
Literature Review
Austin Med Sci. 2021; 6(1): 1044.
Defense and Immune Response to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in COVID-19 Patients: A Narrative Review
Khwiter S*
Medical Technology Department, Faculty of Science, Islamic University Gaza, Palestine
*Corresponding author: Samy Khwiter, Medical Technology Department, Faculty of Science, Islamic University Gaza, Palestine
Received: January 30, 2021; Accepted: February 22, 2021; Published: March 01, 2021
Abstract
In the present review, we aim to determine the defense methods, assessment the profile of acute antibodies response in COVID-19 patients, and to provide accurate date for the usage of antibody test in clinical practice. After exposure to COVID-19, the immune system is responded in different ways and particles in different concentrations according on period of infection graduation. While the main response of immune system includes IgM, IgG and IgA antibodies, and, the most serological diagnosis tests and researches were found that “≥4- fold increase in the IgG titer” is suitable for a majority of COVID-19 patients and after three months is disappeared. IgM and IgG antibodies are the best defense methods. Serologic test method is helpful for the diagnosis of SARSCoV- 2 infection in suspects and close contacts. Antibodies determination in SARS Cov-2 is essential for COVID-19 assessment, treatment and vaccine development. In conclusion, we noticed in most of cases the production of IgM is started after 72 hrs. Of symptoms appears and peak up the production curve in 20-22 days then is disappeared in day 56 of infection. While, the production of IgG is started after 8 days of infection and peak up the production curve in 17-19 day then disappeared in day 80 of infection, but IgA production is started in 5th day of infection.
Keywords: Acute respiratory syndrome; COVID-19; Defense methods; Immune response; Infection; Serological diagnosis tests
Introduction
COVID-19 structure and history
In late December 2019, the first reports of patients with Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) emerged, the COVID-19 cases first started in the seafood market in Wuhan of China. A disease caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [1]. Then the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared as a global pandemic on March 12, 2020 [2]. Therefore, the rapid spread of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) worldwide has raised concern around the world. Now, the COVID-19 outbreak has currently highlighted in the media due to its rapid propagation across the globe through migration processes [3]. Corona virus family was discovered in the decade of the 1960s, this family subdivided into the genera Alphacoronavirus (HCoV-229E, HCoV-NL63) and Betacoronavirus (HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV, MERSCoV), that responsible for infection in humans, and the subfamily Coronavirinae is further subdivided into four (Gammacoronavirus, Deltacoronavirus, Torovirus and Bafinivirus) that cause diseases to animals [4,5], while, SARS-CoV-2 virus is belonged to the genera Betacoranavirus and the family Coronaviridae [6,7].
SARS-CoV-2 virus structure is constituted of four proteins: the Envelope (E) (9-12 kDa), Membrane (M) (23-35 kDa), Nucleocapsid (N) (50-60 kDa) and the Spike (S) (180-220 kDa) (Figure 1) [8,9]. Moreover, the IgM and IgG antibodies are coded against SARSCoV- 2 nucleoprotein and Spike (S) protein antigens [10].
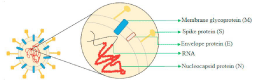
Figure 1: SARS-CoV-2 virus essential structure.
For 19 years ago, three novel coronaviruses have crossed the species barrier to infect humans and cause human-to-human transmission [11]. In addition, four seasonal human coronaviruses (ie, 229E, NL63, OC43, and HKU1) have been identified as causing up to a third of community-acquired upper respiratory tract infections [11]. Moreover, in 2003 there was a SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV virus, with a mortality rate of 9.6% [12] and in 2012, a new disease emerged to MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) [13] with a mortality rate of 34.4% [14]. Therefore, the pathogenesis of COVID-19 by taking into consideration the previous experimental and clinical knowledge obtained from the coronaviruses that were responsible for causing SARS and MERS.
Genetic of SARS-CoV-2
Coronaviridae consist of viruses with the largest genomes (32kb) [15], with a simple positive sense RNA strand, not segmented and enveloped, that is further subdivided into four genera (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta coronavirus). SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 are all betacoronaviruses. The genomic sequence of coronavirus RNA is translated into a long polyprotein that contains proteins involved in RNA replication (Figure 2). The structural proteins, which encompass the Spike (S), Envelope (E), Membrane (M), and Nucleocapsid (N) proteins, while the accessory proteins are involved in immunoevasion, are translated from a nested set of subgenomic RNAs that have the same 50 and 3 ends (Figure 1B) [16].
