
Special Issue - Tuberculosis
Austin J Infect Dis. 2021; 8(1): 1044.
Failure of BCG Necessitates to the Development of New Novel Vaccine
Meena S1,2, Goutam P1 and Meena LS1,2*
1CSIR-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology, Mall Road, Delhi, India
2Academy of Scientific and Innovative Research (AcSIR), CSIR-HRDC, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India
*Corresponding author: Laxman Singh Meena, CSIR-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology, Mall Road, Delhi-110007, India
Received: March 24, 2021; Accepted: April 16, 2021; Published: April 23, 2021
Abstract
The only vaccine available for the deadly disease tuberculosis is Bacillus- Calmette-Guerin (BCG), which is an attenuated vaccine of Mycobacterium bovis. Although this vaccine boosts immune response but it is effective only for 10-20 years, after this there is need to develop immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (M. tuberculosis). As the vaccine is botched to provide sustained effects and to protect against disseminated forms of Tuberculosis (TB), it needs a component to heighten antigen specific immune reactions when used in combination with particular vaccine antigens that can also modulate the immune responses to an antigen to advance them. Adjuvants are the one such factor that can be used in vaccines to crack such problems. Many vaccines are under clinical trials in which subunit vaccine has taken attention because they are safer and can be standardized. There are many adjuvants which have been tested in combinations with BCG to increase the activity of vaccine. Mycobacterial antigen 85 A, B, C, present at outer part of cell wall and have great potential as therapeutic approach towards tuberculosis. MPT64 increases T-cell response in tuberculosis patients but there are less evidence about the role of this secreted mycobacterial protein in patients. ESAT 6 is effective T cell antigen and also pore forming toxin which is crucial for the virulence of bacterium. ESAT 6 separately or in compound form with its chaperone CFP- 10 form, regulates host immune response. They efficiently modify innate and adaptive immune response. This review provides an insight in the direction of the vaccine development on the basis of pre-existing credentials.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; H37Rv; Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG); Adjuvants
Abbreviations
BCG: Bacillus-Calmette-Guerin; Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (M. tuberculosis); TB: Tuberculosis; APCs: Antigen-Presenting Cells; TLRs: Toll Like Receptors; DCs: Dendritic Cells; CFA: Complete Freunds Adjuvant
Introduction
A weakened strain of tuberculosis bacteria is used to make the BCG vaccine. Because the bacterium in the vaccine is weak, it stimulates the immune system to protect against the disease. Even so, the BCGvaccine has been used for over 80 years and there is still a crumb of doubt regarding its significance in protection against tuberculosis, the protection given by BCG vaccination is not life-long, moreover it does not thwart the revival of dormant Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (M. tuberculosis) [1]. Most of the studies have shown that BCG is protective for only 10-20 years. Large population (more than three billion) has been vaccinated with Bacillus-Calmette-Guerin (BCG) [2] , still there remains a shadow of doubt regarding its value in protection against Tuberculosis (TB) as this deadly disease kills single individual every 18s according to WHO, by 2020 to 36 million people will pass-away of tuberculosis every year [1,3]. Thus, it is a need of the hour to design effective tuberculosis shot based on rising the cellular reactions not only compulsory to destroy the bacteria and inhibit the setting-up of infection (against infection & pulmonary disease) but also to elude recurrence or development toward clinical TB in latent patients. Currently numerous vaccines are being tested in different clinical trials but subunit tuberculosis vaccine has received special consideration because, even of their deprived immunogenicity they express high level protection and their manufacture can be standardized. [4,5]. Numerous adjuvants also have been tried for effectiveness in TB vaccines, mostly combining with altered antigens or fusion-proteins. When it was used unaided or in unification with BCG in a “prime boost” approach or co-adjuvanted with cytokines or other molecules, several of these vaccines have been publicized to bestow shielding immunity. Mucosal exteriors are the forefronts for pathogen infections thus oral-mucosal vaccines are being preferred over systemic vaccines as they do not induce a constant mucosal immune reaction. In contrast oral mucosal vaccines considerably have more advantages. Including ease of administration, it completely drain out the requirement of trained person for the administration and risk of infected syringe or sticks, elevated patient conformance and comfort of manufacturing because of a declined requirement to clean bacterial by-products like endotoxin, as the gut already contains trillions of mutual microbes [6,7]. In addition, Mucosal shots can encourage both systemic & mucosal immunity, including Ag-precise reaction, particularly at mucosal outsides. As vaccine is failed to give prolonged effects and to shield against disseminated condition of TB, it needs an ingredient to enhance antigen precised immune responses when used in combination with particular vaccine antigens that can also modulate the immune comebacks to an antigen to advance them. Adjuvants are one such ingredient that can be used in vaccines to solve such problems. Even though controlled number of adjuvant organizations has been permitted for clinical applications, various adjuvant combinations and vaccine delivery have been valued, emerging in propitious initial formulations [7,8].
