging techniques, such as arthrography, computed tomography scanning, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasonography, and nuclear medicine [8].
Over the years at the mention of joint replacement, peoples usually think that it is all about the surgical procedures even earlier researches on these joints’ replacements are mainly focused on the surgical procedures and the role of radio-diagnostic imaging on the joint’s replacements are only discussed with a pinch of salt.
This study therefore is targeted to research in details the impact of radio-diagnostic imaging on the replacement of the joints with fewer emphases on the surgical procedure.
Materials and Methods
Location of the Study
This study was carried out at National Orthopaedic Hospital, Enugu, and National Orthopaedic Hospital, Igbobi Lagos.
Target Population
The target population for this research includes all the radiographers and orthopaedic surgeons working in National Orthopaedic hospital Enugu and Igbobi Lagos within the period of the research. The total population of this study is 42.
Sample Size and Sampling Method
The sample size was determined using Taro Yamane formula which is stated as follows.
Which gave 38.
Source of Data
The data was collected using a structured questionnaire. The data was collected from both the radiographers and the orthopaedic surgeons involved in total hip and knee joint replacement procedures in the hospitals.
Method of Data Collection
Self-administered questionnaires were administered to the personnels involved in the study randomly. The questions were simple and required straight forward answers such as: X-ray investigation conducted before hip include: (a) pelvis (b) both hip (c) single hip arthroplasty.
Method of Data Analysis
Collected data was analyzed using the statistical package for social science (SPSS) program version 25.0.0.0.
Results
The data collected was categorized according to the statement of problem, specific objectives and significance of study. Thus, it was manually analyzed. Descriptive statistics as percentage, frequencies were manually obtained and presented in the following bar charts.
Figure 1 above shows the radiographers and surgeons who took part in the study to be 38 in number. There were more male, 78.8% than female 21.1%. Above 65% of the respondents were between the age bracket of 31-40 years. Majority of the respondents have a work experience between 1 to 15 years which represents more than 70% of the total sample size. The respondents are mostly surgeons with 68.4% while radiographers were only 31.6% of the respondents.
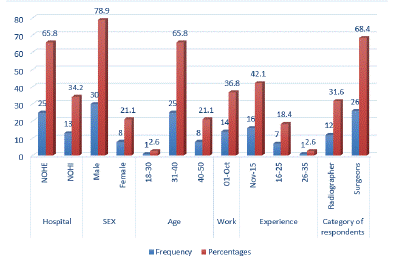
Figure 1: Socio-Demographic characteristics of Respondents (N= 38).
Figure 2 shows that 15.8% of the radiographers have MSc 17.9% have PGD while 5.3% are 2.6% have a BSc as DCR/DIR respectively. Majority of the surgeons (18) are MBBS holders while 5 are MSc holders, 3 who represent 7.9% of the respondents are FWACS holders.
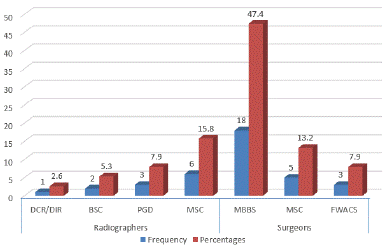
Figure 2: The different qualification of the Respondents (N = 38).
Figure 3 shows that at least one TKR and THR is done in each hospital per week, which amounts to 4 TKR and 4 THR per month and 48 per year in each hospital.
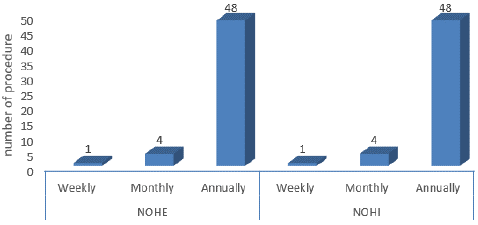
Figure 3: Number of Total Knee & Hip replaced in NOHE and NOHI.
Figure 4 shows that each hospital has convention x-ray and c-arm imaging modalities, only NOHI have CT modality while both hospitals do not have MRI and mobile x-ray units.
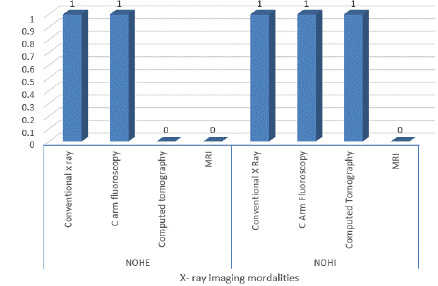
Figure 4: X-ray imaging modalities used in the hospital for the procedure.
