
Research Article
Austin J Infect Dis. 2023; 10(2): 1084.
Hypoalbuminemia, Hyper-a-1/–a-2-Globulinemia Associated with High CRP and IL-6 in COVID-19 Patients in Togo
Gnatoulma Katawa1*; Wemboo Halatoko2; Christèle Nguepou Tchopba1; Yawo Hozo Aloyi2; Adjoa Holali Ameyapoh1; Pélagie Edlom Tchadié1; Marthe Oukoe Amessoudji1; Simplice Damintoti Karou1; Manuel Ritter3; Ameyo M Dorkenoo4,5; Malewe Kolou4
1Unité de Recherche en Immunologie et Immunomodulation (UR2IM)/Laboratoire de Microbiologie et de Contrôle de Qualité des Denrées Alimentaire (LAMICODA), Ecole Supérieure des Techniques Biologiques et Alimentaires, Universite de Lomé, Lomé, Togo
2Institut National d’Hygiène, Lomé, Togo
3Institute for Medical Microbiology, Immunology and Parasitology (IMMIP), University Hospital Bonn (UKB), Bonn, Germany
4Faculté des Sciences de la Santé, Université de Lomé, Lomé, Togo
5Division des Laboratoires, Ministère de la Santé, de l’Hygiène Publique et de l’Accès Universel aux Soins, Lomé , Togo
*Corresponding author: Gnatoulma Katawa Unité de Recherche en Immunologie et Immunomodulation (UR2IM)/Laboratoire de Microbiologie et de Contrôle de Qualité des Denrées Alimentaire (LAMICODA), Ecole Supérieure des Techniques Biologiques et Alimentaires, Universite de Lomé, Lomé, Togo. Email: mahkatawa@yahoo.fr
Received: April 04, 2023 Accepted: May 16, 2023 Published: May 23, 2023
Abstract
Introduction: COVID-19, a viral infectious disease that has caused the global health crisis, is characterized by inflammatory responses. It remains necessary to provide other biomarkers for the pronostic of the disease.
Aim: To determine inflammatory biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease and its severity in Togo.
Methods: Total proteins, C-reactive protein, protein fractions, TNF-a and IL-6 were measured in the serum of COVID-19 positive subjects by respectively Biuret method, immunoturbidimetry, serum protein electrophoresis by capillary method, and sandwich ELISA technique. Logistic regression analyses were performed using SPSS software.
Results: In total, 74 samples were included, among which COVID-19 symptomatic (n=26), asymptomatic (n=18) and COVID-19 negative (n=30). Symptomatic subjects were significantly more aged than other groups, with mean age of 46.31±15.60 years. Data showed elevated total protein in asymptomatic COVID-19; increased a-1 and a-2 globulin concentration and low albumin level in COVID-19 positive patients; high level of a-1 and a-2 globulin associated with a low level of albumin in symptomatic COVID-19 positive subjects; and symptomatic COVID-19 were characterized by elevated CRP level. Logistic regression analysis revealed that increase of IL-6 level was associated with COVID-19 infection.
Conclusion: This study showed that COVID-19 disease is characterized by an upregulation of CRP, IL-6, a-1 and a-2 globulins; and a low level of albumin. The increase in IL-6 level enhances the chance of having COVID-19. Thus these biomarkers may serve as biochemical and serological markers of probable COVID-19 disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hypoalbuminemia; Hyper-a-1-globulinemia; Hyper-a-2-globulinemia protein; CRP; TNF-a; IL-6
Introduction
COVID-19, caused by “severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2” (SARS-CoV-2) [1,2], remains a global health emergency about four years after description of the first case in December 2019 [3]. The virus spread worldwide, causing many deaths: as of 5 March 2023, over 759 million confirmed cases and over 6.8 million deaths reported globally [4]. In Africa, COVID-19 was not as severe as expected, with regards to the high mortality rate registered all over the world. Over the course of time, molecular biomarkers of SARS-CoV-2 [5,6] have been identified, allowing the early detection of the virus and also the development of vaccines [7,8]; and consequently, the reduction of the mortality rate [9]. As of the time of writing this article, no treatment for COVID-19 is available, SARS-CoV-2 obviously entered our lives and it might be useful to identify other biomarkers to be used for the presumptive diagnosis of the disease. Indeed, patients with COVID-19 present a large variety of symptoms, ranging from mild such as fever, dry cough, malaise, sore throat, fatigue, pain, loss of taste or smell; to moderate with dyspnea, diarrhea and pneumonia; and may progress to severe pneumonia and ultimately to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), septic shock and/or multi-organ failure [10,11]. Symptomatic forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection are accompanied by biological changes like increased neutrophil counts, decreased CD4 and CD8 T cells, and in rare cases, decreased hemoglobin and platelets [12,13]. In China, several authors found that an abnormal elevation of the C-reactive protein is observed [14] with immunological disturbances, dominated by considerably elevated serum levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines responsible of the so called “cytokine storm”. The latter includes elevation of IL-6, TNF-a, IL-1β, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-8, IL-17, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IP10, MCP1 and MIP1a (also known as CCL3) [15-17]; and causes tissue damage in the heart, liver, and kidneys, as well as respiratory failure or multi-organ failure [18].
