
Case Report
Ann Hematol Oncol. 2015;2(1): 1017.
PBX/E2A Transcript Positive B-Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL) Presenting with Bilateral Renal and Myocardial Involvement: A Case Report
Carli G1*, Ferrarini I2, Guardalben E2, Bonifacio M2, Meneghini V2, Visco C1 and Ambrosetti A2
1Department of Hematology and Cell Therapy, San Bortolo Hospital, Vicenza, Italy
2Department of Medicine, Section of Hematology, University of Verona, Italy
*Corresponding author: Giuseppe Carli, Dipartimento di Ematologia e Terapie Cellulari, Ospedale San Bortolo, viale Rodolfi 37, 36100 Vicenza (Italy)
Received: November 15, 2014; Accepted: January 05, 2015; Published: January 07, 2015
Abstract
B-Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL) is a neoplasm affecting B-cell precursor and represents 80% of lymphoblastic leukaemias. It is primary a disease of children and usually presents with bone marrow and peripheral blood involvement, leucocytosis, anaemia and thrombocytopenia. Epathosplenomegaly and lymph nodes enlargement are often present and testis involvement is frequent in males. Central Nervous System (CNS) is a frequent site of extramedullary involvement. Other frequent extranodal sites involved are represented by skin, soft tissue and bone.
Here, we describe an adult patient with B-ALL presenting with bilateral renal involvement and myocardial infiltration, harbouring the chromosome translocation t(1;19)(q23;p13) and the molecular transcript PBX1-E2A.
Keywords: B-lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL); t(1;19); PBX1-E2A transcript; Renal involvement; Myocardial involvement
Introduction
B-Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (B-ALL) is a neoplasm affecting B-cell precursors and represents about 80% of lymphoblastic leukaemias. It is primary a disease of children, with 75% of cases occurring under six years of age [1]. It usually presents with bone marrow and peripheral blood involvement, leucocytosis, anaemia and thrombocytopenia. Epathosplenomegaly and lymph nodes enlargement are present in variable degrees and testis involvement is also frequent. CNS is a typical site of extramedullary localization of B-ALL at diagnosis or at relapse. When extranodal involvement is predominant (bone marrow blasts <25%) the disease is defined B-Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (B-LBL). Beside lymph nodes, the most frequent involved sites by B-LBL are skin, soft tissue and bone.
B-ALL/B-LBL is also usually characterized by cytogenetic and molecular abnormalities that play an important role in risk stratification and treatment planning [2].
Here we describe a case of B-ALL presenting in an adult man as bilateral renal involvement and myocardial infiltration harbouring the chromosome translocation t(1;19)(q23;p13) and the molecular transcript PBX1-E2A.
Case Report
On February 2013, a 56-year-old gentleman was admitted to a hospital complaining of vague abdominal pain. The urgent abdomen- Ultrasonography (US) showed multiple bilateral renal lesions without any other abnormality. His medical history was silent and clinical examination revealed an isolated mild abdominal distension. He had no systemic symptoms and laboratory data were in range except for β2-microglobuline (4.53 mg/L). Blood counts showed hematocrit 40%, hemoglobin 13.1 g/dL, White Blood Cells (WBC) count 3.500/mm3 (neutrophils 2.000/mm3, lymphocytes 1.200/mm3, and monocytes 300/mm3) and platelets 172.000/mm3. In the hypothesis of a secondary localization of a solid neoplasm, a total body-CT scan was performed, confirming the presence of multiple bilateral renal lesions in the absence of other abnormalities. A testicular-US was negative. The esophagastroduodenoscopy (EGDS) was normal while colonoscopy showed diverticulosis. A US-guided biopsy of one of the renal lesions demonstrated the presence of a diffuse CD20- lymphoid infiltration with the following characteristics at immunohistochemistry: Bcl-2+, Bcl-6+/-, CD10++, CD19+, , CD45-, Pax-5+, TdT+, CD3-, CD99, Keratin 8/18/19-, Cyclin D1-, Desmin-, K/λ-, Miogenin-, Wilms'tumor protein-, Ki-67 (MIB-1) >50%.
A diagnosis of B-cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (B-LBL) with bilateral renal localization was made.
At the beginning of April 2013, the patient was transferred to our unit where we conducted a diagnostic work-up for B-LBL/ALL. The peripheral blood smear showed 2% of leukemic blasts while the bone marrow aspirate showed massive involvement by leukemic blasts (70- 80% of total cellularity). Flow-cytometry analysis revealed that blasts were CD34-, CD45-, CD10++, CD58++, CD38++, TdT+, CyCD79a+, CD22+, CD66c-, NG2-, CD13-, CD33-, CD15-, cytCD3-, cyIgμ-, MPO-. Molecular analysis by Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) was performed at the Department of Cellular Biotechnologies and Hematology, University "La Sapienza" in Rome, and was positive for PBX1-E2A+ and negative for BCR/ ABL, MLL/AF4, MLL/ENL, SIL/TAL, TEL/AML, NUP/RAP1s and TAF1/NUP214. Karyotype was 46 XY with t(1;19)(q23;p13). We concluded for common B-ALL.