Action-Mechanism of Adjuvants and their Role in Vaccines
Adjuvants are the molecules, compounds or macromolecular complexes that form an essential constituent in most of the deactivated & subunit vaccine. Cautious and correct selection of adjuvants supports in stimulating specific immunity against pathogens at both innate & adaptive levels to draw out the protective immunity, as they are considered effective in boosting, maintaining and potentiate the specific immune response to antigens [9,10]. Adjuvants, in reference of shots, are well explained as components proficient of improving or shaping Ag-précised immune reactions [11]. Adjuvants are mainly categorized into two groups. Adjuvants like, mineral salts, e.g. aluminium-hydroxide, emulsions, liposomes, comes under the category of vehicle adjuvants. Vehicles are usually of particulate nature and they are capable of displaying the selected antigen in multiple-copies, imitating natural display by microbes and are used to deposit the antigen at the site of administration or to increase its transport into APCs (micro-nano particles). Whereas TLR agonists, saponins, cytokines come under immunostimulants, that directly targets and activates cells of immune-system with increasing the immune reaction for antigen [9,12] (Figure 1).
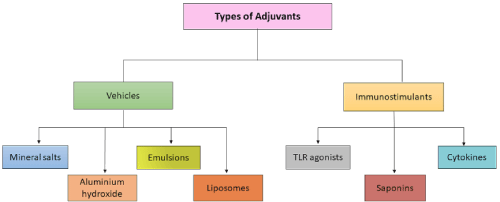
Figure 1: Types of adjuvants. This figure is showing various types of adjuvants.
Adjuvants may role as delivery organizations that can efficiently transport the antigen into the Antigen-Presenting-Cells (APCs) to fuel the elicitation of antigen-specific immune reactions [13] but choosing the optimal adjuvant is of fundamental importance in vaccine formulations to develop of an effective cell-mediated immune reaction. Adjuvants may exert their effects through diverse mechanisms like - (i) Depot formation at shot site; (ii) increased control of cytokines & chemokines heads to cellular staffing at injection spot; (iii) stimulation & maturation of Dendritic Cells; (iv) need of immune-cells; (v) heightening of Ag presentation & uptake; (vi) supporting Ag transportation to draining lymphatic-nodes; (vii) stimulation of inflammasomes, adjuvants trigger innate-immuneoutcome to generate a local immuno-competent milieu at shot spot [14,15] (Figure 2).
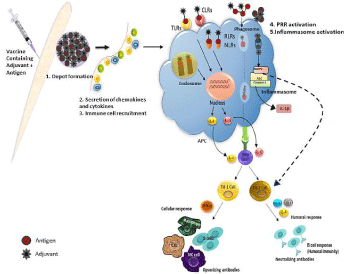
Figure 2: Action mechanism of adjuvants in vaccine. This figure is showing that adjuvants work as delivery system and presents antigen to antigen presenting cells.
This starts a chain mechanism of activation of T-cells and B-cells at the site of injection which leads to the formation of antibodies against antigen.