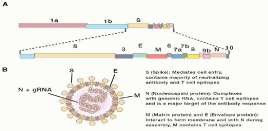
Figure 2: Genomic Organization and Virion Structure.
SARS-CoV-2 falls under the genus b-CoV, as it shares 88% sequence identity with SARS-CoV-like coronaviruses (derived from bat) but is only 79% identical to SARS-CoV and 50% identical to MERS-CoV [17].
Degree of illness
In the beginning the initial asymptomatic phase lasts for about 1–2 days, during which the virus multiplies in the upper respiratory tract, where no major hindrance is caused by the innate immune cells. In addition, within 2-14 days of initial encounter, the common symptoms of COVID-19 start to appear, according on SARS and MARS previous studies, i.e., fever, dry cough, pharyngitis, shortness of breath, joint pain, and muscle tiredness [17]. Soon, the virus begins to move toward the lower respiratory tract via airways, and this triggers a strong innate immune response [17]. Patients at this stage start exhibiting enhanced pro-inflammatory response that leads to viral sepsis accompanied by other complications, including pulmonary edema, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), different organ failures, and death in the worst scenarios [17]. While in infected patients rarely, show the intestinal symptoms like diarrhea that were evident in other coronavirus infections [17]. The clinical symptoms variant depending on the individual’s immune response, with the most well-known symptoms of COVID-19 include the difficulty breathing, high fever, and cough [3], which presenting as asymptomatic (positive for the disease but without clinical manifestation), mild symptomatic (positive for the disease with clinical manifestations) or severe symptomatic (positive for the disease with manifestations in high degree).
The symptomatic presents respiratory failure, requiring mechanical ventilation in Intensive Center Unit (ICU), in addition to leukopenia, lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia and high levels of creatinine, lactate dehydrogenase, liver enzymes, this stage usually develops in the elderly, immunodeficient, diabetics and individuals with chronic diseases or cancer [18,19]. While, for laboratory parameters of the patients, white blood cell, neutrophil D-dimer, hypersensitive troponin I, procalcitonin, CRP (C-Reactive Protein), lactate dehydrogenase, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase were higher in severe/critical patients, while mild patients had higher level of lymphocyte counts, which is consistent with recent reports [20]. While, asymptomatic individual with infection will become a transmission source if not be contained and quarantined. In recent study, it was identified 4.3% (7/164) patients with occult infection, which were missed by symptoms screening and nucleic acid test [21]. As the number of patients infected with SARSCoV- 2 continues to rise, identifying, evaluating, and understanding the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection becomes even more essential [11]. However there is little knowledge of post-infection immunity to SARS-CoV-2, while, the biological and genetic factors responsible for the broad spectrum of disease severity remain unclear [11].
Therefore, early case detection is one of the most important public health interventions in controlling the spread of SARS-Cov-2 [21]. Which COVID-19 cases can be identified based on exposure status, symptoms and chest imaging, but the confirmation of infection requires nucleic acid testing of nasal, pharyngeal or anal swab. Although real-time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)-based viral RNA detection is the sensitive and accurate way to confirm the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in practice, dozens of suspects with clinical symptoms were failed to be diagnosed by RT-PCR test [21]. However, the sensitivity of the PCR technique for coronavirus diagnosis was 86% (95% CI = 84 to 88%); I² =85% [22]. Therefore the importance of antibodies test is preferred for more accurate diagnosis, as shown in other study was used antibodies test, which in a recent study aided to confirm 4 patients with COVID-19 from 52 suspects who failed to be confirmed by RT-PCR and 7 patients from 148 close contacts with negative RT-PCR [21]. As shown in many previous studies, Human immune responses to a novel pathogen with both innate and adaptive arms. One aspect of the adaptive immunity is humoral response that features the production of antibodies recognizing specific determinants of antigens called epitopes [21]. Some of the antibodies produced can protect the host from future infection by the same pathogens [21]. In addition, a constant stimulus caused by the virus infection, these cells continue to produce inflammatory mediators to reduce viral replication, however, this process causes tissue damage that evolves into an intensified pathogenesis. To avoid this process, it is necessary to have a balance in the immune response, with the production of antiinflammatory mediators, such as IL-10 [23]. In addition, the immune system to develop a faster and more efficient response since the cells have already had first contact with the pathogen, the formation of a response will be a specific antigen, and therefore eliminating the pathogen is more effective than a primary response.
