
Case Report
Ann Hematol Oncol. 2021; 8(8): 1358.
Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms with Ringed Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN RS-T)–A Case Report with Literature Review on Diagnosis and Management
Niazi MRK¹*, Yousaf F¹, Asti D², Xue W³ and Skaradinskiy Y²
1Department of Internal Medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell at Staten Island University Hospital, New York, NY, USA
2Division of Hematology & Medical Oncology, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell at Staten Island University Hospital, New York, NY, USA
3Department of Pathology, Staten Island University Hospital, New York, NY, USA
*Corresponding author: Niazi MRK, Department of Medicine, Staten Island University Hospital, 475 Seaview Ave, Staten Island, NY, 10305, USA
Received: April 26, 2021; Accepted: May 26, 2021; Published: June 02, 2021
Abstract
Myelodysplastic syndrome/Myeloproliferative neoplasms with ringed sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN RS-T) is a rare disorder with mixed features of dysplasia and myeloproliferation. This is a relatively new independent entity included in the 2016 WHO classification as MDS/MPN with RS-T. The diagnostic criteria include erythroid lineage dysplasia, ≥15% Ringed Sideroblasts (RS), <1% blast cells in peripheral blood, <5% blast cells in the bone marrow, persistent thrombocytosis with platelet count ≥450×109/L, presence of SF3B1 mutation, absence of BCR-ABL1 gene fusion and rearrangement of PDGFRA, PDGFRB or FGFR1 or PCM1-JAK2. In MDS/MPN RS-T, two mutations are commonly seen JAK 2, which promotes myeloid proliferation, and SF3B1 gene, which causes myelodysplasia with ringed sideroblasts commonly observed in this syndrome.
We present a relatively young 59-year-old woman diagnosed with MDS/ MPN RS-T based on the above guideline criteria. She has low-risk MDS, which favors a good prognosis; however, the presence of Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) favors a poor prognosis. Currently, there is no consensus on the specific management of this entity, given its rarity.
She was referred to an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant center for curative treatment since she had become transfusion dependent. Before curative treatment, the patient was initiated on ruxolitinib as a bridging therapy to bone marrow transplant.
Keywords: Myelodysplastic syndrome, Myeloproliferative neoplasms; Ringed sideroblast; Thrombocytosis; (MDS/MPN RS-T)
Abbreviations
MDS/MPN RS-T: Myelodysplastic Syndrome /Myeloproliferative Neoplasms with Ringed Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis; RS: Ringed Sideroblast; RARS-T: Refractory Anemia with Ring Sideroblasts Associated with Marked Thrombocytosis; MDS/MPN: Myelodysplastic Syndromes/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms; ET: Essential Thrombocythemia; MDS-SLD: Myelodysplastic Syndrome Single Lineage Disorder; RARS: Refractory Anemia with Ringed Sideroblasts; WBC: White Blood Cells; HCT: Hematocrit; AML: Acute Myeloid Leukemia; MCV: Mean Corpuscular Volume; TSF: Thrombosis Free Survival; OS: Overall Survival; ESA: Erythropoietin Stimulating Agent; MDS-MPN-UL: Myelodysplastic Syndrome/ Myeloproliferative Syndrome-Unclassifiable; PV: Polycythemia Vera; FISH: Fluorescent In-Situ Hybridization; RT-PCR: Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Introduction
Refractory Anemia with Ring Sideroblasts Associated with Marked Thrombocytosis (RARS-T) was a provisional entity within the Myelodysplastic Syndromes/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) unclassifiable group in the WHO 2008 classification. It has now been accepted as a distinct entity in the revised WHO 2016 classification as MDS/MPN with RS-T. Given the rarity of this entity, there is not much literature or trials to guide clinical management. There are currently ongoing trials to compare prognosis, survival, and treatment options of MDS/MPN RS-T, with other related disorders like Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), Myelodysplastic Syndrome Single Lineage Disorder (MDS-SLD), Refractory Anemia with Ringed Sideroblasts (RARS). In MDS/MPN RS-T, two mutations commonly seen are JAK 2, which promotes myeloid proliferation, and SF3B1 gene which causes myelodysplasia with ringed sideroblasts.