The first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in Togo on 6 March 2020 by WHO [19] and three years later, on 6 March 2023, 808,684 individuals have been tested of which 39,396 confirmed cases, 290 deaths registered and 25 known active cases [20]. Data on the inflammatory profile of COVID-19 patients in Togo remains unknowned and the reference method for the certainty diagnostic in the country is RT-PCR. Unfortunately, RT-PCR is not available in most of the hospital diagnosis platforms. Therefore, it appears necessary to find other common biomarkers appropriate and affordable for the pronostic of COVID-19.
In this study, we demonstrated the implication of biomarkers such as total proteins, C-Reactive Protein (CRP), protein fractions (albumin, a-1-, a-2-, β-1-, β-2- and γ-globulins) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-a) in COVID-19 disease and its severity in patients infected in Togo.
Material and Methods
Study Population and Samples
This was a cross-sectional study conducted at the Togo’s national laboratory of public health called “Institut National d’Hygiène” (INH) and the immunology and immunomodulation research unit « Unité de Recherche en Immunologie et Immunomodulation (UR2IM) of « Ecole Supérieure des Techniques Biologiques et Alimentaires (ESTBA) », University of Lomé.
The biological material was serum samples collected: 1) on COVID-19 infected patients admitted at the reference center for COVID-19 care named “Centre Hospitalier Regional Lomé Commune” (CHR-LC) during COVID-19 break in Togo; and 2) on patients who visited “Institut National d’Hygiène” (INH) before year 2019, considered as “COVID-19 negative”.
Samples from male and female were randomly selected according to these criteria: age equal or more than 18 years, HIV negative, COVID-19 positive admitted at CHR-LC during COVID-19 break, and COVID-19 negative sampled before year 2019 at INH stored at -80°C. HIV positive, pregnant women and subjects aged less than 18 years were not included.
Definition
COVID-19 positive individuals were diagnosed by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) in the molecular biology laboratory of INH, detecting 2 molecular markers of SARS-CoV-2 (N gene and ORF1ab) in the sera. They were subdivided in 2 groups by the medical practicians trained for COVID-19 diagnosis following WHO recommandations.
COVID-19 symptomatic: individuals diagnosed positive to SARS-CoV-2 and who had COVID-19 related symptoms confirmed by medical practicians following WHO guidelines.
COVID-19 asymptomatic: individuals for who no symptoms were declared or registered following medical consultation. It was about individuals who have been in close contact with symptomatic COVID-19 subjects or have been diagnosed during a screening test for a travel purpose.
Total Protein Assay
The total protein was measured by Biuret colorimetric method using TP2 Total Protein Gen.2 kit (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, USA) on the fully automated biochemical analyzer COBAS c311 (Roche Diagnostics), according to manufacturer’s instructions. Thus, copper ions (Cu2+) react in alkaline solution with the peptide bonds of proteins, forming a characteristic purple complex (biuret reaction). The intensity of the colour is directly proportional to the concentrations of protein in the milieu and is measured by photometry at 546nm.
C-Reactive Protein Assessment
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) was assayed by immunoturbidimetry on latex particles coupled to human anti-CRP antibodies, using CRP4 Tina-quant C-Reactive Protein kit (Roche Diagnostics) and the fully automated biochemical analyzer COBAS c311.
The CRP in the serum, link specifically to the anti-CRP, forming an agglutination of latex particles, this latter agglutination increase the turbidity. The level of CRP in the sample is proportional to the quantity of light absorbed in the turbidimeter.
Determining the Level of Protein Fractions
Protein fractions assay was performed by electrophoresis on the fully automated MiniCap Flex piercing (Sebia, Lisses, France) using Minicap Protein(e) 6-Electrophoresis kit (Sebia) following the manufacturer’s instructions. In brief, proteins were separated in silica capillaries by their electrophoretic mobility and electroosmotic flow at high voltage in an alkaline buffer. Serum proteins submitted to an electric flow in an alcalin buffer are negatively charged and move from cathode (negative side) to anode (positive). Each protein fraction (albumin, a-1 and a-2 globulins, β-1 and β-2 globulins, γ-globulins) was directly detected during migration by UV absorbance which is proportional to the concentration of the protein.