Literature Review
SARS Cov-2 infection pathogenicity
In the beginning the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs when a healthy individual inhales or comes into contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person. And the average incubation period before patients exhibit disease symptoms ranges from 2 to 14 days [24]. The pathogenicity of human infection starts when the virion enters in the host cell, provided by the connection of the viral S protein with the ACE2 receptor (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2) in the case of SARS-CoV-2 however depending on the virus; moreover ACE2 is present on most of human body cells. However, a protease cleaves protein S to release its domains, which is the essential process in viral infection [25]. In addition, the virion enters in the host cell within the endosome, the S2 region of the S protein in virus structure is preferred in the cells of the respiratory tract, epithelial hair cells of the airways and type 2 alveolar pneumocytes in SARSCoV infections [26]. In this stage, the virus is able to fuse with the host cell membrane and release the genomic RNA in the cytoplasm of host cells, and RNA will continue through the translation process. The Open Reading Frames (ORF), ORF1a, and ORF1ab sequences are translated into pp1a and pp1ab (viral replicase polyproteins), then, it will be cleaved into smaller proteins, which join to form a Replicase- Transcriptase (RTC) Complex. In this complex, the formation of a complete negative-strand RNA occurs and several copies are generate and used as a template for the synthesis of a complete positive-strand RNA [26].
COVID-19 and immune reactions
It was reported in previous studies the damages caused during noval Corona viruses infection are of high predominance in the respiratory system. Moreover, up to date there is a several studies that indicated were not knows for sure how this response occurs in SARS-Cov-2 infections. But according on many previous studies in SARS and MARS pathogenicity studies, it was reported that once the virus gains access inside the target cell, and the host immune system recognizes the whole virus or its surface epitopes, which is eliciting the innate or adaptive immune response [17], moreover, as reported in SARS infections it is mention infiltrations by monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils and with a result of the presence of these cells [17].
The adaptive response: T cells: Recognize cells that are infected with a specific virus and rapidly increase in number to tackle the infection. However, in general, coronavirus Infections will be mediated by T-lymphocytes, which will become active the moment the pathogen presented by antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells or macrophages) is recognized [27]. In addition, the cells participate in the innate immune response and are key components in activating an adaptive immune response, during this infection that response fails to activate T cells as shown in (Figure 3). And recognize the viral antigens presented by MHC class I [MHC; Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) in humans], which in turn promotes the cytokine release and cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells [17]. But in some other cases, MHC class II is also found to present SARS-CoV peptides to CD4+ T cells. Due to the genetic polymorphism of HLA, some haplotypes, like HLA-B*07, HLA-B*46, HLA-DRB1*12, and HLA-Cw*08 (ss), are found to be more susceptible to coronavirus infection, whereas the HLA-DRB1*03, HLA-A*02, and HLA-Cw*15 haplotypes are protected from SARS-CoV infection (ss). Similarly, HLA-DRB1*11 and HLA-DQB1*02 were found to be vulnerable to MERS-CoV infection [17].
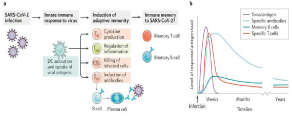
Figure 3: Immune cells response to SARS-CoV-2; a: Infection with SARSCoV-
2 leads to activation of innate immunity and Dendritic Cells (DCs), which
will drive the induction of virus-specific T cell and B cell responses. Little is
currently known concerning the memory response to SARS-CoV-2, but this
will be important for developing an effective vaccine; b: A predicted timecourse
of adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2. CTL: Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte;
TFH: T Follicular Helper Cell; TH: T Helper Cell; Treg: Regulatory T Cell [28].
