
Research Article
Austin J Med Oncol. 2021; 8(2): 1063.
Reduction of Chemotherapy–Induced Side Effects by Complementary Medicine in Breast Cancer Patients
Beuth J¹* and Böwe R²
¹Institute for Naturopathy, University of Cologne, Germany
²Fresenius Hochschule, University of Applied Sciences Colgne, Germany
*Corresponding author: Beuth J, Institute for Naturopathy, University of Cologne, Joseph-Stelzmann-Str. 9, 50931 Cologne, Germany
Received: May 13, 2021; Accepted: June 11, 2021; Published: June 18, 2021
Abstract
This clinical investigation was performed to evaluate the benefit of Complementary Medicine (CM) in breast cancer patients undergoing adjuvant Chemotherapy (ChT).
Patients and Methods: The patients (n=668) were treated according to international guidelines with adjuvant ChT. As to reduce the side effects, the patients were complementarily treated with a combination of sodium selenite, proteolytic plant enzymes (bromelaine and papain) and Lens culinaris lectin. On Case Report Formulas (CRFs) assessment of side effects of ChT was documented at defined times during adjuvant ChT and additional complementary treatment. Validation was carried out by scoring from 1 (no side-effects/optimal tolerability) to 6 (extreme side-effects/extremely bad tolerability), however, only patients suffering from severe side effects (symptom scores 4 and higher) were enrolled into this investigation.
Results: The severity of side-effects of ChT was significantly reduced by complementary treatment. Mean scores of symptoms declined for sleep disorder, fatigue, lack of drive (p<0.05) and for arthralgia, hot flushes, mucosal dryness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, pain of tumour (p<0.001).
Conclusion: This investigation confirms benefits of indication-based complementary treatment with the combination of sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin in breast cancer patients, e.g. reduction of side-effects of adjuvant ChT.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Adjuvant chemotherapy; Side-effects; Complementary medicine
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer death in women worldwide [1]. Evidence-based treatment of breast cancer follows recommendations of international expert panels [2]. They are regularly updated during conferences and comprise indicationbased surgery, Chemotherapy (ChT), Radiotherapy (RT), and Anti- Hormontherapy (AHT) [3]. CT and RT are known to induce a broad range of side-effects [4].
Adjuvant treatment is defined as additional therapy after primary surgery to enhance curation. Primary surgery for breast cancer is accomplished by lumpectomy followed by irradiation or mastectomy. Adjuvant treatment may include local irradiation after mastectomy, systemic therapy with cytotoxic chemotherapy, or endocrine therapy. In several studies a decrease was noted in breast cancer mortality due to the use of adjuvant chemotherapy [2,3].
Complementary medicine is popular all over the world. If these treatments are carefully chosen and managed, they may add to enhanced comfort and well-being [5,6]. Some complementary treatments have been tested, e.g. nutrition, sports, psychooncology [6]. Certain complementary treatments such as sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin have shown clinical benefits, e. g. reduced adverse reactions and enhanced quality of life [7,8].
This clinical investigation was performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of complementary sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin treatment to reduce defined side effects of guideline-based ChT in breast cancer patients.
Patients and Methods
Patients
Women (n=668) with histologically verified breast cancer undergoing adjuvant ChT according to actual international guidelines including Epirubicin plus Cyclophosphamid (E+C) followed by Paclitaxel (P) were enrolled into this investigation.
Complementary treatment
The patients were complementarily treated with an oral medication (Equinovo; Kyberg Pharma GmbH, Oberhaching, Germany, PZN-8820547) containing sodium selenite (300μg/day), proteolytic enzymes (bromelaine 400 mg/day and papain 400mg/day) and Lens culinaris lectin (20 mg/day). Safety and efficacy of sodium selenite and proteolytic enzymes were extensively investigated in clinical trials [7,8]. Their combination with Lens culinaris lectin was found to be an innovative and beneficial complementary approach [6-8]. Other complementary remedies, especially antioxidative vitamins and trace elements and immunoactivation, were not taken by the patients throughout this investigation.
Side-effects of ChT
Case report formulas (CRFs) were used to document self assessed safety and efficacy of the complementary treatment. Patients were routinely checked at day 2-5 after finishing course 2 of E+C-ChT as well as at day 25 after finishing course 4 of E+C-ChT accompanied by complementary treatment starting immediately after course 2 of ChT. The efficacy of the complementary treatment was verified by questioning the severity of side-effects as primary aims of this investigation. Severity of symptoms was quantified by scoring from 1 (no sideeffects) to 6 (extreme side-effects). An average score was calculated for symptoms of the adjuvant therapy to investigate the value of this complementary treatment. The patients investigated suffered from severe side effects of ChT (symptom score 4 and higher).
Statistics
Student’s t-test was performed to calculate statistical significance between mean values of scores for side-effects of ChT and accompaniing complementary treatment.
Results
A total of 668 evaluable breast cancer patients were enrolled into this clinical investigation. Patients investigated suffered from CThinduced arthralgia (207), hot flushes (179), mucosal dryness (281), nausea (169), vomiting (35), diarrhea (85), loss of appetite (124), pain of tumour (116), sleep disorder (272), fatigue (353) and lack of drive (244). Patients suffering from severe side effects with symptom scores of 4 and higher were enrolled into this investigation.