Cytokines Measurement
The Level of cytokines, IL-6 and TNFa was determined in the serum samples by ELISA sandwich technique, using InvitrogenTM Human IL-6 ELISA kit and InvitrogenTM Human TNFa ELISA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bender MedSysthems GmBH, Vienna, Australia) following manufacturer’s instructions. Cytokines concentrations were measured at 450nm on a Huma Reader HS plate reader (Human Diagnostics Worldwide, Wiesbaden, France).
Statistical Analysis
Data were anlysed using SPSS software (IBM SPSS Statistics 21; Armonk, NY) and GraphPad Prism version 9 (GraphPad Software, San Diego California USA). Student's t-test and χ²/Fisher's exact tests were used, respectively, to compare means and frequencies; with a significance level if p-value<0.05. Binary logistic regression was performed by associating each of the inflammation biomarker with a positive COVID-19 on one hand, and with the severity of the COVID-19 disease on the other hand. Odds Ratio (OR) and adjusted odds ratio were considered significant at 95% confidence interval, with p-Value≤0.05 in the univariate model and multivariate model. Also when OR/aOR = 1, there was no association; when OR/aOR>1 the study variable was associated with COVID-19 or COVID-19 severity; and when OR/aOR<1, the study variable was a protective factor against COVID-19 or COVID-19 severity. GraphPad Prism version 9 was essentially used to screen the profile of biomarkers in COVID-19 positive patients on the one hand, and in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients on the other hand. The distribution of values was tested using the d’Agostino-Pearson Omnibus normality test. Since the distribution of our variables was non-parametric, the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the medians between 2 groups; and the Kruskal-wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple analysis to compare medians between 3 groups. Differences were considered significant when the p-value<0.05.
Ethical Considerations
This study received the approval of the ethical board (“Comité de Bioéthique pour la Recherche en Santé”, CBRS) of the Ministry of Health of Togo (N°035/2022/CBRS). All participants were adults and already provided written consent for further use of their samples for research purpose.
Results
Characteristics of the Study Population
Our study population comprised 74 individuals. Among them, 26 were symptomatic, 18 asymptomatic and 30 negative. The mean age was 46.31±15.60 years, 29.50±8.27 and 29.30±9.70 (p=0.025) respectively for symtomatics, asymptomatics and negatives. Most of COVID-19 positive were male (Table 1).
Negative COVID-19 (n= 30)
Asymptomatic COVID-19 (n= 18)
Symptomatic COVID-19 (n= 26)
p-Value
Mean age (years)
29.30±9.70
29.50±8.27
46.31±15.60
0.025
Sex n(%)
0.007
Female
3(10.0)
3(16.7)
12(46.2)
Male
27(90.0)
15(83.3)
14(53.8)
Table 1: Characteristics of study population.
Elevated total protein in COVID-19 Asymptomatic Individuals
The profile of total protein shows that there was no difference in total protein concentration between negative and positive COVID-19 patients (Figure 1A). However, by splitting positive COVID-19 patients into two groups (asymptomatic and symptomatic patients) and comparing them to negative patients, it was found that asymptomatic patients had a significantly higher level of total protein compared to negative patients p=0.0302, (Figure 1B).
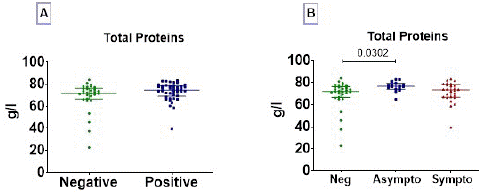
Figure 1: Total proteins profile. Total proteins were measured in serum of subjects. Total proteins concentration data are presented as dot, each representing an individual. Horizontal bars indicate the median with interquartile ranges. (A) The comparison of medians between negative (n=30) and positive (n=44) COVID-19 groups was done by Mann-Whitney U test; and (B) Kruskall-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple analysis were performed to compare medians between negative COVID-19 patients (n=30), asymptomatic (n=18) and symptomatic (n=26) positive patients. p<0.05 is considered significant.
Increased a-1 and a-2 Globulin Concentration and Low Albumin Level in COVID-19 Positive Patients
The serum profiles of the six fractions of proteins (albumin, a-1/a-2 globulin, β-1/β-2, and γ- globulin) are shown in Figure 2. The analysis of these six fractions revealed that albumin levels in COVID-19 positive patients were significantly lower than those in negative patients p=0.0001, (Figure 2A). In contrast, a-1 globulin p=0.0005, (Figure 2B) and a-2 globulin p<0.0001, (Figure 2C) fractions concentration was significantly higher in positive subjects than in negative patients.