In this case report, we present a rare case of a relatively young 59-year-old female diagnosed with MDS/MPN RS-T after initial evaluation of anemia and thrombocytosis. We discuss the morphologic and genomic features associated with this condition and the associated diagnostic challenges in differentiating this entity from other related conditions, and current data available on management.
Case Presentation
A 59-year-old female with the past medical history of multiple sclerosis and diabetes mellitus was referred to our hospital for an incidental finding of hemoglobin of 5.9mg/dl at her primary care provider’s office. She had symptoms of lightheadedness, and shortness of breath elicited on exertion for several months. She endorsed a 20-pound unintentional weight loss due to decreased appetite. On review of systems, she reported having fatigue, headaches, dizziness, mild itching, and sweating.
There were no significant findings on the physical exam, with no signs of hepatosplenomegaly or lymphadenopathy.
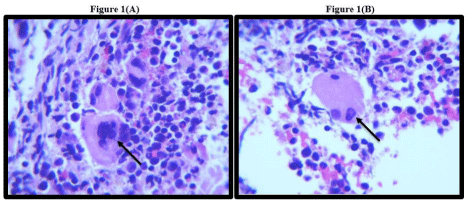
Figure 1(A &B): 100X H & E bone marrow smear: black arrows pointing towards megakaryocyte dysplasia.
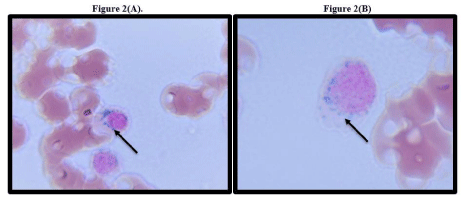
Figure 2(A &B): Bone marrow smear. Arrow pointing towards ring sideroblast.
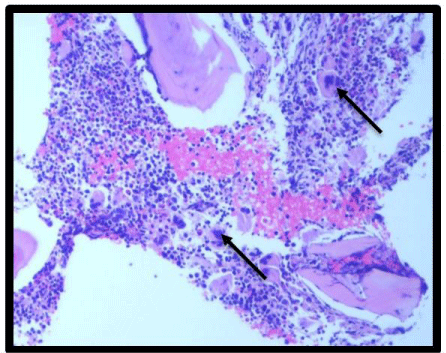
Figure 3: 100X H & E Bone marrow smear: arrow pointing towards
megakaryocyte hyperplasia.
Investigations
Initial laboratory work revealed White Blood Cell (WBC) count of 14.04x109/L with 71% neutrophils, 4.4% eosinophil, 0.9% basophils, 3.5% monocytes, and 16.7% lymphocytes, MCV: 110.2 fl, a hemoglobin concentration of 5.9 g/dL, Hematocrit (HCT) 18.3% and a platelet count of 1,559 k/mL. Vitamin B12 and folate levels were within normal limits. Iron studies were normal with elevated ferritin of 799 ng/ml. She was transfused with one unit of packed red blood cells with an improvement in Hgb to 7.5mg/dl. Her abdominal ultrasound was remarkable for splenic enlargement to upper normal limit measuring 12 cm. Hematology was consulted for further workup.
Diagnosis
Bone marrow biopsy was performed that showed hypercellular bone marrow with erythroid hyperplasia with left shift, dyserythropoiesis, ringed sideroblasts (>15%), atypical megakaryocytes, and marrow fibrosis. Real-time PCR analysis showed V617F activating mutation in JAK2 41.3% and ruled out BCR-ABL1 fusion. Cytogenetic and FISH analysis was performed that revealed trisomy of chromosome 8 in 11% of cells but no PDGFRA rearrangement. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) detected DNMT3A, JAK2, SF3B1, and ASXL1 Mutation. The overall bone marrow findings were supportive of MDS/MPN-RS-T.