Tolerability of adjuvant ChT along with complementary administration of sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin was investigated by self assessment. As shown in Figure 1, mean scores of symptoms declined from 4.79 (during ChT) to 3.04 (during ChT+CM) for arthralgia, from 4.83 to 3.34 for hot flushes, from 4.66 to 2.83 for mucosal dryness, from 4.70 to 2.76 for nausea, from 4.74 to 2.09 for vomiting, from 4.71 to 2.49 for diarrhea, from 4.60 to 2.34 for loss of appetite, from 4.55 to 2.29 for pain of tumour, from 4.76 to 3.36 for sleep disorder, from 4.64 to 3.33 for fatigue and from 4.57 to 3.16 for lack of drive. These results demonstrate that an efficient management of adverse reactions of adjuvant ChT in breast cancer patients is possible by well defined CM.
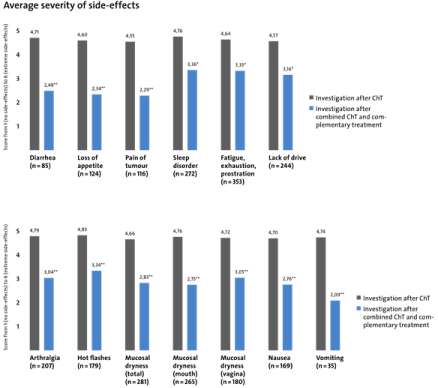
Figure 1: Effect of CM on side effects of ChT in breast cabncer patients.
*p<0.05; statistically significant different from side effects of ChT without CM.
**p<0.01; statistically significant different from side effects of ChT without CM.
No adverse reactions of the complementary medication (sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin) were documented. These data confirm recent trials on the safety of sodium selenite and proteolytic enzymes [7,8].
Discussion
By definition, CM cannot replace the well studied conventional cancer-destructive therapies such as surgery, ChT, RT or AHT. Complementary approaches in oncology that are recommended as an addition to standard treatment claim to optimize these therapies. Data emerging from recent clinical trials show that defined complementary procedures may be beneficial for patients [5-8].
CM may primarily be regarded as an optimization of current standard treatment options in oncology. It is to be differentiated from alternative medicine, which postulates to provide replacements for conventional toxic approaches. Although complementary and alternative medicines are grouped together in the popular acronym CAM, they are in fact quite different in their aims. Since many alternative treatments are still poorly documented [5], equating the two could lead to a misguided and undeserved rejection of all complementary medicine. That complementary recommendations concerning balanced nutrition, physical activity, psychooncologic support, as well as defined medications, proteolytic enzymes or defined trace elements and vitamins, can optimize standard treatment has been shown in clinical studies that have shown an improvement in quality of life [5,6,9]. This clinical investigation was performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of an innovative complementary medication composed of sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin. Whereas sodium selenite and proteolytic enzymes have proven their clinical safety and efficacy in controlled trials [7,8], Lens culinaris lectin was added to the medication because of its stabilizing effects on mucosal surfaces [10]. The scientific rationale of this complementary treatment is enhancement of the tolerability of ChT by reduction of defined adverse reactions to optimize this guideline-based therapy. This investigation shows that complementarily administered sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin significantly reduced defined side-effects of adjuvant ChT in breast cancer patients. The reduced adverse reactions of ChT lead to enhanced tolerability and compliance.
Since the tolerability of adjuvant ChT determines its optimal administration, complementary treatment with sodium selenite, proteolytic enzymes and Lens culinaris lectin may enhance the chance of curing the disease.
References
- American Institute for Cancer Research. Breast Cancer Statistics. Breast Cancer is the Most Common Cancer in Women Worldwide. 2020.
- de Vita VT, Rosenberg SA, Lawrence TS. Cancer. Principles and Practices of Oncology. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA. 2018.
- Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Medizinischen Fachgesellschaften. Interdisziplinäre S3-Leitlinie für die Früherkennung, Diagnostik, Therapie und Nachsorge des Mammakarzinoms. 2020.
- MD Anderson Cancer Center 2020: Side Effects of Cancer Treatment.
- Deng G, Cassileth B. Integrative Oncology: An Overview. In: American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book. 2014; 34: 233-242.
- Krebsgesellschaft NRW. Komplementäre Behandlungsmethoden bei Krebserkrankungen. 2020.
- Beuth J, Schneider B, van Leendert R, Uhlenbruck G. Large-Scale Survey of the Impact of Complementary Medicine on Side-effects of Adjuvant Hormone Therapy in Patients with Breast Cancer. In Vivo. 2016; 30: 73-75.
- Beuth J, van Leendert R, Pempelfort K, Schneider, Grund C, Engelmann U. Complementary Medicine Down-regulates Side-effects of Hormone Therapy in Prostate Cancer Patients. In Vivo. 2016; 30: 73-75.
- Beuth J, Moss RW. Complementary Oncology. Adjunctive Methods in the Treatment of Cancer. Thieme Pbl Stuttgart, New York. 2011.
- Beuth J. Komplementärmedizinische Behandlung von Nebenwirkungen der Krebs Standardtherapie. Thieme Praxis Report. 2016.