
Review Article
Austin J Med Oncol. 2021; 8(2): 1062.
ATPase Effects on Pro-Nutrients-mTOR Release Long Fatty Acids Chains which Under Mitochondrial Phospholipase, Synthase, & Synthetase Effects form Three ROR-Alpha, Beta, Gamma Isoforms
El Tantawi AM*
Biomedical Molecular Studies, Cairo Egypt
*Corresponding author: Ashraf Marzouk El Tantawi, Biomedical Molecular Studies, Toronto Canada, Cairo Egypt
Received: April 13, 2021; Accepted: May 11, 2021; Published: May 18, 2021
Abstract
RORs isoforms are a metabolic strong regulators have their own functions in the lipid metabolism and in genes, subunits, and hormones reproductions, where during their necessary metabolic activities on lipid metabolism with the effects Mitochondrial enzymes on lipid molecules the acyl-CoA-synthase (RORbeta), acyl-CoA-phospholipase (ROR-alpha), and acyl-CoA-synthetase (RORgama) will be synthesised and released for running the lipid metabolic pathways.
Where the RORs isoforms functions are strongly linked to FOX forkhead genes and strongly depending on mitochondrial anabolic active enzymes activities (phospholipase, synthase, synthetase), and are having a strong regulations by mitochondrial OPA1 membrane which act on long fatty acids molecules for releasing the three enzymatic acyl-CoA active molecules for the cholesterol productn, for TNF-a with TXA2 alpha subunits productions, for sestrin-Leu 1 synthesis, for prostaglandins synthesis which reflect the strengthen of ROR-beta with ROR-alpha activities, for S6K1 production, and for estrogen & insulin growth and their ratio biosynthesis.
When lipid associated with absorbed nutrient molecules (pro-lipo-mTOR) will be firstly affect by ATPase and by Cox2 for releasing long fatty acids molecules and will be directed to FOX forkhead and to ROR genes, where first the ATPase and COX-2 will act on lipid molecules for releasing long fatty acids molecules then the mitochondrial anabolic enzymes effects will act fatty acids molecules for releasing the acyl-CoA-phospholipase (ROR alpha isoforms), acyl-CoAsynthase (ROR-beta), and acyl-CoA synthetase (ROR-gama isoforms), where all RORs isoforms are having the same molecular structure but differ only in their terminals.
The decreasing in mitochondrial synthetase enzyme will reflect inhibition or decreasing in acyl-CoA-synthetase enzymatic molecules (ROR-gama) synthesis which adopted for carbohydrate metabolic cycles and the ratio of pyrimidine in biological molecules, that can reflect decreasing in the pyrimidine synthesis from purines which will lead to decreasing in hormone biosynthesis, and sestrin biosynthesis, and decreasing in RORs isoforms stabilities and activities, which can reflect decreasing in FOX genes stabilities, and decreasing in Thymine kinases molecules activities which consequently lead to inhibition or decreasing in cholesterol biosynthesis, and in estrogen or insulin hormones biosynthesis pathways.
Long-fatty acyl-CoAs are produced due to the effects of mitochondrial anabolic enzymes on the long fatty acids molecules which produced from the effects of ATPase and mitochondrial COX-2 on the lipid molecules, which considered as necessary anabolic regulatory and intermediates molecules in lipid metabolic pathways and in the active kinases molecules resynthesis during the binding of Pro-nutrients-mTOR molecules.
Following the long fatty acids formation by the effects of ribosomal ATPase is the effect of mitochondrial OPA1 membrane activities for producing its necessary anabolic mitochondrial enzymes (phospholipase, synthase, and synthetase) for producing the three RORs isoforms active enzymatic molecules acyl-CoA-phospholipase (ROR-alpha), acyl-CoA synthase (ROR-beta), acyl- CoA synthetase (ROR gama).
The RORs isoforms consedered as three structures of RORs isoforms, each isoform bind to one of the anabolic mitochondrial enzymes (synthase, synthetase, and phospholipase enzymes)to form its own ROR-isoforms, and each of RORs isoforms has its own specific functions and pathological pathways but is contributing with others RORs-isoforms for running and completing their specific biosynthesis pathways during lipids metabolism.
Those RORs (the enzymatic acyl-CoA) isoforms molecules are having same molecular structures but differs only in their terminal amino acids, and are incorporated into acylated proteins and complex active fatty molecules like triacylglycerol, phospholipids, and cholesterol esters for activating the brain metabolic processes, for the liver metabolic activities, and for the strengthen of immune efficiency through TNF-Alpha and TXA2 subunits productions by the acyl-CoA-synthase (ROR beta isoforms ) and for sestrin-Leu biosynthesis through the regulation of acyl-CoA-synthetase (ROR gama isoforms).
The synthesis of each of acyl-CoA isoform firstly by the effects of ATPase and COX-2 on lipid molecules followed by the mitochondrial OPA1 activaties for releasing its active enzymatic acyl-CoA isoforms during lipid metabolism.
As ribosomal ATPase act on lipo-mTOR protein will release long fatty acids molecules then will be followed by mitochondrial effects on long Fatty molecules for producing enzymatic acyl-CoAs (RORs) isoforms.
Where acyl-CoA isoforms molecules will be binded to whether synthetase, phospholipase, or to synthases enzymes as intermediates for brain activities, for liver functions etc., depending on the type of signals activities received from brain and from cells to form RORs isoforms.