Figure 5 shows that AP and lateral projection for knee joint is taken before the TKR procedure in each hospital.
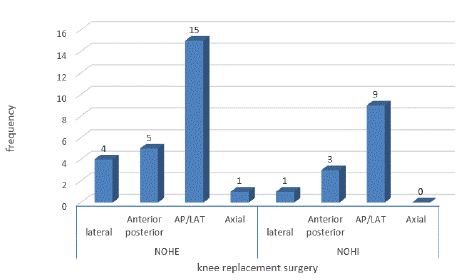
Figure 5: Projections for Total Knee Replacement.
Figure 6 shows that most of the respondents at NOHE and NOHI agreed that fluoroscopy and Conventional X-rays are frequency used in the examination while other modalities are seldom used.
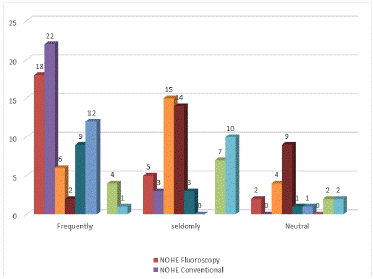
Figure 6: Use of the modalities for the procedure.
Figure 7 shows that the respondents generally agree that X-ray imaging of the affected joints is taken before, during and after the joint replacement, which responses close to 100% of the respondent.
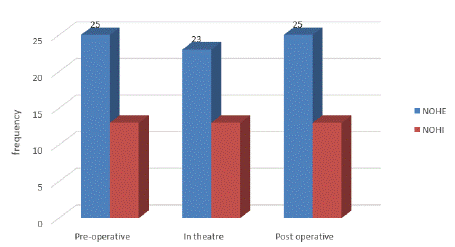
Figure 7: Use of X-Rays at each stage of the Procedures (N = 38).
Figure 8 shows that the most used post-operative modality is conventional x-ray.
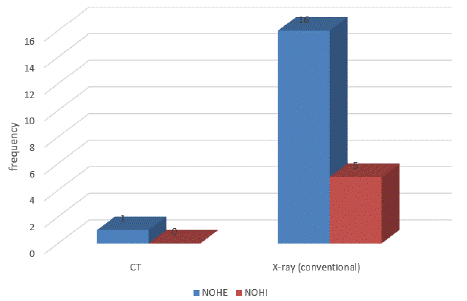
Figure 8: Post-operative modalities used.
Figure 9 shows that most of the respondents at NOHE were of the opinion that Right knee and Right Hip is the most frequency operated while most of the respondents and NOHI are of the opinion that left knee and Right Hip are frequently operated.
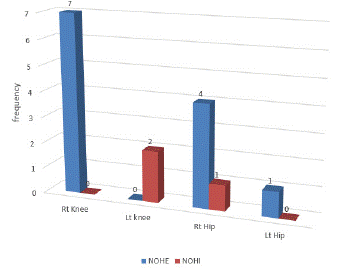
Figure 9: The side of the knee & hip frequency operated.
Summary of Recommendations of Respondents on what Radiographic Improvements to be Made to Improve Arthroplasty
i. Acquiring of modern imaging modalities such as digital radiographs, mobile X-ray machines, EOS X-ray, C-arm, standard fluoroscopy machine,
ii. Special training for radiographers on the proper use of these modalities.
iii. Specialization of radiographers in area of Arthroplasty.
iv. Knowledge on the methods of acquisition of special X-ray projections of the hip and knee joints to add extra information to patient management
Discussion and Summary of Findings
The study to assess the role of radio-diagnostic imaging on total hip and knee replacement procedures in National Orthopedic Hospital Enugu and National Orthopedic Hospital Igbobi Lagos arose due to the need to ascertain the role that radio-diagnostic imaging play on the total replacement of severely damaged hip and knee joint. This study is very important because the procedures of total hip and knee replacement appear to be a new practice here in Nigeria and as such, the study is well aimed at identifying the role radio-diagnostic imaging play during the procedure, which will also help to x-ray the areas of imaging that need to be improved upon to ensure better outcome.
