
Mini Review
Austin J Environ Toxicol. 2018; 4(1): 1024.
Biodegradation of Methyl Parathion and its Application in Biosensors
Kumar J*, Mishra A and Melo JS
Nuclear Agriculture and Biotechnology Division, India
*Corresponding author: Jitendra Kumar, Nuclear Agriculture and Biotechnology Division, Mumbai, India
Received: March 15, 2018; Accepted: May 09, 2018; Published: May 19, 2018
Introduction
Methyl parathion is an Organo Phosphate (OP) insecticide which is being used in agriculture to protect the crops from insects. It causes many health problems in humans, related to acetyl cholinesterase inhibition. Methyl parathion is classified as Category Ia (extremely toxic) by the World Health Organization (WHO) and as Toxicity Category I (most toxic) insecticide by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). Organ Phosphorus Hydrolyses (OPH) (E.C.3.1.8.1) was discovered in soil micro-organisms and hydrolyzes methyl parathion into p-nitro phenol (PNP) and Di Methyl Thio Phosphate (DMTP). Hydrolyzed product PNP can be detected by electrochemical and optical methods. This review is a compilation of the work reported on OPH based enzymatic and microbial biosensor for detection of methyl parathion pesticide.
Introduction
Methyl parathion is an organophosphate insecticide, nematicide, and acaricide/miticide used to control boll weevils and many insect pests of agricultural crops [1-6]. Methyl parathion is produced by the reaction of O,O-dimethyl phosphorochloridothionate and the sodium salt of 4-nitrophenol in acetone solvent [7-8]. Bayer has developed this pesticide and has long been the ‘parent’ company with its well-known brand ‘Folidol’. However, there have also been a number of other manufacturers globally. The main manufacturers of Methyl parathion are All India Medical Co (India), Bayer India, Bayer Mexico, Cheminova (Denmark), Rallis India, Sundat (Singapore) and Velpol Company (Mexico) [5,9]. The IUPAC chemical name of MP is O,O-dimethyl O-4-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate. Its chemical structure is shown below:
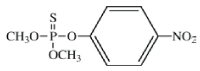
Methyl parathion kills pests by acting as a stomach poison and act as potent irreversible acetyl cholinesterase inhibitor. It was used to control a variety of insects and mites, including thrips, weevils, aphids and leafhoppers, in a very wide range of crops including cereals, fruit, nuts, vines, vegetables, ornamentals, cotton, and field crops [5,7,10]. Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC) in India recommended it in two different forms either in 2% DP or 50% EC for controlling the insect pests from the cotton, paddy, wheat, pulses such as green gram and black gram and oilseeds such as ground nut and mustard crops.
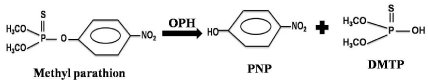
Figure 1: Structural presentation of methyl parathion hydrolysis with OPH.
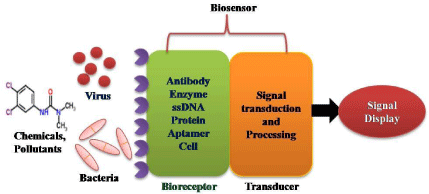
Figure 2: Principle of biosensors.
Methyl parathion binds into the acyl pocket at the active site of acetyl cholinesterase enzyme. The binding of a phosphate group to the serine amino acid at the active site of acetyl cholinesterase changes the configuration of the enzyme molecule, stabilizing it and preventing it from functioning and inactivating permanently [11]. When inhaled by human being, the first adverse effects are a bloody or runny nose, coughing, chest discomfort and difficulty in breathing. Skin contact may cause localized sweating and involuntary muscle contractions. Following exposure by any route, other systemic effects may begin within a few minutes, or be delayed for up to 12 hours. These may include pallor, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, headache, dizziness, eye pain, blurred vision, constriction or dilation of the pupils, tears, salivation, sweating and confusion [7,12]. In severe cases, poisoning will affect the central nervous system, producing in-coordination, slurred speech, loss of reflexes, weakness, fatigue, and eventual paralysis of the body extremities and respiratory muscles. Death may be caused by respiratory failure or cardiac arrest [7,12,13].