T cells can be stimulated by 14 epitopes in SARS-Cov-19, most of which are observed to be located on ORF3 and the S protein in SARS patients [17]. Then, CD8+ response was against the S and N proteins along with some of the M/E epitopes [17]. In the acute phase of infection responses, occurs lymphopenia [27,29]. And it is still believed that decrease of lymphocytes in SARS-CoV infections must failures in their activation, through strategies developed by the virus as an escape from the immune response [30,31]. And in the later stage of the disease, when memory T cells are activated, However, Pathogen Recognition Receptors (PRRs) present on immune cells, mainly Toll-like receptors 3, 7, and 8, are the first to identify the virus, however, the activation of T-lymphocytes lead to enhanced to production the pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-a, IL- 1, IL-6, IL-12, TNF) and chemokine’s (CCL2, CXCL9, CXL10). And T-lymphocytes responsible by the activation and recruitment of other types of cells. Their proliferation and survival depends on the predominance of the immune response is directs by lymphocytes. These are probably responsible for diffuse alveolar damage (edema, fibrosis, the formation of a hyaline membrane), in addition, the alveolar collapse, desquamation of epithelial and alveolar cells, and damage to other organs (spleen, liver, bone marrow, among others) [32,33]. And the inflammatory response is predominant with the production of TNF-a, IL-6, CXCL-10, CCL-2, CCL-3, CCL-5, and IL-8 contributing to tissue damage [34]. The production of inflammatory mediators (IFN-I, TNF-β, IL-1, IL-6, CCL2) and probably the production of perforin and granzym B, processes that usually occur in others airways infections [35,36]. Their proliferation and survival depends on cytokine stimulation, such as IL-15 and IL-7 and are cells with a half-life that vary from 8 to 15 years, which become the responsible for the great part of the eliminated pathogens throughout an individual’s life [37,38].
The CD8+ cytotoxic T cells kill the cells in which the virus is multiplying and help to slow down or stop the infection. In addition, CD4+ helper T cells bring in other cells of the immune system and stimulate B-Cells to produce antibodies specific to that virus.
COVID-19 and antibodies production
Adaptive response B cells, the major function of host innate immune cells is impaired during SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infection by their non-structural proteins, which affects the overall cytokine production [39,40]. While humoral response against SARSCoV- 2 has been found to be similar to that against other coronavirus infections, which involved the characteristic IgG and IgM production. And antibodies could be detected after 4-8 days from the appearance of initial symptoms [41,42]. Memory B cells (usually IgG) differentiate into plasma cells (antibody producer) or return to the germinal center (usually IgM) produce antibodies that are specific to that virus. They are also capable of producing cytokines and are long-lasting cells [43,44]. Otherwise, Antibody detection rate based on the number of days after onset of symptoms were determined and summarized in Figure 4 [22]. This referred that the positive rates of IgG and IgM antibodies increased gradually along with days after symptoms onset [22].
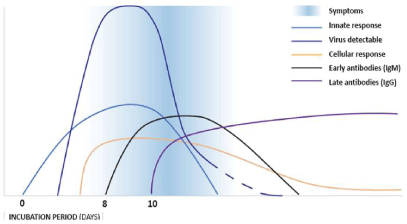
Figure 4: The immune response to viral infection in general mechanism.
In general, in most of the previous studies, on SARS and MERS showed that IgM antibodies are detected first in 80%-100% patients for at least 2 weeks after illness onset [45-47], and can persist for at least 12 years [48]. But IgG antibodies are produced at the same time or 2-3 days later, and titers usually remain for at least 16th months (memory cells). Once the infection is over, while in another studies have demonstrated specific antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 peaked at 4 months, and persisted for 24 months in patients who recovered from SARS (1106) [6], antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were disappeared in a convalescent COVID-19 patient within 3 months [10], but some cells will remain, as shown in Figure 5. The IgM titers gradually increase in patients with mild and severe forms over time, in the positive rate is higher in groups with the mild form [49]. And it is possible to observe that the IgG and IgM titers are high in the severe group in relation to the non-severe group [50,51], but it is important to consider that the IgM values tend to appear within 2 weeks since the beginning of the infection. As soon as, considering that symptoms of the infection can occur within 2 weeks, in most cases it is difficult to accurately determine when a patient contracted the virus. Consequently, if immunoglobulin values are not high enough at the time of the test, false negatives could be recorded. SARS-CoV-2 infection can also be transmitted among asymptomatic patients, who can have a high viral load without showing any symptoms. While, others study reported SARS-CoV-2 specific IgA, IgG, and IgM antibodies were detected after the onset of symptoms at different time points in infected patients. A persistent level of IgG was detected for a longer period, whereas IgM levels started to decline after 3 months [52]. In an observational case study of 16 SARS-CoV-2 patients, anti- S-RBD IgG was detected in all of the subjects, whereas anti-N IgG and anti-S-RBD IgM were detected in 15 patients and anti-N IgM in 14 patients (tt). IgM and IgA antibodies were detected 5 days after the onset of initial symptoms, whereas IgG was detected after 14 days [53].
