
Clinical Image
Ann Hematol Oncol. 2018; 5(2): 1191.
Pleural Effusion in a 17-Year-Old-Male with Chronic Miyeloid Leukemia due to the use of Imatinib
Patiroglu T¹*, Ozcan A¹, Kose S¹, Unal E¹, Karakukcu M¹ and Coskun A²
¹Department of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology, Erciyes University Medical Faculty, Turkey
²Department of Pediatric Radiology, Erciyes University Medical Faculty, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Patiroglu T, Erciyes University Medical Faculty, Department of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology38039, Kayseri, Turkey
Received: January 10, 2018; Accepted: February 12, 2018; Published: February 20, 2018
Keywords
Pleural effusion;Imatinib
Clinical Image
A 17-year-old male admitted to our department with a complaint of right thoracal pain. The patient wasdiagnosed as adult type chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) 45 days ago. After diagnose, he used imatinib in a dose of maximum 400 mg per day for treatment of CML. On examination, he was afebrile, liver and spleen were slightly palpable. Respiratory system examination revealed decreased breath sounds at the middle and down regions of right lung. The other systems examination was normal. The chest radiography revealed pleural effusion on the right side (Figure 1). About 0.7 litres of hemorrhagical fluid was aspirated under local anesthesia from right pleural space. The pleural fluid examination did not reveal any pathogenic microorganism. In the cytology report was mentioned no leukemic infiltration. Although investigations of pleural fluid ruled out infection and malign cell infiltration we thought that pleural effusion occurred due to using of imatinib. Therefore, use of the drug was stopped. He had exactly normal chest radiography 7 days after interruption of imatinib. At follow up, he had no pleural effusion.
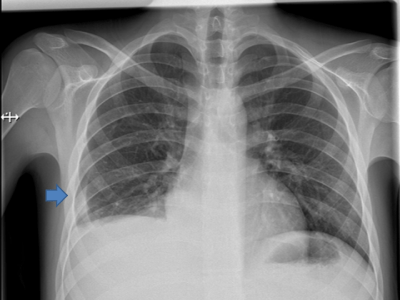
Figure 1:
Thyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are generally very well tolerated but possible side effects include the following: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle cramps, skin rash, gynecomastia [1,2]. Furthermore, the use of TKIs such as dasatinib has been associated with pleural effusion [3]. Pleural effusion due to the use of imatinib is very rare.
References
- Akay OM, Mutlu F, Gülbas Z. Platelet Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Does Imatinib Mesylate Improve It? Turk J Haematol. 2016; 33: 127-130.
- Eskazan AE, Salihoglu A, Erturan S, Soysal T. Interstitial pneumonitis in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia. Turk J Haematol. 2013; 30: 435-436.
- Zhang ZC, Qaio JH, Ai HS. [A case report of refractory pleural effusion associated with dasatinib in the treatment of chronic myeloied leukemia]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015; 23: 401-406.