
Research Article
Austin J Infect Dis. 2021; 8(2): 1047.
Development of Computed Tomography Image Processing Procedure for the Diagnosis of Human Respiratory Infectious Diseases: COVID-19
Boopathi M1,2, Khanna D1, Vennila R3, Rajan R3, Maidili T3, Pooja S3, Jothimeena K4, Aarthi A4, Megala R4 and Venkatraman P4*
1Department of Physics, School of Arts, Media and Management, Karunya Institute of Technology and Science, Coimbatore -641114, Tamilnadu, India
2Dharan Cancer Speciality Centre Pvt Ltd, Salem, Tamilnadu, India
3Department of Medical Physics, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore-641046, Tamilnadu, India
4Department of Medical Physics, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli-620024, Tamilnadu, India
*Corresponding author: Khanna D, Department of Physics, School of Science, Arts, Media and Management, Karunya Institute of Technology and Science, Coimbatore -641114, Tamilnadu, India
Received: March 30, 2021; Accepted: April 24, 2021; Published: May 01, 2021
Abstract
Computed Tomography (CT) is a non-invasive method to give CT images of every part of the human body without superimposition of end-to-end structures. Some issues in measurements with CT are limiting too few parameters like quantum noise, beam hardening, X-ray scattering by the patient, and nonlinear partial volume effects. Image processing with Adobe Photoshop, ImageJ, and Origin software have been used to achieve good quality images for numerical analysis. Statistical functions permit to investigate the general characteristics of a human respiratory infections disease. Using Automatic Diagnosis system, differentiation in diseases can be filtered out with the help of CT images. Data can be analyzed from the CT images to distinguish between a human respiratory infections disease, a common disorder like Major Depression (MD) or Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and a normal lung.
Keywords: Computed tomography; X-ray; Major depression; Obsessivecompulsive disorder
Introduction
As a result of recent pandemic of novel corona virus, respiratory infections are a leading cause of disability and death. Radiology diagnosis using cross-sectional and projectional imaging techniques such as chest radiography and Computed Tomography (CT) remains the most important modality for the first-line assessment of acutely illness patients [1]. However, radiologic evaluation is significantly inhibited due to the similar appearance of the infections due to its low specificity, inflammation, some neoplastic abnormalities. This low specificity of radiological diagnosis is due to the lack of verified measures the severity of the diseases. Continuous bacterial and viral multiplication leads to the activation of macrophages and granulocytes leading to pulmonary hyper inflammation through the release of large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines resulting in a ‘Cytokine storm’. This mainly leading to Severe Acute Respiratory Distress, the main cause of mortality from the disease.
These limitations are the possibility the radiologists’ assessment of respiratory infections diseases could be enhanced with Medical Image Processing (MIP). MIP usage to size Measuring of pulmonary disease could also gives numerical data for correlation with fever, leukocyte counts and other measurable laboratory variable size.
The diagnostic equipment used in diagnosing COVID are Radiography, Computed Tomography and Ultrasound. Radiation use in imaging doesn’t harm its vision. Low levels of Low Dose Radiation Therapy (LDRT) is being explored around the world and its potential benefits are well documented in the literature [1,2]. LDRT acts via polarization of macrophages to an M2 phenotype [3], which is the basis for its anti-inflammatory effects in tuberculosis-associated pneumonia. It also regulates the lymphocyte counts and controls bacterial co-infections in patients with tuberculosis. LDRT stands unique among other treatment modalities as it is especially suited for severely afflicted patients, like in those with full-blown pneumonia, ARDS with Cytokine storm. Further, in this study medical image processing is carried out to the CT machine.
Materials and Methods
Thirty patients with human respiratory infections were examined with CT unit, were classified as “normal”, “COVID-19”, “without COVID-19”, “Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)”, “other pneumonia”, “bacterial pneumonia”, “SARS”, “lung cancer”, “Type A influenza (influ-A)”, and “severity”. Therefore, we categorized the studies into four main functions include: COVID-19, normal, non- COVID-19 pneumonia, and COVID-19 severity classification. Non COVID-19 patients include any other infection or its combination except COVID-19. Non COVID-19 pneumonia may include patient is affected with pneumonia from bacterial/viral infections or SARS [4-12]. Last category includes patients suffering from the severity of the disease to the non-severity ones.
Many studies were going on with the detection of the COVID-19 using CT scan continues, the researchers take into account of all the studies obtained from the journals. Medical imaging process is used to make decisions on tasks using both numerical and image-based data, in which people will find difficult to interpret. A deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is the most widely used one among the machine learning methods. It is one of the first preferred neural networks, especially in image-based problems. Since it contains both feature extraction and classification stages, so that it can produce very effective results. The CNN model or other models produced from CNN are widely encountered in image based COVID-19 researches.