The oldest and broadly recognized action-mechanism of adjuvants is development of depot at the site of vaccination. Adjuvants such as oil emulsions and aluminum hydroxide gel function as transport systems by producing depots that trap antigens at the injection site, Antigen fooling and slow discharge at the site of vaccination confirms continuous and elongated trigger of the immune structure for creation of high Abs titers. This effect can be accomplished as a long or short term depot, which later gives either a persistent or pulsed release. Probably the local responses specifically produced by oil-emulsions induced inflammatory reaction, which fascinate primarily Ag presenting macrophages. Further, granulocyte cells & neutrophil cells facilitate the adjuvant action through generating cytokines. Current versions of depot adjuvants are micro-capsules and decomposable nano sphere. These nano spheres are made up of decomposable, bio-compatible synthetic polymer in which the antigen is dispersed. There are several other adjuvants which were exposed to perform through depoteffect to create elongated & continual high Ab titers, like water-in-oil emulsions [Complete-Freunds-Adjuvant (CFA)] and bio-degradable micro & nano-particles. There is no conclusive confirmation that depot-outcome considerably helps in adjuvant action [14-16]. Recent studies on adjuvant mechanism are mainly done on the need of innate-immune-cells at shot location. These adjuvants intensify the antigen persistence at the injection spot and increase recruitment and activation of Antigen-Presenting-Cells (APCs). Chemokines, show a serious function in tissue precise relocation of immune-cells, were exposed to be up-regulated by adjuvants at shot spot. Increased function of cytokines and chemokines leads to cellular staffing at shot location. The recruited cells especially neutrophil cells, monocyte cells, and B-cells take-up both Ag & adjuvant and tailback to draining lymph-nodes. Neutrophil cells are one of the highest in numbers and recruited first at the site of adjuvant injection. Particulate adjuvants generate a local pro-inflammatory milieu to appoint more immune cells [17,13]. Alum generally activates the complement cascade and recruits cells from blood to generate an inflammatory atmosphere at spot location [13,18]. There are few adjuvants which are also capable of guiding antigen presentation by the Major-Histocompatibility- Complexes (MHCs). The first stage by which adjuvant can stimulate Ag processing is its attachment to APCs and its internalization. Particulate adjuvants (e.g. alum) are capable to attach with antigens and form multi-molecular collections which will boost the uptake through APCs [19]. More on, numerous adjuvants stimulate secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines at shot location [20].
Dendritic Cells are skilled APCs and more operational in antigen presentation to lymphocytes than macrophages. While there is huge information on antigen processing & presentation by APCs to T-cells, there are partial numbers of reports regarding adjuvants influence. Stimulation of Dendritic Cells is crucial to induce adaptive immune reactions. Amplified expression of MHC-class-II, stimulation marker CD-86 and maturation marker CD83, heads to boosted capacity of APCs to induce T-lymphocytes stimulation and differentiation [21]. Inflammasomes have probable function in adjuvant action and fit in to the NLR family, which also comprises many added receptors, like the NODs (NOD1- 5), NLRPs (NLRP1-14), NLRP1 (NAIP), NLRC4 (IPAF), and the major histocompatibility Complex II Trans Activator (CIITA) [22]. Equated to others, NOD-like receptor family, pyrindomain- containing 3 (NLRP3) is the likely chosen inflammasome receptor in regards to adjuvant strategies. Antigen size performs significant function in modifying the Ag presentation efficacy. Large lipid vesicles end-up in early endosome/phagosomes and enhance Ag presentation whereas small vesicles quickly translocate to late lysosomes leading to decreased Ag presentation [23].
One of the adjuvant that can be used in BCG vaccine is LTK63. LT is an effective toxin, which endorses Ab & broad T-cell responses, similar to cholera toxin. When used as shot adjuvant, LT has been presented to improve Ag presentation, stimulate T-cell proliferation & cytokine generation, and stimulate strong mucosal IgG and IgA Ab reactions [24]. Genetic detoxification in A subunit alters it into an effective non-toxic mucosal adjuvant with increasing capability to increase Th1 outcomes [25].
Protein-Based Vaccines
These are also known as subunit vaccines which can be used to improve the BCG vaccines due to their several properties like ease of production, safety, quality control and specificity [26,27]. Proteinsubunit- shots have been revealed to enhance Th1 immune reaction, which is typically the reaction mainly related with defense against TB. These responses are characterized via formation of cytokines like gamma-interferon (IFN-g), which is responsible for macrophage stimulation; Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-a) is essential for granuloma enlargement and repair; and interleukin 2 (IL-2), which is responsible for clonal expansion of T-lymphocyte cells and is thus engaged in immune reaction keep up [28,29]. Because of features, numerous protein-subunit-vaccines are presently in advanced clinical trials [30].