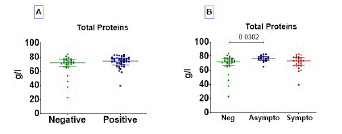
Figure 2: Albumin, a-1/a-2 globulin, β-1/β-2 globulin and gamma globulin profile in COVID-19 infected and uninfected patients. The six protein fractions were quantified in the serum of subjects. Protein concentration data are presented as dot, each representing an individual. Horizontal bars indicate the median with interquartile ranges. The comparison of means between negative (n= 30) and positive (n= 44) COVID-19 groups was done by Mann-Whitney U test. p<0.05 is considered significant.
High Level of a-1 and a-2 Globulin Associated with a Low Level of Albumin in Symptomatic COVID-19 Positive Subjects
The concentration of albumin was significantly lower in symptomatic patients than in asymptomatic patients (p=0.0058) and negatives (p<0.0001) (Figure 3A). In opposite, the concentrations of a-1 and a-2 globulins were significantly elevated in symptomatics than in asymptomatics and negatives (Figure 3B and 3C).
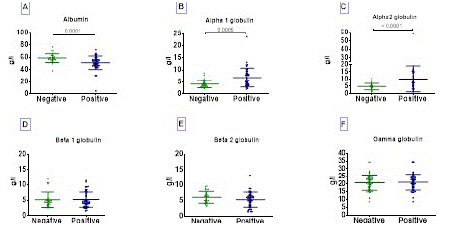
Figure 3: Albumin, a1/a2 globulin, beta1/beta2 globulin and gamma globulin profile in symptomatic COVID-19 positive patients. The six protein fractions were quantified in serum of subjects. Protein concentration data are presented as dot, each representing an individual. Horizontal bars indicate the median with interquartile ranges. Kruskall-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple analysis were performed to compare medians between negative COVID-19 patients (n=30), asymptomatic (n=18) and symptomatic (n=26) positive patients. p<0.05 is considered significant.
Symptomatic COVID-19 are Characterized by Elevated CRP Level
A significantly high CRP level was observed in COVID-19 positive compared to negative (p<0.0001). Interestingtly, symptomatic COVID-19 individuals were characterized by elevated CRP proteins and there was no difference between uninfected and asymptomatic individuals (Figure 4B).
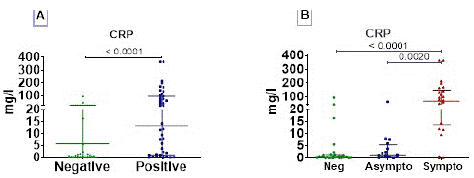
Figure 4: C- reactive protein (CRP) profile. The CRP was measured in serum of subjects. CRP concentration data are presented as dot, each representing an individual. Horizontal bars indicate the median with interquartile ranges. (A) The comparison of means between negative (n= 30) and positive (n= 44) COVID-19 groups was done by Mann-Whitney U test ; and (B) Kruskall-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple analysis were performed to compare medians between negative COVID-19 patients (n=30), asymptomatic (n=18) and symptomatic (n=26) positive patients. p<0.05 is considered significant.
COVID-19 Symptomatic Characterized by Elevated IL-6 Associated to Dampened TNF-a
The serum profile of TNF-a and IL-6 cytokines is presented in Figure 5. Concerning TNF-a, we observed that there was no difference between COVID-19 positive compared to uninfected (Figure 5A); this cytokine was dampened in COVID-19 symptomatic individuals compared to asymptomatics (Figure 5B). In contrast, COVID-19 infected people were characterized by elevated IL-6 levels; and there was no difference between COVID-19 symptomatic and asymptomatic (Figure 5C and D).
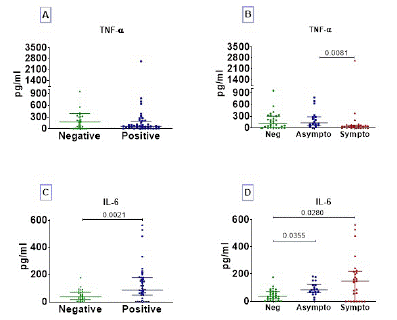
Figure 5: TNF-a and IL-6 cytokine profile. Cytokines were assayed in serum of subjects. Cytokine concentration data are presented as dots, each representing an individual. Horizontal bars indicate the median with interquartile ranges. The comparison of medians between negative (n= 30) and positive (n= 44) COVID-19 groups was done by Mann-Whitney U test (A and C); and Kruskall-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple analysis were performed to compare medians between negative COVID-19 patients (n=30), asymptomatic (n=18) and symptomatic (n=26) positive patients (B and D). p<0.05 is considered significant.