Treatment and Outcomes
Given her transfusion dependence, she was started on epoetin alfa (Procrit) and was referred to a specialized center for an allogeneic bone marrow transplant. Given her severe thrombocytosis, the patient was also started on treatment with ruxolitinib as a bridging therapy while awaiting a transplant.
Discussion
Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms with ringed sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN RS-T) is one of the least common types of sideroblastic anemias that is characterized by ringed sideroblasts and thrombocytosis with or without leukocytosis (previously known as RARS-T refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts associated with marked thrombocytosis). Since the association of spliceosome gene SF3B1 mutation with ringed sideroblasts formation, there has been enough data to call it separate diagnosis. It has been now recognized as a separate entity as a MDS/ MPN subtype according to the 2016 revision of WHO classification of acute leukemias and myeloid neoplasms.
The diagnostic criteria [1] include:
• Anemia associated with erythroid lineage dysplasia without multilineage dysplasia, ≥15% RS, <1% blasts in peripheral blood and <5% blasts in the bone marrow.
• Persistent thrombocytosis with platelet count ≥450×109/L
• Presence of SF3B1 mutation, or in the absence of SF3B1 mutation, no history of recent cytotoxic or growth factor therapy to account for the MDS/MPN features.
• No BCR-ABL1 fusion gene, no rearrangement of PDGFRA, PDGFRB or FGFR1; or PCM1-JAK2; no (3;3) (q21; q26), inv(3) (q21q26) or del(5q) (5)
Median age of disease presentation is usually mid 70s whereas it ranges from 18-95 [2]. Spliceosomes work by splicing precursor mRNAs (messenger RNA) into final products. SF3B1 gene encodes factor 3 of protein subunit 1 that fixes spliceosomes on its precursor mRNA. Extensive studies used technologies like parallel sequencing to find out the prevalence of this point mutation among patients with MDS, MDS/MPN and AML, where it was found to have causal relationship with ringed sideroblasts [3]. SF3B1 mutation regulates mitochondrial iron homeostasis leading to ringed sideroblast formation. Studies reveal that SF3B1 mutation is associated with better prognosis among MDS patients. Decreased level of these mutations are associated with increased risk of disease progression to AML. This cannot only be used in stratification systems for better evaluation of the risk of the disease, but also for designing the therapeutic strategies against it [4,5].
Most of the time SF3B1 is co-mutated with JAK2 V617F mutation and less commonly with other mutations like CALR, or MPL genes which is the true reason behind hybrid nature of this myeloid neoplasm. Gene mutations commonly seen in MDS/MPN RS-T include SF3B1 (85%), JAK2V617F (33%), ASXL1 (29%), DNMT3A (13%), SETBP1 (13%) and TET2 (10%). JAK2V617F and SF3B1 mutations are found in 50% of the patients [6,7]. It is important to note here that JAK2V617F mutation is associated with favorable prognosis [8].
Sometimes, these cases can be misdiagnosed as ET (essential thrombocythemia), if it presents with thrombocytosis with increased Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) and close to normal hemoglobin values. Prussian stain should be used to diagnose Ringed Sideroblasts (RS) in bone marrow in order to differentiate it from ET [9].
When compared with other disorders like MDS-RS and ET, MDS/ MPN RS-T was observed to have a better OS (overall survival) than MDS-RS-SLD (myelodysplastic syndrome with ringed sideroblastssingle lineage disorder) and an inferior OS than ET [10]. The rate of leukemic transformation over 100 years was found to be comparable among MDS/MPN RS-T and MDS-RS-SLD, but higher as compared to ET [10].
Treatment is mostly conservative management involving transfusions and ESAs (erythropoietin stimulating agents) among MDS-RS and MDS/MPN RS-T respectively [9,10]. Neither JAK 2 mutation, nor the platelet threshold (> or <600x109) is seen to affect survival among MDS/MPN RS-T or MDS-RS patients [10].
