
Review Article
Austin Med Sci. 2024; 9(1): 1078.
A Comprehensive Review of Nano-Deposition Methods for the Preparation of Nano-Carriers: Polymers, Drugs, and Drug Release Models
Helia Heydarinasab; Vahid Haddadi-Asl*; Hanie Ahmadi
Department of Polymer Engineering and Color Technology, AmirKabir University of Technology, Iran
*Corresponding author: Vahid Haddadi-Asl, Department of Polymer Engineering and Color Technology, Amir Kabir University of Technology, P.O. Box 15875-4413, Tehran, Iran. Email: haddadi@aut.ac.ir
Received: October 07, 2024; Accepted: October 28, 2024 Published: November 04, 2024
Abstract
Controlled drug release has developed as a critical area of research in modern medicine and drug delivery, providing several clinical benefits such as increased efficiency and better targeting when compared to older techniques. A popular option for achieving controlled release is the creation of polymerdrug nano- or microcapsules, which can be created using a variety of synthetic processes and materials. This review aims to provide a detailed examination of the nano-deposition method used to create nano-carriers, focusing on the types of polymers and pharmaceuticals involved, as well as the numerous drug release models used. As the demand for effective drug delivery systems develops, nano-carriers have demonstrated significant promise due to their ability to improve bioavailability, increase therapeutic efficacy, and reduce side effects. This article will look at the mechanics underpinning nano-deposition, the criteria for picking polymers and pharmaceuticals, and how alternative drug release models affect the functionality of nano-carriers.
Keywords: NanoPrecipitation; Core-shell particle; Controlled drug release; Drug Release Models
Introduction
Numerous methods for producing nano and micro-particles have been documented in research, with nanoprecipitation being one of the most widely used techniques. This approach is also known as solvent displacement or interfacial precipitation. Introduced by Fessi and colleagues in 1989, nanoprecipitation has been adapted for encapsulating hydrophobic drug molecules. Various polymers, including biodegradable polyesters like polylactide, poly(lactide-coglycolide), and polycaprolactone, have been employed in this process. According to Fessi et al., the method begins by preparing solvent and nonsolvent phases, after which one phase is added to the other while gently stirring with a magnetic stirrer, as illustrated in Figure 1. As the organic solvent evaporates at room temperature, nanoparticles are generated. Subsequently, ultracentrifugation and freeze-drying can be used to ensure the complete removal of water [1].
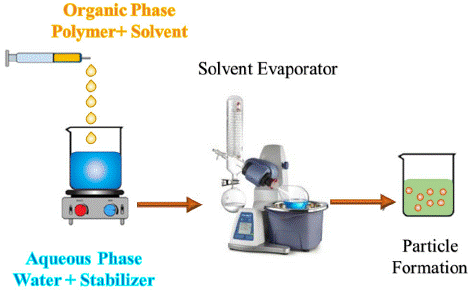
Figure 1: A schematic representation of the nano precipitation method.
Typically, the solvent phase consists of film-forming agents, one or more drug molecules, a lipophilic surfactant, and various organic solvents. The solvent and nonsolvent phases are commonly known as organic and aqueous phases. Film-forming agents can be natural, synthetic, or semi-synthetic polymers. Adding a surfactant to the formulation can help prevent the aggregation of nanoparticles. Surfactants can have a considerable impact on the properties of nanoparticles. The most frequently used solvents in the nanoprecipitation method include ethanol, acetone, hexane, methylene chloride, and dioxane. The aqueous or nonsolvent phase is generally water, though hydrophilic agents may also be incorporated into this phase. Adjustments in numerous parameters during this process can lead to significant changes in physical properties such as particle size and drug encapsulation efficiency [2].
Mechanism of Nanoparticle Formation
The precipitation of nanoparticles is based on the reduction of the solvent quality in which the main components are dissolved. The variables present in the solvent can be altered by changing the pH, the concentration of components, solubility conditions, or by adding a nonsolvent phase. Nonsolvent-based precipitation includes four stages: supersaturation of the sample, nucleation, growth, and aggregation. These stages are illustrated graphically in Figures 2.
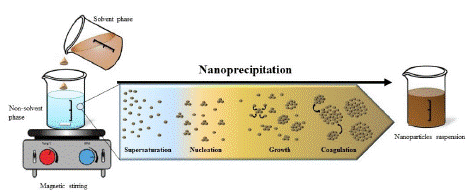
Figure 2: Precipitation mechanism illustrate [3].
Supersaturation occurs when the solution contains a solubility agent in excess of the amount specified in the saturation equation. In fact, the addition of a nonsolvent reduces the solvent's ability to dissolve the solubility agent, and in this case, the system is in a supersaturated state. The degree of supersaturation is represented as follows:
Where is the particle solubility ratio at the interaction boundary and is the bulk solubility. The degree of supersaturation can affect the final properties of the particles; thus, higher supersaturation reduces the particle size. After this stage, the nucleation phase begins to achieve thermodynamic stability. In fact, this phase starts when the saturation of the system reaches a critical level. In other words, to create a nucleus, the energy barrier (ΔG) must be overcome.
Where represents a constant, denotes the surface tension at the solid-liquid interface, is the molar volume of the solute, refers to Boltzmann's constant, and $ signifies the temperature. Local concentration fluctuations resulting from supersaturation lead to initial nucleation. Consequently, the particle size grows until it reaches a stable critical size that resists solubility. The nucleation phase persists until the growth of primary nuclei depletes the saturation. The nucleation rate (Nr) can be expressed using the following mathematical
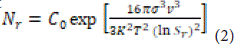
Where is a constant, represents the surface tension at the solid-liquid interface, denotes the molar volume of the solute, is Boltzmann's constant, and indicates the temperature. Local concentration fluctuations caused by supersaturation lead to initial nucleation. Consequently, particle size increases until it reaches a critical size that remains stable against solubility. The nucleation stage persists until the growth of primary nuclei disrupts saturation. The nucleation rate (Nr) can be determined using the following math
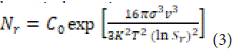
When the solute concentration decreases to the critical concentration of supersaturation, nucleation ceases, and the nucleus grows through compaction or coagulation. Aggregation involves the addition of individual molecules to the particle surface and occurs in two steps: a permeation step, in which the solute is transported from the bulk fluid through the solute boundary layer to the core surface, and a sedimentation step, during which the adsorbed solute molecules enter the core matrix. Aggregation stops when the concentration of unabsorbed solute drops to the saturation concentration. Additionally, the rate of shrinkage decreases with coagulation.
Conversely, coagulation refers to the process by which particles adhere to one another when the attractive forces surpass the repulsive forces. The key factor influencing the coagulation phase is the frequency of collisions, which is determined by the concentration, size, and movement of the particles. The term "collision efficiency" describes the number of collisions that lead to coagulation. To inhibit coagulation, a stabilizing agent is introduced during the preparation phase. These agents adhere to the surface of the particles, generating repulsive forces [2,6].
Core-Shell Particles
Core-shell particles, or capsules, are small particles that contain an active substance or core surrounded by a membrane made of a different material. These capsules protect the active ingredient from the external environment until the optimal release time. Materials can be released through various mechanisms, such as breaking, dissolving, melting, or penetrating the capsule wall, facilitated by heat, pressure, or the dissolution of the wall. Polymer encapsulation is a technique that traps solids, liquids, and even gases within a coating of polymer particles. These capsules find applications across various industries, including pharmaceuticals (for controlled drug release), food production, agriculture (for pesticides and fertilizers), and disinfectants for fugitive gases. Notably, nano- and microencapsulation methods have garnered significant attention in the field of drug delivery [7].