Inflammatory Biomarkers Associated with COVID-19 Severity
To investigate the inflammatory biomarkers associated to COVID-19, logistic regression analyses were performed. Results showed that IL-6 (OR=1.014; 95% CI [1.005–1.024]), CRP (OR=1.034; 95% CI [1.006-1.062]), a1 globulin (OR=1.518; 95% CI [1.165-1.978]) and a2 globulin (OR=1.378; 95% CI [1.137 -1.671]) were associated with COVID-19 positive; whereas albumin (OR=0.891; 95% CI [0.825–0.962]) was associated with absence of disease. After analysis in the multivariate model, only IL-6 (aOR=1.019; 95% CI [1.006–1.032]) was related to COVID-19 positive (Table 2).
COVID-19 (Negative vs Positive)
Biomarkers
Univarable
Multivariable
OR (95% CI)
p-Value
aOR (95% CI)
p-Value
TNF-a
1.000(0.999 – 1.001)
0.907
IL-6
1.014(1.005 – 1.024)
0.003
1.019(1.006 – 1.032)
0.004
CRP
1.034(1.006 -1.062)
0.016
1.015(0.989 – 1.051)
0.409
Total proteins
1.042(0.991 – 1.051)
0.107
Albumin
0.891(0.825 – 0.962)
0.003
1.009(0.888 – 1.147)
0.895
a-1-globulin
1.518(1.165 -1.978)
0.002
1.055(0.713 – 1.563)
0.788
a-2-globulin
1.378(1.137 -1.671)
0.001
1.295(0.961 – 2.747)
0.090
β-1-globulin
1.014(0.836 – 1.231)
0.887
β-2-globulin
0.855(0.685 – 1.067)
0.165
γ-globulin
1.012(0.922-1.111)
0.807
OR: Odd Ratio; aOR: Adjusted Odd Ratio; CI: Confidence Interval; Bold Values: Significant P-Values.
Table 2: Inflammatory biomarkers associated to COVID-19.
The relation between inflammatory biomarkers and disease severity is presented in Table 3. In univariate model, the results indicated that CRP (OR=1.063; 95% CI [1.008–1.122]), a-1-globulin (OR=1.431; 95% CI[1.093–1.873]), and a-2-globulin (OR=1.410; 95% CI [1.128–1.763]) are associated with COVID-19 symptomatic status; whereas albumin (OR=0.878; 95% CI [0.792–0.973]) and gamma-globulin protein (OR=0.864; 95% CI [0.748–0.998]) were associated with the COVID-19 asymptomatic. Using a backward stepwise logistic regression analysis, it appeared that in a model with CRP, albumin and gamma-globulin protein, albumin (OR=0.713; 95% CI [0.574-0.886]) and gamma-globulin protein (OR=0.532; 80% CI [0.345–0.822]) were associated with the COVID-19 asymptomatic status.
COVID-19 positive (asymptomatic vs symptomatic)
Biomarkers
Univariable
Multivariable
OR (95% CI)
p-Value
aOR (95% CI)
p-Value
TNF-a
1.000(0.998 – 1.001)
0.546
IL-6
1.005(0.998 – 1.011)
0.142
CRP
1.063(1.008 – 1.122)
0.026
1.031(0.982 – 1.084)
0.223
Total proteins
0.886(0.784 – 1.001)
0.052
Albumin
0.878(0.792 – 0.973)
0.013
0.784(0.615 -0.997)
0.048
a-1-globulin
1.431(1.093 – 1.873)
0.009
a-2-globulin
1.410(1.128 – 1.763)
0.003
β-1-globulin
1.238(0.936 -1.637)
0.134
β-2-globulin
1.081(0.833 – 1.405)
0.557
γ-globulin
0.864(0.748 – 0.998)
0.046
0.594(0.375 – 0.944)
0.027
OR: Odd Ratio; aOR: Adjusted Odd Ratio; CI: Confidence Interval; Bold Values: Significant P-Values
Table 3: Inflammatory biomarkers associated to severity of COVID-19.
Discussion
COVID-19 is a disease that has engaged researchers worldwide. To enhance the knowledge of the pathophysiology of patients in Togo, the overall objective of this study was to determine inflammatory biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease and its severity in Togo.
In our study, COVID-19 symptomatic subjects were significantly more aged than COVID-19 asymptomatic and uninfected subjects. These results are similar to those of El-Ghitany et al who found that the proportion of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was significantly more in all age categories except the age group aged less than 15 years [21]. Indeed COVID-19 is a disease which severity is associated to age [22,23]. Indeed aging is associated with an enhancement of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE-2) expression, the receptor for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which accelerates viral replication in the old population [24].
