
Clinical Image
Austin J Gastroenterol. 2015;2(1): 1034.
Bridging Pancreatic Duct Stent - A Rare Adverse Event
Arya V*, Bansal V and Kabul V
Department of Gastroenterology, Wyckoff Height Medical Center, USA
*Corresponding author: Arya V, Department of Gastroenterology, Wyckoff Heights Medical Center, 374 Stockholm Street, Brooklyn, NY 11237, USA
Received: January 29, 2015; Accepted: February 03, 2015; Published: February 05, 2015
Keywords
Pancreatic duct stent; Duodenal perforation
A 42-year-old female with history of chronic pancreatitis, status post pancreatic duct ( PD) stent placed at another institution presented to the Emergency Department with acute-onset epigastric pain associated with nausea and vomiting. The quality and severity of pain was not different than usual chronic pancreatitis pain. The physical exam was significant for epigastric tenderness. A CT scan (Figure 1) of the abdomen was reported as PD stent eroding the duodenal wall up to the fat planes but no sign of perforation. An EGD (GIF H180,Olympus) revealed the PD stent -bridging the ampulla with the opposite duodenal wall forming a mound of inflammatory tissue (Figure 2 ). For a novice, both sides look alike although it is well known that ampulla is on medial side. The stent was grabbed near the ampulla with a rat- tooth foreign body removal forceps and with a gentle tug it was dis-impacted and subsequently pulled out. Grabbing the stent near perforated site would not form a fulcrum and could be more traumatic leading to perforation. There is no best technique reported in literature regarding removal of perforated stents. After stent (7 Fr 10 cm straight) removal, pain started getting better and she became asymptomatic in 24 hrs.
Adverse events of PD stent placement include pancreatic parenchymal changes, proximal and distal stent migration with bowel perforation. Incidence of stent migration is 7.5% distally and 5.2% proximally [1]. Given that the majority of complications associated with stent migration and perforation are seen with straight stents [2-10], we suggest that longer and larger diameter PD stents should be avoided. The straight stent would not perforate if the distal end is aligned parallel to the duodenal lumen. A > 3-5 cm long PD stent with distal end aligned perpendicular to lumen would have higher probability of duodenal perforation.
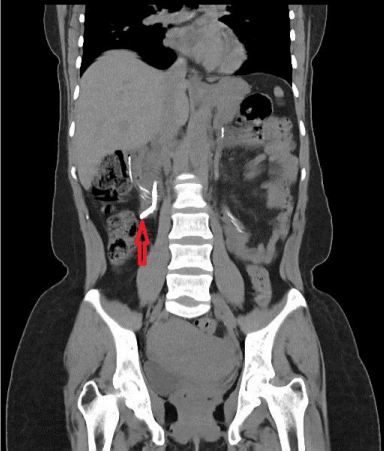
Figure 1: CT Abdomen Coronal view showing pancreatic duct stent eroding the duodenal wall up to the fat planes (red arrow).
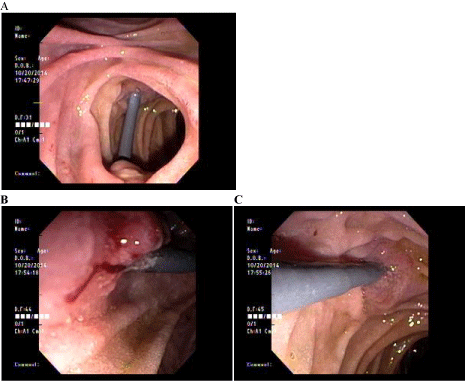
Figure 2: (A) Endoscopic view of duodenum showing pancreatic duct stent bridging the ampulla and opposite duodenal wall. (B) Stent eroding duodenal wall (C) Ampullary side.
References
- Johanson JF, Schmalz MJ, Geenen JE. Incidence and risk factors for biliary and pancreatic stent migration. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992; 38: 341-346
- Smits ME, Badiga SM, Rauws EA, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K. Longterm results of pancreatic stents in chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995;42: 461-467
- Bagul A, Pollard C, Dennison AR. A review of problems following insertion of biliary stents illustrated by an unusual complication. Bagul. Annals Of The Royal College Of Surgeons Of England Volume: 92 Issue: 4 (2010-05-01) p. W27-31
- Liebich-Bartholain L, Kleinau U, Elsbernd H, Buchsel R. Biliary pneumonitis after proximal stent migration. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 54: 382-4.
- Diller R, Senninger N, Kautz G, Tubergen D. Stent migration necessitating surgical intervention. Surg Endosc. 2003; 17: 1803-7.
- Mistry BM, Memon MA, Silverman R, Burton FR, Varma CR, Solomon H et al. Small bowel perforation from a migrated biliary stent. Surg Endosc 2001; 15: 1043.
- Basile A, Macri A, Lamberto S, Caloggero S, Versaci A, Famulari C. Duodenoscrotal fistula secondary to retroperitoneal migration of an endoscopically placed plastic biliary stent. Gastrointest Endosc 2003; 57: 136-8.
- Klein U,Weiss F, Wittkugel O. Migration of a biliary Tannenbaum stent with perforation of sigmoid diverticulum. Rofo 2001; 173: 1057.
- Marsman JW, Hoedemaker HP. Necrotizing fasciitis: fatal complication of migrated biliary stent. Aust Radiol. 1996; 40: 80-3.
- Mofidi R, Ahmed K, Mofidi A, JoyceWP, Khan Z. Perforation of ileum: an unusual complication of distal biliary stent migration. Endoscopy 2000; 32: 67.