The mitochondrial enzymes effects are necessary (anabolic snd antiinflammatory enzymes) for RORs isoforms biosynthesis, and are considered as anti-inflammatory regulating enzymes that synthase and synthetase are so necessary for TNF-a and for thromboxane-A (TXA2) biosynthesis, and regulate the releasing of the active four kind of kinases proteins during the FOX binding activities, and act as mediators for anti inflammations pathways as for prostaglandins productions, and are acting releasing the ROR-alpha isoforms which are active isoforms for phospholipid membranes and for antigen biosynthesis.
Liver X Receptors (LXRs) are nuclear receptors, that LXRs were originally considered as ‘orphan’ nuclear receptors, and it’s origin depend on the synthesis of acyl-CoA phospholipase isoforms which is the basic of liver cells phospho-lipo-membrane. However, those receptors were ‘adopted’ for running lipid metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, and phospholipid membranes which act as so imp biological filter for and from nucleus.
The phospholipid membranes formed from acyl-CoA-phospholipase (RORalpha) isoforms functions, where phospholipid are imp molecules for skeletal muscle development, for photoreceptor development and for liver activities.
IFN gamma depending on biosynthesis effects of synthetase enzymes on long fatty acids chains for producing fatty acyl-CoAs synthetase which act as a protective IFN-gamma in regulating the retinal hydrations.
PLC-gamma1 is implicated in a variety of cellular signalings and processes including mitogenesis and calcium entry.
The Nerve growth factor is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, and proliferation that has imp roles in carbohydrate biosynthesis for maintaining the necessary balances of purines related to pyrimidine nucleotides through the pyrimidines synthesis where their results will feed the sensor nerve and neuronal hyper reactivity for nerve activities. The effects of synthase and phospholipase on the productions of RORs beta and alpha isoforms respectively are cooperating together for running so imp osteogenic repressor in regulating bone formation and in new blood cells synthesis with their effective phospholipid membranes, and are imp for TNF-a and TXA2 alpha subunits productions, where PSTC-kinases (mTORC1) and thromboxane-A2 can used for the autophagy reactivities and biosynthesis.
Heart failure is associated with decreased myocardial fatty acid metabolic pathways and decreasing in fatty acids functioning and oxidation capacity and has been likened to energy starvation. As the adenosine metabolism in tissues have been consumed due to extra ATPase and COX-2 activities as energy utilization will increased from breaking and analyzing genes and fatty acyl-CoA molecules and from pyrimidine molecules lead to precipitation of ub normal molecules which can block blood fluidity in arteries and veins leads to decreasing in heart muscle lead to heart failure.
Keywords: acyl-CoA; Receptor-related orphan receptors; mTOR; ATPase
Introduction
The retinoic acid Receptor-related Orphan Receptors (RORs) isoforms are member of the nuclear receptors superfamily, that plays a very necessary roles in regulations of nutrients-mTOR biosynthesis, of lipid metabolism, of carbohydrate metabolism, and the circadian rhythm in the expression of enzymatic acyl-CoA isoforms, and the expression of genes and subunits involved in lipid and protein biosynthesis pathways.
The Retinoid-related Orphan Receptors (RORs) alpha, beta, and gamma isoforms comprise one nuclear orphan receptors gene subfamily, where the effects of mitochondrial enzymes on ROR genes will differentiate the ROR genes structure, activities, and specificity of functions.
The first steps of the pathways of the synthesis of the three RORs isoforms structures molecules is started by the effects of ATPase and COX-2 enzymes on lipid-nutrients (pro-nutients-mTOR) molecules for generating long fatty acids molecular chains, which will be affected by mitochondrial anabolic enzymes (synthetase, synthase and phospholipase)on their molecular chains to form three active RORs isoforms molecules (RORs alpha, beta, and ganma), that will have same molecular structures but differ only in their terminal amino acids.
Active RORs isoforms belong to 1st DNA strand where, DNAbinding domain is highly conserved among RORs isoforms, that are carrying basic imp characteristics sequences able to moderate the received pro-nutrient-mTOR with its conjugated complexed lipid to a proper active carboxylated long fatty acyl-CoA enzymatic molecules for regulating cholesterol productions, for hormones biosynthesis, for regulating active subunits and genes, for regulating steroid metabolic process, cells proliferations, cGMP metabolic process, for autophagosome membrane formations, for reactivating autophagy, and for circadian regulations of genes expression etc.
Lipid metabolism start by the effects of ATPase and COX-2 on the pro-nutrients-mTOR molecules for releasing long fatty acids molecules directed to FOX forkhead genes for binding with the effects of mitochondrial OPA1 functions on fatty acids molecular chains, where lipid will be separated by effect of mitochondrial enzymes (phospholipase, synthase, synthetase) through OPA1 genes functions for the enzymatic acyl-CoA-”phospholipase, synthase, or synthetase” isoforms for fat, and for lipoproteins biosynthesis.
The biosynthesis of acyl-CoA phospholipase RORalpha, acyl- CoA-synthase the ROR-beta, acyl-CoA synthetase ROR-gamma, are strongly depending on the mitochondrial enzymes effects on fatty molecules, but firstly depends on the effects of ATPase and Cox2 enzymes on the lipid conjugated to mTOR” molecules.
The Retinoid-related Orphan Receptors (RORs) alpha, beta, and gamma isoforms comprise one nuclear orphan receptor genes subfamily, where the effects of mitochondrial enzymes on lipid molecules can differentiate the RORs isoforms activities through the chromosomal regulations and ribosomal ATPase regulations.