We observed that the level of total proteins was significantly elevated in asymptomatic compared to negative and there was no difference between symptomatic and negative subjects. Proteins, major building blocks of body tissues, regulate signaling involved in most cellular activities; furthermore, hypoproteinemia predicts disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 [25]. Moreover, the analysis of protein fractions showed hypoalbuminemia and hyper-a-1 and a-2 globulin, signing acute inflammation early phase or inflammatory syndrome among COVID-19 positive compared to COVID-19 negative [26,27]. Interestingly, the same profile was observed in symptomatics compared to asymptomatics and uninfected. Thus, the inflammatory syndrome was related not only to COVID-19 positivity, but also to the severity. These findings are aligned with those of already published on COVID-19 which states that COVID-19 is an acute inflammatory disease but also a multisystem inflammatory syndrome [1,28,29].
We also noticed a significantly high production of CRP in COVID-19 positive regarding negative patients; and also in symptomatic positive patients compared to asymptomatic. The increase in CRP, observed in symptomatic forms of the disease, is similar to the results of El Aidaoui et al [30] in Morocco, Yu et al [31], Zheng et al [32] in China who observed an increase in CRP in severe forms and in patients who died of COVID-19. The elevation of CRP in the pathology could be linked to the immune response. CRP binds to pathogens and promotes their elimination by phagocytic cells, functioning as the host's first line of innate defence [33]. Indeed, traditionally utilized as a marker of infection and cardiovascular events, there is now growing evidence on the important role of CRP in inflammatory processes and responses of host to infection, including the complement pathway, apoptosis, phagocytosis, Nitric Oxide (NO) release, and the production of cytokines, particularly TNF-a and IL-6 [34,35]. The latter justifies our finding of high IL-6 concentration in COVID-19 positive patients. IL-6 is a cytokine of innate response which has been associated to cytokine storm with other mediators including TNFa [36-38]. Our study revealed a trend of TNF-a opposite to that of IL-6. Since the fundamental role of TNFa in almost acute inflammatory responses, as an amplifier and even as a coordinator of inflammation, is well established [39], our result suggests that patients were not at the acute stage of COVID-19 which is marked by Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).
Logistic regression analysis allowed us to notice that in univariate model, IL-6, CRP, a-1 globulin and a-2 globulin were associated with COVID-19 positive; whereas albumin was associated with absence of disease. After analysis in the multivariate model, only IL-6 was related to COVID-19 positive. Thus, an increase in IL-6 level leads to an increase of chance to having COVID-19. This is consistent with the finding of some authors who clearly stipulated that IL-6 is associated not only to the disease but also directly associated with the severity of COVID-19 [40,41]. Also, Chen et al corroborates that detectable serum levels of SARS-CoV-2 correlated with drastically elevated IL-6 level in critically ill patients with COVID-19. IL-6 is secreted by a plethora of immune and stromal cells such as monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, B and T cells, hepatocytes, keratinocytes, adipocytes, dendritic cells, and fibroblasts. Indeed, it exerts effects on a similarly broad array of cellular targets expressing the functional IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) such as T cells, B cells, vascular endothelial cells, monocytes, and hepatocytes [36,42,43]. Such diversity of targets leads to functional pleiotropy as the synthesis of acute-phase proteins in the liver like CRP; the decreased production of albumin; the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells; and hematopoiesis and other metabolic and neurologic processes. The role of IL-6 in COVID-19 is so well established that some authors demonstrated IL-6 inhibition associated with clinically meaningful improvements in outcomes for patients admitted with COVID-19; nevertheless, long-term benefits of IL-6 inhibition, its effectiveness across healthcare systems, and implications for differing standards of care remained to be demonstrated [44].
Screening for the biomarkers associated to disease severity in our cohort, we obtained in univariate model that CRP, a-1-globulin and a-2-globulin were associated with COVID-19 symptomatic status; whereas albumin and gamma-globulin protein were associated with the COVID-19 asymptomatic. Thus not are only CRP, a-1-globulin and a-2-globulin elevated in COVID-19 symptomatic, they are also independently associated to the disease severity. Using a backward stepwise logistic regression analysis, it appeared that in a model with CRP, albumin and gamma-globulin protein, albumin and gamma-globulin protein were associated with the COVID-19 asymptomatic status. So, in presence of an increase of CRP level, a decrease of albumin and γ-globulin levels leads to a chance of having an asymptomatic status. In contrast with our results, several authors noticed that low level of serum albumin is a predictor of vulnerability to COVID-19 [45,46] and hypogammaglobulinemia associated to a poor outcome in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in a non-intensive care setting [47]. This contradiction may be justified by the difference in sample sizes or by the location of study site. Nonetheless, an investigation on a large sample size could tell us whether this difference is relevant.
This study, although very informative, has some limitations. Despite the fact that some data are quite similar to the literature, several discrepancies are noticed. A large sample size could bring more insightful data.