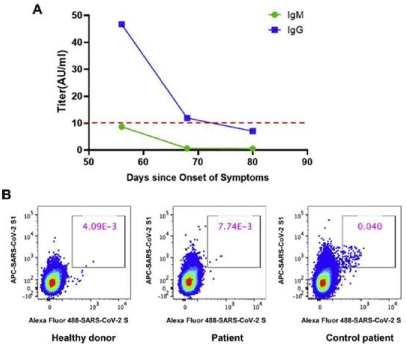
Figure 5: Detection of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies and S proteinspecific
B cells. (A) Temporal changes in IgM and IgG antibodies against
SARS-CoV-2; (B) Frequency of SARS-CoV-2 S-specific B cells.
For more accuracy, the positive rate of IgG reached 100% at around 17-19 days after symptoms onset, while IgM seroconversion rate reached its peak of 94.1% at around 20-22 days after symptoms onset (Figure 3). However, the patients were further divided into 4 groups based on symptoms onset days (1 week, 2 weeks, 3 weeks and >3 weeks of symptoms onset). During the first 3 weeks of symptoms onset, there was an increase in the titer of IgG and IgM antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. In addition, the antibody level IgM showed a slightly decrease in the patient group with >3 weeks of symptoms onset when compared with the ≤3 weeks group. While, in other study it was reported that the positive rate for IgG reached 100% around 20 days after symptoms onset [22]. The median day of seroconversion for both lgG and IgM was 13 days after symptoms onset. Seroconversion of IgM occurred at the same time, or earlier, or later than that of IgG. IgG levels in 100% patients (19/19) entered a platform within 6 days after seroconversion. The criteria of “IgG seroconversion” and “ ≥4-fold increase in the IgG titers in sequential samples” together diagnosed 82.9% (34/41) of the patients [22].
Moreover, in another study it was mentioned the antibody level of the patients in different clinical courses were 20 severe patients who were at the 2nd week after symptoms onset when sampling, in contrast, 13 severe patients were at the 3rd week when sampling, IgG and IgM titers in severe group were higher than those in the nonsevere group, although significant statistic difference is only observed in IgG level of 2 weeks group (P=0.001) [22]. However, (43.9%) of patients were IgG negative at the first week seroconverted afterwards (in the observation period [22]. But that is may due to first week is needed to appear the symptoms. Also in other recent study referred that the assay of IgM and IgG are developed against SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein and spikes protein antigens were first measured using a chemiluminescent immunoassay assay according to manufacturer’s protocol (YHLO Biotechnology). The IgM and IgG antibodies were considered positive when their titers were greater than 10AU/ml. Antiviral IgM was shown to be negative on day 56, day 68, and day 80 post disease onset. Moreover, antiviral IgG titers dropped from 46.69 on day 56 to 11.90AU/ml on day 68, and were negative (7.03AU/ml) on day 80 after the onset of the symptoms, indicating disappearance of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 [10]. Then the rbust cellular immunity persists for at least for six months after even mild or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, research has shown [55]. Moreover in other study of 100 people showed that all had a cellular immune response against SARS-CoV-2 six months after infection although the size of response was 50% higher in those who had experienced symptomatic disease [55]. While, the author Moss said the finding that the T cell response was 50% higher in those who had experienced symptoms did not necessarily mean that asymptomatic people may be more susceptible to reinfection as they may just be better at fighting off the virus without the need to generate a large immune response [55].
The WHO was recommended that a 4-fold increase in the IgG titer in acute (ideally during the first week of illness) and convalescent serum samples can be used to confirm MERS-CoV infection. We thus analyzed if this criterion is also suitable for the diagnosis of COVID-19 [56].
Antibodies are developing against different proteins that are part of a virus. As soon as antibodies against one type of viral protein might neutralize the virus, while others might not. The neutralizing antibodies generated in SARS infections would be specific to (receptor-binding Domain) RBD domain of protein S, demonstrating to be an immunogenic protein [57]. In addition as shown in of Hoffmann and collaborators study 2020 raise the hypothesis that antibodies generated during this infection could have a certain influence on partial protection against SARS-CoV-2. In patients infected with SARS-CoV-1, detection of humoral markers of immunity were measurable for 2–3 years, but these markers were absent when patients were re-tested 5–6 years later [58,59]. While, viral proteins may change so much that antibodies produced against the virus won’t recognize the antigens if they meet again later. (This phenomenon is shown in COVID-19). In addition, the infection process is also generate neutralizing antibody and that remains after infection and they are responsible for connecting directly to the virus that prevents it from entering the host cell [60], which are defensive and useful, there are numerous non-neutralizing antibodies in the system that aids the infection of immune cells and APCs. Previously existing SARS-CoV antibodies may promote the viral infection in FcR-expressing cells [61]. This ACE2-independent pathway of viral entry does not result in viral replication; rather, viral shedding by macrophages enhances inflammation and tissue injury by myeloid cell activation. This mechanism of viral entry through non-neutralizing antibody that results in aberrant activation of immune cells is called ADE (Antibody- Dependent Enhancement) [62,63]. ADE has been observed in a number of viral infections, including SARS and MERS. In the case of SARS, anti-S antibodies were observed to be involved in ADE to gain entry into FcR-expressing cells [64], while in MERS, a neutralizing Mab (Mersmab1) targeting RBD aided in MERS pseudovirus entry via the DPP4 pathway [65]. Although there is no clear evidence regarding ADE in SARSCoV-2 infection, it is still necessary to consider all of the odds in the pursuit of developing vaccines and treatment regimens involving antibodies [66].