The first pathways of RORs isoforms activities is will be activated by effect of mitochondrial enzymes (synthetase, synthase and phospholipase) on fatty acids molecules to form active RORs enzymatic isoforms molecules alpha, bêta, and gama isoforms, where all RORs isoforms have the same molecular structure but are differ only in their terminal amino acids.
The mitochondrial enzymes will act on long fatty acids (which released from the effects of ATPase on Pro-nutrients-mTOR molecules) to form active long fatty RORs enzymatic isoforms molecules (the RORs isoforms) where each will start their own pathway regulations and contributions to the other two RORs isoforms pathways.
The synthesis of each of acyl-CoA isoforms are by mitochondrial effects on fatty molecules for releasing the three enzymatic acyl-CoA isoforms in the lipid metabolic pathways, in the pathogenesis of metabolic disease and carcinogenesis [1].
Increasing in fatty acid results in an induction of genes promoting fatty acid oxidation [2].
Where, increasing in fatty acids will stimulate mitochondrial effects for releasing its enzymes for the three enzymatic acyl-CoA isoforms synthesis for cholesterol productn which is the substrate for estrogen and insulin during their synthesis.
The increasing in the enzymatic fatty acyl-CoAs by mitochondrial effects will increase. Inductions of genes by promoting fatty acid oxidation, but in case of deficiency in the OPA1 activity the ATPase and COX-2 catabolic processes on analyzing lipid molecules will increase for releasing irregular results of oxidative fatty molecules which will be the basic of irregular subunits synthesis the will be the main reason for fat deposits in the arteries walls, and the reason for the symptoms of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
The decreasing in long fatty acids chains productions and in ROR isoforms synthesis, will lead to increasing in complexed irregular fatty molecules availabilities for energy utilization and for catabolic processes that will reflect inhibition in pyrimidine synthesis and inhibitions in beta and alpha oxidative processes, that will lead to inhibition in normal cholesterol synthesis that will lead to IGF-I productions with inhibition in the proper original estrogen (dépend on type of inhibitions ) and in normal insulin production, lead to precipitation of fatty acid irregular lipo-molecules in capillaries and blood vessels lead to Arteriosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, and osteoarthritis.
Where, Lipid molecules+ATPase ¬¬>long Fatty acids molecules +mitochondrial active phospholipase + ribosomal ATPase (in a control limit) ¬-> long Fatty acid-acyl-CoA phospholipase (which is ROR-alpha active isoforms), ¬¬>>Fatty acyl-CoA-synthase which is ROR beta active genes, and ¬¬>> fatty acyl-CoA-synthetase (which is ROR-gama isoforms ) then both ROR-alpha and ROR-gama +AMP ¬> isopentanyl PP+ Leu (or Meth ) amino acids ¬> leu-pentapeptides (or Meth-pentapeptides) active molecules for activating enkephalin tissue in brain.
The decreasing or inhibition of synthases, synthetase or in phospholipase enzymes for releasing RORs active isoforms during Pro- Nutrients-mTOR metabolic pathways will reflect the increasing in random irregular oxidative fatty acids due to oxidative processes by ATPase and by COX-2 enzyme with inhibition in enzymatic acyl- CoA isoforms productions lead to several precipitations of unknown lipo-molecules and fatty acids in capillaries that will block blood follow in blood vessels and will inhibit other dependent pathways steps lead to decreasing in muscles activities and heart functions.
That acetylation of the fatty acid β-oxidative enzymes, and in β-HAD (β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase) is associated with an increase in activity and fatty acid oxidation in heart from obese mice with heart failure [3] where, increasing of acetylation of beta hydroxyacyl- CoA which is the main component of mitochondrial matrix and originally formed by feedbacks of RORs isoforms, will lead to increasing in +ve gps in B-HAD molecules that will alter the BHAD active sites in mitochondrial matrix, that will lead to reductions or inhibition in mitochondrial filtration (where fatty acids need to pass through mitochondrial membrane to reach matrix for B kit-acyl- CoA synthsis during pro-nutrients-mTOR metabolic pathways) that will lead to reductions or inhibition in releasing the mitochondrial enzymes which will lead to reduction or inhibition in releasing the RORs isoforms, reduction or inhibition in lipid and protein metabolism, and reductions or inhibition in regular cholesterol biosynthesis and consequently will lead to reduction or inhibition in estrogen and in insulin biosynthesis.
3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-COA (HMG CoA) reductase produces mevalonate, an important intermediate in the synthesis of cholesterol and essential nonsterol isoprenoids [4]. Where, 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase is the product of mitochondrial matrix through the passages of fatty acids molecules through mitochondrial membrane to reach the BHAD that synthase enzymes will act on fatty acids molecules for releasing the ROR-synthase isoforms (ROR-beta) and HMG-CoA which intermediate the mevalonate molecules productions which intermediate the cholesterol synthesis.
Where mevalonate also is an intermediate molecules for reactivating brain acetylcholine and enkephalin tissue for both Meth and leu-pentapeptides biosynthesis in enkephalin in brain tissue.
The BHAD and HMG-CoA are both intermediate molecules through the activity of acyl-CoA-synthase (ROR-beta isoforms) for mevalonate productions, for estrogen and normal insulin biosynthesis.
Protagonistes 1 PGs, are a family of fatty acid ecosanoids synthesized from arachidonic acid via cyclooxygenase enzymes [5].
That Rho proteins due to effects of ATPase and COX-2 on phospholipid membranes and are involved in the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, Rac proteins modulate Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), whereas Ras protein are synthesised from acyl-CoAphospholipase (ROR-gama isoforms) functions and are involved in cell proliferation, and cell adhesion [6].