While the symptom management is almost the same as in low risk MDS and MPN, the risk of thrombosis in MDS/MPN RS-T is relatively higher and patients need antiplatelet therapy. In a prior study, RARS-T patients with SF3B1 mutation (n=15), 6 of 10 (60%), had increased risk of thrombotic events when compared to patients without this mutation [11]. Another study was conducted at Mayo clinic to determine the thrombotic events among patients with MDSRS- T. Among total patients, 63% were seen to have cardiovascular risk factors, 11% had thrombotic events after being diagnosed with MDS-RS-T. Almost all of these thrombotic events were provoked, a few had pulmonary embolism and one patient had portal vein thrombosis [12]. One univariate analysis revealed that hemoglobin of <10 g/dl (P=0.008), history of thrombosis (P=0.02) and presence of SF3B1 mutations (P=0.017) were associated with an inferior Thrombosis Free Survival (TFS). Thrombotic events either prior or after the diagnosis of MDS-RS-T, cardiovascular risk factors and JAK- 2 mutations do not affect the OS [12]. Risk of thrombosis in the MDS/ MPN-RS-T patients is similar to that in ET but high as compared to MDS-RARS patients with the same platelet count [13]. According to one study, sixty percent of patients with SF3B1 mutation were known to have thrombotic events, whereas there were no thrombotic events in patients without this mutation [14].
Given recent discovery, the management of MDS-RS-T is based upon treatment strategies used for MDS-RS and ET in the past. In patients with anemia, ESA and blood transfusion are the mainstay of treatment, but there are case reports for the use of lenalidomide as transfusion-sparing therapy [15,16]. Newer agents like luspatercept and the novel telomerase inhibitor imetelstat have also shown promising effect in MDS patients whose anemia is refractory to ESAs [17,18]. Recently in April 2020 luspatercept has been approved by Federal Drug Authority (FDA) for this use.
Also these patients are usually stratified as low risk (0 risk factor), high risk (1 or 2 factors) based on risk factors- age >60 years or prior thrombotic events. Patients who are low risk can benefit from aspirin 81-162 mg with significant improvement in arterial and venous thrombotic risk. In patients with aspirin resistance or those requiring dual antiplatelet therapy, clopidogrel, ticagrelor or prasugrel can be used. High risk patients can benefit from aspirin and/or cytoreductive therapy with medications like hydroxyurea (if tolerable) [19]. Patients with severe thrombocytosis (>1000×109/L), are at risk of developing ristocetin factor deficiency with subsequent increased risk of bleeding with aspirin use. These patients should be evaluated for acquired von Willebrand deficiency. Cytoreductive measures in these cases usually improve bleeding parameters.
Treatment with cytoreductive therapy is usually deferred unless the risk of thrombosis secondary to thrombocytosis is very high. This is because cytoreductive therapy worsens anemia [20]. Hydroxyurea is the most common agent used for this purpose and has been reported to decrease thrombotic events when studied in patients with ET [21]. Alternative cytoreductive therapies are used in cases where resistance to hydroxyurea or refractoriness is observed. These include lenalidomide, busulfan and alpha interferon. Lenalidomide is seen to decrease transfusion dependency and sufficiently decreasing the platelet count among MDS/MPN-RS-T patients [22], Recent studies with interferon alpha have revealed complete remission in the ET and PV with significant decrease in the JAK-2 Kinase allele burden [23]. Also there are some case reports for successful use of ruxolitinib–JAK 1/2 inhibitor for the treatment of hydroxyurea-resistant leukocytosis and erythrocytosis in patients with MDS/MPN-U (myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative syndrome-unclassifiable) [24].
