
Mini Review
Austin J Med Oncol. 2021; 8(1): 1061.
Medicinal Functions of Physalis Fruits for Biomedical Applications
Abdel-Fattah WI* and El-Bassyouni GT
Department of Ceramics and Building Materials, Biomedical Materials Group 33 Elbuhouth st. National Research Centre, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Wafa I Abde-Fatah, Department of Ceramics and Building Materials, Biomedical Materials Group 33 Elbuhouth st. National Research Centre, 12622, Cairo, Egypt
Received: April 06, 2021; Accepted: April 30, 2021; Published: May 07, 2021
Introduction
Drug innovation using natural products is an interesting mission for planning new leads. It describes the bioactive compounds resulting from natural resources, characterization and pharmacological examination. It emphases on the triumph of these resources in the process of finding and realizing new and effective drug compounds that can be beneficial for human resources. For medicinal devotions and for the progress of pharmaceutical substances, medicinal plants were used such as Physalis angulata L which is a medicinal plant used for numerous therapies including wound healing [1].
Physalis peruviana (golden berry) is an herbaceous annual plants belongs to the family Solanaceae [2]. This plant has a tremendous medicinal value for curing out different diseases: cancer, leukemia, diabetes, ulcers, malaria, asthma, hepatitis, dermatitis, rheumatism and several other diseases [3]. The golden berry fruit tastes like a sweet tomato and includes high levels of vitamin C, vitamin A and the vitamin B-complex. The fruit was demonstrated to have both antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties [4,5].
Herbal specialists and local people of several countries have used many extracts of medicinal plants to achieve and treat various diseases comprising wound healing [6]. Physalis with its notable benefits related to high nutrients and bioactive compounds with extraordinary antioxidant activity and other several medicinal properties have been ascribed to these compounds [7,8]. The bioactive compounds are formed as primary and secondary metabolites of the fruits. These compounds are biologically active with cytotoxic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antiviral, fungicidal, insecticidal, tranquilizing, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and contraceptive actions, among others. Such compounds are used for several dedications, such as in medical therapy, to cure diseases, in the cosmetics, and in the food industry as antioxidants or flavorings [9] (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Physalis angulata L Fruits within its cover [16].
Wounds are well-defined as a break in the cellular integrity of the anatomic continuousness of a tissue generally because of a chemical, microbial, physical or thermal injury [10]. Recently, wounds have become a very exciting pathological problem. Abdul-Nasir-Deen et al., explored the antiinflammatory and wound healing properties of methanol leaf extract of Physalis angulata L [11]. They indicated that such extract possesses anti-inflammatory and wound healing activity which may justify its medicinal uses in the treatment of wounds. The PAL formulated cream at several concentrations of 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10% w/v verified wound healing properties with obvious angiogenesis, collagenation and re-epithelization distinctive of fibrous tissue formation in wound bed [12] as presented in Figure 2.
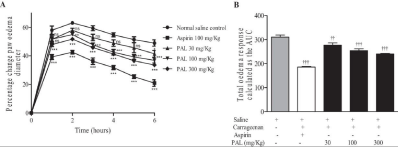
Figure 2: Therapeutic effect of methanol leaf extract of Physalis angulata on
carrageenaninduced oedema in rats. A: Time-course curve, B: Area under
the curve of carrageenan induced oedema, Saline: Normal Saline Control
group, Aspirin: Aspirin-treated group, PAL: methanol leaf extract of Physalis
angulate. Values are mean ± SEM (n=5). nsp>0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01,
***p<0.001, yyp< 0.001, yyyp<0.0001 compared with normal saline control [11].
Moreover, the methanol leaf extracts of Physalis angulate with the existence of secondary metabolites including flavonoids and tannins justify the biological and pharmacological achieved activities Figure 3.
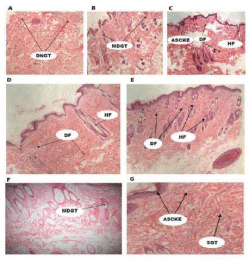
Figure 3: Histological images (x 400) showing influence of PAL on excised
wound tissues from both treated and untreated wound tissues. A: Untreated
wound tissues; B: vehicle treated (aqueous cream only) wound tissues; C:
1% w/w silver sulphadiazinetreated wound tissues; D: 10% w/w PAL-treated
wound tissues, E: 5% w/w PALtreated wound tissues; F: 2.5% w/w PALtreated
wound; G: 1.25% w/w PAL-treated wound; DNGT: Diffuse necrotic
granulation tissue, MDGT: Moderate diffuse granulation tissue, HF: hair
follicle, DF: Dense fibrous tissue, ASCKE: Atrophic squamous cell keratinized
epithelium, SGT: Reduced granulation tissue, SeG: Sebaceous gland, SwG:
Sweat gland [11].
To formulate a porous carbon material that had an abundance of surface functional groups and a huge specific surface area; Physalis alkekengi L. husk (PH) was used for the first time as a carbon source from PH and designated as porous carbon Physalis alkekengi L. husk (PCPH) by Zhang et al. [13]. The experimental results demonstrate that (PCPH) prepared from PH has good adsorption performance for Malachite Green (MG). MG was used as a model dye for evaluating the adsorption performance of PCPH. Zhang et al concluded that PCPH has excellent application potential in the treatment of environmental water pollution. Therefore, the preparation of PCPH with high adsorption performance has upright scenarios treatment of wastewater from printing and dye industries, and similarly affords a hypothetical basis for the inclusive use of shell-based agricultural waste [14]. The possible adsorption mechanisms of PCPH for MG are anticipated; which comprises H-bond interaction, pore filling, p-p interaction, and electrostatic attraction (Figure 4) [15].