Due to cells death the phospholipid membranes will be break and analyzed by ATPase and COX-2 enzymes effects for releasing cyclooxygenase enzyme that will Determine and characterized its molecular structure and functions.
Phospholipid membrane are mainly formed by the function of long fatty acyl-CoA-phospholipase (upon the effects of mitochondrial phospholipase enzymes on long fatty acids chains ) which directed for phospholipid membrane biosynthesis.
As the Pro-nutrients-mTOR molecules directed to FOX forkhead genes and to ROR genes with the regulation of mitochondrial enzymes effects, as the FOX genes will begin for releasing the four types of kinases proteins and the three RORs isoforms will be synthesis from fatty acids molecules molecules through the effects of mitochondrial effects (that fatty acids molecules formula by effects of ATPase and COX-2 on lipid molecules for generating long fatty acids chains ) on the long fatty acids molecules for generating the three enzymatic acyl-CoA molecules “RORs isoforms” for cholesterol synthesis and for estrogen and insulin hormones biosynthesis.
The most necessary mitochondrial enzymes in lipid metabolism is the phospholipase enzyme, which responsible for releasing acyl- CoA-phospholipase (ROR-alpha isoforms) which is necessary for the formation the cell phospho-lipid membranes, for cells antigen synthesis,for cells proliferations, and for brain cells biosynthesis.
The Pro-nutrients-mTOR molecules + ATPase +COX-2 ¬¬>>long Fatty acids molecules + +mitochondrial enzymes effects ¬>¬>1) acyl-CoA phospholipase molecules (ROR-alpha isoforms), 2) acyl-CoA synthase molecules (ROR-beta), and 3) acyl-CoA synthetase molecules (ROR gama isoforms), where those enzymatic fatty acyl-CoA proteins molecules (RORs isoforms) are having same molecular structure but differ only in their terminal amino acids, and each has its own activity and Participate in the other two RORs isoforms activities.
RORs isoforms activities are giving the soft, flexibility, and malleable characters to synthesis protein and genes that can help living cells to gains the persistence to high-temperature and lowtemperature characteristics during their cellular metabolism.
The RORs isoforms are formed through the effects of mitochondrial enzymes synthetase, synthase and phospholipase on long fatty molecules (which produced from the effects of ATPase and some cases with mitochondrial COX-2 enzymes) for producing 1) acyl-CoA synthase 2) acyl-CoA synthetase and 3) acyl-CoA phospholipase (Figure 1) which have the function of lipoprotein synthesis, antigen synthesis, cells phospholipid-membrane synthesis, and TNF-a, TXA2 synthesis etc.
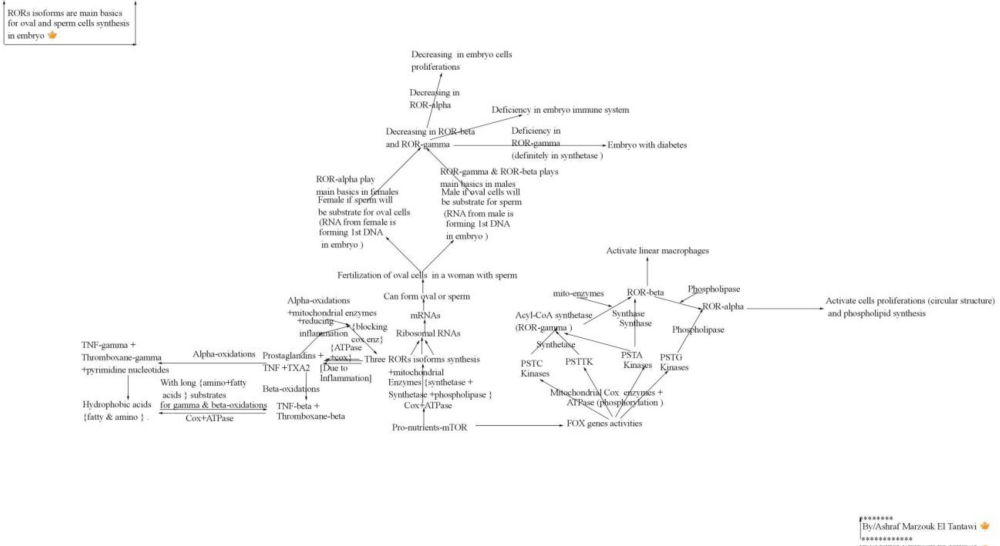
Figure 1: Estrogen insulin synthesis.
Where, all RORs molecules have same molecular structure and differ only on their terminal amino acids.
liver has two major sources of blood. The portal vein brings in blood-rich-nutrients from the digestive system, and the hepatic artery carries oxygenated blood and metabolized genes and protein.
Bile productions by liver helps lipid metabolism and metabolizing some vitamins, that bile consists of bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin and which are needed for metabolizing fats molecules then for estrogen and insulin biosynthesis.
Metabolizing carbohydrates within liver, are needed for maintain normal glucose levels, where that process is carried and done by acyl-CoA-synthetase functions (gamma isoforms)where the main function of carbohydrate processes is converting purines to necessary pyrimidines for rebuilding necessary hydrophobic amino acids for others two RORs isoforms processes and for Sestrins-Leu synthesis which is necessary for liver activities.
Then the results from the effects of acyl-CoA synthetase ROR gamma on carbohydrate is the glycogen which stored and released whenever a quick burst of energy is needed.
The liver store vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12 which will be metabolized for RORs isoforms biosynthesis and hormones synthesis.