Vaccines and other COVID-19 treatment
In future Memory cells respond rapidly if they come in contact with the same virus again, which kills the virus and accelerates an antibody response. The potential of lymphocytes in SARS infection has been demonstrated, the generation of memory is essential in reinfection processes. However, the understanding of the mechanisms for short-duration immunity after a live viral infection is important because these processes might have considerable implications for the protection and durability of immunity induced by vaccines. And these findings have implications in vaccine development, because the cellular response was directed against a range of proteins from the virus, including the spike protein that is being used as a target in most vaccine studies. In that study, it was suggested the T cell responses were also directed against additional nucleoprotein and membrane proteins these could also be valuable targets for future vaccines strategies [55]. Therefore, the development of a vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 is urgently needed. According to Shang W et al., the combination of subunit vaccines with adjuvants may represent a good strategy to speed up the clinical development [67]. A solution could be represented by the passive immunization, which is the administration of serum containing specific antibodies taken from patients from SARS-CoV-2 [68]. Unlike active immunization, this approach does not require the activation of the recipient’s immune responses and generates an immediate immune response. However, this would be an emergency solution and not a substitute for any vaccination therapy.
Conclusion
According on many study the best method for recovery and COVID-19 prevention is the immune respond either immune responds and antibodies production or by use a suitable vaccine, while the period of antibodies production against SAR-CoV-2 infection until now is still not clear, This finding indicates that SARSCoV- 2 infection can be ruled out if antibody against SARS-CoV-2 is not optimal in all cases but is more accurate for patient diagnosis and monitoring. Particularly, the molecular rtPCR specificity is 86%.
According on most of studies about SARS, MARS and SARSCoV- 2, we noticed in most of cases the production of IgM is started after 72hrs. Of symptoms appears and peak up the production curve in 20-22 days then is disappeared in day 56 of infection. While, the production of IgG is started after 8 days of infection and peak up the production curve in 17-19 day then disappeared in day 80 of infection, but IgA production is started in 5th day of infection.
In other hand, don’t forget for COVID-19 diagnose, 85% of patients are asymptomatic or with symptoms or chest imaging evidence simultaneously, we should use serological IgM and IgG assays for diagnosis and monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine development. The asymptomatic infection poses a special challenge in the prevention of COVID-19, since symptoms are usually used as important indicator for COVID-19. In contrast the asymptomatic patients are considered a hidden transmission vectors. Therefore the serological IgM, IgG and IgA antibodies assays are more indicator than others tests. Moreover, the best method for COVID-19 treatment, control or prevention is immune respond, which is by viral infection exposure or vaccine use. Therefore, the patients should be support his immune system. Fresh plasma and antibodies replacement is a useful method for immune supporting. Use the immune assays help us to understanding the mechanisms for shortduration immunity after a live viral infection, which is considered an important issue because these processes might have considerable implications for the protection and durability of immunity induced by vaccines.
References
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020; 579: 270-273.
- Quan-xin Long. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients: the perspective application of serological tests in clinical practice. 2020.
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020; 382: 727-733.
- JS Kahn, K Mcintosh. History and recent advances in coronavirus discovery. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2005; 24: 223–227.
- RJ De Groot. Family Coronaviridae. Virus taxonomy. 2012: 806–828.
- KH Chan, Cheng VCC, Woo PCY, Lau SKP, Poon LLM, Guan Y, et al. Serological responses in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection and cross-reactivity with human coronaviruses 229e, Oc43, and Nl63. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005; 12: 1317-1321.