Several Antigens Used for M. tuberculosis Vaccines
Ag85B
Antigen 85 protein is a 30kDa protein and holds a great potential as therapeutic approach for tuberculosis treatment. Their position on the outer of cell-wall makes them highly accessible. As, humans does not have mycolyl transfer, so disturbing this process is unlikely to upset patients. 3 variations of Ag-85 proteins: A, B & C are produced by M. tuberculosis [31,32]. They are secreted, and located in phagosomal area and on the bacterial cell-wall. The each variant catalyse the transfer of mycolyl residues, and the relocation of mycolic-acid from one trehalose 6-monomycolate to another, developing Trehalose 6,6’-Dimycolate (TDM), a glycolipid situated at the outermost layer of the cell-wall that helps to maintain the integrity of the cell wall [33,34]. The antigen-85 enzyme is also cable of binding with fibronectin that is an extra-cellular milieu of glycoprotein involved in several biological processes including immune responses. This contact seems to decrease phagocytosis of M. tuberculosis, supporting infection [35].
MPT64
It is presented to be precise for M. tuberculosis complex organisms. It is 26-KD secreted mycobacterial protein [36,37]. Secreted mycobacterial proteins are involved in encouraging defensive immunity [38], and are considered immunodominant and but there are less evidences for the function of MPT64 in host immune capacity. This Ag induces T-cell responses in TB patients [39] and has been spotted in the macrophages of humanoid & mouse TB wounds [40,41]. The region that encodes for the equivalent MPT64 gene is removed from various bacillus-Calmette-Guerin strains which has been associated with a fall in virulence in animal infection-models and condensed vaccine lesions in humans, proposing a function of MPT64 in mycobacterial virulence [42,43].
ESAT-6
It is an Early-Secreted-Antigenic-Target (ESAT-6, EsxA) 6-kDa protein of M. tuberculosis. It not only acts as a key-player for virulence but also exhibits a solid immunotherapeutic potential against M. tuberculosis. It was first recognized as an effective T-cell Ag, and it is now known as a pore-creating toxin which is crucial for virulence of M. tuberculosis. ESAT-6 individually, or in compound form with its chaperone CFP-10 (ESAT-6: CFP-10), is shown to regulate host immune reactions. ESX-1 secretion system (Type VII) of M. tuberculosis secrets ESAT-6 and is also responsible to mediate mycobacterial cytosolic trans-location within the host macrophages by breaking the phagosomal membranes [44]. ESAT-6 & CFP-10 together create a compact dimer and are dependent on each other for their steadiness and secretion [45-47]. Along with the ESX-1 secretion system, ESAT-6 and CFP-10 have been involved with numerous virulence strategies of mycobacteria. They are efficient in converting both innate & adaptive immune reactions and deactivation of ESAT- 6 outcomes in conclusively decreased virulence of M. tuberculosis [48,49].
Hypothesis
According to literature, intravenous management of BCG greatly modifies the defensive reactions of M. tuberculosis- challenge in nonhuman primates (Macaca mulatta). Equated with intra-dermal or aerosol transport, intravenous vaccination stimulated substantially more antigen-responsive CD4 & CD8 T cell responses in blood, spleen, bronchoalveolar lavage and lung lymph nodes. Moreover, intravenous vaccination induces a great frequency of Ag-responding T-cells across all lung parenchymal tissues [49].
So, as mentioned in this article, Ag85B and ESAT6 are two essential antigens secreted by M. tuberculosis during its infection. Both the antigens are capable of inducing immune response against M. tuberculosis. The combination of these two antigens when given with the adjuvant LTK63 produces more antibodies against M. tuberculosis infection.
Here, we can hypothesize if the combination of Ag85B-ESAT6 along with the mucosal adjuvant LTK63 or other M. tuberculosis antigen with suitable adjuvant will be given intravenously so this might help in fighting the infection well by inducing more antigen responsive T-cells responses in blood & lung lymph nodes as compared to the intradermal and aerosol mode of administration (Figure 3).
