
Research Article
Austin J Gastroenterol. 2020; 7(1): 1107.
Can the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score and Meld-Sodium Scores be used to Predict Portal Vein Pressure?
Syed A*, El-Tawil KM, Alwayn I, Walsh MM and Molinari M
Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology, University of Calgary, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada
*Corresponding author: Ahsan Syed, Internal Medicine and Gastroenterology, University of Calgary, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada
Received: February 04, 2020; Accepted: February 25, 2020; Published: March 03, 2020
Abstract
Introduction: Portal Vein Pressure (PVP) measurements are prognostic and useful for the clinical management of cirrhotic patients as gastroesophageal varices, encephalopathy and ascites are associated with Portal Vein Hypertension (PHT). PVP measurements via hepatic vein catheterization are invasive, costly, and not readily accessible. The goal of this study was to investigate the discriminating and predictive function of the Model for End- Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score and the MELD-Sodium (MELD-Na) for PHT in cirrhotic subjects.
Methods: A prospective cohort of 55 cirrhotic patients on the wait list for liver transplantation (OLT) was recruited during the period of May 2009 to May 2011 at a tertiary Canadian university center. MELD and MELD-Na scores were calculated at the time of OLT and PVP was directly measured by cannulation of the portal vein with a 22 Gauge needle connected to a digital transducer. For each patient, three consecutive readings of the PVP were obtained. Linear regression and receiver-operating curves (ROC) were generated to assess the correlation and discrimination functions of MELD/MELD-Na for PVH.
Results: In our population, MELD had a poor predictive function for PVP (R2=0.039, P=0.151). MELD-Na was a better predictor although correlation with PVP was weak (R2=0.102, P=0.033) (Figure 1). ROC curves revealed that the MELD-Sodium was only moderately useful (AUROC=0.73) at discriminating patients with PVP values equal or above 25mmHg.
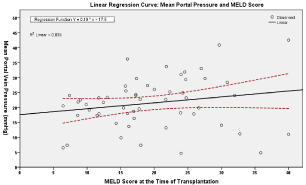
Figure 1: Linear regression analysis of MELD score and PP in 55 end-stage
cirrhotic patients (R2=0.039, P=0.151).
Conclusions: In conclusion, our findings would suggest that MELD and MELD-Na are inadequate instruments to predict PVP measurement in cirrhotic patients undergoing OLT
Keywords: MELD-Na; Portal Vein Pressure; Portal Vein Hypertension
Introduction
Cirrhosis of the liver is the end-stage of chronic liver disease and leads to the development of Portal Hypertension [1]. Portal hypertension is associated with important and potentially lethal clinical manifestations, such as Gastroesophageal (GE) bleeds, ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, renal failure and hepatic encephalopathy [2,3]. Portal Hypertension is defined as a Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient (HVPG) of greater or equal to 5mmHg [4]. In the overwhelming majority of cases, it has been found that the complications associated with portal hypertension do not manifest until HVPG is at least 10mmHg [2,4-8]. Patients with HVPG at or above this threshold are considered to have Clinically Significant Portal Hypertension (CSPH). Onset of complications is a sign of decompensated cirrhosis, which is associated with significantly worse prognosis [3,9,10].
Besides the symptomatic treatment and management of complications, the only known curative treatment for decompensated cirrhosis is a liver transplant. The source of liver transplant donors is primarily cadaveric, and the demand far exceeds the supply in most countries [11] leading to a high mortality rate of patients on the waitlist [12]. To minimize the risk of mortality for individuals waiting for liver transplantation, stratification of the severity of disease is currently done by using the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in the United states and other European countries [13]. The MELD score has been validated to predict 3-month mortality of patients with liver cirrhosis [14,15] and thus, is highly useful in prioritizing patients waiting for transplant. The MELD score is based on the values of a patient’s serum bilirubin level, International Normalized Ratio (INR) of Prothrombin time, and serum creatinine levels.