- YX Lim, Ng YL, Tam JP, Liu DX. Human coronaviruses: a review of virus host interactions. Diseases. 2016; 4: 26.
- AR Fehr, S Perlman. Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis, in: Coronaviruses. Humana Press. 2015; 1282: 1-23.
- Phan MVT, Tri TN, Anh PH, Baker S, Kellam P, Cotten M. Identification and characterization of Coronaviridae genomes from Vietnamese bats and rats based on conserved protein domains. Virus evolution. 2018; 4: 35.
- Liu A. Disappearance of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in a -COVID-19 patient after recovery, Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2020.
- Gregory A, Inna G, Richard B. SARS-CoV-2 immunity: review and applications to phase 3 vaccine candidates. Lancet. 2020; 396: 1595-606.
- CDC-Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Update: severe acute respiratory syndrome-worldwide and United States. 2003.
- AM Zaki Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012; 367: 1814-1820.
- D Cavanagh. Coronaviridae: a review of coronaviruses and toroviruses. In: Coronaviruses with Special Emphasis on First Insights Concerning SARS. Birkh¨auser Basel. 2005: 1-54.
- WHO-World Health Organization, Coronavirus disease. Coronavírus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation.
- Alan S and Stanley P. Lessons for COVID-19 Immunity from Other Coronavirus Infections. 2020.
- Alan Sariol and Stanley Perlman. Lessons for COVID-19 Immunity from Other Coronavirus Infections. 2020.
- S Alsolamy, YM Arabi. Infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Can. J. Respir. Ther.: Cjrt= Rev. Canadienne Ther. Respir. Rctr. 2015; 51: 102.
- WHO-World Health Organization, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China Lancet. 2020.
- GA Schellekens, BA de Jong, FH van den Hoogen. Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritisspecific autoantibodies. 1998; 101: 273-281.
- Idevaldo Floriano, Antonio Silvinato and Wanderley M Bernardo. Accuracy of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test in the diagnosis of acute respiratory syndrome due to coronavirus: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020; 66: 880-888.
- BT Rouse, S Sehrawat. Immunity and immunopathology to viruses: what decides the outcome? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010; 10: 514-526.
- Ong SWX, Tan YK, Chia PY, Lee TH, Ng OT, Wong MSY, et al. Air, surface environmental, and personal protective equipment contamination by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from a symptomatic patient. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc. 2020; 323: 5–7.
- Raj VS, Mou H, Smits SL, Dekkers DHW, Muller MA, Dijkman R, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature. 2013; 495: 251-254.
- KC Chow. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome–associated coronavirus in pneumocytes of the lung. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004; 121: 574- 580.
- G Li. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J Med Virol. 2020; 92: 424-432.
- Rebecca J Cox, Karl A Brokstad. Not just antibodies: B cells and T cells mediate immunity to COVID-19. 2020.
- Channappanavar R, Zhao J, Perlman S. T cell-mediated immune response to respiratory coronaviruses. Immunol. Res. 2014; 59: 118-128.
- Teijaro JR. Type I interferons in viral control and immune regulation. Curr Opin Virol. 2006; 16: 31-40.
- Prompetchara E, Ketloy C, Palaga T. Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020; 38: 1-9.
- Gu J, Korteweg C. Pathology and pathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am. J. Pathol. 2007; 170: 1136-1147.
- Liu J, Zheng X, Tong Q, Li W, Wang B, Sutter K, et al. Overlapping and discrete aspects of the pathology and pathogenesis of the emerging human pathogenic coronaviruses SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and 2019-nCoV. J Med Virol. 2020; 92: 491-494.
- Chu H, Zhou J, Wong BHY, Li C, Cheng ZS, Lin X, et al. Productive replication of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in monocytederived dendritic cells modulates innate immune response. Virology. 2014; 1: 197-205.
- Chu H, Zhou J, Wong BHY, Li C, Cheng ZS, Lin X, et al. Productive replication of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in monocytederived dendritic cells modulates innate immune response. Virology. 2014; 1: 197-205.
- Li X, Geng M, Peng Y, Meng L, Lu S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharmaceut. Anal. 2020; 10: 102-108.
- ND Pennock, JT White, EW Cross, Cheney EE, Tamburini BA, Kedi RM, et al. T cell responses: naive to memory and everything in between. Adv Physiol Educ. 2013; 37: 273-283.
- Lauvau G, Soudja SMH. Mechanisms of memory T cell activation and effective immunity. Crossroads Innate Adapt. Immun. V. 2015; 850: 73-80.
