Abstract
Background: Vestibular Schwannomas are benign primary brain tumors that are generally asymptomatic, however when symptomatic it is secondary to mass effect. The onset of these tumors is typically in the fifth decade of life, however recent findings have suggested a relationship with pregnant females leading to an earlier onset. With the concomitant diagnosis of a brain tumor while pregnant, management and treatment options are further complex.
Case Presentation: A 28 year old Haitian Creole-speaking female with no significant past medical history presented with bilateral ear pain, chest pain and abdominal pain. The patient reported that the symptoms had been present for several months, however within the last few weeks a significant decline in bilateral hearing was noted. Upon further evaluation, the patient was found to be nineteen weeks pregnant. After an OB-GYN consultation and imminent danger to the fetus was ruled out, a brain MRI was ordered. This study found a large lobulated mass centered in the left cerebellopontine angle cistern with extension into the left internal auditory canal. A diagnosis of vestibular schwannoma was made and immediate transfer to higher-level care was achieved.
Conclusion: Current research has been done to explore why vestibular schwannomas have presented prematurely in pregnant patients. Though much work has been done, further research is needed to fully understand the pathogenesis. This case report sought to shed some light on why these tumors may occur during pregnancy and the various diagnostic and treatment options at a physician’s disposal.
Keywords: Pregnancy; Vestibular schwannoma; Acoustic neuroma; Tumor; Hearing loss
Introduction
Vestibular Schwannomas, also called Acoustic Neuromas, are primary brain tumors that most commonly arise in the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve [1]. These are Schwann cell-derived tumors that comprise approximately 8% of all intracranial tumors and 80-90% of the tumors arising from the cerebellopontine angle [2]. Recent data suggests an apparent increase in incidence likely due to increasing use of MRI and CT scans in modern medicine [2,3].
Vestibular Schwannomas are generally a very benign tumor with the rare potential for malignant degeneration. They have a greater incidence in females with a median age of onset of 50 years old [2]. Unilateral presentation is more common, with a bilateral presentation commonly seen in the hereditary condition known as Neurofibromatosis Type 2. The characteristic pattern on histology demonstrates zones of alternating dense and sparse cellularity, known as Antoni A + B respectively [2]. Diagnosis is typically made via physical exam, audiometry (best screening tool) and MRI (procedure of choice) [2,4].
The clinical presentation of a vestibular schwannoma is due to cranial nerve involvement, cerebellar/brainstem compression and/ or tumor progression. The most common presenting symptom is hearing loss with or without associated tinnitus. This is due to tumor involvement of cranial nerve 8, specifically leading to an asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss. Other cranial nerves reportedly involved include the trigeminal and facial nerves. These may lead to symptoms such as facial paresthesia, pain and possible taste disturbances. Cerebellum and brainstem compressive symptoms may lead to ataxia and unsteadiness, obstructive hydrocephalus, and even cerebellar tonsil herniation and death.
The purpose of this report is to describe the finding of a vestibular schwannoma in a pregnant patient. Specifically, we wanted to investigate if pregnancy had a part to play in the presentation of this tumor. Also, due to the complexity of having a brain tumor while pregnant, treatment and management options were explored.
Case Presentation
A 28 year old Creole speaking Haitian female with no significant past medical history presented to Orange Park Medical Center in Orange Park, FL with complaints of bilateral ear pain with tinnitus, chest pain, abdominal pain, headaches and blurry vision. She reported symptoms had been present for several months, however within the month prior to presentation there was a notable worsening in hearing and an increase in double vision. Patient denied changes in weight, rash and joint/muscle aches. Additionally, our patient was found to be 19 weeks pregnant. She immigrated from Haiti two years ago and at the time of presentation was working in a seafood warehouse. She denied any sick contacts or recent travel abroad. No medications were reported. Translator on site was able to ascertain the medical history. Upon questioning, the patient was noted to read lips, which suggested to us that a chronic issue was likely responsible for her hearing problems.
On initial evaluation in the emergency department, the patient was also found to have a urinary tract infection which met the sepsis criteria. After consultation with Obstetrics, the patient was immediately begun on IV antibiotics. An ECG demonstrated sinus tachycardia and troponin values were negative. Chest X-ray was within normal limits and fetal ultrasound was significant for a single live intrauterine gestation with no placenta abruption or previa noted. Serology was negative for influenza A/B and Streptococcus pneumoniae. ENT was consulted due to the concern over her worsening hearing loss and double vision. Radiology studies were recommended.
Though hesitant at first, with extensive reassurance that her unborn child would be safe, the patient underwent a temporal bone CT without contrast and a brain MRI. Both were significant for a 4.9cm lobulated mass centered in the left cerebellopontine angle cistern extending to fill the left internal auditory canal (Figure 1). The mass compressed the brainstem, left cerebellum and fourth ventricle. Distention of the lateral and third ventricles was indicative of noncommunicating hydrocephalus. Per radiology, this study was significant for an extra-axial schwannoma. Emergent neurosurgery consult was placed with subsequent transfer to UF Shands in Gainesville, FL for higher level of care. Due to the transfer, follow-up on the patient’s status and treatment was unable to be ascertained.