Methyl parathion was initially registered in 1954 in the United States for application as insecticide [14] but its uses was restricted in 1978 as a result of detrimental effects to humans [13,14]. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has now classified methyl parathion as a restricted-use pesticide and has given approval for outdoor use only [10]. It was classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a Category Ia (extremely toxic) and by the United States EPA (U.S. EPA) as a Toxicity Category I (most toxic) insecticide [10]. Although banned in developed countries, it is still being used in India as a restricted insecticide. As per CIBRC in India, formulations of MP, 50% EC and 2% DP are banned for use on fruits and vegetables (S.O.680 (E) dated 17thJuly, 2001), and its use is restricted to only those crops where honeybees are not acting as pollinators. (S.O.658 (E) dated 04th Sep., 1992) [15].
S.No.
Microbial cells/ Enzyme
Type of detector
Detection range
Ref.
Based on hydrolysis of methyl parathion by immobilized microbial cells
1
Escherichia coli cells OPH intracellularly
Potentiometric
Not reported
[44]
2
Escherichia coli cells expressing OPH on cell surface
Potentiometric
0.06-0.91 mM
[45]
3
Moraxella sp. express INPNC-OPH on the cell surface
Amperometric
Upto 175 µM
[46]
4
Pseudomonas putida JS444, express OPH on the cell surface
Amperometric
Upto 2 µM
[47]
5
Pseudomonas putida JS444 expressing OPH on cell surface
Dissolve oxygen electrode
0.2-50 µM
[48]
6
Escherichia coli strain surface displayed mutant OPH (S5)
Amperometric
0.08-30 µM
[49]
7
E. coli was having high periplasmic expression of OPH
Cyclic voltammetric
2-80 µM
[50]
8
Flavobacterium sp.
Optical
4-80 µM
[51]
9
Sphingomonas sp.
Optical
4-80 µM
[52]
10
Sphingomonas sp.
Optical
4-80 µM
[53]
11
Sphingomonas sp.
Optical
0.1-1ppm
[54]
Based on hydrolysis of methyl parathion by immobilized OPH enzyme
12
OPH Enzyme
Electrochemical impedance spectra
Linear Voltammetry5.0-200 ng/mL and
200-1000 ng/mL[55]
13
OPH Enzyme
Potentiometric
0.1-0.43 mM
[56]
14
OPH Enzyme
Amperometric
Up to 140 µM
[57]
15
OPH Enzyme
Amperometric
1-10 µM
[58]
16
OPH Enzyme
Amperometric
Up to 40 µM
[59]
17
OPH Enzyme
Amperometric
Cyclic voltammetryUp to 2 µM
[60]
18
OPH Enzyme
Chrono amperometric
4.6-46 µM
[61]
Table 1: Biosensors for detection of methyl parathion.
Biodegradation of methyl parathion
Organ Phosphorus Hydrolase (OPH) (E.C.3.1.8.1) was first discovered in soil micro-organisms Pseudomonas diminuta MG and Flavobacterium sp. and hydrolyzes methyl parathion into P-Nitro Phenol (PNP) and Di Methyl Thio Phosphate (DMTP) [16-21]. This hydrolytic reaction is the first steps of degradation of methyl parathion by soil microorganism which was extensively studied. OPH was first found in Pseudomonas diminuta, and then in Flavobacterium sp., both are soil microbes [22]. OPH also has been found in a variety of organisms such as squid, protozoa, mammals, yeast, fungi and soil bacteria [22,23]. OPH is also known as phosphotriesterase, parathion hydrolase, paraoxonase, DFPase, somanase, sarinase, phosphorothiolase and parathion aryl esterase [24-27]. The gene encoding OPH, opd (organo phosphate degradation), has been expressed in various systems including Escherichia coli, Drosophila melanogaster, Streptomyces lividans and insect cells [23,24,28]. OPH has been studied extensively over the years [24,29-31] and several genetically engineered variants have been produced in an effort to improve its catalytic ability [31-33].
Below is the structural presentation of methyl parathion hydrolysis with OPH into P-Nitro Phenol (PNP) and Di Methyl Thio Phosphate (DMPT) (Figure 1).
PNP is an optically detectable product which can be detected by electrochemical and colorimetric methods. Thus, this hydrolytic step has been extensively exploited to develop the biosensor for detection of methyl parathion.
Biosensors for detection of methyl parathion using biodegradation step
A biosensor is a self-contained integrated device which is capable of providing specific quantitative or semi-quantitative analytical information using a biological recognition element which is in direct contact with a transducer element. Biosensors consists of three basic components: (i) a biological component to interact with analyses which generate some physico-chemical signal, (ii) a transducer to convert the generated signal in to output signal (mostly electrical) and (iii) a signal processing system to process the output signal into the appropriate form that can be displayed on device (Figure 2) [5-6,34-36].