For the fact that out of the three National Orthopeadic Hospital in Nigeria, two of them were used to carry out this study, this study can give a clear view on the role of medical imaging on total hip and knee replacement in Nigeria at large.
From the responses gathered, it was shown that the frequency at which these examinations were performed in the hospitals is very high, this means that the selected hospitals are adequate and reliable for data collection on the topic. Each procedure is performed at least once in a week in each hospital. This is in line with the study carried out by AU Katchy in 2012 on Total Hip Replacement in Nigeria: A Preliminary Report with the result that approximately 52 total hip replacement surgeries are performed in 2 years at NOHE and higher numbers expected in successive years.
For total knee replacements, most of the respondents are of the opinion that an x-ray of both knees should be performed before total knee replacement surgery. This means that there is no strict rule guiding the number of knees to be x-rayed before carrying out the replacement. Also, based on the responses from the respondents on the x-ray taken before total hip replacement surgery, almost all the respondents are of the opinion that x ray of pelvis and both hips should be taken. This is also in line with earlier findings by Clement RW et.al on their research on Radiographic Methods in Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty whereby antero-posterior and lateral x-ray projections of the hip were taken during the procedure. From this, one can see that AP and Lateral x-ray imaging of these joints is of a great importance before commencing the replacement procedures.
From the data collected from the hospitals, it shows that fluoroscopy in form of c-arm plays a significant role in total hip and knee replacement. Though some respondents are of the opinion that in as much as dedicated fluoroscopy equipment is not used in the hospitals that the answer to the question should be that fluoroscopy is not used. Most people are of the opinion that c-arm equipment should be a good replacement for a dedicated fluoroscopy unit. Therefore, fluoroscopy in the form of c-arm is used and it has a significant impact during the replacement of these joints.
While responding to the question on the adequacy of radiography in planning total hip and knee replacement, most of the respondents said that radiographic techniques is adequate but a good number of them disagreed stressing that other tests apart from radiographic techniques are conducted before the replacement and as such radiographic techniques cannot be adequate. From the reason given by those that disagreed, one can say that most times the result from the radiographic examination performed during the planning can be adequate while other times there is need for further test during the planning stage.
From the responses given on the important modalities for total hip replacement and total knee replacement surgery, it shows that conventional x ray is the most used, the second used modality is the CT scan followed by C- arm fluoroscopy. Other modalities are seldom used. So, for the fact that these number of modalities are used while performing the arthroplasty of the joints, it is an indication that radio-diagnostic imaging which covers the modalities of imaging has a great impact and significance in carrying out the joint’s arthroplasty. This finding correlates with that of A. Blum and D. Mole on Developments in imaging methods used in hip arthroplasty: a diagnostic algorithm which showed that the modalities earlier mentioned were used for the procedure.
On the issue bordering on the use of contrast media, more than 78% of the respondents said that no contrast media is used which means that generally no contrast is used for the joint’s replacement. The remaining respondents who said that contrast media is used may be a pointer that some cases warrant the use of contrast media. So therefore, contrast media have little or no impact on the procedures.
While answering the question on the equipment used for theatre imaging during the joint replacement procedures, the respondents, nearly all of them said that c arm x ray unit is used. This also shows that radio-diagnostic imaging also has an impact in the theatre procedure. More than 90% of the respondents also support that imaging of the hip and knee is very useful in the theatre procedure which signifies its impact. The respondents, more than 68% of them said that during the theatre procedure anterior- posterior and lateral x ray projection was taken, others close to 20% said that only AP is taken. This shows that the routine projection is AP and lateral projection.
Responding to the question bordering on the interval for radiographs post operation, many of the respondents said that it should be done from 1 to 4 weeks while others manually wrote immediately because there is no option for immediately on the questionnaire distributed. This means that there may be some respondents within the 1 to 4 weeks range that took it to have covered the option for immediately. Therefore, from the responses, the post operation radiograph is taken immediately after the procedures.
From the responses on the frequency of report on complication during recovery, the respondents are generally of the opinion that complications are seldom reported. This shows that proper use of imaging techniques and good surgical procedures has a positive impact on getting the patients back to normal with little or no complication.
From the answers of the respondents on the usefulness of imaging in confirming the complications when there is suspected complication, they generally agreed that there is a regular use of imaging in confirming complications. Only few respondents said that imaging is seldom used. Therefore, imaging is routinely used for confirming complications except in few situations. Their responses also show that x-ray, CT scan, ultrasound is used for confirming complication with x-ray taking the lead.