Liver stores iron from hemoglobin in the form of ferritin, ready to make new red blood cells through the acyl-CoA-phospholipase alpha isoforms activities within liver too.
Liver adopted for interstitium fluid synthesis which carried out by hepatic arteries, and the liver has a major function which is filtering blood from inflammations, from irregular oxidized molecules etc.
Liver contains high numbers of Kupffer cells that are involved in immune activity, where the metabolizing proteins and Filtering the blood within liver need the activity of beta isoforms acyl-CoAsynthase for TNF-a and TXA2, water production which will help the processes which need to be done by others two RORs isoforms.
Liver X Receptors (LXRs) are nuclear receptors, that LXRs were originally considered as ‘orphan’ nuclear receptors, and it’s origin depend on the synthesis of acyl-CoA phospholipase isoforms which is the basic of liver cells phospho-lipo-membrane. However, those receptors were ‘adopted’ for running lipid metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, and phospholipid membranes which act as so imp biological filter for and from nucleus.
The phospholipid membranes formed from acyl-CoAphospholipase (ROR-alpha) isoforms functions, where phospholipid are imp molecules for skeletal muscle development, for photoreceptor development and for liver activities.
The heterodimer binding to LXR-Responsive Elements (LXREs) in DNA consists of Direct Repeats (DRs) of the core sequence {AGGTCA} separated by 4 nucleotides (DR-4) [7].
The direct repeats of binding with DNA is Arg, Ser (where Ser is the so necessary preserved amino acids for acyl-CoA phospholipase, synthase, and synthetase in liver X receptor activities where Liver X receptor during lipid metabolism and for kind of “PSTk” protein kinases productions through FOX binding mechanism. And it has been
Revealed that liver X Receptor-Retinoid X Receptor (LXRRXR) Heterodimer Cistrome Reveals Coordination of LXR and AP1 Signaling in Keratinocytes [8], LXRs activate lipid metabolism through the production of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs) and their distribution into phospholipids via the control of FA desaturases, FA elongases, Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase (LPCAT3), and Phospholipid Transfer Protein (PLTP) [9].
The LXRs and Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) are coordinate for phospholipids biosynthesis through the acyl-CoA phospholipase activity on the catalyzing the transacylation reaction between phosphotidylcoline (LPC) molecules for generating diacylphospholipid.
Also, fatty acyl-CoA phospholipase isoforms (ROR gamma) has imp roles in reactivating brain cells through the biological transacylations between phosphotidylcoline by acyl-CoA phospholipase isoforms for generating diacylphospholipid which reactivate enkephalin cells.
The negative feedback regulation of cholesterol metabolism in mammalian cells ensures the responsibility and functions of RORalpha genes and the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs) molecules production in cholesterol biosynthesis, and the function of RORalpha isoforms for phospholipids synthesis and their distributions for ensuring nucleus activities.
That it has been approved the negative feedback regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis in mammalian cells ensure the proper balance of cholesterol with other membrane lipids, principal among these being the major phospholipid Phosphatidylcholine (PC) [10]. Indicating that fatty acyl-CoA-phospholipase which have the function of phospholipid membranes biosynthesis are having the same function of cholesterol biosynthesis where both cholesterol and phospholipids membranes are having proper balance in lipid metabolism and in lipoprotein biosynthesis, and indicating that the fatty acyl-CoA-phospholip isoforms are having the function of activating brain functions through phospholipid phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and consequently by reactivating the enkephalin pentapeptides (Meth and Leu) in brain.
The Polar Head Modified Phospholipids by Phospholipase D-Catalyzed Transformations of Natural Phosphatidylcholine [11]. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) synthesis is necessary for remodeling of exogenous phospholipids, necessary for prostaglandins synthesis during anti-inflammatory processes, and for autophagosome membrane. That Phosphatidylcholine (PC) synthesis is required for autophagosome membrane formation and maintenance during autophagy [12].
Phospholipases A2 (PLA2s) are essential enzymes in cells, where are not only responsible for maintaining the structural organization of cell membranes, but also play a pivotal role in the contributions of the regulations of cells functions through its contributions to the others active two RORs beta and gamma isoforms.
That the acyl-CoA phospholipase are playing imp roles during inflammation that catalyze the transacylation of phosphatidylcholine for phospholipid membranes synthesis.
The Lysophospholipase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the carboxyl ester bonds of lysophos-pholipids. Some lysophospholipase isoforms are known to catalyze a transacylation reaction between two lysophosphacholine LPC molecules, leading to the formation of a diacylphospholipid PC and GPC [13].
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is formed from the phospholipase effects on long fatty acids molecules for releasing acyl-CoA synthetase ROR-gamma) isoforms, where, IFN-gamma receptors are mainly localized to the basolateral membrane of human retinal pigment epithelium and has a protective roles in retinal hydrations across the outer blood-retinal barrier in inflammatory disease, and provide the basis for possible therapeutic interventions [14].
During IFN intervention to any foreign molecules related to cells, will act by analyzing and break down those molecules and convert some of its components into acceptable units by living cell throughout the mechanism of converting purines into pyrimidines, which contribute the possibility of implementing Beta-oxidative processes to produce modified TNF-a and Thromboxane-A units (upon the inflammation stimulators factors), that previous mechanism includes hydration production through cells metabolic processes. IFN gamma depending on biosynthesis effects of synthetase enzymes on long fatty acids chains for producing fatty acyl-CoAs synthetase which act as a protective IFN-gamma in regulating the retinal hydrations.
PLC-gamma1 is implicated in a variety of cellular signalings and processes including mitogenesis and calcium entry.