In order to identify and manage liver cirrhotics with CSPH, it is important to regularly monitor their HVPG, which is an indirect measurement of actual portal vein blood pressure (PP) [16]. Once patients have been determined to have CSPH, their prognosis can be improved with prophylactic interventions, such as the use of nonselective beta blockers or prophylactic GE band ligation [17,18]. The HVPG has been found to be the best estimate for the true PP [19], and is conventionally used to report PP. However, this procedure is undesirable to perform on a routine basis.
Due to the need to serially monitor the PP of cirrhotics, many researchers have already investigated several different non-invasive techniques to predict PP [2,3,5,20-25]. Most of these researchers have had limited success. Among them, there has been one study that found statistically significant correlations between the MELD score and HVPG [26]. This study noted that MELD score is positively associated with HVPG. Another tool that is similar to the MELD score is the MELD-Sodium (MELD-Na) score. This score amalgamates the MELD score with serum Sodium levels. In patients with cirrhosis, low serum sodium levels have been shown to be associated with the development of ascites [27]; which is a complication that the original MELD score inadequately takes into account. In addition, low serum sodium is a strong independent predictor of mortality in cirrhotics [28]. Therefore, the MELD-Na was included in our investigation. The intent of this study was to validate the results from the previous study [26] but to use direct portal vein pressure measurements as the comparison (rather than HVPG), which has not been done before. In the present study, all subjects had end-stage liver cirrhosis and underwent liver transplantation, which allowed for PP to be measured pre-operatively. There have been no previous studies that have prospectively assessed the correlation between MELD and MELD-Na scores with direct portal pressure.
We hypothesized that MELD and MELD-Na would be significantly associated with the direct PP’s of patients undergoing liver transplantation. We prospectively followed a cohort of wellidentified patients awaiting liver transplants to: 1) Detect a correlation between MELD and MELD-Na with direct PP; 2) Validate the findings of the previous observational studies in a subset of patients with end-stage cirrhosis; and 3) Develop a model whereby PP could be accurately predicted.
Materials and Methods
Patients
All patients referred to the Queen Elizabeth Medical Center in Halifax, Nova Scotia for decompensated liver disease requiring transplantation from May 2009 to May 2011 without preoperative diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis were recruited for this study. Decompensated liver disease was diagnosed on the basis of clinical presentations of individuals with one or more of the following: encephalopathy, cholestasis, coagulopathy, and ascites.
Preoperative Lab data that was collected included: serum creatinine, serum bilirubin, serum total bilirubin, serum sodium levels, Prothrombin Time (PT), International Normalized Ratios (INR) and serum Sodium levels.
The MELD score was calculated using the following equation:
MELD = 9.57 loge [Creatinine (mg/dL)] + 3.78 loge [Bilirubin (mg/dL)] + 11.20 loge [International Normalized Ratio] + 6.43
Bilirubin, Creatinine and INR values ‘less than 1’ were considered as ‘1’. Patients on hemo-dialysis were given creatinine values of ‘4’.
The MELD-Na score was calculated using the following equation:
MELD-Na = MELD + 1.59x (135 – [Na]); (where the serum [Na] is bound between 120 and 135mmol/L)
Preoperative Demographic data and clinical data included: Patient’s age, gender, weight, height, Body Mass Index (BMI), and indication for liver transplantation.
Intraoperative direct portal vein pressures were measured by cannulation of the portal vein with a 22-gauge bore needle connected to a computerized manometer. A total of three portal vein pressures were calculated intraoperatively, each with a systolic and a diastolic component. In assessing the predictive ability of the tested models, the mean PP (average of 3 readings) was used. Ascites was determined via preoperative imaging studies (either CT or MRI) and was classified as either absent, mild or severe. The degree of pre-operative encephalopathy was recorded as either absent, mild or severe.
