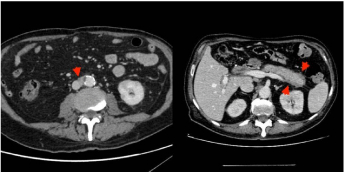
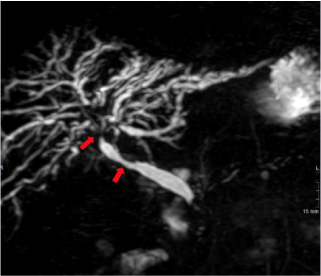
Clinical Image
Austin J Gastroenterol. 2019; 6(1): 1101.
Immunoglobulin IgG4 Sistemic Disease with Colangitic Onset
Cravero F1*, Giorgis V2, Tabone M3 and Rolla G2
¹Gastroenterology, AOU Città della, Salute Turin, Italy
²Immunology, AO Mauriziano, University of Turin, Italy
³Gastroenterology, AO Mauriziano, Turin, Italy
*Corresponding author: Federico Cravero, Gastroenterology, AOU Città della Salute, Turin, Italy
Received: May 15, 2019; Accepted: June 18, 2019; Published: June 25, 2019
Clinical Image
A 76 years old male was admitted to our unit for jaundice and progressive weight loss (20 kilos in 3 months). Blood tests showed increased values of bilirubin 1,2 mg/dl (conjugated 0,83mg/dl), Gamma-glutamyltransferase 767mg/dl alkaline phosphatase 509mg/ dl and polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia. Abdominal contrastenhanced CT scan showed intrahepatic biliary dilation, diffuse pancreas enlargement with a halo of edema surrounding its body and tail, ectasia of Wirsung’s collateral ducts, concentric thickening of the sub-renal aortic wall (Figure 1). Colangio-NMR showed segmentary thickening of common bile duct and I-II order biliary ducts causing stricture and upstream dilation (Figure 2). Suspecting IgG4-RD, serum IgG4 level was measured, resulting greatly increased (>1275 mg/dl). Based on typical imaging and lab-test findings IgG4-RD diagnosis was made [1]. The patient was treated with prednisone 30mg/day for 6 weeks, followed by 5mg/week tapering with rapid resolution of cholestasis and weight regain. Typical imaging and prompt response to steroid treatment may favour the diagnosis, even in the absence of biopsy.