The Nerve growth factor is a neurotrophic factor and neuropeptide primarily involved in the regulation of growth, maintenance, and proliferation that has imp roles in carbohydrate biosynthesis for maintaining the necessary balances of purines related to pyrimidine nucleotides through the pyrimidines synthesis where their results will feed the sensor nerve and neuronal hyper reactivity for nerve activities.
The phospholipase activity of PLC-gamma1 plays an essential role in Nerve Growth Factor (NGF)-triggered Raf/MEK/MAPK pathway activation in PC12 cells [15].
The PLC-gamma1 is the Phospholipase-alpha (PLC-alpha) associated to and with ROR-gamma activities for the contributions of the synthesis of nerve growth factor neuropeptides activities which need the fatty acyl-CoA synthetase acting on carbohydrate for pyrimidines synthesis which needed for hydrophobic amino and fatty acids synthesis with the contributions of fatty acyl-CoA phospholipase isoforms for neuropeptides synthesis.
The ROR gamma isoforms molecule is the effect of synthetase on long fatty acids molecules to form long fatty acyl-CoAs synthetase which act on carbohydrate molecules (which is necessary for regulating the pyrimidine synthesis from purines molecules) for TNF-a and TXA2 subunits productions and hydration productions for assisting the others two RORs isoforms activities.
Each of those RORs isoforms structures will be synthesis through the effects of mitochondrial enzymes on long fatty molecules to generate long enzymatic acyl-CoA isoforms where each has its own specificity with its contributions to the other two RORs isoforms (where all three RORs isoforms are strongly and closely related to each other) for phospholipid synthesis and to give the vitality to tissues through fat, proteins, and carbohydrate biosynthesis pathways.
Citrate Synthase (CS) is a direct effect of ROR-beta isoforms on long fatty molecules during fat biosynthesis by which ROR-beta regulates carbohydrate and fat biosynthesis via regulation of CS expression.
CS plays a critical role in providing citrate derive acetyl-CoA for lipogenesis and cholesterol genesis [16].
The Retinoid-related Orphan Receptor gamma-t (RORγt) did not generate Th cells with robust IL-17 and IFN-γ expression [17].
Where, the robust IL-17 and IFN-γ in tissue reflect the robust acyl-CoA synthetase reflect enough robust ROR-gamma isoforms for acting on inflammations without need for more T-helper cells reproductions.
The effects of synthase and phospholipase on the productions of RORs beta and alpha isoforms respectively are cooperating together for running so imp osteogenic repressor in regulating bone formation and in new blood cells synthesis with their effective phospholipid membranes, and are imp for TNF-a and TXA2 alpha subunits productions, where PSTC-kinases (mTORC1)and thromboxane-A2 can used for the autophagy reactivities and biosynthesis.
The ROR-beta (ROR-β) isoforms, act as a member of the orphan nuclear receptor family which plays so important regulatory role in the maintenance of a variety of physiological and pathological processes under the stimulations of the inflammatory factors, where the effect of synthase on long fatty acids molecules is considered as a maintenance steps which release TNF-a and TXA2 during pathological processes. RORβ has been determined to act as an osteogenic repressor in regulating bone formation, and is involved in regulating circadian rhythm [18].
The ROR alpha isoforms molecule is the effect of phospholipase enzymes on long fatty acids chains to generate ROR-alpha genes molecules, the ROR beta is the effect of synthase on ROR gene to generate ROR-beta genes molecules, but ROR-gamma molecule is the effect of mitochondrial synthetase enzymes on ROR gene to generate ROR-gama gene molecules.
During inflammation effect the acyl-CoA synthase and acyl-CoAsynthetases of (ROR gamma) will be released to act on inflammations molecules to ensure converting some of purines (which involved in inflammations) to pyrimidine nucleotides for rebuilding necessary hydrophobic amino acids then will be followed by acyl-CoA-synthase for TNF and TXA2 synthesis. Where synthase (CS) plays a critical role in providing citrate derived acetyl-CoA for lipogenesis and cholesterol genesis [19], that the mitochondrial synthase enzyme is necessary for the reactivating ROR-beta isoforms and for FOX genes activities through PSTTK, PSTGK and PSTCk synthesis during the pro-mTOR pathways for phospho-lipo-protein and cholesterol biosynthesis and for estrogen and insulin biosynthesis.
Peroxisomes, are like lysosomes are enclosed by a single membrane. Peroxisomes are resemble lysosomes in being filled with enzymes. However, peroxisomes bud off from the endoplasmic reticulum, not the Golgi (which package proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins destined to be exported from the cell) as lysosome.
Peroxisomes is organelles for manufacturing cell needs in favor of inner cells components such as phospholipid membranes, lipoproteins, and production of TNF-a and TXA2 subunits which can be Headed later to lysosomes for T-cells and autophagy reactivations.
Peroxisomes are indispensable for proper functioning of human cells. They efficiently compartmentalize enzymes responsible for a number of metabolic processes, including the absolutely essential beta-oxidation of specific fatty acid chains. These and other oxidative reactions produce hydrogen peroxide, which is, in most instances, immediately processed in situ to water and oxygen [20].
As phospholipase enzyme in peroxisomes decreased or inhibited will lead to accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and downstream of reactive oxygen species including beta oxidative processes and alpha oxidative processes in the heme-containing tetrameric enzyme, catalase.
Peroxisomes are ubiquitous organelles which participate in a variety of essential biosynthesis pathways including lipid metabolism and fatty acids biosynthesis.