Statistical analysis
The Mann-Whitney U-Test was used to compare continuous variables, while qualitative variables were compared using the Chi- Square test. The receiver operating characteristics curves (ROC curves) were applied to calculate and compare the accuracy of the MELD and MELD-Na scores for the prediction of CSPH (PP ≥ 10mmHg). The validity of predictive models was measured via the concordance (c)-statistics (REF 31 in Proposal). A model with a c-index above 0.7 was considered useful, while a c-index between 0.8 and 0.9 was considered excellent. For both the MELD and MELDNa, a cut-off value was used to assess sensitivity, specificity, Negative Predictive Value (NPV), Positive Predictive Value (PPV), and positive and negative likelihood ratios for the diagnosis of CSPH. Data was reported as means and standard deviations; while percentages were reported as absolute values with a 95% confident interval. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all analysis.
Results
Overall, 64 patients were analyzed in this study. Their demographic and clinical characteristics are presented in Table 1. The mean age of these patients was 53.0 years and 62.5% of them were male. The average MELD and MELD-Na scores were 20.6 and 22.6, respectively. All subjects had portal hypertension, with the exception of one patient who had Fulminant Hepatic Failure (FHF). Of the 55 patients with available PP measurements, 52 (95%) of them had CSPH. The other 2 patients who did not have CSPH had liver cirrhosis due to non-frequent causes (‘other’). The most common indication for liver transplant was due to alcoholic cirrhosis (21.9%), followed by Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and other causes (both 17.2%). The mean PP was 21.4mmHg, with a range of 4.7 to 42.5mmHg.
Variable
Values
Age, years (Mean, SD)
53.0 (11.2)
Gender (Number, Percentage)
Male
40 (62.5%)
Female
24 (37.5%)
Height, centimeters (Mean, SD)
170 (7.59)
Weight, kilograms (Mean, SD)
80.1 (16.5)
Main Indication for Liver Transplantation (Number, Percentage)
Alcohol
14 (21.9)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
11 (17.2%)
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
9 (14.1%)
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
8 (12.5%)
Viral Hepatitis C
3 (4.7%)
Autoimmune Hepatitis
3 (4.7%)
Non Alcoholic Steato Hepatitis
3 (4.7%)
Viral Hepatitis B
1 (1.6%)
Fulminant Hepatic Failure
1 (1.6%)
Other Causes
11 (17.2%)
Models for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD, MELDNa) at the Time of Transplantation (Mean, SD)
MELD
20.5 (8.7)
MELDNa
22.7 (10.5)
Body Mass Index (Mean, SD)
27.5 (5.5)
Number of Comorbidities (Charlson Score) (Mean, SD)
2.8 (1.5)
Documented Gastroesophageal Varices (Number, Percentage)
Present
25 (39.1%)
Absent
25 (39.1%)
Unknown
14 (21.8)
Documented Gastric Varices (Number, Percentage)
Present
8 (12.5%)
Absent
41 (64.1%)
Unknown
15 (23.4%)
Previous Episodes of Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage (Number, Percentage)
Yes
12 (18.8%)
No
38 (59.4%)
Unknown
14 (21.9%)
Use of Prophylactic Beta-Blockers (Number, Percentage)
Yes
24 (37.5%)
No
25 (39.1%)
Unknown
15 (23.4%)
Use of Non Adsorbable Oral Disaccharydes (Number, Percentage)
Yes
21 (32.8%)
No
29 (45.3%)
Unknown
14 (21.9%)
Use of Oral Antibiotics for Hepatic Encephalopathy or Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Yes
22 (34.4%)
No
28 (43.8%)
Unknown
14 (21.9%)
Use of Diuretics for Treatment of Ascites
Yes
31 (48.4%)
No
19 (29.7%)
Unknown
14 (21.9%)
Table 1: Patient Demographics.
Characteristics
Range
Mean ± SD
PT (INR) Value
0.90-4.1
1.74 ± 0.8
Serum Albumin (?)
14-47
29.1 ± 7.2
Serum Creatinine (?)
30-498
122.7 ± 96.4
Serum Total Bilirubin (?)
9-513
97.1 ± 101.9
Serum Sodium (?)