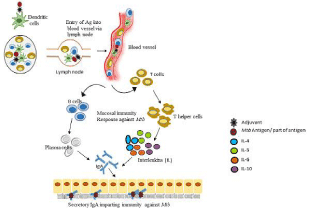
Figure 3: Hypothetical demonstration of intravenous vaccine effect. This figure is presenting a hypothesis of this review paper. If M. tuberculosis antigen with suitable adjuvant will be given intravenously so this might induce more antigen-responsive T cells responses in blood and lung lymph nodes.
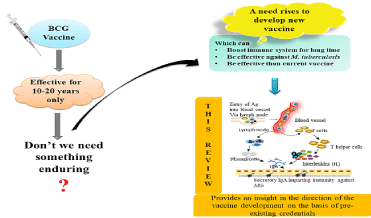
Graphical Abstract 1: This figure is showing that the BCG vaccine is effective only for 10-20 years, so there a need rises to develop a new vaccine which is long
lasting and effective against M. tuberculosis H37Rv. This paper provides an understanding into the literature which might be helpful in completing the requirement
of new vaccine.
Discussion
As it is well noted about the deadly disease tuberculosis that it has the solitary vaccine for its treatment which is given in childhood to every person as prevention but this vaccine is effective only up to 10-20 years in dealing with host immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. So there is strong need to develop a vaccine that can enhance the effective duration of BCG or itself can act on the pathogen to break its chain with host. In this context adjuvants would work well as these helps in increasing innate and adaptive immunity and also well-thought-out as booster of immune response against the pathogen. By selecting the precise adjuvant of fundamental significance in vaccine formulations for the generation of an effective cell-mediated immune reaction, immune response can be increased. Here, we have given a hypothesis to develop vaccine against the pathogen, which can be helpful in increasing the BCG affectivity or immune response against the pathogen. According to hypothesis, mycobacterial antigen 85 A, B and C exist at outer portion of cell wall and have pronounced potential as therapeutic approach to tuberculosis. MPT64 upturns T-cell response in tuberculosis patients but there are fewer proof about the role of this secreted mycobacterial protein in patients. ESAT-6 is an effective T-cell antigen and also pore forming toxin which is crucial for the virulence of bacterium. ESAT-6 individually or in compound form with its chaperone CFP-10 form, regulates host immune response. They efficiently modify innate and adaptive immune response. So by combining these antigens with effective adjuvants and giving the combination either by intravenous or oral way to patient, can fulfil the need of vaccine up to some extent.
Acknowledgment
The author acknowledges financial support from the Department of Science and Technology-SERB, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology under the research project GAP0145 (SERB-DST Grant no: EEQ/2016/000514).
References
- Khademi F, Derakhshan M, Yousefi-Avarvand A, Tafaghodi M, Soleimanpour S. Multi-stage subunit vaccines against Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an alternative to the BCG vaccine or a BCG-prime boost? Expert review of vaccines. 2018; 17: 31-44.
- Meena LS, Rajni. Survival mechanisms of pathogenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. FEBS J. 2010; 277: 2416-2427.
- Raviglione MC, Snider DE, Kochi A. Global epidemic of tuberculosis: morbidity and mortality of a worldwide epidemic. JAMA. 1995; 273: 220-226.
- Gupta N, Garg S, Vedi S, Kunimoto DY, Kumar R, Agrawal B. Future path toward TB vaccine development: boosting BCG or re-educating by a new subunit vaccine. Frontiers in immunology. 2018; 9: 2371.
- Baldwin SL, Bertholet S, Kahn M, Zharkikh I, Ireton GC, Vedvick TS, Coler RN. Intradermal immunization improves protective efficacy of a novel TB vaccine candidate. Vaccine. 2009; 27: 3063-3071.
- Kim SH, Lee KY, Jang YS. Mucosal immune system and M cell-targeting strategies for oral mucosal vaccination. Immune network. 2012; 12: 165-175.
- Owen JL, Sahay B, Mohamadzadeh M. New generation of oral mucosal vaccines targeting dendritic cells. Curr opin chem boil. 2013; 17: 918-924.
- Ranasinghe C. New advances in mucosal vaccination. Immunol let. 2014; 161: 204-206.