Among the most important purposes of encapsulation, the following can be mentioned:
• Preventing the destruction of materials;
• Increasing the storage time of materials;
• Stability against thermal sterilization;
• High biocompatibility;
Controlled release [8]
Methods of Producing Core-Shell Particles
The synthesis of core-shell structured particles is carried out through various methods, all of which involve continuous stirring. Initially, three immiscible chemical phases are formed; then, a polymer layer precipitates onto the core, and finally, this polymer layer hardens. One of these methods is the nano-precipitation method. In summary, the nano-precipitation method, also known as solvent displacement, is a simple two-step process that involves mixing an organic phase, consisting of a hydrophobic compound dissolved in a solvent, with an aqueous phase, consisting of emulsifiers soluble in ionized water, under magnetic stirring, followed by the evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure [9].
Factors Affecting Particle Size in the NanoPrecipitation Method
Mixing Speed
In the nano-precipitation method, increasing the mixing speed leads to a reduction in particle size. This reduction occurs due to the enhanced diffusion rate of the solvent into the reactant solution, which increases the homogeneity of the distribution and accelerates the formation of new nuclei. With increased nucleation and reduced particle growth, the final particle size decreases. In other words, higher mixing speeds result in better dispersion of solvent molecules and reduce the opportunity for further particle growth, resulting in smaller particles with a more uniform size distribution. This process improves the properties of nanoparticles, including higher specific surface area and greater chemical activity.
Organic Phase Flow Rate
In the nano-precipitation method, an increase in the flow rate of the organic phase can lead to larger particle sizes. This happens because a higher flow rate boosts the nucleation rate, resulting in more nuclei forming in a shorter period. With a greater number of nuclei, deposition reactions occur more quickly, and the resources needed for particle growth are distributed among a larger number of nuclei. Consequently, the growth rate of each particle increases, leading to a larger final particle size. Additionally, a higher organic phase flow may shorten the time required to reach equilibrium in the system and alter the dynamics of the reactions, further contributing to the formation of larger particles. This process can significantly impact the final properties of nanoparticles, including their dispersion and chemical reactivity.
The Ratio of Organic to Aqueous Phase
In the nano-precipitation method, the ratio of organic to aqueous phase has a nuanced impact on particle size. Initially, as this ratio increases, the concentration of polymer in the aqueous phase decreases, leading to smaller particle sizes due to a reduced availability of polymer molecules for nucleation. However, as the organic phase ratio continues to rise, the time required for organic solvent evaporation also increases, which accelerates the penetration of the miscible solvent into the aqueous phase. This enhanced solvent penetration creates better conditions for nucleation and particle growth. At a certain critical point, the solvent penetration becomes so rapid that the polymer precipitates prematurely, before complete particle formation. Consequently, the particle size initially decreases but then increases again with further increases in the organic phase ratio, as the extended evaporation time and increased solvent penetration create optimal conditions for additional particle growth. These variations can significantly influence the final properties of nanoparticles, including their size distribution and both physical and chemical characteristics.
Stabilizer Concentration
In the nano-precipitation method, increasing the stabilizer concentration has a dual effect on particle size. At first, a higher stabilizer concentration prevents the aggregation and accumulation of nanoparticles, as the stabilizer coats the particle surfaces, preventing them from sticking together. This results in smaller particles and a more uniform size distribution. However, as the stabilizer concentration continues to rise, the viscosity of the aqueous phase increases significantly. This heightened viscosity reduces shear stress in the system, which slows down the processes of droplet breakup and nucleation. Consequently, the particles have more opportunity to grow, leading to an increase in their size. These successive changes, from a decrease to an increase in particle size, highlight the complex and multi-faceted influence of stabilizer concentration on deposition dynamics and the final properties of nanoparticles.
Polymer Concentration
In the nano-precipitation method, increasing the polymer concentration leads to a direct increase in particle size. This size increase is primarily attributed to the rise in viscosity of the organic solution, which inhibits the movement of molecules and the formation of new nuclei as the solution becomes more concentrated. Higher viscosity hampers the uniform dispersion of molecules, favoring the growth of existing particles over the formation of new ones. Additionally, under these conditions, the nucleation process occurs less frequently, and the growth of existing particles accelerates due to limitations in droplet breakup and material diffusion. Consequently, the final particles become larger, and this change can significantly impact the final properties of nanoparticles, including their specific surface area and chemical reactivity.
Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Drug Encapsulation in Nanoparticles Obtained by the Nanoprecipitation Method
Polymer Concentration
In the nanoprecipitation method, increasing the polymer concentration enhances the efficiency of drug encapsulation due to the resulting increase in particle size. As the polymer concentration rises, the organic solution becomes more viscous, leading to the formation of larger particles. These larger particles provide more internal space to accommodate drug molecules, thereby increasing encapsulation capacity. Furthermore, larger particle sizes result in a reduced free surface area, which minimizes drug leakage from the particle surface and boosts overall encapsulation efficiency. This aspect is particularly crucial in drug delivery applications, as higher polymer concentrations and larger particle sizes can improve drug release control and enhance stability in biological environments, ultimately leading to greater therapeutic efficacy.
The Ratio of Organic to Aqueous Phase
In the nanoprecipitation method, increasing the volume of the aqueous phase results in a decrease in drug encapsulation efficiency. This reduction occurs because a larger aqueous phase leads to greater drug loss, as more of the drug dissolves in this phase rather than being encapsulated within the nanoparticles. Consequently, a portion of the drug that should be contained inside the nanoparticles is lost to the aqueous medium due to its higher solubility in that environment. This lowers the drug concentration in the organic phase, ultimately diminishing encapsulation efficiency. Additionally, a larger aqueous phase can disrupt the phase balance and prolong the evaporation time of solvents, further negatively impacting encapsulation efficiency. This decline in efficiency can adversely affect the performance of nanoparticles in drug delivery and release control, highlighting the need to optimize the ratio of aqueous to organic phases when designing drug delivery nanosystems.
Drug Concentration
In the nanoprecipitation method, increasing drug concentration can result in a decrease in drug encapsulation efficiency. As drug concentration rises, the amount of drug in the solution may surpass the polymer's capacity to encapsulate it. Polymers have a finite ability to incorporate drug molecules, and when the concentration is too high, not all drug molecules can be contained within the polymer matrix. Consequently, some of the drug remains in the aqueous or organic medium, leading to its exclusion from the encapsulation process. This not only reduces encapsulation efficiency but may also cause faster and uncontrolled release of the drug from the nanoparticles. Additionally, high drug concentrations can compromise system stability, resulting in particle aggregation and a decline in the overall effectiveness of the drug delivery system. Therefore, to ensure high encapsulation efficiency and optimize nanoparticle performance, it is essential to maintain a careful balance between drug concentration and the polymer's encapsulation capacity. Table 1 shows the factors affecting the particles resulting from NanoPrecipitation.
Result
Parameter
Change Made
Explanation
Size
Decrease
Mixing speed
Increase
Increasing the rate of solvent penetration
Increase
Organic phase flow rate
Increase
Increasing the rate of nucleation
Decrease then increase
The ratio of organic to aqueous phase
Increase
First, reducing the concentration of the polymer, followed by increasing the time required for the evaporation of the organic solvent, enhances the penetration of the miscible solvent in water. At a certain point, the penetration of the solvent into the aqueous phase accelerates to such an extent that the polymer suddenly precipitates before the formation of particles
Decrease then increase
Stabilizer concentration
Increase
First, prevent the interference of particles, and then reduce the shear stress to break the droplets, resulting from the increased viscosity of the aqueous phase
Increase
Polymer concentration
Increase
Increasing the viscosity of the organic solution
Increase
Molecular weight of the polymer
Increase
Increasing the viscosity of the organic solution
Increase
Polymer concentration
Increase
Increase in particle size
Drug encapsulation efficiency
Decrease
The ratio of organic to aqueous phase
Increasing the volume of the aqueous phase
Increasing drug loss in the aqueous phase occurs as a result of a higher amount of drug dissolved in that phase.