122-149
135.8 ± 5.3
Mean PP (mmHg)
4.7-42.5
21.4 ± 8.4
NA: Not Applicable; MELD: Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; INR: International Normalized Ratio; BMI: Body Mass Index; PP: Portal Vein Blood Pressure; N: Number of Patients with Complete Data for Respective Characteristic.
*Note: MELD and MELD-Na refers to patient’s scores at time of transplantation.
Table 2: Patient’s Blood Variables and Mean Portal Pressure.
MELD and PP
Figure 1 shows the relationship between MELD score at the time of transplantation and mean PP measured before surgery in all 64 patients. The relationship between MELD and PP seemed to have positive tendencies but was not statistically significant (R2=0.039, P=0.151).
MELD-Na and PP
The MELD-Na score showed greater positive tendencies, was more significantly correlated with PP and did reach the level of statistical significance (R2=0.102, P=0.033), as demonstrated in Figure 2.
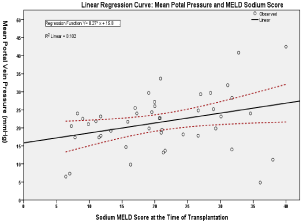
Figure 2: Linear regression analysis of MELD-Sodium score and PP in 55
end-stage cirrhotic patients (R2=0.102, P=0.033).
PP Predictive value of MELD and MELD-Na.
Table 3 and 4 show the values of the ‘Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics’ (AUROC) curves of the MELD and MELD-Na scores in identifying patients that have PP higher or equal to 15mmHg, 20mmHg, and 25mmHg.
PP Cut-off (mmHg)
Positive (%)
Negative (%)
AUROC
15
78.2
21.8
0.437
20
52.7
47.3
0.519
25
29.1
70.9
0.72
Table 3: Predictive ability of MELD score of various stages of CSPH in 55 endstage cirrhotics.
PP Cut-off (mmHg)
Positive (%)
Negative (%)
AUROC
15
80
20
0.478
20
55.6
44.4
0.502
25
26.7
73.3
0.732
Table 4: Predictive ability of MELD-Sodium score of various stages of CSPH in 45 end-stage cirrhotics.
Discussion
The focus of this study was on being able to non-invasively predict PP in end-stage cirrhotic patients. When PP is abnormally elevated (CSPH), the frequency and severity of complications significantly increases [4-8]. Upon onset of complications, an individual enters the phase of decompensated cirrhosis; which is associated with drastically worse prognosis [3,9]. GE bleeds have a mortality rate of 20% within 6 weeks of the first bleed [2,29]. Development of ascites itself is associated with a 20% mortality rate per year [9], and patients with ascites and a GE bleed have a 57% yearly mortality rate [9]. These lethal complications necessitate the need to monitor PP in cirrhotics for providing optimal healthcare. The current gold standard in estimating PP is the catheterization of the hepatic vein to measure the HVPG [30]. In this procedure, a balloon tipped catheter which is connected to a manometer is inserted either via the femoral or jugular veins and is guided towards the hepatic vein. Once there, the catheter allows blood to flow unobstructed and the pressure is recorded. This is called the Free Hepatic Vein Pressure (FHVP). The balloon is then inflated to fully occlude the lumen of the hepatic vein and a pressure reading is taken. This is known as the Wedged Hepatic Vein Pressure (WHVP). The HVPG is then calculated by finding the difference between the FHVP and WHVP. Though the HVPG is an accurate surrogate measure of PP, the procedure is quite invasive, expensive, requires expertise to perform and is not available in all healthcare centers; which make it undesirable for both patients and for the health care system to perform on a routine basis.