However, it is used to design a CT image segmentation and classification methods for lung boundaries and abnormality detection. The presence of pathologies is determined by a proposed technique in three steps (stages) [12-16]. In most cases, X-ray images (or image sets) have noticeable noise and different contrast levels due to the device’s technical characteristics. Thus, noise evolved from CT image is suppressed with the median filter and contrast enhancement is conducted as the first step. In the second step, lung boundaries are detected. During this step, thresholding Otsu’s method and formation of the convex hull of outer ring points is performed. The third step is devoted to image classification (pathology detection) and feature extraction. The feature extraction from image classification is made by the PNN classifier. Figure 1 depicts a principal scheme of the proposed approach [17-28].
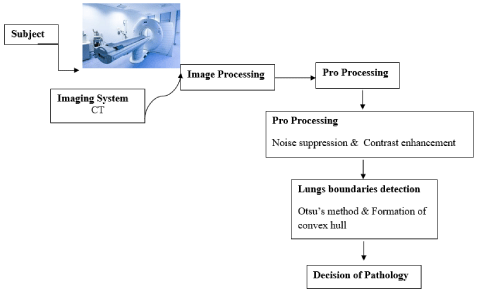
Figure 1: The flow chart for image processing and analyzing the X-ray images.
Results
These are the main results of our work. CT scan data is not available should be investigated from single image. There are sequences of consecutive images (like videos) for medical diagnosis, there are more a slice image has to be analysis than an image. Based on this condition, the proposal develop a method for automatic diagnosis system must be developed to evaluate their system differently compared to other image classification systems. As we know that, we are the pioneers to set the model in this way. Our proposed fully automated system will check the infection of COVID-19 for a patient by taking all CT scans images as input. Then it processes them with the proposed CT scan selection algorithm to select the lung visible scan images. Those chosen images will be fed to the deep neural network to be classified as COVID-19 or normal. We must set a threshold to understand the condition of the patient’s health. The CT scans of each patient will be evaluated, if it exceeds the preset threshold value, they will be considered as a COVID positive patient. This threshold value depends on the precision of the model. In trained models with high accuracy, the threshold can be set to zero, which means even if one of the CT scans of the patient exceeds that value, and then he/she is considered to be infected.
The COVID-19 is a new class of infection, which causes mild to severe pneumonia depending upon the infection rate and age of the individuals. The existing clinical level detection of the infection involves laboratory analysis with RT-PCR, imaging-based detection with CTSI and chest X-ray. Due to various restrictions, the collection of the radiology images from patients is a challenging task; further, the COVID-19 is a new category of disease and hence the Medical Image Processing database existing is very limited. The proposed work considered the images of the Medical Image Processing database for the evaluation. Shared the clinical-grade chest X-ray and CTSI for the research purpose. This work used the clinical-grade CTSI of coronalview images of case studies, for the experimental investigation. Along with the above said images, CTSI of case study 30 is also considered to test the performance of proposed procedure on the axial-view images. From each case study, ten numbers of 2D CTSI are extracted and examined. Further, this work also considered the COVID-19 images available in the examination as shown in Figure 2. This dataset consist the axial and coronal-view of the CTSI recorded with and without the contrast agent.
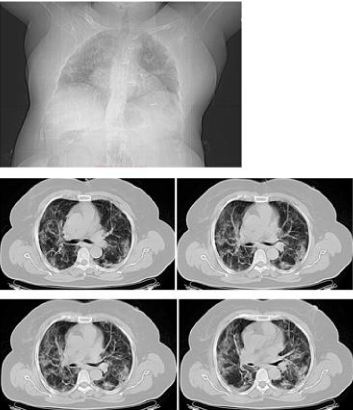
Figure 2: Few test CT chest images of COVID-19 dataset.
Discussion
We understand that our proposed model produced better accuracy in evaluating in COVID infection. The Effects of current trends in the Medical Device Mechanisms that Maximize the efforts required for clinical trials of New medical imaging procedures cannot be observed to this day. It will hence be an interesting point to follow the trend of translation of scientific results of future clinical applications. Further, the development of image processing methodology allows an automated system for lung boundaries detection and classification of CT images. The proposed methodology consists of three key steps. First, a CT image enhancement is attained by noise reduction, and contrast adjustment is conducted. Second, the lung regions are detected.
Finally, we compute a set of features for an enhanced CT image and use them as input to the PNN binary classifier, which will classify the given image as normal or abnormal. According to the Jaccard and Dice similarity coefficients, the proposed method of lung region detection gives accuracy, which is comparable with other methods. However, the system based on proposed methods can be used as a decision support system for medical specialists for respiratory diseases. We hope that our shared dataset and codes can help other researchers to improve AI models and use them for advanced medical diagnosis.