- Le Bon A, Tough DF. Links between innate and adaptive immunity via type I interferon. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002; 14: 432-436.
- Hu W, Yen YT, Singh S, Kao CL, Wu-Hsieh BA. SARS-CoV regulates immune function-related gene expression in human monocytic cells. Viral Immunol. 2012; 25: 277-288.
- Wu HS, Hsieh YC, Su IJ, Lin TH, Chiu SC, Hsu YF, et al. Early detection of antibodies against various structural proteins of the SARS associated coronavirus in SARS patients. J Biomed Sci. 2004; 11: 117-126.
- Wu HS, Hsieh YC, Su IJ, Lin TH, Chiu SC, Hsu YF, et al. Early detection of antibodies against various structural proteins of the SARS associated coronavirus in SARS patients. J Biomed Sci. 2004; 11: 117-126.
- Kurosaki T, Kometani K, Ise W. Memory B cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015; 15: 149-159.
- Weisel F, Shlomchik M. Memory B cells of mice and humans. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017; 35: 255-284.
- Meyer B, Drosten C, Muller MA. Serological assays for emerging coronaviruses: challenges and pitfalls. Virus Res. 2014; 194: 175-183.
- Corman VM, Albarrak AM, Omrani AS. Viral Shedding and Antibody Response in 37 Patients With Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2016; 62: 477-483.
- Li G, Chen X, Xu A. Profile of specific antibodies to the SARS-associated coronavirus. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349: 508-509.
- Guo ZGX, Duan C. Long-Term Persistence of IgG Antibodies 1 in SARS-CoV Infected Healthcare Workers. medRxiv. 2020.
- Shen L. Delayed specific Igm antibody responses observed among COVID 19 patients with severe progression. Emerg Microb Infect. 2020; 9: 1096- 1101.
- Long QX. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. 2020.
- L Shen, Wong C, Zhao J, Tang X, Shen Y, Lu M, et al. Delayed specific Igm antibody responses observed among COVID-19 patients with severe progression. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020; 9: 1096-1101.
- Li Gang, Chen Xuejuan AX. Profile of specific antibodies to the SARSassociated coronavirus. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349: 508-509.
- To KK, Tak O, Tsang Y, Leung W, Tam AR, Wu T, et al. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody. 2020.
- Guo L, Ren L, Yang S, Xiao M, Cheng D, Yang F, et al. Profiling early humoral response to diagnose novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Clin Infect Dis. 2020; 71: 778-785.
- Floriano I, Silivinato A, Bernardo WM, Reis JC, Soledade G. Accuracy of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test in the diagnosis of acute respiratory syndrome due to coronavirus: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2020; 66: 7.
- Drosten C, Meyer B, Muller MA, Corman VM, Al-Masri M, Hossain R, et al. Transmission of MERS-coronavirus in household contacts. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371: 828-835.
- Z Cao, L Liu, L Du. Potent and persistent antibody responses against the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein in recovered patients. Virol. J. 2010; 7: 299.
- Wu LP, Wang NC, Chang YH. Duration of antibody responses after severe acute respiratory syndrome. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007; 13: 1562-1564.
- Payne DC, Iblan I, Rha B. Persistence of antibodies against Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016; 22: 1824-1826.
- F Weisel, M Shlomchik. Memory B cells of mice and humans. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017; 35: 255–284.
- Iwasaki A, Yang Y. The potential danger of suboptimal antibody responses in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020; 20: 1-3.
- Ricke DO, Malone RW. Medical countermeasures analysis of 2019-nCoV and vaccine risks for antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE). Preprint. 2020: 1-24.
- Yip M, Leung H, Li P. Antibody-dependent enhancement of SARS coronavirus infection and its role in the pathogenesis of SARS. Hong Kong Med J. 2016; 22: 25-31.
- Xu J, Jia W, Wang P. Antibodies and vaccines against Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019; 8: 841-856.
- Wan Y, Shang J, Sun S. Molecular mechanism for antibody-dependent enhancement of coronavirus entry. J Virol. 2020; 94: 1-15.
- Peeples L. Avoiding pitfalls in the pursuit of a COVID-19 vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020; 117: 4-7.
- Shang W, Yang Y, Rao Y, Rao X. The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia calls for viral vaccines. NPJ Vaccines. 2020; 5: 18.
- Chen L, Xiong J, Bao L, Shi Y. Convalescent plasma as a potential therapy for COVID-19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020.