Decrease
Drug concentration
Increase
Exceeding the drug amount beyond the polymer's capacity to encapsulate it.
Table 1: Factors affecting particles resulting from nanoprecipitation [2-5].
Drug Release
Releasing a drug directly at the affected site can be more effective than administering higher doses orally. This method not only accelerates the onset of the drug's effects but also minimizes the side effects associated with traditional delivery methods. Controlled release provides several clinical advantages, including reduced dosing frequency, improved patient acceptability, targeted delivery to specific areas, and enhanced overall efficacy [10,11]. Core-shell systems are recognized as reliable carriers for controlled and targeted drug release due to their unique structures, high surface area, and the potential for surface modification and functionalization [12]. Ideally, a controlled release system should exhibit a zero-order release profile, indicating a constant release rate over time. The release of drugs from core-shell polymer nanoparticles occurs through two primary mechanisms:
1. Passive Penetration: This mechanism involves the release of molecules from the particle's surface, which occurs due to the washing effect on the outer wall as it hydrates.
2. Polymer Degradation: This mechanism entails a slower and more stable release of the drug from the inner part of the particle, occurring concurrently with polymer degradation.
Several factors influence the release profile, including the intrinsic properties of the polymer—such as molecular weight and crystallinity—the characteristics of the loaded drug, its activity and distribution, as well as the morphology, size, and porosity of the capsules. A crucial factor in determining the release profile is the size of the particles encapsulating the active molecules. Smaller particles, which have a larger surface-to-volume ratio, penetrate liquids more easily, leading to quicker degradation of the polymer substrate and improved drug release. The particle size is tailored to their intended application and loading capacity. Additionally, particle size distribution plays a significant role in controlling drug release, as it allows for precise management of drug distribution within the medium, facilitating faster breakdown and release rates, and thereby enhancing the cellular response mechanism [13].
Types of Drugs Investigated in the NanoPrecipitation Method
The nano deposition technique is predominantly employed for encapsulating hydrophobic molecules. Nevertheless, it has also shown promising outcomes with hydrophilic compounds. The majority of research on drug encapsulation has centered on substances with low water solubility or amphiphilic compounds, which can dissolve in both aqueous and organic solvents, particularly those that are soluble in water-miscible organic solvents.
Doxorubicin: Doxorubicin (DOX) is a prominent chemotherapeutic agent utilized in the treatment of various cancers, including breast, uterine, ovarian, lung, and cervical cancers. Recognized as an essential medicine by the WHO, its significance in cancer therapy is well-established [14]. However, the use of DOX is constrained by dose-dependent toxicity. Numerous studies have indicated the necessity for innovative drug delivery systems to reduce its cytotoxic effects in the treatment of malignant diseases. DOX is synthesized through chemical semi-synthesis from specific strains of Streptomyces coeruleorubidus or Streptomyces peucetius, which are part of the Streptomycetaceae family [15]. It is administered intravenously as DOX hydrochloride, with a composition of no less than 98% and no more than 102% of C27H29NO11•HCl, calculated on a solvent-free and anhydrous basis. As an anthracycline antibiotic, DOX was discovered in 1969 as a modified version of daunorubicin, which exhibited greater cardiac toxicity [16]. Serving as a prototype for anthracycline antibiotics, DOX is predominantly used in treating acute leukemias and lymphomas, as well as being effective against a range of solid tumors, including those of the breast, thyroid, ovary, bladder, lung, sarcomas, and neuroblastoma. In terms of its physical properties, DOX appears as an orange-red crystalline powder with a slight ethanolic odor, is hygroscopic, and is water-soluble, although it has only limited solubility in methanol [17-20].
The study of T.Yildiz introduces biodegradable and biocompatible polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) as theranostic agents for cancer, synthesized through nanoprecipitation using PLGA-PLL and PLAPEG blends. The NPs are capable of delivering doxorubicin-fluorescein B (Dox-FB) and exhibit fluorescence activation in the presence of proteolytic enzymes. They demonstrate low toxicity and high cytocompatibility, which enhances their suitability for both imaging and therapeutic applications. Future investigations will focus on their in vivo behavior and targeting abilities. Overall, these nanoparticles represent a promising advancement in cancer therapy(Figure 3) [18].
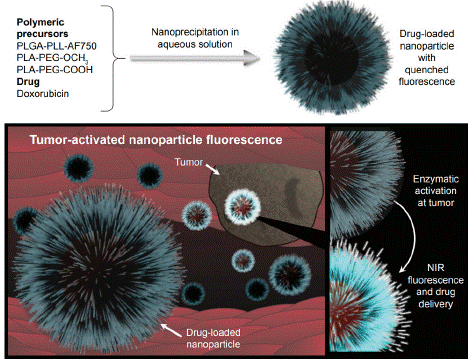
Figure 3: General structure of nanoparticles and their function as contrast
and therapeutic agents [18].
In the research of S. Pieper, doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles based on PLA and PLGA were synthesized using emulsion diffusion and solvent displacement methods, enabling the customization of particle size, loading efficiency, and drug release profiles. Experiments conducted on the neuroblastoma cell line UKF-NB-3 revealed that smaller nanoparticles with high drug loading achieved efficacy comparable to that of doxorubicin in solution. Notably, PLGAPEG nanoparticles produced via solvent displacement exhibited the smallest size and highest drug loading, resulting in significant anticancer effects. However, these formulations did not successfully overcome transporter-mediated drug efflux, indicating the necessity for further studies to develop drug carriers capable of circumventing this resistance mechanism [21].
Curcumin: Curcumin, a polyphenol extracted from turmeric, is recognized for its wide-ranging anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects when administered either orally or topically. In addition to its strong antioxidant properties at both neutral and acidic pH levels, curcumin operates through various mechanisms. These include the inhibition of multiple cell signaling pathways, modulation of enzymes such as cyclooxygenase and glutathione S-transferases, immune system modulation, and impacts on angiogenesis and cell adhesion. Its capacity to influence gene transcription and induce apoptosis in preclinical studies is particularly significant for cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy in clinical settings [22].
In 2019, Reddy and his team conducted research on core-shell liposomal nanoparticles loaded with acetyl curcumin, utilizing the electrospray method alongside the biocompatible polymer PLGA. They synthesized and examined the nanoparticles with a focus on controlled release characteristics. The findings indicated that the maximum drug release reached 48.5% after four days. Additionally, cytotoxicity studies were performed on human neck cancer cells, revealing that the nanoparticles facilitated a greater release of curcumin compared to the free drug. This enhanced release was attributed to the interactions between polar groups and the polarpolar interactions between the lipid components and curcumin [23].
In 2020, P .Bagher and his colleagues published a study titled "Biological Effects Induced by Streptococcus mutans Following Curcumin-PLGA Sonodynamic Antimicrobial Chemotherapy on Off-Target Cells." In their research, they prepared polymer-drug nanoparticles using the electrospray method, demonstrating their spherical and core-shell structures through SEM and TEM analyses. They measured the release profile of the nanoparticles, finding that 6-8% of the drug was released during the burst phase, with a total of 67% released over six days. Subsequently, they examined the impact of these nanoparticles on human gingival fibroblast cells, revealing an increase in the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes, while noting no significant effects on cell viability or DNA fragmentation [24].