A total body CT scan (Figure 1) showed bilateral renal enlargement (16 cm right and 15 cm left) with multiple hypodense confluent parenchymal lesions and some enlarged lymph nodes at the hepatic hilus and in para-aortic region. A thickening of the left ventricular wall was also detected.
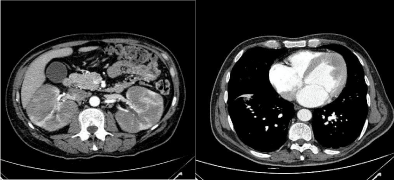
Figure 1: CT scan showing bilateral renal enlargement (left) and left ventricular wall thickening (right).
Whole body 18FDG-PET (Figure 2) revealed intense inhomogeneous uptake in kidneys (standardized uptake value -SUVmax 6.5), intense uptake at anterior myocardial wall (SUV max 5.8) and diffuse uptake of the bone marrow.
Figure 2: 18FDG-PET scan showing intense glucose uptake in kidneys, anterior myocardial wall and diffuse uptake of bone marrow.
Electrocardiography was normal, while the echocardiogram demonstrated a diffuse and severe dilatative cardiomyopathy in the absence of hypokinetic regions.
The patient underwent Hyper CVAD/HD-MTX-Ara-C regimen, achieving an early disease response. After the first cycle the bone marrow aspirate with flow-analysis revealed hematological complete remission while an abdomen-US showed bilateral initial reduction of renal enlargement (from 16-15 cm to 12 cm).
After 4 cycles of Hyper CVAD regimen (2 courses A and 2 courses B) the 18FDG-PET demonstrated the disappearance of myocardial and renal parenchymal pathological uptake (Figure 3) but persistent bone marrow uptake (Figure 4a). Indeed, the bone marrow aspirate showed a significant quote of blasts (10%), indicating disease relapse (Figure 4b).
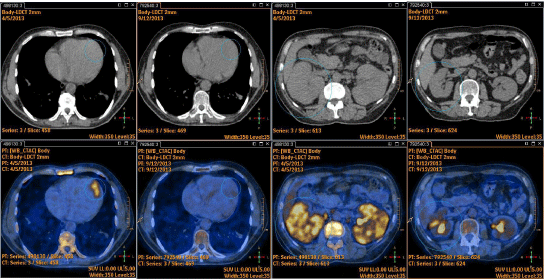
Figure 3: 18FDG-PET showing disappearance of myocardial and renal parenchymal pathological uptake after 4 cycles of Hyper CVAD/HD-MTX-Ara-C regimen.
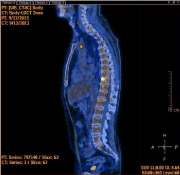
Figure 4a: Persistent bone marrow uptake at 18FDG-PET after 4 cycles.
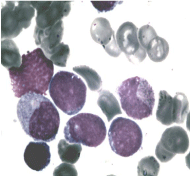
Figure 4b: Bone marrow blasts.
The patient history was then characterized by disease refractoriness to administered therapies (3 cycles FLAG-Myocet, 1 cycle IVAC, Vincristine + Cyclophosphamide and finally Mercaptopurine). Nineteen months after being diagnosed the patient died of a septic shock.
Discussion
Renal involvement is uncommon in ALL at disease presentation, while it has been reported in later stages of the disease, especially in children [3-5]. Few reports describe large bilateral renal involvement as primary presentation of ALL in the paediatric setting [6-8].
The differential diagnosis of nephromegaly includes hydronephrosis, congenital anomalies, deposit diseases and primary or metastatic malignancies. Our case report indicates that it might be useful, before performing a renal biopsy, to critically analyse the peripheral blood smear and eventually a bone marrow aspirate. In our patient, although laboratory data were in range, both peripheral blood smear and bone marrow aspirate revealed presence of leukemic blasts.
Cardiac involvement is also a rare feature in ALL/LBL at diagnosis [9]. It has been reported as intracardiac mass, with or without symptoms of heart failure while in other cases heart is involved as myocardial infiltration [10-12]. Our patient had no specific symptoms and the infiltration was documented by staging procedures. In particular, 18FDG-PET, compared with traditional imaging techniques, was more sensitive in identifying cardiac lesions, and served as a useful tool for following-up disease and response.
Interestingly, the t(1;19)(q23;p13) chromosome translocation was present at diagnosis in our patient, as confirmed by the presence of the hybrid transcript PBX1-E2A. t(1;19) occurs in about 5 % of pediatric ALL, but only rarely in adult patients with ALL. In pediatric patients treated with intensive chemotherapy regimens it is associated with a favorable prognosis, while in adult patients, due to the rarity of this finding, the prognostic significance is uncertain [13,14].