The respondents while responding to which modality is important or not important in the follow-up of arthroplasty, they said that only conventional x ray is very important while other modalities are not too important in the follow up studies. This is in accordance with the findings of Yulin Li, Lixi Chu et.al on their work Efficacy of Different Frequency TEAS in Acute Pain after Total Knee Trial Replacement: A Study Protocol for a Parallel Group Randomized where they found out that Conventional radiography is the mainstay in the post-operative assessment of hip and knee prosthetic replacements.
When asked if they support the discontinuation of x ray imaging in view of the radiation dose involved, most respondents said no to that and none said yes. This means that x ray even though it has negative effect due to the radiation dose to the patients, the benefits outweigh the risk and therefore in the arthroplasty of the hip and knee joints, its impact is so beneficial that it can be used despite the negative effect of radiation.
When confronted with the question on which procedure is most challenging, from their responses it shows that both hip joint is most challenging followed by right knee joint. The right is possibly due to the fact that it is the most frequently affected side because most people are right dominant.
Even though many of the respondents did not respond to the question about what radiographic improvements to be made to improve arthroplasty, few gave their recommendation which include the following;
i. Specialization of radiographers in area of arthroplasty
ii. Acquiring of modern imaging modalities such as digital imaging
iii. Mobile x-ray machine
iv. Eos x-ray
v. C-arm
vi. Dedicated fluoroscopy equipment
vii. Knowledge on the methods of acquisition of special x ray projections of the hip and knee joints to add extra information to the patient management.
Therefore, from these recommendations, one can easily see that despite the great positive impact of radio-diagnostic imaging on total hip and knee replacement procedure, there is still room for improvement to ensure a better outcome of treatment and general wellbeing of the patients.
Summary of Findings
1. There is a high number of knee and hip arthroplasty done in the hospitals.
2. The imaging modalities used include conventional x ray, c-arm unit, computed tomography, skeletal ultrasound and MRI in that order.
3. The x ray projections undertaken for the procedure include anterior posterior projection of the knee, lateral projection of the knee, and Anterior- posterior projection of the both hip and pelvis, lateral projection of the hips, and additional views which depends on the nature of injury.
4. Axial projections are rarely used according to the data collected.
5. Fluoroscopy using C-arm has a great significance especially in theatre procedures.
6. The role of CT scan and MRI in arthroplasty of the joint is generally not too important according to the data collected. They are used as additional modalities for some special cases.
7. From the data collected, post-arthroplastic imaging plays a very significant role in maintaining the joint stability and conventional x rays is the modality of choice.
Conclusion
From the result of this research, it shows that radio-diagnostic imaging has a great impact on total hip and knee replacement procedures in these hospitals and its use should be encouraged. More research is required for comprehensive conclusions.
References
- Rissanen P, Aro S, Slätis P, Sintonen H, Paavolainen P. Health and quality of life before and after hip or knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1995; 10: 169-75.
- March LM, Cross MJ, Lapsley H, Brnabic AJ, Tribe KL, Bachmeier CJ, et al. Outcomes after hip or knee replacement surgery for osteoarthritis. A prospective cohort study comparing patients’ quality of life before and after surgery with age-related population norms. Med J Aust. 1999; 171: 235-8.
- Jones CA, Voaklander DC, Johnston DW, Suarez-Almazor ME. Health related quality of life outcomes after total hip and knee arthroplasties in a community-based population. J Rheumatol. 2000; 27: 1745-52.
- Ethgen O , Bruyère O, Richy F, Dardennes C, Reginster JY. Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86: 963-74.
- Jones CA, Voaklander DC, Suarez-Alma ME. Determinants of function after total knee arthroplasty. Phys Ther. 2003; 83: 696-706.
- Rand JA, Trousdale RT, Ilstrup DM, Harmsen WS. Factors affecting the durability of primary total knee prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85: 259-65.
- Ingvarsson T, Hägglund G, Jónsson H, Jr, Lohmander LS. Incidence of total hip replacement for primary osteoarthrosis in Iceland 1982-1996. Acta Orthop Scand [Comparative Study Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. 1999; 70: 229-33.
- Lohmander LS, Engesaeter LB, Herberts P, Ingvarsson T, Lucht U, Puolakka TJ. Standardized incidence rates of total hip replacement for primary hip osteoarthritis in the 5 Nordic countries: similarities and differences. Acta Orthop [Comparative Study Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. 2006; 77: 733-40.