In 2019, Mengqian and colleagues published a study titled "Antibacterial Activity and Improved Solubility of Curcumin by Encapsulation in PLGA Oil-Core Nanocapsules." In this research, they successfully developed curcumin nanocapsules using a modified nanoprecipitation method, achieving minimal size and uniform distribution. The study demonstrated that these nanocapsules enhanced the aqueous solubility of curcumin, indicating their potential for medical applications. The release profile of curcumin was examined over ten days, revealing an initial burst release of 31.92% within the first 24 hours, followed by a sustained release that reached 48.5%. These results suggested that curcumin nanocapsules can remain effective for ten days, potentially increasing patient compliance and lowering treatment costs. Additionally, the findings indicated that encapsulating curcumin in PLGA nanocapsules improved its antibacterial activity against the tested bacterial strains [25].
In 2020, Prabhuraj and his colleagues investigated the dual release of curcumin and niclosamide using PLGA nanoparticles to assess their therapeutic effects on breast cancer cells. The researchers employed a solvent transfer method with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as a stabilizer to prepare the nanoparticles. Their findings indicated that the PVA coating on the nanoparticles effectively prevented condensation and clumping, delaying sedimentation for up to two weeks. The study also examined the single and dual release profiles of the nanoparticles at pH levels of 6 and 7.4 over ten days, revealing a two-phase release pattern characterized by an initial burst followed by a sustained release. Notably, at pH 6, a higher drug release was observed compared to pH 7.4, attributed to the hydrolysis of the polymer in the acidic environment. Additionally, niclosamide exhibited a greater release than curcumin. Confocal microscopy and flow cytometry further confirmed the controlled release of curcumin. Overall, the results suggested that PLGA nanoparticles are capable of simultaneously loading two anticancer drugs, which may enhance drug solubility and therapeutic efficacy against breast cancer cells [9].
Heparin: Heparin is a Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) made up of repeating disaccharide units, specifically consisting of 1,4-linked uronic acids (either D-glucuronic acid (GlcA) or L-iduronic acid (IdoA)) and D-glucosamine (GlcN). This linear polysaccharide is distinguished by its high negative charge density, resulting from the presence of carboxylic and sulfonate groups. Heparin is synthesized in the body within the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus of mast cells located in connective tissues, such as those in the intestines, liver, and lungs, through a series of enzymatic reactions. Techniques such as Ehsan nanoprecipitation and emulsion/solvent evaporation can be employed to prepare heparin-based nanoparticles [26].
The study of N.E. Eleraky employed nanoprecipitation to create PLGA nanoparticles by dissolving enoxaparin in a solvent and rapidly mixing it with a non-solvent. It explored the hydrophobic ion pairing of enoxaparin with the cationic surfactant Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) to enhance its encapsulation within PLGA nanoparticles. This approach significantly increased the encapsulation efficiency of the hydrophilic anticoagulant, resulting in a threefold enhancement in gastrointestinal permeation compared to the free enoxaparin solution. Mechanistically, CTAB was found to diminish the paracellular barrier properties of the intestinal mucosa, thereby improving the transepithelial flux of the nanoparticles. Key advantages of this method include higher encapsulation efficiency, improved gastrointestinal permeation, enhanced drug delivery through reduced mucosal barriers, and promising outcomes that indicate the potential for a viable oral delivery system, ultimately improving patient acceptance and compliance [27].
Melatonin: Melatonin (MEL), also known as N-acetyl-5- methoxytryptamine, is a neurohormone primarily secreted by the pineal gland in the brain. It was first identified in the mid-20th century by dermatologist Aaron Lerner and his team. The term "melatonin" is derived from the prefix "mela-" (related to melanin) and the suffix "-tonin" (indicating its precursor, serotonin). As an indoleamine, melatonin is classified as a dietary supplement regulated by the FDA for the management of circadian rhythms. A deficiency in melatonin is linked to aging and various health disorders, and it plays a crucial role in addressing circadian rhythm disturbances, such as delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS). Furthermore, melatonin is recognized for its strong antioxidant properties, effectively neutralizing a range of free radicals [28,29]. The study of A.Farid developed melatoninloaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles (Mel- PLGA NPs) to provide protection against liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in male Sprague Dawley rats. These nanoparticles displayed smooth, spherical characteristics with sizes ranging from 87 to 96 nm and achieved an encapsulation efficiency of 59.9%. In vitro assessments revealed their antioxidant, antiinflammatory, and anticoagulant properties. In vivo results indicated that the nanoparticles significantly improved liver histopathology, normalized enzyme levels, and reduced inflammatory markers at an effective dose of 5 mg/kg. Overall, Mel-PLGA NPs demonstrated enhanced liver targeting, improved bioavailability, and restored liver function, offering significant protection against CCl4 toxicity with fewer adverse effects [30].
Types of Polymers Investigated in the NanoPrecipitation Method
Polylactic Acid (PLA): Polylactic Acid (PLA) is considered one of the most promising biopolymers due to its production from non-toxic, renewable resources. PLA has gained significance as a polymeric material for biomedical applications because of its favorable properties, including biocompatibility, biodegradability, mechanical strength, and ease of processing [42].
Researchers investigated the encapsulation of a hydrophilic drug (porphyrin) within hydrophobic Polylactic Acid (PLA) nanoparticles with varying crystallinity to examine their release behaviors. They employed a modified nanoprecipitation method to produce both homo and stereocomplexed PLA nanoparticles by adjusting the concentrations of the polymer and the ratios of solvents. The findings revealed that these modifications did not significantly affect the size or morphology of the nanoparticles. Stereocomplexed PLA nanoparticles demonstrated comparable entrapment efficiency to neat PLLA nanoparticles while offering a more sustained drug release profile. Furthermore, incorporating the drug-loaded nanoparticles into electrospun PLGA nanofibers led to a 50% reduction in the drug release rate after 24 hours compared to direct loading. Overall, slight adjustments in processing parameters effectively optimized drug release without impacting the properties of the drug or polymer [43].
N.Varga and his colleague encapsulated three drugs with varying hydrophilicity in poly-lactide (PLA) and Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles through ring-opening polymerization. They achieved a high entrapment efficiency of 90% for the lipophilic drug a-tocopherol (TP) in PLGA75 nanoparticles, compared to 69% in PLA. The study revealed that the synthesized PLGAs exhibited narrower weight distributions than commercial alternatives, enhancing the size distribution of the nanoparticles. Additionally, the selection of solvent and stabilizing agent had a significant impact on nanoparticle size and stability, with Pluronic F127 yielding the smallest nanoparticles [44]. Polycaprolactone) PCL): PCL is biodegradable but exhibits greater stability compared to polylactides due to having fewer ester bonds per monomer, resulting in a longer degradation time for PCL chain fragments to be enzymatically hydrolyzed in the body. The degradation process is influenced by factors such as molecular weight, shape, residual monomer content, and autocatalysis. Generally, complete degradation of PCL occurs over a period of 2 to 3 years in biological media characterized by constantly changing interstitial fluid [45].
The study of L.Kolluru focused on developing polymeric nanoparticles from Poly-ε-Caprolactone (PCL) and pluronic F108, which were loaded with the anticancer drug docetaxel and a nearinfrared dye (DiR) for tracking purposes in a breast cancer model. Utilizing a nanoprecipitation method, the nanoparticles were characterized in terms of size, zeta potential, drug entrapment efficiency, and release kinetics. In vitro experiments were conducted on BT-474 breast cancer cells to evaluate the anticancer efficacy of the nanoparticles and the role of pluronic F108 in enhancing cellular uptake. Near-infrared imaging was employed to assess the localization of the nanoparticles at the tumor site. The optimized nanoparticles exhibited a size range of 100–300 nm and demonstrated diffusion-mediated drug release. The results indicated an increased accumulation of the nanoparticles in vivo, highlighting their potential as an effective targeted drug delivery system for cancer treatment [46].