- Sarkar I, Garg R, van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S. Selection of adjuvants for vaccines targeting specific pathogens. Expert rev vaccines. 2019; 18: 505- 521.
- Reed SG, Orr MT, Fox CB. Key roles of adjuvants in modern vaccines. Nat Med. 2013; 19: 1597-1608.
- Kashiwagi S, Brauns T, Poznansky MC. Classification of laser vaccine adjuvants. Journal of vaccines & vaccination. 2016; 7: 307.
- Apostólico JDS, Lunardelli VAS, Coirada FC, Boscardin SB, Rosa DS. Adjuvants: classification, modus operandi, and licensing. J Immunol Res. 2016; 2016: 1459394.
- Buckley PR, Alden K, Coccia M, Chalon A, Collignon C, Temmerman ST, et al. Application of Modeling Approaches to Explore Vaccine Adjuvant Modeof- Action. Front immunol. 2019; 10: 2150.
- Alderson MR, McGowan P, Baldridge JR, Probst P. TLR4 agonists as immunomodulatory agents. J endotoxin res. 2006; 12: 313-319.
- Awate S, Babiuk LAB, Mutwiri G. Mechanisms of action of adjuvants. Front immunol. 2013; 4: 114.
- Marrack P, McKee AS, Munks MW. Towards an understanding of the adjuvant action of aluminium. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9: 287-293.
- Didierlaurent AM, Morel S, Lockman L, Giannini SL, Bisteau M, Carlsen H, et al. AS04, an aluminum salt-and TLR4 agonist-based adjuvant system, induces a transient localized innate immune response leading to enhanced adaptive immunity. J Immunol. 2009; 183: 6186-6197.
- Goto N, Akama K. Histopathological studies of reactions in mice injected with aluminum-adsorbed tetanus toxoid. Microbiol Immunol. 1982; 26: 1121-1132.
- Garçon N, Segal L, Tavares F, Van Mechelen M. The safety evaluation of adjuvants during vaccine development: the AS04 experience. Vaccine. 2011; 29: 4453-4459.
- Van Pinxteren LA, Cassidy JP, Smedegaard BH, Agger EM, Andersen P. Control of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection is dependent on CD8 T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2000; 30: 3689-3698.
- Cooper AM, Dalton DK, Stewart TA, Griffin JP, Russell DG, Orme IM. Disseminated tuberculosis in interferon gamma gene-disrupted mice. J Exp Med. 1993; 178: 2243-2247.
- Awate S, Wilson HL, Lai K, Babiuk LA, Mutwiri G. Activation of adjuvant core response genes by the novel adjuvant PCEP. Mol Immunol. 2012; 51: 292- 303.
- Mohan T, Verma P, Rao DN. Novel adjuvants & delivery vehicles for vaccines development: a road ahead. Indian J Med Res. 2013; 138: 779-795.
- Junqueira-Kipnis AP, Marques Neto LM, Kipnis A. Role of fused Mycobacterium tuberculosis immunogens and adjuvants in modern tuberculosis vaccines. Front Immunol. 2014; 5: 188.
- Ottenhoff TH. New pathways of protective and pathological host defense to mycobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2012; 20: 419-428.
- Abebe F, Bjune G. The protective role of antibody responses during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009; 157: 235-243.
- Tebianian M, Hoseini AZ, Ebrahimi SM, Memarnejadian A, Mokarram AR, Mahdavi M, et al. Cloning, expression and immunogenicity of novel fusion protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on ESAT-6 and truncated C-terminal fragment of HSP70. Biologicals. 2011; 39: 143-148.
- Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Mosmann TR, Howard M, O’garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. Journal Immunol. 1991; 147: 3815-3822.
- Belisle JT, Vissa VD, Sievert T, Takayama K, Brennan PJ, Besra GS. Role of the major antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in cell wall biogenesis. Science. 1997; 276: 1420-1422.
- Baldwin SL, D’souza CD, Orme IM, Liu MA, Huygen K, Denis O, et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of DNA vaccines encoding secreted and non-secreted forms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ag85A. Tubercle and Lung Disease. 1999; 79: 251-259.