- Pedersen AB, Johnsen SP, Overgaard S, Søballe K, Sørensen HT, Lucht U. Total hip arthroplasty in Denmark – Incidence of primary operations and revisions during 1996-2002 and estimated future demands. Acta Orthop. 2005; 76: 182-9.
- Steel N, Melzer D, Gardener E, McWilliams B. Need for and receipt of hip and knee replacement—a national population survey. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006; 45: 1437-41.
- Robertsson O, Dunbar MJ, Knutson K, Lidgren L. Past incidence and future demand for knee arthroplasty in Sweden: a report from the Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register regarding the effect of past and future population changes on the number of arthroplasties performed. Acta Orthop Scand [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. 2000; 71: 376-80.
- Coyte P, Wang PP, Hawker G, Wright JG. The relationship between variations in knee replacement utilization rates and the reported prevalence of arthritis in Ontario, Canada. J Rheumatol. 1997; 24: 2403-12.
- Wells VM, Hearn TC, McCaul KA, Anderton SM, Wigg AER, Graves SE. Changing incidence of primary total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17: 267-73.
- Abbott KC, Bucci JR, Agodoa LY. Total hip arthroplasty in chronic dialysis patients in the United States. J Nephrol. 2003; 16: 34-9.
- Clark DA, Mason KT, Belmont P. Incidence and outcomes of total hip arthroplasty among US Army aviators. Mil Med. 2001; 166: 132-4.
- Kim HA, Koh SH, Lee B, Kim IJ, Seo YI, Song YW, et al. Low rate of total hip replacement as reflected by a low prevalence of hip osteoarthritis in South Korea. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008; 16: 1572-5.
- Mehrotra C, Remington PL, Naimi TS, Washington W, Miller R. Trends in total knee replacement surgeries and implications for public health, 1990-2000. Public Health Rep. 2005; 120: 278-82.
- Kim HA, Kim S, Seo YI, et al. The epidemiology of total knee replacement in South Korea: national registry data. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47: 88-91.
- Jüni P, Dieppe P, Donovan J, Peters T, Eachus J, Pearson N, et al. Population requirement for primary knee replacement surgery: a cross-sectional study. [comment] Rheumatology (Oxford) [Comment Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003; 42: 516-21.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Racial disparities in total knee replacement among Medicare enrollees--United States, 2000-2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009; 58: 133-8.
- Järvholm B, From C, Lewold S, Malchau H, Vingård E. Incidence of surgically treated osteoarthritis in the hip and knee in male construction workers. Occup Environ Med. 2008; 65: 275-8.
- Kurtz S, Mowat F, Ong K, Chan N, Lau E, Halpern M. Prevalence of primary and revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 1990 through 2002. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87: 1487-97.
- Melzer D, Guralnik JM, Brock D. Prevalence and distribution of hip and knee joint replacements and hip implants in older Americans by the end of life. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2003; 15: 60-6.
- Wells V, Hearn T, Heard A, Lange K, Rankin W, Graves S. Incidence and outcomes of knee and hip joint replacement in veterans and civilians. ANZ J Surg. 2006; 76: 295-9.
- Melton LJ, 3rd, Stauffer RN, Chao EY, Ilstrup DM. Rates of total hip arthroplasty; a population-based study. N Engl J Med. 1982; 307: 1242-5.
- Johnsson R, Lidgren L. Incidence of hip replacement in southern Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 1987; 58: 226-30.
- Birrell F, Johnell O, Silman A. Projecting the need for hip replacement over the next three decades: influence of changing demography and threshold for surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999; 58: 569-72.
- Hoaglund FT, Oishi CS, Gialamas GG. Extreme variations in racial rates of total hip arthroplasty for primary coxarthrosis: a population-based study in San Francisco. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995; 54: 107-10.
- Puolakka TJ, Pajamäki KJ, Halonen PJ, Pulkkinen PO, Paavolainen P, Nevalainen JK. The Finnish Arthroplasty Register: report of the hip register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001; 72: 433-41.
- Havelin LI, Engesaeter LB, Espehaug B, Furnes O, Lie SA, Vollset SE. The Norwegian Arthroplasty Register: 11 years and 73,000 arthroplasties. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000; 71: 337-53.