Conclusion
In this paper, we have discussed a fully automated system for COVID-19 detection from lung HRCT scans. Our contribution to respiratory medicine: feature detection, lung segmentation, and countless other works in the pulmonary imaging field enabled our clients to give the means to physicians to save lives by giving faster and more appropriate treatment to all kinds of respiratory diseases. The proposed methodology is efficient and promising for respiratory disease detection.
References
- Calabrese EJ, Dhawan G, Kapoor R, Kozumbo WJ. Radiotherapy treatment of human inflammatory diseases and conditions: optimal dose. Human & experimental toxicology. 2019; 38: 888-898.
- Calabrese EJ, Dhawan G. How radiotherapy was historically used to treat pneumonia: could it be useful today? The Yale journal of biology and medicine. 2013; 86: 555-570.
- Gilroy DW, Tomlinson A, Greenslade K, Seed MP, Willoughby DA. The effects of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors on cartilage erosion and bone loss in a model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced monoarticular arthritis in the rat. Inflammation. 1998; 22; 509-519.
- P Venkatraman, Joshua Sahay, T Maidili, Rajisha Rajan, S Pooja. “Breakthrough of COVID-19 using radiotherapy treatment modalities”. Radiotherapy and Oncology. 2020; 148: 225-226.
- Rajpurkar P, et al. CheXNet: radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning. 2017.
- Bhandary A, et al. Deep-learning framework to detect lung abnormality-A study with chest X-Ray and lung CT scan images. Pattern Recogn Lett. 2020; 129: 271-278.
- Nascimento IBD, et al. Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and MetaAnalysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020; 9: 941.
- Li K, Fang Y, Li W, et al. CT image visual quantitative evaluation and clinical classification of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Eur Radiol. 2020.
- Song, F, Shi, N, Shan, F, Zhang, Z, Shen, J, Lu, H et al. Emerging Coronavirus 2019-nCoV Pneumonia. Radiology. 2020; 295: 210-217.
- Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, Zhang N, Huang M, Zeng X, et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology. 2020; 295: 202-207.
- CT outperforms lab diagnosis for coronavirus infection.
- Bernheim A, et al. Chest CT Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to Duration of Infection. Radiology. 2020; 295.
- Wan Ahmad, Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah, Wan Mimi Diyana Wan Zaki, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, and Wooi Haw Tan. “Classification of Infection and Fluid Regions in Chest X-Ray Images”. IEEE International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA). 2016: 1-5.
- Candemir Sema, Stefan Jaeger, Kannappan Palaniappan, Jonathan P Musco, Rahul K Singh, Zhiyun Xue, et al. “Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration”. IEEE transactions on medical imaging. 2014; 33: 577-590.
- Carrascal Francisco M, José M Carreira, Miguel Souto, Pablo G Tahoces, Lorenzo Gómez and Juan J Vidal. “Automatic calculation of total lung capacity from automatically traced lung boundaries in postero-anterior and lateral digital chest radiographs”. Medical physics. 1998; 25: 1118-1131.
- Qin Chunli, Demin Yao, Yonghong Shi and Zhijian Song. “Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: a survey”. Biomed Eng Online. 2018; 17: 113.
- Yan R, et al. Chest CT Severity Score: An Imaging Tool for Assessing Severe COVID-19. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 2020; 2.
- Wang Y, et al. Temporal Changes of CT Findings in 90 Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Longitudinal Study. Thoracic Imaging. 2020; 296.
- Shi H, et al. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20: 425-434.
- Fang Y, et al. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology. 2020; 296: E115-E117.
- Bai HX, et al. Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from viral pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology. 2020; 296: E46-E54.
- Chua F, et al. The role of CT in case ascertainment and management of COVID-19 pneumonia in the UK: insights from high-incidence regions. Lancet Resp Med. 2020; 8: 438-440.
- Liu K-C, et al. CT manifestations of coronavirus disease-2019: A retrospective analysis of 73 cases by disease severity. Eur J Radiol. 2020; 126: 108941.
- Zhou Z, Guo D, Li C, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019: initial chest CT findings. Eur Radiol. 2020; 30: 4398-4406.
- Yoon SH, et al. Chest Radiographic and CT Findings of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Analysis of Nine Patients Treated in Korea. Korean J Radiol. 2020; 21: 494-500.
- Fong SJ, Li G, Dey N, Crespo RG, Herrera-Viedma E. Finding an Accurate Early Forecasting Model from Small Dataset: A Case of 2019-nCoV Novel Coronavirus Outbreak. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence. 2020; 6: 132-140.
- Fong SJ, Li G, Dey N, Crespo RG, Herrera-Viedma E. Composite Monte Carlo Decision Making under High Uncertainty of Novel Coronavirus Epidemic Using Hybridized Deep Learning and Fuzzy Rule Induction. 2020; 9.
- Santosh KC. AI-Driven Tools for Coronavirus Outbreak: Need of Active Learning and Cross-Population Train/Test Models on Multitudinal/Multimodal Data. J Med Syst. 2020; 44: 93.