One of the rationales in this study to try and correlate the MELD and MELD-Na scores with PP is that these scores are normally calculated as standard clinical practice in most of North America for patients with end-stage cirrhosis [13] and a previous study had demonstrated a significant correlation between the MELD score and PP in cirrhotics [26]. The MELD score is inexpensive, widely available, and non-invasively obtained. If the MELD score could be validated to predict PP in cirrhotics, it would forgo the need to determine the HVPG. This would provide savings for the healthcare system, allow for surgeons to make more efficient use of their time, increase patient comfort, and avoid extra visits to the hospital or clinic. One of the ways we built upon previous research [26] is by using direct portal vein measurements as the comparison. The direct cannulation of the portal vein is the most accurate way of measuring PP. This method is an extremely invasive procedure as it requires puncturing of the portal vein and can only be done surgically or percutaneously. It is not routinely performed and presents a serious risk of complications to cirrhotics that have coagulopathy [21]. The opportunity to collect direct PP measurements arose from the fact that each patient in this cohort underwent a liver transplant. The PP measurements were taken a total of 3 times on the same patient, and were taken at the end of expiration to cancel out any perturbations in PP due to respiratory factors.
Our study failed to find a significant correlation between the MELD score and PP. However, a statistically significant correlation was found between the MELD-Na score and PP. Even with this significant result, the predictive ability the MELD-Na score failed to be high enough to be utilized in clinical decision-making (Table 4). This study is the only one to date that has used direct portal vein measurements as a comparison and is the only study that has solely used liver transplant patients as subjects.
The only other study that has investigated the relationship between MELD and PP has been that of Huo et al. [27]. Huo et al.’s study utilized HVPG as a surrogate measure of PP and included cirrhotic patients that were at various stages of their disease. Their study was done retrospectively and they excluded all patients that had previous hepatic encephalopathy, HCC, variceal bleeds, or use of beta blockers. By choosing this as exclusion criteria, their study dealt with patients at a much milder stage of cirrhosis than our study. Compared to our study, their study involved patients that were predominately male (88% vs. 62.5%), had much lower average MELD scores (13.1 vs 20.5), and were much older (63 years-old vs. 53 years-old). The etiology of liver cirrhosis in Huo et al’s study was vastly different from ours. The majority of cirrhosis in their study was caused by Hepatitis B virus (59% vs. 1.6%) and Hepatitis C virus (15% vs. 4.7%). These major demographic differences could account for the discrepancies seen in the results. Huo et al. found a positive linear correlation between the MELD score and PP (r=0.255, P ‹0.001). Although this was a statistically significant result, due to the low correlation coefficient, Huo et al. concluded that the MELD score is only slightly associated with HVPG, and is by no means predictive of it.
It has been found that both the PP (measured as HVPG) and the MELD scores are both tools that assess the severity of chronic liver disease. However, our results and those of Huo et al. show that it is unlikely that the MELD score can be used to non-invasively predict PP. However, it may not necessarily be the case that the link between MELD and PP is as weak as demonstrated in this study because our study had a few limitations. Firstly, our study only utilized patients that were in the decompensated end-stage of cirrhosis and required a liver transplant. It may be that patients that are in earlier stages of cirrhosis or in compensated cirrhosis, may demonstrate a different link between MELD and PP. Secondly, our sample size was very heterogenous in terms of etiology of liver disease. The etiology of liver cirrhosis can have a drastic effect as MELD and/or may not be useful as a prognostic marker in one etiology as compared to another. For instance, in our cohort of patients that had Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), their mean MELD score was 14.1, as compared to alcoholic cirrhotics that had a MELD score of 20.6. Even the correlation between MELD and PP was quite different among various etiologies. For instance, in patients that had cirrhosis from other causes, their correlation of PP and MELD yielded a high coefficient (r=0.78). This was also found in patients that had HCC (r=0.75). In contrast, patients with alcoholic cirrhosis demonstrated a much weaker correlation (r=0.16). Thirdly, though we had plenty of subjects overall, we did have a limited sample size in terms of representation of various etiologies. The highest proportion of our subjects were alcoholic cirrhotics, (n=14, 21%) followed by HCC (n=11, 17.2%) and other causes (n=11, 17.2%). Future studies in this area need to be undertaken to delineate the relationship between MELD and PP, with emphasis on focusing on a limited number of etiologies.
References
- Bosch J and JC Garcia-Pagan. Complications of cirrhosis. I. Portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2000; 32: 141-156.