An intimate interrelationship between peroxisomes and mitochondria is emerging in mammals by effects of mitochondrial enzymes on long fatty acids chains for producing the three enzymatic active RORs isoforms which I consider that the three acyl-CoA RORs isoforms are stored in the forms of peroxisomes for rapid effects in anti-inflammations in fat biosynthesis including phospholipids synthesis, in hydrophobic fatty acids and amino acids synthesis, and in carbohydrate biosynthesis, where both organelles cooperate in fatty acid β-oxidation and cellular lipid homeostasis. acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases (ACADs) are bona fide peroxisomal proteins in fungi and mammals and together with acyl-CoA Oxidases (ACOX) belong to the basic enzymatic repertoire of peroxisomes [21].
Peroxisomal organelles are made basically by mitochondrial effect on fatty acids due to RORs genes transcriptional filter and consist of the three RORs isoforms receptors alpha, beta, & gamma) for easier fastest processes for alpha beta, and gamma oxidations.
The beta oxidative process occur due to the activity of synthase for running the TNF-a and TXA2 biosynthesis for increasing immune effecincy, alpha oxidative processes is the fatty acyl- CoA phospholipase activities for lipoprotein and phospholipid biosynthesis where that alpha and beta oxidations are linked and contributing together for running their activities and producing H2O from the peroxisomal processes, but gamma oxidative processes are linked to type of nutrients mTOR molecules, and to avaliablities of Ser amino acids for releasing Thymine kinases proteins for the acyl- CoA synthetase biosynthesis, and linked to Thymine pyrimidine and production from purines nucleotides during carbohydrate metabolism.
At the time of decreasing or inhibition in acyl-CoA phospholipase and in gamma acyl-CoA synthetase will lead to accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and downstream of reactive oxygen species.
Specific peroxisomal acyl-CoA Synthetase (ACS) participate in peroxisomal pathways in lipid metabolism [22]. Peroxisomal ACSs has its imp roles in maintaining the proper balance of purines related to pyrimidines that can be done through its functions in carbohydrate biosynthesis, and that ACSs (ROR gamma) have overlapped responsibilities with the others alpha and beta isoforms, because these enzymes are so depending on each others and play critical roles through their contributions together for the proper cellular fat+carbohydrate +proteins biosynthesis.
RORβ, act as a member of the orphan nuclear receptor family, plays an important regulatory role in the maintenance of a variety of physiological and pathological processes. RORβ has been determined to act as an osteogenic repressor in regulating bone formation, and is involved in regulating circadian rhythm [23].
Beta oxidative biosynthesis are processes that the synthase enzymes (conjugated to fatty acids molecules whether fatty acetylCoA or fatty acyl-CoA) are acting on inflammations molecules and on nutrients-mTOR for producing TXA2 and TNF-a subunits, which are involved in bone formation and are considered as prostanoids by some scientists. Where, prostanoids synthesis profile is dependent on differences in enzymatic expression in cells under inflammation factors, and specifically depend on the regulations of synthase enzymes which regulate TNF-a and Thromboxane-A productions under the stimulations of inflammations. Macrophages, for instance, release prostaglandins PGE2 and TXA2 [24].
Where during inflammation the effects of synthase enzymes as the ROR beta isoforms on inflammations and on irregular nutrients mTOR molecules for producing TNF-a and TXA2, and in the main time phospholipase as in the ROR-alpha isoforms will act on the same inflammation molecules for releasing prostaglandins (if possible) where both RORs isoforms playing so imp roles in osteogenic repressor in regulating bone formation with the new blood cells production with their effective phospholipid membranes.
Conclusion
The effects of ATPase and COX-2 enzymes start firstly on pronutrients- mTOR molecules in protein, lipid, and carbohydrate biosynthesis for releasing the long fatty acids molecules, then secondly the mitochondrial effects on the long fatty acids chains for producing the three RORs active isoforms which ara considered as are three active enzymatic acyl-CoA each is containing one of mitochondrial enzymes: 1) Enzymatic acyl-CoA-phospholipase (ROR-alpha ) which has the imp roles in anti-inflammatory function and in phospholipid synthesis, 2) acyl-CoA synthase (ROR-beta) which has the beta oxidative biosynthesis for TNF-a and TXA2 subunits synthesis, 3) acyl-CoA-synthetase (ROR-gamma) which has the function of carbohydrate biosynthesis where maintain the proper balance of purines related to pyrimidine in blood tissues and has the necessary roles for hydrophobic amino acids and fatty acids biosynthesis.
Peroxisomal organelles are made basically by mitochondrial effect on fatty acids due to RORs genes transcriptional filter and consist of the three RORs isoforms receptors alpha, beta, & gamma) for easier fastest processes for alpha beta, and gamma oxidations.
The beta oxidative process occur due to the activity of synthase for running the TNF-a and TXA2 biosynthesis for increasing immune effecincy, alpha oxidative processes is the fatty acyl- CoA phospholipase activities for lipoprotein and phospholipid biosynthesis where that alpha and beta oxidations are linked and contributing together for running their activities and producing H2O from the peroxisomal processes, but gamma oxidative processes are linked to type of nutrients mTOR molecules, and to avaliablities of Ser amino acids for releasing Thymine kinases proteins for the acyl- CoA synthetase biosynthesis, and linked to Thymine pyrimidine and production from purines nucleotides during carbohydrate metabolism.
At the time of decreasing or inhibition in acyl-CoA phospholipase and in gamma acyl-CoA synthetase will lead to accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and downstream of reactive oxygen species.