The study of R.Ca.Lino focused on developing Poly-ε- Caprolactone (PCL) nanoparticles for the encapsulation of β-carotene using the nanoprecipitation method. Researchers assessed various lipophilic surfactants and carrier agents, ultimately optimizing the formulation with Caprylic/Capric Triglycerides (CCT) and soybean lecithin. Through response surface methodology (RSM), they identified the optimal conditions for the nanocapsules as 0.216 mg/ mL of β-carotene, 232.42 μL of CCT, and 2.59 mg/mL of soy lecithin. The optimized nanoparticles demonstrated over 95% encapsulation efficiency, a particle size of less than 200 nm, and good colloidal stability. These results suggest their potential for effectively protecting β-carotene and facilitating controlled release in food systems [47].
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid): Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) is a highly recognized polymer that has been approved by both the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for use in medical applications, particularly as a drug carrier. PLGA is a biodegradable synthetic polymer that can be easily metabolized through the Krebs cycle. Its complete biocompatibility, high drug loading capacity, ability for site-specific drug targeting, and controlled drug release through regulated degradation time make it widely utilized in various drug delivery systems [31].
In the research by Mangrio et al. in 2017, focused on optimizing various parameters such as liquid flow rate and voltage to produce particles measuring 2 μm in size, achieving an encapsulation efficiency of 87% ± 5.6 and a loading efficiency of 11.7%. Figures 4(a) present an abstract image of these particles. The in vitro release studies demonstrated a stable release of artemether from the coreshell structure in comparison to artemether alone [32].
In 2017, Esmaili and colleagues conducted research aimed at preparing and characterizing electrosprayed nanoparticles for the encapsulation of curcumin. They investigated the effects of polymer solution concentration, solvent system type (chloroform/ dimethylformamide and acetonitrile/dimethylformamide), and applied voltage on the morphology, particle size, and curcumin release profile. The results revealed that increasing the voltage led to a decrease in particle size, while higher polymer concentration resulted in larger particles. Additionally, the average particle size using the chloroform/dimethylformamide solvent system was significantly smaller than that produced with the acetonitrile/dimethylformamide system, attributed to the high volatility of chloroform. The particles obtained from the chloroform/dimethylformamide system were predominantly spherical in shape, making this solvent system more favorable. Ultimately, due to its normal two-step release profile, this system was identified as an effective anti-inflammatory release mechanism for application in skin tissues [33].
In 2020, Ahmadi and colleagues studied the shear resistance and antibiofilm properties of modified orthodontic adhesive incorporating PLGA nanoparticles and curcumin. This research focused on optimizing electrospraying parameters, including voltage, solvent system, and distance between the needle and collector, which were set at 20 kV, chloroform/dimethylformamide, and 20 cm, respectively. The primary emphasis was placed on optimizing polymer concentration and flow rate. Based on the SEM images, a flow rate of 2 ml/h was determined to be optimal due to the production of spherical and fine particles. Although a flow rate of 1 ml/h yielded smaller particles at a lower polymer concentration, it resulted in a wider particle size distribution and reduced drug loading. Through the optimization of various process and material parameters, fine nanoparticles with spherical morphology, narrow size distribution, and an appropriate biphasic release profile (6-8% release in the first phase and 67% in the second phase) were successfully developed for application in orthodontic adhesives [34].
In 2021, Pourhaji Bagher and colleagues conducted a study on the potent photodynamic and antimicrobial effects of curcumin-poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles against COVID-19. Utilizing the electrospinning technique, they successfully produced spherical and core-shell PLGA-CUR particles with a yield of 87.6% and a loading efficiency of 8.42% (see Figure 4 (b). The presence of SARS-CoV-2 in plasma samples from patients suspected of having COVID-19 was confirmed, and these plasma samples were subsequently exposed to Vero cells along with PLGA-CUR nanoparticles and blue laser light. The effects on the treated cells were then assessed. The findings demonstrated that this treatment process exhibited anti-COVID-19 activity without causing toxicity to the cells [35].
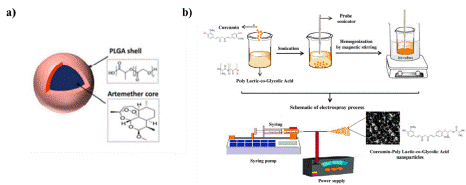
Figure 4: a) Artemether loaded PLGA-MPs [32] b) The schematic diagram
of Cur@PLGA-NLs synthesis [35].
In 2020, Kandili and colleagues conducted a study on the preparation of nanoparticles loaded with levetiracetam and carbamazepine using the nano deposition method. This approach relies on the complete miscibility of an organic solvent containing the polymer with water, leading to the precipitation of dissolved materials upon mixing the aqueous and organic phases. For this purpose, PLGA was chosen as the polymer, Pluronic F127 as the stabilizing agent, and acetone as the organic solvent. The resulting nanoparticles, which contained both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs at a targeted therapeutic dose, demonstrated sustained and prolonged drug release with fewer side effects and improved drug targeting due to enhanced penetration. The study investigated the anticonvulsant properties of the polymer particles containing the combination of Carbamazepine (CBZ) and Levetiracetam (LEV) in rabbits. A release profile for the CBZ nanoparticles was established, showing that the combination of these two drugs exhibited greater antiepileptic effects compared to CBZ and LEV alone. The release study revealed that CBZ displayed a biphasic release profile, characterized by an initial burst followed by sustained release, with 90% released within 2 days. In contrast, 80% of LEV was released within the first 30 minutes. Thus, the use of these nanoparticles may be beneficial for the treatment of epilepsy [36].
In 2014, Yalapo and colleagues published a study titled "Anticancer Activity of Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Curcumin in Prostate Cancer." Using the nano deposition method, they synthesized PLGA and curcumin nanoparticles and assessed their anticancer effects on both androgen-dependent and non-androgen-dependent prostate cancer cell models. The findings indicated that these nanoparticles effectively penetrate cancer cells and release curcumin within the cytosol, facilitating effective treatment. Additionally, cell proliferation studies demonstrated that the prepared nanoparticles inhibited the growth of cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro [37].
In 2019, Mojokoro and colleagues explored the combination and co-delivery of Methotrexate (MTX) and curcumin. They utilized the nano deposition method to prepare PLGA nanoparticles containing both drugs. The results demonstrated that the combination of chemotherapy with MTX and curcumin not only occurs within a safe treatment range but also reduces the dose-dependent toxicity of the drugs. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the combined treatment and co-delivery was observed at lower drug concentrations. The release profile indicated a sudden release of both curcumin and MTX on the 22nd day, likely due to the non-degradation of the carrier in water. Interestingly, despite relatively similar encapsulation efficiencies, the cumulative release of curcumin was lower than that of MTX in both formulations, which may be attributed to curcumin being encapsulated within the polymer matrix, resulting in a delayed release over time [25].
In 2020, Das and colleagues published a study titled "Chitosan- Decorated PLGA Core/Shell Nanoparticles Containing Flavonoids to Reduce Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer's Treatment." Curcumin is known for its significant oxidative stress reduction in Alzheimer's disease treatment; however, it suffers from low solubility and bioavailability. To address this issue, curcumin and PLGA nanoparticles were prepared using the nano deposition method and functionalized with chitosan. The presence of the chitosan coating on the particles enhanced the release of curcumin [38].
In 2015, Klipstein et al. conducted a study on curcumin-loaded PEG-functionalized PLGA nanocapsules for intracorporeal colon therapy. Building on previous research, the authors prepared these nanocapsules using the nano deposition process. The results indicated that the nanocapsules exhibited higher loading efficiency compared to the empty drug and demonstrated improved cellular penetration, enhancing therapeutic activity. The release of curcumin from the nanocapsules was evaluated over 24 hours both in the presence and absence of serum. Curcumin dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide served as a control for 100% release. The study observed an initial burst release of 50% within the first 30 minutes and 100% by 4 hours. Notably, the presence of serum did not alter the release profile; however, it significantly increased drug release at all time points. After 24 hours, approximately 66% of the drug was released from the nanocapsules without serum, while 80% was released in the presence of serum, indicating a stable release profile throughout the study [39].