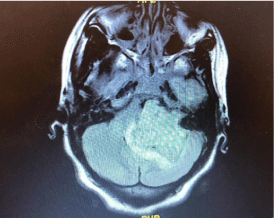
Figure 1: 4.9cm lobulated T2 heterogenous mass centered in left
cerebellopontine angle cistern with extension into the left internal auditory
canal. Mass compresses the brainstem, left cerebellum and fourth ventricle.
Discussion/Conclusion
This case report discusses the significance of vestibular schwannomas and their presentation in a young pregnant female. Though traditionally these tumors account for about 8% of all intracranial tumors, the incidence appears to be rising and a unique relationship has been noticed with pregnant women [6,7]. It would appear that pregnancy may have an effect on tumor growth and thus more rapid symptom presentation. Given the chronicity of some of our patient’s symptoms, including her ability to read lips, we believe that her tumor was likely present before becoming pregnant. However, with the physiologic changes associated with pregnancy, her symptoms became more rampant. Specifically, one of the most common physiologic changes in pregnancy is fluid retention. The excess fluid may lead to increased tumor edema and thus engorgement of various vascular tumors, such as a vestibular schwannomas [4,5,8]. As mentioned earlier, many of these tumors are asymptomatic and incidental, thus this may help to explain why a pregnant female can present with new onset of symptoms. Additionally, pregnancy has a widespread effect on the body as a whole, notably through the rampant sex hormones produced. Many publications have suggested that these hormones may play a role in the acceleration of growth via estrogen and progesterone receptors found within the tumor [4,5-9]. However, much more research needs to be done as there appears to be very conflicting evidence as to whether the hormones have any significant effect or if there are even receptors present within the tumor [4,5-9].
Treatment of vestibular schwannomas consists of three options: observation, radiation and surgery. Observation is used for the tumors that are asymptomatic and is the ideal treatment in pregnancy until delivery is possible [4,5]. Hydrocephalus is a common presentation of these tumors. For the cases that will be observed or for those waiting for surgery, a ventriculoperitoneal shunt may be placed to relieve the pressure. Radiation is typically used for very small or inoperable tumors, specifically in the elderly population where surgery may not be an option. Surgery is the definitive treatment, though it too may lead to further complications. Recurrence is common if the tumor isn’t fully resected [2,5]. The most significant side effect are post-operative headaches, which are expected to resolve with time. Additionally, patients must be counseled on the fact that though surgery can prevent further hearing damage, only rarely does hearing improve [2]. If surgery is needed in a pregnant patient, the second trimester is the ideal time frame, as complications to both the fetus and mother are less [9]. Regardless of treatment approach, yearly scans are required to monitor for tumor progression and/or recurrence.
Vestibular schwannomas are a very rare medical diagnosis, however they can cause serious distress among patients. This case report detailed the presentation and work up of a young pregnant female that was ultimately discovered to have this tumor. We attempted to discuss the relationship with pregnancy and the treatment options available. An early diagnosis and treatment can lead to a favorable outcome.
Disclosure Statement
This research was supported by HCA Healthcare and/or an HCA Healthcare affiliated entity. The views expressed in this publication represent those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of HCA Healthcare or any of its affiliated entities.
References
- Beni-Adani, Liana, et al. “Huge Acoustic Neurinomas Presenting in the Late Stage of Pregnancy.” Acta Obstetricia Et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 2001; 80: 179–179.
- Park, John, et al. “Vestibular Schwannoma (Acoustic Neuroma).” UpToDate, 2018.
- Michaud, Dominique, and Tracy Batchelor. “Risk Factors for Brain Tumors.” UpToDate, 2017.
- Shah, Kushal, and Roukoz Chamoun. “Large Vestibular Schwannomas Presenting during Pregnancy: Management Strategies.” NCBI, 2014.
- Goma, Hala M. “Management of Brain Tumor in Pregnancy - An Anesthesia Window.” Intech Open, IntechOpen. 2013.
- Isla, Alberto, et al. “Brain Tumor and Pregnancy.” NeuroImage, Academic Press. 1999.
- Kasper, Ekkehard, et al. “A Pregnant Female with a Large Intracranial Mass: Reviewing the Evidence to Obtain Management Guidelines for Intracranial Meningiomas during Pregnancy.” Surgical Neurology International.
- Lee, Men-Jean, and Susan Hickenbottom. “Neurologic Disorders Complicating Pregnancy.” UpToDate, 2018.
- Patel, Andrew K., et al. “Vestibular Schwannoma Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Expression of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors.” The Laryngoscope. 2008; 118: 1458–1463.