At least to our knowledge, this is the first report showing an association between this chromosome translocation and unusual extranodal presentations. The translocation led to the fusion gene PBX1-E2A involving E2A on chromosome 19 and PBX1 on chromosome 1. E2A is a regulator of lymphocyte differentiation while PBX1 is a homeobox gene that appears to be expressed in all tissues but not in B or T lymphocytes [15]. PBX1-E2A gene leads to the abnormal trans-activation of several genes involved in major cellular processes and has an important oncogenic potential although additional genetic events are needed for leukemic transformation [15,16]. It could be speculated that the extranodal tissue involvement may be related to a promotion and expansion of the cell adhesion and extravasation mechanisms induced by the PBX1-E2A activity. This hypothesis is further supported by the increased risk of CNS relapse in patients with t(1;19) leukemia [17]. Studies of gene expression profiling in ALL revealed peculiar features of PBX1-E2A positive ALL [18,19]. The up-regulation of genes involved in cell shape, adhesion and motility like moesin and synaptopodin may explain this tissue tropism and the aggressive clinical behavior.
References
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, (Eds) et al. WHO Classification of Tumor of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC: Lyon 2008.
- Iacobucci I, Papayannidis C, Lonetti A, Ferrari A, Baccarani M, Martinelli G. Cytogenetic and molecular predictors of outcome in acute lymphocytic leukemia: recent developments. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2012; 7: 133-143.
- Hann IM, Lees PD, Palmer MK, Gupta S, Morris-Jones PH. Renal size as a prognostic factor in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer. 1981; 48: 207-209.
- Taccone A, De Bernardi B, Comelli A, Dini G, Bartolini M, Banderali A, et al. [Renal changes in acute leukemia in children at onset. Incidence and prognostic value]. Pediatr Med Chir. 1982; 4: 107-113.
- Gupta S, Keane S. Renal enlargement as a primary presentation of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Radiol. 1985; 58: 893-895.
- Basker M, Scott JX, Ross B, Kirubakaran C. Renal enlargement as primary presentation of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Indian J Cancer. 2002; 39: 154-156.
- Ali SH, Yacoub FM, Al-Matar E. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia presenting as bilateral renal enlargement in a child. Med Princ Pract. 2008; 17: 504-506.
- Erdem E, Kayiran P, Ozcelik G, Ozel A, Yildiz Yildirmak Z. Rare presentation of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: nephromegaly at time of diagnosis. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2011; 27: 43-45.
- Bassi D, Lentzner BJ, Mosca RS, Alobeid B. Primary cardiac precursor B lymphoblastic lymphoma in a child: a case report and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2004; 13: 116-119.
- Manabe M, Yoshii Y, Mukai S, Sakamoto E, Kanashima H, Nakao T, et al. Precursor B-lymphoblastic lymphoma involving an intracardiac mass and myocardial infiltration: a case report. Intern Med. 2012; 51: 315-319.
- Hahn B, Rao S, Shah B. Case report of precursor B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma presenting as syncope and cardiac mass in a nonimmunocompromised child. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2007; 23: 576-579.
- Kuo TT, Yang CP, Lin CH, Chang CH. Lymphoblastic lymphoma presenting as a huge intracavitary cardiac tumor causing heart failure. Pediatr Pathol. 1987; 7: 341-349.
- Chessels JM, Swansbury GJ, Reeves B, Bailey CC, Richards SM. Cytogenetics and prognosis in childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia: results of MRC UKALL X. Medical Research Council Working Party in Childhood Leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1997; 99: 93-100.
- Burmeister T, Gökbuget N, Schwartz S, Fischer L, Hubert D, Sindram A, et al. Clinical features and prognostic implications of TCF3-PBX1 and ETV6-RUNX1 in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2010; 95: 241-246.
- Aspland SE, Bendall HH, Murre C. The role of E2A-PBX1 in leukemogenesis. Oncogene. 2001; 20: 5708-5717.
- Diakos C, Xiao Y, Zheng S, Kager L, Dworzak M, Wiemels JL. Direct and indirect targets of the E2A-PBX1 leukemia-specific fusion protein. PLoS One. 2014; 9: 87602.
- Jeha S, Pei D, Raimondi SC, Onciu M, Campana D, Cheng C, et al. Increased risk for CNS relapse in pre-B cell leukemia with the t(1;19)/TCF3-PBX1. Leukemia. 2009; 23: 1406-1409.
- Ross ME, Zhou X, Song G, Shurtleff SA, Girtman K, Williams WK, et al. Classification of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia by gene expression profiling. Blood. 2003; 102: 2951-2299.
- Yeoh EJ, Ross ME, Shurtleff SA, Williams WK, Patel D, Mahfouz R, et al. Classification, subtype discovery, and prediction of outcome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia by gene expression profiling. Cancer Cell. 2002; 1: 133-143.