Biological materials play a very significant role in biosensor field as one of the main components which provide selectivity and specificity of the system for interest of analyze. The principle of detection is the specific binding of the analyze of interest to the complementary biological material immobilized on a suitable support matrix. The specific interaction results in a change in one or more physico-chemical properties like change in pH, electron transfer, mass changes, heat transfer, uptake or release of gases or specific ions, which can be detected and produce an electronic signal, which is proportional to the concentration of a specific analyze or group of analyses. Now days, biosensor plays an important role as alternative detection method replacing the traditional analytical methods such as spectrophotometer, gas–liquid chromatography, thin-layer chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, capillary electrophoresis and mass spectrometry etc [37-41]. Biosensor facilitate onsite detection of large number of sample with no or low preparation, less time requirement and no requirement of expensive apparatus and trained personnel which are generally limitation in traditional analytical methods.
On the basis of bio component, if enzyme is used as bio component, it is known as enzymatic biosensor and if microbial cells are used, it is called microbial biosensor. Both bio components (enzyme/microbial cells) have certain limitations and advantages. Purified enzymes have very high specificity for their substrates or inhibitors, their application in biosensor construction may be limited by the tedious, time-consuming and costly enzyme purification steps and requirement of cofactor/coenzyme to generate the measurable product. Microbes provide an ideal alternative to these bottle-necks [35,42,43]. The enzymes and co-factors that co-exist in the microbes give the ability to consume and hence detect large number of analyses. Microbial cells can be easily manipulated and adapted to consume and degrade new substrates under certain cultivating condition. Additionally, the progress in molecular biology/recombinant DNA technology has opened endless possibilities of tailoring the microorganisms to improve the activity of an existing enzyme or express foreign enzyme/protein in host cell. All of the above makes microbial cells an excellent biosensing element for developing biosensor. The use of microbial cells has been demonstrated as an alternative biological catalyst without compromising on cost of purifying enzymes [35,42,43].
OPH enzyme and the microbial cells having OPH have been extensively utilized for developing biosensor to detect methyl parathion pesticide (Table 1). Enlist the publications where different microbial cells expressing OPH and purified OPH enzyme have been immobilized on a suitable matrix and further used as biosensor.
Conclusion
This review focuses on biodegradation of methyl parathion using OPH enzyme which is present in soil microorganism. It lists many reports where microbe carrying OPH and purified OPH were used for hydrolysis of methyl parathion which further applied in biosensors for detection of methyl parathion pesticide.
References
- Adhya TK, Barik S, Sethunathan N. Fate of fenitrothion, methyl parathion, and parathion in anoxic sulfur-containing soil systems. Pesticide Biochem Physiol. 1981; 16: 14-20.
- Adhya TK, Barik S, Sethunathan N. Hydrolysis of selected organophosphorus insecticides by two bacteria isolated from flooded soil. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981; 50: 167-172.
- Adhya TK, Barik S, Sethunathan N. Stability of commercial formulation of fenitrothion, methyl parathion, and parathion in anaerobic soils. J Agric Food Chem. 1981; 29: 90-93.
- Brahmaprakash GP, Panda S, Sethunathan N. Relative persistence of hexachlorocyclohexane, methyl parathion and carbofuran in an alluvial soil under flooded and non-flooded conditions. Agric Ecosyst Environ. 1987; 19: 29-39.
- Kumar J, Melo JS. Microbial biosensors for methyl parathion: From single to multiple samples analysis. Advances in Biosensors Research. 2015; 89-111.
- Kumar J, Melo JS. Overview on Biosensors for Detection of Organophosphate Pesticides. Curr Trends Biomedical Eng Biosci. 2017; 5: 555663.
- ATSDR. Toxicological profile for methyl parathion. Draft for public comment. Atlanta, GA, US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. 1999.
- EPA. Production, distribution, use, and environmental impact potential of selected pesticides [final report]. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Pesticide Programs. EPA 540/1-74-001. 1974; 181-188.
- Methyl Parathion, Prior Informed Decision Guidance Document, (FAO/UNEP, Joint Database, IRPTC, Geneva), Update 17, September 1996. (PAN International Website, Methyl Parathion Fact Sheet).
- US EPA. Interim Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Methyl Parathion. Case No. 0153. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2003.
- Sultatos LG. Mammalian toxicology of organophosphorus pesticides. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1994; 43: 271-289.
- IPCS. Environmental Health Criteria 145, Methyl Parathion. International Programme on Chemical Safety. 1993.
- Garcia SJ, Abu-Qare AW, Meeker-O’Connel WA, Borton AJ, Abou-Donia MB. Methyl parathion: A review of health effects. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003; 6: 185-210.