Our patient presented to the hospital after an incidental finding of hemoglobin of 5.9 mg/dl and thrombocytosis platelet count ~1,559×109/L. Bone marrow biopsy fulfilled diagnostic criteria for MDS/MPN-RS-T. RT-PCR showed SF3B1 mutation and activating JAK2 V617F mutation. Cytogenetics and FISH analysis revealed trisomy of chromosome number 8 that is fairly common among MDS and MPN syndrome. Trisomy of chromosome 8 is the most common, albeit nonspecific, numerical chromosome abnormality in myeloid hematopoietic disorder such as Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) or chronic myeloproliferative diseases. It is present in 20-30 % of MDS and 10-15 % of all AML cases.
Regarding our patient, all the diagnostic criteria for MDS/MPNRS- T were met. Since she had become transfusion dependent, she was referred to a specialized center for Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for curative treatment. Prior to curative treatment, patient was initiated on ruxolitinib, which is shown to induce symptomatic improvement in MPN-ET, because her symptoms were mostly related to MPNs (fatigue, itching, headaches, dizziness and sweating), which did not resolve after giving her transfusion.
Hydroxyurea which is often the first line drug for MPN-ET, would definitely reduce her platelet count, but may not provide symptomatic improvement and would likely cause further worsening of her anemia. Due to this consideration, the patient was not started on hydroxyurea instead Ruxolitinib drug was chosen for management. Soon after starting Ruxolitinib, her symptoms have tremendously improved. It is currently being used for bridging purposes, until she finds matching donor for Hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Learning Points
MDS-MPN-RT is a relatively new entity in hematology. Given its morphologic and genomic characteristics overlap with other related disorders like MDS-RS and ET, it is emphasized that clinicians should be wary of this clinical dogma. Recent advancements in diagnostics and molecular genetics have made it possible for us to diagnose and control these patients’ symptoms. Further studies are required to develop disease-specific guidelines for treatment and control of the symptoms.
Acknowledgement
We wish to record our deep sense of gratitude and thanks to Dr. Douglas Tremblay, from Department of Hematology and Oncology, Mount Sinai hospital, NY for keeping us updated on patient after she was transferred.
Informed Consent
Patient was contacted during the hospital stay and after the discharge. Consent was obtained over the telephone for the use of patient data and imaging studies for the publication of case for purely educational and research purposes to which the patient agreed. Written consent could not be obtained due to the patient’s limited visitations to outpatient clinic for follow up.
Author Contributions
Dr. Yousaf and Dr. Asti were part of the patient’s primary team during her care on the medicine floor. They came up with the idea of writing this case and wrote the case presentation. Dr. Yousaf helped with writing the introduction and abstract of the case reports. Dr. Niazi did the literature review and completed the discussion part. Dr. Xue, a pathology fellow, helped with the procurement of images of peripheral smear bone marrow biopsy and guided in writing the case report. Dr. Skaradinskiy and Dr. Asti reviewed the final version of the write-up and made some changes to it according to his expertise.
Data Availability
Any inquiries related to supporting data availability of this study should be directed to corresponding author.
References
- Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016; 127: 2391-2405.
- Clara JA, Sallman DA, Padron E. Clinical management of myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm overlap syndromes. Cancer Biol Med. 2016; 13: 360-372.
- Papaemmanuil E, Cazzola M, Boultwood J, Malcovati L, Vyas P, Bowen D, et al. Chronic Myeloid Disorders Working Group of the International Cancer Genome Consortium. Somatic SF3B1 mutation in myelodysplasia with ring sideroblasts. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365: 1384-1395.
- Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E, Bowen DT, Boultwood J, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, et al. Clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood. 2011; 118: 6239-6246.
- Cazzola M, Rossi M, Malcovati L. Biologic and clinical significance of somatic mutations of SF3B1 in myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2013; 121: 260-269.
- Patnaik MM, Lasho TL, Finke CM, Hanson CA, King RL, Ketterling RPA, et al. Predictors of survival in refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (RARS-T) and the role of next-generation sequencing. Am J Hematol. 2016; 91: 492-498.