The Purpose of this Study
Understanding the main origin of the three RORs isoforms molecules and the main function of each isoforms in lipid metabolism and in fat biosynthesis, dependent on mitochondrial enzymes effects on the long fatty acids chains (which produced from the effects of ATPase and COX-2 on lipid molecules) for producing :
1) acyl-CoA phospholipase (ROR-alpha),
2) acyl-CoA synthase (ROR-beta),
3) acyl-CoA-synthetase (ROR-gamma).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The Author declare that the research work has been conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships, that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Material
• FOX forkhead genes
• RAR-related orphan receptor A (ROR alpha)
• Mitochondrial OPA1 gene and their effective enzymes synthetase, synthase, and phospholipase enzymes.
• Pro-mTOR protein conjugated with lipid molecules
• Ser/Thr sequences (included in Pro-mTOR protein) phosphorylation mechanism
• Phosphatidylcholine,
• Acetylcholine,
• Phospholipases A2 (PLA2s),
• Phospholipid membranes.
• Autophagosome membrane,
• Long acyl-CoA synthase (ROR beta),
• Long acyl-CoA synthetase (ROR gamma),
• Long acyl-CoA phospholipase (ROR alpha ).
• Lysosomes, peroxisomes membranes granules,
• Thromboxane-A2, _tumor necrosis
• Factor - alpha (TNF-a) subunits,
• Prostaglandins
• Liver X Receptor (LXR),
• Retinoid X Receptor (RXR), _Keratinocytes
• Interferon-gamma
• (IFN-gamma),
• Nerve growth factor
References
- Grevengoed TJ, Klett EL, Coleman RA. Acyl-CoA Metabolism and Partitioning. Nutr. 2014; 34: 1-30.
- Rennison JH, McElfresh TA, Okere IC, Patel HV, Foster AB, Patel KK, et al. Enhanced acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity is associated with improved mitochondrial and contractile function in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2008; 79: 331-340.
- Abo Alrob O, Lopaschuk GD. Role of CoA and acetyl-CoA in regulating cardiac fatty acid and glucose oxidation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014; 42: 1043- 1051.
- DeBose-Boyd RA. Feedback regulation of cholesterol synthesis: sterolaccelerated ubiquitination and degradation of HMG CoA reductase. 2008.
- Panel Matt T. Bianchi. Prostaglandins. S.E. Gad, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition). 2014.
- Zhu R, Ou Z, Ruan X, Gong J. Role of liver X receptors in cholesterol efflux and inflammatory signaling (Review). 2012.
- Shen Q, Bai Y, Nagpal S, et al. Liver X Receptor-Retinoid X Receptor (LXRRXR) Heterodimer Cistrome Reveals Coordination of LXR and AP1 Signaling in Keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2011.
- Jalil A, Bourgeois T, Masson D, et al. Revisiting the Role of LXRs in PUFA Metabolism and Phospholipid Homeostasis. 2019.
- Lagase TA. Phosphatidylcholine: Greasing the Cholesterol Transport Machinery. 2016.
- Allegretti C, Denuccio F, Rossato L, D’Arrigo P. Polar Head Modified Phospholipids by Phospholipase D-Catalyzed Transformations of Natural Phosphatidylcholine for Targeted Applications: An Overview Catalysts. 2020; 10: 997.
- Andrejeva G, Gowan S, Shamsaei E. Phosphatidylcholine synthesis is required for autophagosome membrane formation and maintenance during autophagy. 2019; 1044-1060.
- Acyl-Coenzyme A, Lysophosphatidic Acid Acyltransferase. Coenzyme A-Dependent Transacylation Activity Toward Lysophosphatidic Acid Catalyzed. JBC Papers in Press. 2001.
- Li R, Maminishkis A, Banzon T, Wan Q, Jalickee S, Chen S, et al. IFN{gamma} regulates retinal pigment epithelial fluid transport. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009; 297: C1452-1465.
- Rong R, Ahn JY, Chen P, Suh PG, Ye K. Phospholipase activity of phospholipase C-gamma1 is required for nerve growth factor-regulated MAP kinase signaling cascade in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278: 52497- 52503.
- Crumbley C, Wang Y, Burris TP. Regulation of Expression of Citrate Synthase by the Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor a (RORa). PLoS One. 2012; 7: e33804.
- Wang Y, Godec J, Lazarevic V. The transcription factors T-bet and Runx are required for the ontogeny of pathogenic interferon-γ-producing T helper 17 cells Immunity. 2014; 40: 355-366.
- Feng S, Xu S, Wen Z, Zhu Y. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor RORβ, circadian rhythm abnormalities and tumorigenesis (Review). 2015; 1493- 1500.
- Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research. 2015; 1853: 111-125.
- Pyrimidine within Tyrosine kinase and other (PSTGk, PSTCk, PSTAk) kinases produced from mTOR-FOX binding through effects of Ser/Thr phosphorylation mechanism play necessary rules for removing insulin resistance, and tumors, MAR Microbiology 2.3. Medical and Research Publications. 2021; 2.
- Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. Peroxisomes and Aging. 2007; 1763: 1749- 1754.
- Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 2015; 1853: 111-125.
- Watkins PA, Ellis JM. Peroxisomal acyl-CoA synthetases. 2012.
- Feng S, Xu S, Wen Z, Zhu Y. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor RORβ, circadian rhythm abnormalities and tumorigenesis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2015; 35: 1493-500.
- Lisowska B, Kosson D, Domaracka K, Lights and shadows of NSAIDs in bone healing: the role of prostaglandins in bone metabolism. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018.