In 2019, Xie and colleagues explored curcumin-loaded nanoparticles coated with red blood cell membranes to enhance chemotherapy. In this study, porous PLGA nanoparticles containing curcumin were prepared using the nano deposition method, and their surfaces were coated with the red blood cell membrane to improve biological efficacy. In vitro results indicated that drug release from non-porous nanoparticles was slow, with most of the drug remaining trapped within the nanoparticles. In contrast, the release from porous nanoparticles was significantly accelerated, and with the membrane coating, they exhibited a stable release profile over 48 hours. This approach facilitates cancer treatment while minimizing side effects [40].
In 2015, Yan and colleagues conducted research on the targeted release of nanomedicine for prostate cancer treatment. By encapsulating two drugs, docetaxel and curcumin, they aimed to create a beneficial synergistic effect for cancer therapy. The study focused on preparing polymer-fat hybrid nanoparticles to encapsulate these drugs using the nano precipitation method. The evaluation of the nanoparticles included assessments of particle size, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, and drug release. Cytotoxicity was also tested on PC3 prostate tumor cells. The nanoparticles exhibited an average size of approximately 169.9 nm and a zeta potential of 35.7 mV. In vitro tests demonstrated that these nanoparticles had a significant cytotoxic effect with minimal side effects. The novel drug release methods developed in this study greatly facilitated the dual delivery of drugs to cancer cells. The researchers noted that several factors, including the physicochemical properties of the encapsulated drugs and the interactions between the drugs and the core materials, influenced the release patterns. Overall, the release profiles indicated that these polymer-fat hybrid nanoparticles exhibited more stable behavior compared to polymer-only nanoparticles, likely due to the lipid surface that hinders the release of the core material. Additionally, the drug release from capsules containing a single drug was found to be similar to that from those containing two drugs [41].
Principles of Drug Release Kinetics
Noyes-Whitney Law: The estimation of drug release kinetics using the main Noyes-Whitney rule was proposed in 1897 in the form of the following equation [48]:
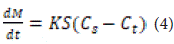
where M is the mass transferred over time by dissolution from the particle surface S, influenced by the dominant stimulus concentration. In the expression in parentheses, Cs is the concentration at equilibrium dissolved at the experimental temperature, and Ct is the concentration at time t. The unit of the solubility rate
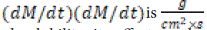
Nernest-Brunner film theory: “Nernest and Bruner established a relationship between the constant in equation 1-12 and the soluble diffusion coefficient, as described by Fick's diffusion law”.

“Where D is the penetration coefficient, γ is the volume of the solvent, and h is the thickness of the layer through which penetration occurs. In their relationship, Nernst and Bruner assumed that the concentration gradient in the solvent layer adjacent to the material surface is linear. In this context, changes in the surface during the dissolution time of the drug were not taken into account”.
Kinetic Modeling of Release
It has always been desirable to use models that can predict the functioning of the system in the body’s environment. For this reason, most initial drug release tests are performed in vitro. The methods for detecting release kinetics are divided into three general categories:
• Statistical methods: data analysis methods, repeated measurement design, multiple deviations approach;
• Model-dependent methods: zero order, first order, Higuchi, etc.;
• Model-independent methods: difference factor, similarity factor.
Model-Dependent Methods
These methods are based on various mathematical equations that explain the dissolution curve. Once the appropriate equation is selected, the dissolution behavior is estimated based on the parameters derived from the model.
Zero Order Model: The dissolution of the drug from a substance that maintains its structure while slowly releasing the drug is described by the following equation [49]:
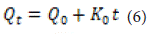
Where is the amount of dissolved drug at time t, is the initial amount of the drug in the solvent (which is often zero), and is the zero-order release constant with units of concentration per time.
First Order Model: This model is used to describe drug absorption or elimination; however, the theory behind this model cannot be easily explained [50,51].
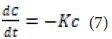
Where K is the first-order velocity constant with units of concentration per time. Equation 1-15 can be written as follows:
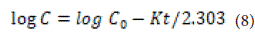
Where C0 is the initial concentration of the drug and K is the firstorder rate constant. The slope obtained at the end of Equation 16-1 results from plotting the experimental data of the drug remaining in the environment as a function of time in logarithmic form. The given equation is applicable when the drug is dissolved in water and the scaffold is porous.
Higuchi Model: In 1961, Higuchi developed the first mathematical model of drug release from a bed. This model was originally formulated for smooth surfaces, although the possibility of calculating more complex geometries and porous surfaces was later incorporated. The assumptions of this model are as follows [50,52]:
• The initial concentration of the drug in the environment is much higher than the solubility of the drug;
• Drug penetration is unidirectional;
• The drug particles are much smaller than the thickness of the surface through which penetration occurs;
• The bed does not dissolve and does not swell;
• Drug penetration is continuous;
• The submerged state of the bed always prevails.
According to these assumptions, the model is described by the following equation:
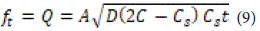
Where Q is the amount of drug released at time t per surface area A, C is the initial concentration of the drug, Cs is the solubility of the drug in the medium of the bed, and DD is the permeability (permeation coefficient) of the drug molecules in the bed. This equation is valid as long as the drug remains in the bed. When solubility occurs from a non-uniform bed system, and the concentration of the drug in the bed is less than its solubility, with penetration occurring through pores, the equation is as follows:
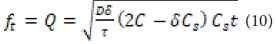
Where D is the penetration coefficient of drug molecules in the solvent, d is the porosity of the substrate, and t is the non-uniformity of the substrate. Non-uniformity is defined based on the diameters and branching directions of pores and bed channels. It is possible to isolate the term before time in Equation 18-1 to obtain the simplified Higuchi equation:
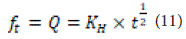
Where KH is Higuchi's solubility constant. The data obtained from drug release should be plotted against the square root of time. This equation is applicable when the drug is dissolved in water and the substrate is in the form of tablets or plates.
Hixson Crowell Model: In 1931, Hickson and Crowell discovered that the surface area of a particle is related to the cube root of its volume [53]:
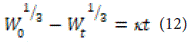
Where is the initial amount of the drug, is the remaining amount of the drug at time t t, and kk is the surface-tovolume constant. Equation 20-1 describes the release from a system where the surface area and volume of the tablet or particle are variable. By plotting the cube root of the percentage of the remaining drug against time, the release kinetics can be described. This model can be used if the drug release occurs from the surface and from parallel planes, with its geometric dimensions maintained by dissolving the tablet or particle.
Korsmeyer-Peppas Model and Its Modification: In 1983, Korsmeyer and his colleagues presented a simple relationship that can be used to estimate drug release from polymeric systems. Initially, 60% of the drug release data was fitted to the following equation [54,55]:
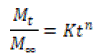
Where the expression on the left represents the fraction of drug released at time tt, KK is the release rate constant, and nn is the release index. Cylindrical beds exhibit different release characteristics. By adding the variable bb to Equation 1-21, the Korsmeyer-Peppas correction model is obtained, which provides a description of the path of drug penetration in the carrier by taking into account the width from the origin of the release profile.
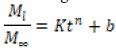
For cylindrical tablets, when nn is greater than 0.45, the Fickian penetration mechanism is observed. For nn between 0.45 and 0.89, a non-Fickian transition occurs. When nn equals 0.89, it indicates a second case transition (relaxation transition), and for nn greater than 0.89, the transmission of two cases is dominant. To determine nn, you should avoid using values from the graph when the expression on the left side of the equation is less than 0.6.