- Pabreja S, Garg T, Rath G, Goyal AK. Mucosal vaccination against tuberculosis using Ag85A-loaded immunostimulating complexes. Artif cells nanomed biotechnol. 2016; 44: 532-539.
- Xu Z, Xia A, Li X, Zhu Z, Shen Y, Jin S, et al. Rapid loss of early antigenpresenting activity of lymph node dendritic cells against Ag85A protein following Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. BMC immunology. 2018; 19: 19.
- Mustafa T, Wiker HG, Mørkve O, Sviland L. Differential expression of mycobacterial antigen MPT64, apoptosis and inflammatory markers in multinucleated giant cells and epithelioid cells in granulomas caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Virchows Archiv. 2008; 452: 449-456.
- Harboe M, Nagai S, Patarroyo ME, Torres ML, Ramirez C, Cruz N. Properties of proteins MPB64, MPB70, and MPB80 of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immunol. 1986; 52: 293-302.
- Hoel IM, Sviland L, Syre H, Dyrhol-Riise AM, Skarstein I, Jebsen P, et al. Diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis using the MPT64 antigen detection test in a high-income low tuberculosis prevalence setting. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2020; 20: 130.
- Ronning DR, Vissa V, Besra GS, Belisle JT, Sacchettini JC. Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85A and 85C structures confirm binding orientation and conserved substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279: 36771-36777.
- Khan A, Bakhru P, Saikolappan S, Das K, Soudani E, Singh CR, et al. An autophagy-inducing and TLR-2 activating BCG vaccine induces a robust protection against tuberculosis in mice. NPJ vaccines. 2019; 4: 34.
- Kusuma SAF, Parwati I, Rostinawati T, Yusuf M, Fadhlillah M, Ahyudanari RR, et al. Optimization of culture conditions for Mpt64 synthetic gene expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) using surface response methodology. Heliyon. 2019; 5: e02741.
- Toihir AHOS, Rasolofo V, Andrianarisoa SH, Ranjalahy GM, Ramarokoto H. Validation of an immunochromatographic assay kit for the identification of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2011; 106: 777-780.
- Sibley L, Reljic R, Radford DS, Huang JM, Hong HA, Cranenburgh RM, et al. Recombinant Bacillus subtilis spores expressing MPT64 evaluated as a vaccine against tuberculosis in the murine model. FEMS microbiology letters. 2014; 358: 170-179.
- Peng X, Sun J. Mechanism of ESAT-6 membrane interaction and its roles in pathogenesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Toxicon. 2016; 116: 29-34.
- Gilbert RJC. Pore-forming toxins. CMLS. 2002; 59: 832-844.
- Ilghari D, Lightbody KL, Veverka V, Waters LC, Muskett FW, Renshaw PS, et al. Solution Structure of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis EsxG·EsxH Complex Functional implications and comparisons with other M. tuberculosis esx family complexes. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286: 29993-30002.
- Fortune SM, Jaeger A, Sarracino DA, Chase MR, Sassetti CM, Sherman DR, et al. Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. PNAS. 2005; 102: 10676-10681.
- Brandt L, Elhay M, Rosenkrands I, Lindblad EB, Andersen P. ESAT-6 Subunit Vaccination against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infection and Immunity. 2000; 68: 791-795.
- Brodin P, Rosenkrands I, Andersen P, Cole ST, Brosch R. ESAT-6 proteins: protective antigens and virulence factors? Trend microbial. 2004; 12: 500- 508.
- Dillon DC, Alderson MR, Day CH, Bement T, Campos-Neto A, Skeiky YA, et al. Molecular and Immunological Characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis CFP-10, an Immunodiagnostic Antigen Missing in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J clin microbial. 2000; 38: 3285-3290.
- Renshaw PS, Lightbody KL, Veverka V, Muskett FW, Kelly G, Frenkiel TA, et al. Structure and function of the complex formed by the tuberculosis virulence factors CFP-10 and ESAT-6. The EMBO journal. 2005; 24: 2491-2498.
- Darrah PA, Zeppa JJ, Maiello P, Hackney JA, Wadsworth MH, Hughes TK, et al. Prevention of tuberculosis in macaques after intravenous BCG immunization. Nature. 2020; 577: 95-102.