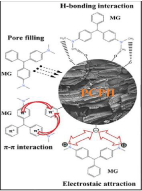
Figure 4: The adsorption mechanism diagram of PCPH to MG [13].
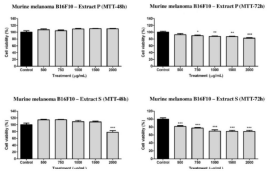
Figure 5: Viability graphs of cells of murine melanoma lineage (B16F10)
exposed to different concentration s for 48 and 72 h of hydroalcoholic extracts
of Pulp (P) and Seed (S). *The greater the number of asterisks, the higher the
significance [8].
Recently, Zimmer et al., concluded that the extracts of the Physalis fruit have functional properties of great importance, being a source of phenolic compounds possessing antioxidant, antibacterial, and antitumor activities [8]. The pulp and seed extracts displayed moderately active inhibition halos in the existence of Gram-positive bacteria. Both pulp and seeds extracts were talented to reduce the cell viability percentage. The Pulp (P) and Seed (S) hydroalcoholic extracts of Physalis pubescens showed moderate antibacterial activity against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes [16]. The Pulp (P) and Seed (S) extracts showed moderate antitumor activity against the rat glioblastoma cell line (C6) and murine melanoma cell line (B16F10).
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Academy of Scientific Research and Technology (ASRT) for the bilateral Egyptian/Indian project entitled ‘Metal cross-linked oxygenated multi-layer polymeric scaffold for diabetic foot ulcer wound healing’. Special thanks are due to the National Research Centre (NRC) for hosting the project.
References
- Barku VY. Wound healing: Contributions from plant secondary metabolite antioxidants. In Wound Healing-Current Perspectives. IntechOpen. 2019.
- Ramírez F, Fischer G, Davenport TL, Pinzón JCA, Ulrichs C. Cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana L.) phenology according to the BBCH phenological scale. Scientia Horticulturae. 2013; 162: 39-42.
- Arun M, Asha VV. Preliminary studies on antihepatotoxic effect of Physalis peruviana Linn. (Solanaceae) against carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury in rats. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2007; 111: 110-114.
- Wu SJ, Tsai JY, Chang SP, Lin DL, Wang SS, Huang SN, et al. Supercritical carbon dioxide extract exhibits enhanced antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of Physalis peruviana. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2006; 108: 407-413.
- Pardo JM, Fontanilla MR, Ospina LF, Espinosa L. Determining the pharmacological activity of Physalis peruviana fruit juice on rabbit eyes and fibroblast primary cultures. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis Sci. 2008; 49: 3074-3079.
- Xiong Y, Gao M, van Duijn B, Choi H, van Horssen F, Wang M. International policies and challenges on the legalization of traditional medicine/herbal medicines in the fight against COVID-19. Pharmacological Research. 2021; 105472.
- Valdenegro M, Fuentes L, Herrera R, Moya-León MA. Changes in antioxidant capacity during development and ripening of goldenberry (Physalis peruviana L.) fruit and in response to 1-methylcyclopropene treatment. Postharvest biology and technology. 2012; 67: 110-117.
- Zimmer TBR, Otero DM, Pedra NS, Bona NP, Zarnott L, Spanevello RM, et al. Biological potential of hydroalcoholic extracts of Physalis pubescens L. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology. 2021; 31: 101895.
- Rozwalka LC, Lima MLRZDC, Mio LLMD, Nakashima T. Extratos, decoctos e óleos essenciais de plantas medicinais e aromáticas na inibição de Glomerella cingulata e Colletotrichum gloeosporioides de frutos de goiaba. Ciência Rural. 2008; 38: 301-307.
- Dons T, Soosairaj S. Evaluation of wound healing effect of herbal lotion in albino rats and its antibacterial activities. Clinical Phytoscience. 2018; 4: 6.
- Abdul-Nasir-Deen AY, Boakye YD, Osafo N, Agyare C, Boamah D, Boamah VE, et al. Anti-inflammatory and wound healing properties of methanol leaf extract of Physalis angulata L. South African Journal of Botany. 2020; 133: 124-131.
- Ambika AP, Nair SN. Wound healing activity of Plants from the Convolvulaceae family. Advances in wound care. 2019; 8: 28-37.
- Zhang B, Jin Y, Qi J, Chen H, Chen G, Tang S. Porous carbon materials based on Physalis alkekengi L. husk and its application for removal of malachite green. Environmental Technology & Innovation. 2021; 21: 101343.
- Li M, Li YW, Yu XL, Guo JJ, Xiang L, Liu BL, et al. Improved bio-electricity production in bio-electrochemical reactor for wastewater treatment using biomass carbon derived from sludge supported carbon felt anode. Science of the Total Environment. 2020; 726: 138573.
- Saxena M, Sharma N, Saxena R. Highly efficient and rapid removal of a toxic dye: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm, and mechanism studies on functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Surfaces and Interfaces. 2020; 21: 100639.
- Radomir AM, Stan R, Vizitiu DE. Obtaining biological material by in vitro multiplication at Physalis peruviana species, an important medicinal plant. Analele Universitatii din Craiova-Biologie, Horticultura, Tehnologia Prelucrarii Produselor Agricole, Ingineria Mediului. 2018; 23: 209-214.