- US EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Methyl Parathion Risk Management Decision. 1999.
- CIBRC. Pesticides Restricted for Use in India. Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee. Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine and Storage, Department of Agriculture and Cooperation, India. 2007.
- Dumas DP, Caldwell SR, Wild JR, Raushel FM. Purification and properties of the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. J Biol Chem. 1989; 264: 19659-19665.
- Gaberlein S, Spener F, Zaborosch C. Microbial and cytoplasmic membrane-based potentiometric biosensors for direct determination of organophosphorus insecticides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000; 54: 652-658.
- Mulbry WW, Karns JS. Parathion hydrolase specified by the Flavobacterium opd gene: Relationship between the gene and protein. J Bacteriol. 1989; 171: 6740-6746.
- Mulbry WW, Karns JS. Purification and characterization of three parathion hydrolases from gram-negative bacterial strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989; 55: 289-293.
- Munnecke DM, Hsieh DP. Microbial decontamination of parathion and p nitrophenol in aqueous media. Appl Microbiol. 1974; 28: 212-217.
- Munnecke DM. Enzymatic detoxification of waste organophosphate pesticides. J Agric Food Chem. 1980; 28: 105-111.
- Caldwell SR, Newcomb JR, Schlecht KA, Raushel FM. Limits of diffusion in the hydrolysis of substrates by the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Biochem. 1991; 30: 7438-7444.
- Phillips JP, Xin JH, Kirby K, Milne CP, Krell P, Wild JR. Transfer and expression of an organophosphate insecticide-degrading gene from pseudomonas in drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1990; 87: 8155-8159.
- McDaniel CS, Harper LL, Wild JR. Cloning and sequencing of a plasmid-borne gene (opd) encoding a phosphotriesterase. J Bacteriol. 1988; 170: 2306-2311.
- Lai K, Stolowich NJ, Wild JR. Characterization of P-S bond hydrolysis in organophosphorothioate pesticides by organophosphorus hydrolase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995; 318: 59-64.
- Singh BK. Organophosphorus-degrading bacteria: Ecology and industrial applications. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009; 7: 156-164.
- Singh BK, Walker A. Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2006; 30: 428-471.
- Omburo GA, Kuo JM, Mullins LS, Raushel FM. Characterization of the zinc binding site of bacterial phosphotriesterase. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267: 13278-13283.
- Dumas DP, Raushel FM. Chemical and kinetic evidence for an essential histidine in the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265: 21498-21503.
- Dumas DP, Durst HD, Landis WG, Raushel FM, Wild JR. Inactivation of organophosphorus nerve agents by the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990; 277: 155-159.
- Lai K, Grimsley JK, Kuhlmann BD, Scapozza L, Harvey SP, DeFrank JJ, et al. Rational enzyme design: Computer modeling and site-directed mutagenesis for the modification of catalytic specificity in organophosphorus hydrolase. Chimia. 1996; 50: 430-431.
- Di Sioudi BD, Miller CE, Lai K, Grimsley JK, Wild JR. Rational design of organophosphorus hydrolase for altered substrate specificities. Chem Biol Interact. 1999; 119-120: 211-223.
- DiSioudi B, Grimsley JK, Lai K, Wild JR. Modification of near active site residues in organophosphorus hydrolase reduces metal stoichiometry and alters substrate specificity. Biochem. 1999; 38: 2866-2872.
- Kumar J, Melo JS. A tutorial on biosensors. Souvenier cum bulletin of ISEAC. 2018; 4: 32-43.
- D'Souza SF. Microbial biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2001; 16: 337-353.
- D'Souza SF. Immobilization and stabilization of biomaterials for biosensor applications. Appl Biochem Biotech. 2001; 96: 225-238.
- Beck J, Sherman M. Detection by TLC of organophosphorus insecticides in acutely poisoned rats and chickens. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol. 1968; 26: 35-40.
- Camoni I, Gandolfo N, Ramelli GC, Sampaolo A, Binetti L. Analytical procedure for the detection and determination of parathion and methyl-parathion in food products. Bollettino dei Laboratori Chimica Provinciali. 1968; 19: 615-629.
- Suzuki K, Goto S, Kashiwa T. Residue analysis of agricultural chemicals. I. Determination of parathion-methyl in rice grains by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. Japan Analyst. 1968; 17: 187-191.
- Kawahara FK, Lichtenberg JJ, Eichelberger JW. Thin layer and gas chromatographic analysis of parathion and methyl parathion in the presence of chlorinated hdrocarbons. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1967; 39: 446-457.