Conclusion
This study provided evidence of the implication of inflammatory biomarkers in the physiopathology of COVID-19 in Togo. The disease is characterized by an upregulation of CRP, IL-6, a-1 and a-2 globulins; and a low level of albumin. Moreover, an elevation of IL-6 level leads to an increase of chance to have COVID-19. These biomarkers may serve as for the presumption diagnosis of COVID-19 disease.
Author Statements
Acknowledgement
We thank all those individuals who gave their consent for their samples to be used for further research purpose.
Authors Contribution
G.K., M.R. and M.K. Conceived and designed the study. G.K. and M.R. contributed reagents/materials. A.M.D. carried out the sampling process. Y.H.A., M.O.A. and P.E.T. selected samples and data, performed the experiments. G.K., C.N.T., A.H.A, A.W. Analyzed and interpreted the data, prepared the draft of the manuscript and participated in writing-review and editing. M.K and S.D.K. participated in writing-review.
Funding
Gnatoulma Katawa and Manuel Ritter are funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG; Grant LA2746/1-1, LA27 46/2-1 and RI3036/1-1).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare not having competing interests.
References
- Tchopba C, Ataba E, Katawa G, Gambogou B, Ritter M, et al. COVID-19: epidemiology, pathogenesis and immununological basis. Al-Nahrain Journal of Science. 2020; 4: 1-12.
- Al-Qahtani AA. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Emergence, history, basic and clinical aspects. Saudi journal of biological sciences. 2020; 27: 2531-8.
- WHO. Statement on the fourteenth meeting of the International Health Regulations. Emergency Committee regarding the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. 2005.
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19. 2023.
- Safiabadi Tali SH, LeBlanc JJ, Sadiq Z, Oyewunmi OD, Camargo C, et al. Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021; 34: e00228-20.
- Dinnes J, Deeks JJ, Adriano A, Berhane S, Davenport C, et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2020; 8: Cd013705.
- Poland GA, Ovsyannikova IG, Crooke SN, Kennedy RB. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Development: Current Status. Mayo Clinic proceedings. 2020; 95: 2172-88.
- Katawa G, Tchopba CN, Tchadié PE, Simfele CH, Kamassa EH, et al. Systematic Review on COVID-19 Vaccines: Comparative Study of AstraZeneca, Pfizer-BioNTech, Sputnik V, Johnson & Johnson, Moderna and Corona Vac. International Journal of Innovative Research in Medical Science. 2021; 6: 784 - 94.
- Huang YZ, Kuan CC. Vaccination to reduce severe COVID-19 and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences. 2022; 26: 1770-6.
- Alimohamadi Y, Sepandi M, Taghdir M, Hosamirudsari H. Determine the most common clinical symptoms in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of preventive medicine and hygiene. 2020; 61: E304-e12.
- Tay MZ, Poh CM, Rénia L. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. 2020; 20: 363-74.
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020; 395: 497-506.
- Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Lancet Respiratory medicine. 2020; 8: 420-2.
- Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, et al. Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA internal medicine. 2020; 180: 934-43.
- Yi Y, Lagniton PNP, Ye S, Li E, Xu RH. COVID-19: what has been learned and to be learned about the novel coronavirus disease. Int J Biol Sci. 2020; 16: 1753-66.
- Liu J, Li S, Liu J, Liang B, Wang X, et al. Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. E BioM edicine. 2020; 55: 102763.
- Yang L, Gou J, Gao J, Huang L, Zhu Z, et al. Immune characteristics of severe and critical COVID-19 patients. 2020; 5: 179.
- Cao X. COVID-19: immunopathology and its implications for therapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020; 20: 269-70.
- OMS. Epidémie à Coronavirus, COVID-19, le Togo déclare un premier cas confirmé. https://wwwafrowhoint/fr/news/epidemie-coronavirus-covid-19-le-togo-declare-un-premier-cas-confirme. 2020.
- Gouv.tg. Coronavirus: situation au Togo. https://covid19gouvtg/situation-au-togo/. 2023.
- El-Ghitany EM, Hashish MH, Farghaly AG, Omran EA, Osman NA, et al. Asymptomatic versus symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: a cross-sectional seroprevalence study. Tropical Medicine and Health. 2022; 50: 98.
- Neves MT, de Matos LV. COVID-19 and aging: Identifying measures of severity. 2021; 9: 20503121211027462.
- Sohrabi M-R, Amin R, Maher A, Bahadorimonfared A, Janbazi S, et al. Sociodemographic determinants and clinical risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity: a cross-sectional analysis of over 200,000 patients in Tehran, Iran. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2021; 21: 474.