- de Franchis R, A Dell’Era and M Primignani. Diagnosis and monitoring of portal hypertension. Dig Liver Dis. 2008; 40: 312-317.
- de Franchis R and A Dell’Era. Non-invasive diagnosis of cirrhosis and the natural history of its complications. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007; 21: 3-18.
- Ripoll C, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts clinical decompensation in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133: 481-488.
- Lemoine M, et al. Liver stiffness measurement as a predictive tool of clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with compensated hepatitis C virus or alcohol-related cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 28: 1102-1110.
- Garcia-Pagan JC, et al. Propranolol compared with propranolol plus isosorbide-5-mononitrate for portal hypertension in cirrhosis. A randomized controlled study. Ann Intern Med. 1991; 114: 869-873.
- Moitinho E, et al. Prognostic value of early measurements of portal pressure in acute variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117: 626-631.
- Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Portal pressure, presence of gastroesophageal varices and variceal bleeding. Hepatology. 1985; 5: 419-424.
- D’Amico G, G Garcia-Tsao, and L Pagliaro. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006; 44: 217-231.
- Alvarez MA, et al. Long-term Clinical Course of Decompensated Alcoholic Cirrhosis: A Prospective Study of 165 Patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011.
- Shah SA, et al. Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006; 20: 339-343.
- Molinari M, et al. Clinical epidemiological analysis of the mortality rate of liver transplant candidates living in rural areas. Transpl Int. 2011; 24: 292-299.
- Leise MD, et al. A revised model for end-stage liver disease optimizes prediction of mortality among patients awaiting liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140: 1952-1960.
- Lv XH, et al. Validation of model for end-stage liver disease score to serum sodium ratio index as a prognostic predictor in patients with cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24: 1547-1553.
- Ripoll C, et al. Influence of hepatic venous pressure gradient on the prediction of survival of patients with cirrhosis in the MELD Era. Hepatology. 2005; 42: 793-801.
- Lin HC, et al. Comparison between portal vein pressure and wedged hepatic vein pressure in hepatitis B-related cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1989; 9: 326-330.
- Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2007; 46: 922-938.
- Alempijevic T, et al. Right liver lobe/albumin ratio: contribution to non-invasive assessment of portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13: 5331- 5335.
- Boyer TD, et al. Direct transhepatic measurement of portal vein pressure using a thin needle. Comparison with wedged hepatic vein pressure. Gastroenterology. 1977; 72: 584-589.
- Thabut D, R Moreau and D Lebrec. Noninvasive assessment of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2011; 53: 683-694.
- Singal AK, M Ahmad, and RD Soloway. Duplex Doppler ultrasound examination of the portal venous system: an emerging novel technique for the estimation of portal vein pressure. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55: 1230-1240.
- Baik SK. Haemodynamic evaluation by Doppler ultrasonography in patients with portal hypertension: a review. Liver Int. 2010; 30: 1403-1413.
- Kim MY, et al. Damping index of Doppler hepatic vein waveform to assess the severity of portal hypertension and response to propranolol in liver cirrhosis: a prospective nonrandomized study. Liver Int. 2007; 27: 1103-1110.
- Vizzutti F, et al. Liver stiffness measurement predicts severe portal hypertension in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2007; 45: 1290-1297.
- Tasu JP, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradients measured by duplex ultrasound. Clin Radiol. 2002; 57: 746-52.
- Huo TI, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease score to serum sodium ratio index as a prognostic predictor and its correlation with portal pressure in patients with liver cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2007; 27: 498-506.
- Gines P, et al. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: from pathogenesis to treatment. Hepatology. 1998; 28: 851-864.
- Biggins SW, et al. Evidence-based incorporation of serum sodium concentration into MELD. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130: 1652-1660.
- D’Amico G and R De Franchis. Upper digestive bleeding in cirrhosis. Posttherapeutic outcome and prognostic indicators. Hepatology. 2003; 38: 599- 612.
- Groszmann RJ and S Wongcharatrawee. The hepatic venous pressure gradient: anything worth doing should be done right. Hepatology. 2004; 39: 280-282.