- Jeromin S, Haferlach T, Weissmann S, Meggendorfer M, Eder C, Nadarajah N, et al. Refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and marked thrombocytosis cases harbor mutations in SF3B1 or other spliceosome genes accompanied by JAK2V617F and ASXL1 mutations. Haematologica. 2015; 100: e125-e127.
- Schmitt-Graeff AH, Teo SS, Olschewski M, Schaub F, Haxelmans S, Kirn A, et al. JAK2V617F mutation status identifies subtypes of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts associated with marked thrombocytosis. Haematologica. 2008; 93: 34-40.
- Chauffaille MLLF, Perazzio AB, Gouvea CP. Marrow iron staining should always be performed to diagnose Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocythemia. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2019; 41: 279-280.
- Broseus J, Florensa L, Zipperer E, Schnittger S, Malcovati L, Richebourg S, et al. Clinical features and course of refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts associated with marked thrombocytosis. Haematologica. 2012; 97:1036- 1041.
- Visconte V, Makishima H, Jankowska A, Szpurka H, Traina F, Jerez A, et al. SF3B1, a splicing factor is frequently mutated in refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts. Leukemia. 2012; 26: 542-545.
- Patnaik MM, Lasho TL, Finke CM, Hanson CA, King RL, Ketterling RP, et al. Vascular events and risk factors for thrombosis in refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis. Leukemia. 2016; 30: 2273-2275.
- Visconte V, Makishima H, Jankowska A, Szpurka H, Traina F, Jerez A, et al. SF3B1, a splicing factor is frequently mutated in refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts. Leukemia. 2012; 26: 542-545.
- Fenaux P, Platzbecker U, Mufti GJ, Garcia-Manero G, Buckstein R, Santini V, et al. Luspatercept in Patients with Lower-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382: 140-151.
- Nicolosi M, Mudireddy M, Vallapureddy R, Gangat N, Tefferi A, Patnaik MM. Lenalidomide therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome/ myeloproliferative neoplasm with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/ MPN-RS-T). Am J Hematol. 2018; 93: E27-E30.
- Huls G, Mulder AB, Rosati S, van de Loosdrecht AA, Vellenga E, de Wolf JT. Efficacy of single-agent lenalidomide in patients with JAK2 (V617F) mutated refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis. Blood. 2010; 116: 180-182.
- Fenaux P, Platzbecker U, Mufti GJ, Garcia-Manero G, Buckstein R, Santini V, et al. Luspatercept in Patients with Lower-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382: 140-151.
- Tefferi A, Al-Kali A, Begna KH, Patnaik MM, Lasho TL, Rizo A, et al. Imetelstat therapy in refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts with or without thrombocytosis. Blood Cancer J. 2016; 6: e405.
- Michiels JJ, Berneman Z, Schroyens W, Finazzi G, Budde U, van Vliet HH. The paradox of platelet activation and impaired function: platelet-von Willebrand factor interactions, and the etiology of thrombotic and hemorrhagic manifestations in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006; 32: 589-604.
- Tefferi A, Barbui T. Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2015 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2015; 90: 162-173.
- Cortelazzo S, Finazzi G, Ruggeri M, Vestri O, Galli M, Rodeghiero F, Barbui T. Hydroxyurea for patients with essential thrombocythemia and a high risk of thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332: 1132-1136.
- Nichele I, Ruggeri M, Rodeghiero F. Effectiveness of lenalidomide in a patient with refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis with JAK2 (V617F) mutation. Am J Hematol. 2015; 90: E148-E149.
- Kiladjian JJ, Cassinat B, Chevret S, Turlure P, Cambier N, Roussel M, et al. Pegylated interferon-alfa-2a induces complete hematologic and molecular responses with low toxicity in polycythemia vera. Blood. 2008; 112: 3065- 3072.
- Wang Q, Dai HP, Liu DD, Xie JD, Yao H, Ding ZX, et al. Efficacy of ruxolitinib in a patient with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm unclassifiable and co-mutated JAK2, SF3B1 and TP53. Leuk Res Rep. 2020; 14: 100229.