- Farshbafnadi M, Kamali Zonouzi S, Sabahi M, Dolatshahi M, et al. Aging & COVID-19 susceptibility, disease severity, and clinical outcomes: The role of entangled risk factors. Experimental gerontology. 2021; 154: 111507.
- Ali AM, Kunugi H. Hypoproteinemia predicts disease severity and mortality in COVID-19: a call for action. Diagnostic Pathology. 2021; 16: 31.
- Vavricka SR, Burri E, Beglinger C, Degen L, Manz M. Serum protein electrophoresis: an underused but very useful test. Digestion. 2009; 79: 203-10.
- Feketea GM, Vlacha V. The Diagnostic Significance of Usual Biochemical Parameters in Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19): Albumin to Globulin Ratio and CRP to Albumin Ratio. Frontiers in Medicine. 2020; 7: 566591.
- Wang Y, Perlman S. COVID-19: Inflammatory Profile. Annual review of medicine. 2022; 73: 65-80.
- Manjili RH, Zarei M, Habibi M, Manjili MH. COVID-19 as an Acute Inflammatory Disease. The Journal of Immunology. 2020; 205: 12-9.
- El Aidaoui K, Haoudar A, Khalis M, Kantri A, Ziati J, et al. Predictors of Severity in Covid-19 Patients in Casablanca, Morocco. Cureus. 2020; 12: e10716.
- Yu C, Lei Q, Li W, Wang X, Li W, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 1663 hospitalized patients infected with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a single-center experience. Journal of infection and public health. 2020; 13: 1202-9.
- Zheng Y, Xu H, Yang M, Zeng Y, Chen H, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and clinical features of 32 critical and 67 noncritical cases of COVID-19 in Chengdu. Journal of clinical virology : the official publication of the Pan American Society for Clinical Virology. 2020; 127: 104366.
- Peisajovich A, Marnell L, Mold C, Du Clos TW. C-reactive protein at the interface between innate immunity and inflammation. Expert review of clinical immunology. 2008; 4: 379-90.
- Sproston NR, Ashworth JJ. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Frontiers in immunology. 2018; 9: 754.
- Han H, Ma Q, Li C, Liu R, Zhao L, et al. Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors. 2020; 9: 1123-30.
- Copaescu A, Smibert O, Gibson A, Phillips EJ, Trubiano JA. The role of IL-6 and other mediators in the cytokine storm associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020; 146: 518-34.e1.
- Frisoni P, Neri M, D’Errico S, Alfieri L, Bonuccelli D, et al. Cytokine storm and histopathological findings in 60 cases of COVID-19-related death: from viral load research to immunohistochemical quantification of major players IL-1β, IL-6, IL-15 and TNF-a. 2022; 18: 4-19.
- Shafiek HK, El Lateef HMA, Boraey NF, Nashat M, Abd-Elrehim GAB, et al. Cytokine profile in Egyptian children and adolescents with COVID-19 pneumonia: A multicenter study. 2021; 56: 3924-33.
- Montazersaheb S, Hosseiniyan Khatibi SM, Hejazi MS, Tarhriz V, Farjami A, et al. COVID-19 infection: an overview on cytokine storm and related interventions. 2022; 19: 92.
- Coomes EA, Haghbayan H. Interleukin-6 in Covid-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. 2020; 30: 1-9.
- Talwar D, Kumar S. Interleukin 6 and Its Correlation with COVID-19 in Terms of Outcomes in an Intensive Care Unit of a Rural Hospital:A Cross-sectional Study. 2022; 26: 39-42.
- Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. The biology and medical implications of interleukin-6. Cancer immunology research. 2014; 2: 288-94.
- Uciechowski P, Dempke WCM. Interleukin-6: A Masterplayer in the Cytokine Network. Oncology. 2020; 98: 131-7.
- Tharmarajah E, Buazon A, Patel V, Hannah JR, Adas M, et al. IL-6 inhibition in the treatment of COVID-19: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. The Journal of infection. 2021; 82: 178-85.
- Johnson AS, Polese G, Johnson M, Winlow W. Appropriate Human Serum Albumin Fluid Therapy and the Alleviation of COVID-19 Vulnerabilities: An Explanation of the HSA Lymphatic Nutrient Pump. COVID. 2022; 2: 1379-95.
- Huang W, Li C, Wang Z, Wang H, Zhou N, et al. Decreased serum albumin level indicates poor prognosis of COVID-19 patients: hepatic injury analysis from 2,623 hospitalized cases. Science China Life sciences. 2020; 63: 1678-87.
- Scarpa R, Dell’Edera A, Felice C, Buso R, Muscianisi F, et al. Impact of Hypogammaglobulinemia on the Course of COVID-19 in a Non-Intensive Care Setting: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Frontiers in immunology. 2022; 13: 842643.