- Nielsen PG. Quantitative analysis of parathion and parathion-methyl by combined capillary column gas chromatography negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1985; 12: 695- 698.
- Lei Y, Chen W, Mulchandani A. Microbial biosensors. Anal Chim Acta. 2006; 568: 200-210.
- Su L, Jia W, Hou C, Lei Y. Microbial biosensors: A review. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011; 26: 1788-1799.
- Mulchandani A, Mulchandani P, Chauhan S, Kaneva I, Chen W. A potentiometric microbial biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents. Electroanal. 1998; 10: 733-737.
- Mulchandani A, Mulchandani P, Kaneva I, Chen W. Biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents using recombinant Escherichia coli with surface-expressed organophophorus hydrolase. 1. Potentiometric microbial electrode. Anal Chem. 1998; 70: 4140-4145.
- Mulchandani P, Chen W, Mulchandani A, Wang J, Chen L. Amperometric microbial biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate pesticides using recombinant microorganism with surface expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. Biosens Bioelectron. 2001; 16: 433-437.
- Lei Y, Mulchandani P, Wang J, Chen W, Mulchandani A. Highly sensitive and selective amperometric microbial biosensor for direct determination of p-nitrophenyl-substituted organophosphate nerve agents. Environ Sci Technol. 2005; 39: 8853-8857.
- Lei Y, Mulchandani P, Chen W, Mulchandani A. Direct determination of p-nitrophenyl substituent organophosphorus nerve agents using a recombinant Pseudomonas putida js444-modified clark oxygen electrode. J Agric Food Chem. 2005; 53: 524-527.
- Tang X, Zhang T, Liang B, Han D, Zeng L, Zheng C, et al. Sensitive electrochemical microbial biosensor for p-nitrophenylorganophosphates based on electrode modified with cell surface-displayed organophosphorus hydrolase and ordered mesopore carbons. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014; 60: 137-142.
- Kumar J, D'Souza SF. Microbial biosensor for detection of methyl parathion using screen printed carbon electrode and cyclic voltammetry. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011; 26: 4289-4293.
- Kumar J, Jha SK, D'Souza SF. Optical microbial biosensor for detection of methyl parathion pesticide using Flavobacterium sp. whole cells adsorbed on glass fiber filters as disposable biocomponent. Biosens Bioelectron. 2006; 21: 2100-2105.
- Kumar J, D'Souza SF. An optical microbial biosensor for detection of methyl parathion using Sphingomonas sp. immobilized on microplate as a reusable biocomponent. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010; 26: 1292-1296.
- Kumar J, D'Souza SF. Immobilization of microbial cells on inner epidermis of onion bulb scale for biosensor application. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011; 26: 4399-4404.
- Mishra A, Kumar J, Melo JS. An optical microplate biosensor for the detection of methyl parathion pesticide using a biohybrid of Sphingomonas sp. cells-silica nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017; 87: 332-338.
- Du D, Chen W, Zhang W, Liu D, Li H, Lin Y. Covalent coupling of organophosphorus hydrolase loaded quantum dots to carbon nanotube/Au nanocomposite for enhanced detection of methyl parathion. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010; 25: 1370-1375.
- Mulchandani P, Mulchandani A, Kaneva I, Chen W. Biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents. 1. Potentiometric enzyme electrode. Biosens Bioelectron. 1999; 14: 77-85.
- Mulchandani P, Chen W, Mulchandani A. Flow injection amperometric enzyme biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents. Environ Sci Technol. 2001; 35: 2562-2565.
- Wang J, Krause R, Block K, Musameh M, Mulchandani A, Schöning MJ. Flow injection amperometric detection of OP nerve agents based on an organophosphorus-hydrolase biosensor detector. Biosens Bioelectron. 2003; 18: 255-260.
- Mulchandani A, Mulchandani P, Chen W, Wang J, Chen L. Amperometric thick-film strip electrodes for monitoring organophosphate nerve agents based on immobilized organophosphorus hydrolase. Anal Chem. 1999; 71: 2246-2249.
- Deo RP, Wang J, Block I, Mulchandani A, Joshi KA, Trojanowicz M, et al. Determination of organophosphate pesticides at a carbon nanotube/organophosphorus hydrolase electrochemical biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2005; 530: 185-189.
- Wang J, Chen L, Mulchandani A, Mulchandani P, Chen W. Remote biosensor for in-situ monitoring of organophosphate nerve agents. Electroanal. 1999; 11: 866-869.