Baker-Lonsdale Model
In 1974, Baker and Lonsdale expanded on the Higuchi model and presented the drug release from a spherical bed as follows [56]:
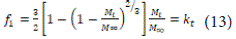
Where kk is the release rate constant, obtained from the slope of the graph. To study the kinetics of release, the in vitro data are plotted as the inverse of the square of time. This equation can be used to linearize the release data from microcapsules and microspheres.
Weibull Model
This model is used to describe different types of solubilities [57]:
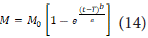
Where M is the amount of drug dissolved over time, is the total amount of drug released, T is the delay time in dissolution, parameter a is related to time, and parameter b is related to the shape of the solubility curve. For b=1, the shape of the curve matches that of the exponential function, where k=a1.
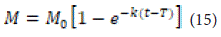
If b is greater than 1, the shape of the curve changes to a C or S shape and exhibits a turning point. For b less than 1, the slope of the curve is steeper than when b equals 1.
The time related to the release of 50% and 90% of the drug for each formulation can be obtained using the inverse function of the Weibull equation:
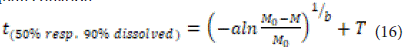
The Weibull model is particularly applicable when studying the release behavior of drug-carrying beds.
Hopfenberg Model
Hopfenberg presented a mathematical model to describe drug release from erosion-surface polymers, under the condition that the area remains constant during erosion. The fraction of the total drug released at time tt is given by the following equation [58]:
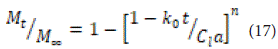
where k0 is the zero-order rate constant that describes polymer destruction (surface erosion). The initial loading of the drug in the system is indicated by CL , the half-thickness of the system (for example, the radius of the sphere or cylinder) is indicated by a, and the variable representing the system geometry is indicated by n. This model is used to determine the release mechanism of optimized organic spheres using data obtained from the composite profile. Additionally, one of the features of this model is its ability to depict the kinetics of two-phase release in a specific context.
Gompertz Model
Typically, the in vitro solubility curve is described by a simpler exponential model known as the Gompertz model:
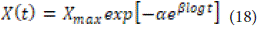
In this equation, the expression on the left represents the percentage dissolved at time tt divided by one hundred, while the first expression on the right indicates the maximum solubility. The undissolved fraction at time t=1 is determined by a (the location or degree parameter), and the solubility rate over time is determined by β (the shape parameter). This model exhibits a steep slope at the beginning and then gradually approaches the assumed maximum solubility value. Additionally, it is effective in comparing the release profiles of drugs that have good solubility and medium release speed.
Conclusion
Currently, targeted drug delivery is a critical field of research in the pharmaceutical industry. Traditional therapies, whether given orally or by injection, frequently fail to produce regulated release of therapeutic molecules, resulting in rapid drug release and absorption. Furthermore, the short half-life of many of these compounds results in a rapid loss of biological activity upon implantation or rapid clearance by the body's metabolic processes. Molecular therapy is frequently administered in large dosages repeatedly to address this problem, which can lead to unpredictable variations in drug concentration, raise costs, and perhaps cause consequences for cells and tissues. In conclusion, this review includes a complete examination of the nano-deposition process for the manufacturing of nano-carriers, highlighting the different types of polymers and pharmaceuticals used, as well as the numerous drug release models used. As the demand for effective drug delivery methods grows, nano-carriers have emerged as a promising approach for increasing bioavailability, boosting therapeutic efficacy, and lowering side effects. This paper investigated the mechanics of nano-deposition, the criteria for selecting appropriate polymers and pharmaceuticals, and the impact of various drug release models on the performance of nano-carriers, highlighting their potential for enhancing drug delivery systems.
References
- Martínez Rivas CJ, Tarhini M, Badri W, Miladi K, Geige-Gerges H, Nazari QA, et al. Nanoprecipitation process: From encapsulation to drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2017; 532: 66-81.
- Luque-Alcaraz AG, Lizardi-Mendoza J, Goycoolea FM, Higuera-Ciapara I, Argüelles-Monal W. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation and their ability as a drug nanocarrier. RSC Adv. 2016; 6: 59250–59256.
- Madani F, Esnaashari SS, Mujokoro B, Dorkoosh F, Khosravani M, Adabi M. Investigation of Effective Parameters on Size of Paclitaxel Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Adv Pharm Bull. 2018; 8: 77-84.
- Beck-Broichsitter M. Solvent impact on polymer nanoparticles prepared nanoprecipitation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng Asp. 2021; 625: 126928.
- Miladi K, Sfar S, Fessi H, Elaissari A. Polymer Nanoparticles for Nanomedicines. 2016.
- Lammari N, Louaer O, Meniai AH, Elaissari A. Encapsulation of Essential Oils via Nanoprecipitation Process: Overview, Progress, Challenges and Prospects. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12: 431.
- Khatami M, Alijani H, Nejad M, Varma R. Core@shell Nanoparticles: Greener Synthesis Using Natural Plant Products. Appl Sci. 2018; 8: 411.
- Kumari A, Singla S, Guliani A, Yadav SK. Nanoencapsulation for drug delivery. EXCLI J. 2014; 3: 265-86.
- Prabhuraj RS, Bomb K, Srivastava R, Bandyopadhyaya R. Dual drug delivery of curcumin and niclosamide using PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic effect on breast cancer cells. J Polym Res. 2020; 27: 133.
- Boughton E, Mclennan SV. Biomimetic scaffolds for skin tissue and wound repair. Biomimetic Biomaterials Elsevier. 2013: 153–180.
- Baghersad S, Hajir Bahrami S, Mohammadi MR, Mojtahedi MSM, Milan PB. Development of biodegradable electrospun gelatin/aloe-vera/ poly(e-caprolactone) hybrid nanofibrous scaffold for application as skin substitutes. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018; 93: 367–379.
- Kumar R, Mondal K, Panda PK, Kaushik A, Abolhassani R, Auja R, et al. Core–shell nanostructures: perspectives towards drug delivery applications. J Mater Chem B. 2020; 8: 8992-9027.
- Castro Coelho S, Nogueiro Estevinho B, Rocha F. Encapsulation in food industry with emerging electrohydrodynamic techniques: Electrospinning and electrospraying – A review. Food Chem. 2021; 339: 127850.
- Vyas M, Simbo DA, Mursalin M, Mishra V, Bashary R, Khatik GL. Drug Delivery Approaches for Doxorubicin in the Management of Cancers. Curr Cancer Ther Rev. 2019; 16: 320-331.
- Du Y, Xia L, Jo A, Davis RM, Bissel P, Ehrich MF, et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Doxorubicin-Loaded Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2018; 29: 420–430.
- Carvalho C, Santos RX, Cardoso S, Correia S, Oliveira PJ, Santos MS, et al. Doxorubicin: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly Effect. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16: 3267-3285.
- Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR. Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013; 65: 157-170.
- Yildiz T, Gu R, Zauscher S, Betancourt T. Doxorubicin-loaded proteaseactivated near-infrared fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles for imaging and therapy of cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018; 13: 6961–6986.
- Kciuk M, et al. Doxorubicin—An Agent with Multiple Mechanisms of Anticancer Activity. Cells. 2023; 12: 26-32.
- Betancourt T, Brown B, Brannon-Peppas L. Doxorubicin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation: Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Nanomedicine. 2007; 2: 219-232.
- Pieper S, Onafuye H, Mulac D, Cinatl J, Wass MN, Michaelis M, et al. Incorporation of doxorubicin in different polymer nanoparticles and their anticancer activity. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2019; 10: 2062-2072.
- Sharma RA, Gescher AJ, Steward WP. Curcumin: The story so far. Eur J Cancer. 2005; 41: 1955-1968.
- Reddy AS, Lakshmi BA, Kim S, Kim K. Synthesis and characterization of acetyl curcumin-loaded core/shell liposome nanoparticles via an electrospray process for drug delivery, and theranostic applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019; 142: 518-530.
- Pourhajibagher M, Ahmadi H, Roshan Z, Bahador A. Streptococcus mutans bystander-induced bioeffects following sonodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy through sonocatalytic performance of Curcumin-Poly (Lacticco- Glycolic Acid) on off-target cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020; 32: 102022.
- Gao M, Long X, Du J, Teng M, Zhang W, Wang Y, et al. Enhanced curcumin solubility and antibacterial activity by encapsulation in PLGA oily core nanocapsules Food Funct. 2020; 11: 448-455.
- Zare EN, Khorsandi D, Zarepour A, Yilmaz H, Agarwal T, Hooshmand S, et al. Biomedical applications of engineered heparin-based materials. Bioact Mater. 2023; 31: 87–118.
- Eleraky NE, Swarnakar NK, Mohamed DF, Attia MA, Pauletti GM. Permeation-Enhancing Nanoparticle Formulation to Enable Oral Absorption of Enoxaparin. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2020: 21.
- Romeo A, Kazsoki A, Musumeci T, Zelkó R. A Clinical, Pharmacological, and Formulation Evaluation of Melatonin in the Treatment of Ocular Disorders—A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25: 3999.
- Ashfaq R, Rasul A, Asghar S, Kovács A, Berkó S, Budai-Szucs M. Lipid Nanoparticles: An Effective Tool to Improve the Bioavailability of Nutraceuticals. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24: 15764.
- Farid A, Michael V, Safwat G. Melatonin loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles reduce inflammation, inhibit apoptosis and protect rat’s liver from the hazardous effects of CCL4. Sci Rep. 2023; 13: 16424.
- Roshan Z, Haddadi-Asl V, Ahmadi H, Moussaei M. Curcumin-Encapsulated Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles: A Comparison of Drug Release Kinetics from Particles Prepared via Electrospray and Nanoprecipitation. Macromol Mater Eng. 2024; 309: 1-12.
- Mangrio FA, Dwivedi P, Han S, Zhao G, Gao D, Si T, et al. Characteristics of Artemether-Loaded Poly (lactic- co -glycolic) Acid Microparticles Fabricated by Coaxial Electrospray: Validation of Enhanced Encapsulation Efficiency and Bioavailability. Mol Pharm. 2017; 14: 4725-4733.
- Esmaili Z, Bayrami S, Dorkoosh FA, Javar HA, Seyedjafari E, Zargarian SS,
et al. Development and characterization of electrosprayed nanoparticles for
encapsulation of
C urcumin. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2018; 106: 285-292. - Ahmadi H, Haddadi-Asl V, Ghafari HA, Ghorbanzadeh R, Mazlum Y, Bahador A. Shear bond strength, adhesive remnant index, and anti-biofilm effects of a photoexcited modified orthodontic adhesive containing curcumin doped poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles: An ex-vivo biofilm model of S. mutans on the enamel slab bonded bra. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020; 30: 101674.
- Pourhajibagher M, Azimi M, Haddadi-Asl V, Ahmadi H, Ghorbanzadeh R, Mazlum Y, et al. Robust antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with curcuminpoly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles against COVID-19: A preliminary in vitro study in Vero cell line as a model. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021; 34: 102286.
- Kandilli B, Kaplan ABU, Cetin M, Taspinar N, Ertugrul MS, Aydin IC, et al. Carbamazepine and levetiracetam-loaded PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation method: in vitro and in vivo studies. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020; 46: 1063-1072.
- Yallapu MM, Khan S, Maher DM, Ebeling MC, Sundram V, Chauhan N, et al. Anti-cancer activity of curcumin loaded nanoparticles in prostate cancer. Biomaterials. 2014; 35: 8635-8648.
- Dhas N, Mehta T. Intranasal delivery of chitosan decorated PLGA core /shell nanoparticles containing flavonoid to reduce oxidative stress in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2021; 61: 102242.
- Klippstein R, Wang JTW, El-Gogary RI, Bai J, Mustafa F, Rubio N, et al. Passively Targeted Curcumin-Loaded PEGylated PLGA Nanocapsules for Colon Cancer Therapy In Vivo. Small. 2015; 11: 4704-4722.
- Xie X, Wang H, Williams GR, Yang Y, Zheng Y, Wu J, et al. Erythrocyte Membrane Cloaked Curcumin-Loaded Nanoparticles for Enhanced Chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11: 429.
- Hong Y, Li Y, Yin Y, Li D, Zou G. Electrohydrodynamic atomization of quasimonodisperse drug-loaded spherical/wrinkled microparticles. J Aerosol Sci. 2008; 39: 525-536.
- Singhvi MS, Zinjarde SS, Gokhale DV. Polylactic acid: synthesis and biomedical applications. J Appl Microbiol. 2019; 127: 1612-1626.
- Forouharshad M, Ajalloueian F. Tunable self-assembled stereocomplexedpolylactic acid nanoparticles as a drug carrier. Polym Adv Technol. 2022; 33: 246-253.
- Varga N, Hornok V, Janovák L, Dékány I, Csapó E. The effect of synthesis conditions and tunable hydrophilicity on the drug encapsulation capability of PLA and PLGA nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 2019; 176: 212-218.
- Malikmammadov E, Tanir TE, Kiziltay A, Hasirci V, Hasirci N. PCL and PCLbased materials in biomedical applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018; 29: 863-893.
- Kolluru LP, Chandran T, Shastri PN, Rizvi SAA, D’Souza M. Development and evaluation of polycaprolactone based docetaxel nanoparticle formulation for targeted breast cancer therapy. J Nanoparticle Res. 2020: 22.
- Lino RC, et al. Development and Characterization of Poly-e- caprolactone Nanocapsules Containing β-carotene Using the Nanoprecipitation Method and Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. Brazilian Arch Biol Technol. 2020: 63.
- Cogswell S, Berger S, Waterhouse D, Bally MB, Wasan EK. A parenteral econazole formulation using a novel micelle-to-liposome transfer method: In vitro characterization and tumor growth delay in a breast cancer xenograft model. Pharm Res. 2006; 23: 2575-2585.
- Elmas A, Akyuz G, Bergal A, Andac M, Andac O. Mathematical Modelling of Drug Release. 2020.
- Dash S, Murthy PN, Nath L, Chowdhury P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. - Drug Res. 2010; 67: 217–223.
- Atif R, Salah Eldeen T, Ahmed L, Yahya I, Omara A, Eltayeb M. Study the Using of Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery System Based on Mathematical Models for Controlled Release. Int J Latest Technol Eng. 2019; 8: 52-56.
- Trucillo P. Drug Carriers: A Review on the Most Used Mathematical Models for Drug Release. 2022; 10: 1094.
- Rehman Q, Akash MSH, Rasool MF, Rehman K. Role of Kinetic Models in Drug Stability,” in Drug Stability and Chemical Kinetics, Singapore: Springer Singapore. 2020: 155–165.
- Talevi A, Ruiz ME. Korsmeyer-Peppas, Peppas-Sahlin, and Brazel-Peppas: Models of Drug Release, in The ADME Encyclopedia, Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2022: 613–621.
- Permanadewi I, Kumoro AC, Wardhani DH, Aryanti N. Modelling of controlled drug release in gastrointestinal tract simulation. J Phys Conf Ser. 2019; 1295: 012063.
- Talevi, Ruiz ME. Baker-Lonsdale Model of Drug Release, in The ADME Encyclopedia, Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2022: 95–101.
- Papadopoulou V, Kosmidis K, Vlachou M, Macheras P. On the use of the Weibull function for the discernment of drug release mechanisms. Int J Pharm. 2006; 309: 44-50.
- Siepmann J, Siepmann F. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2008; 364: 328-343.