
Editorial
Austin J Musculoskelet Disord. 2017; 4(1): 1042.
What is Deficiency or Inadequency of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D? - How does it Harm Healthy Individuals Physically and Mentally?
Okuyama K1*, Miyakoshi N², Sasaki H¹, Tajimi K¹, Kawamura Y³ and Shimada Y²
¹Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Akita Rosai Hospital, Japan
²Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Akita University School of Medicine, Japan
³Department of Clinical Laboratory, Akita Rosai Hospital, Japan
*Corresponding author: Okuyama K, Editorial Board of Austin Journal of Musculoskeletal Disorders, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Akita Rosai Hospital, Karuizawa Aza Shimotai 30, Odate, Japan
Received: February 02, 2017; Accepted: February 07, 2017; Published: February 09, 2017
Keywords
25-Hydroxyvitamin D; Employed Worker; Latitude 40° North Area; Health Status; Depression
Abbreviations
25[OH]D: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; PTH: Parathyroid Hormone; NIH: National Institute of Health; SF-36Ver 2®: Medical Outcome Study Short-Form 36-Health SurveyVersion 2; GH: General Health; MC: Mental Component; VDR: Vitamin D Nuclear Receptor
A Letter to Dr. Mark R
Vitamin D or cholecalciferol is a collective structurally related to metabolites obtained from dietary foods, supplements and sunlight. The importance of vitamin D is well recognized in the skeleton. It regulates calcium and phosphorus level in the blood by promoting their absorption from the intestine, and also stimulates bone formation and mineralization. The article titled “Vitamin D and Cartilage: Does Vitamin D Influence Cartilage Integrity?” by Dr. Marks R is very timely and insightful [1]. Detailed mechanism between the articular cartilage of the joint and vitamin D was discussed in his article. As I’ m actually engaged in a lot of operations for degenerative disorders of the joint and the spine as an orthopedic surgeon, the potential links, proposed by Dr. Marks R, between the impact of vitamin D insufficiency and osteoarthritis sounds very intriguing [1].
The potential links are following.
- Articular cartilage dysfunction
- Bone dysfunction
- Cardiovascular comorbidities
- Depression
- Falls + fractures
- Inflammation
- Neurological problems
- Muscle dysfunction
- Obesity
- Poor health status
- Sensory dysfunction
Need for the further research of vitamin D function in the human body is mentioned in his discussion. I also guess that there are lots of unknown aspects of vitamin D in the human body. Especially, relationship with falls, muscle dysfunction, neurological impairment, depression, poor health status, the incidence of colo-rectal and breast cancer, the exacerbation of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so forth should be disclosed in the near future. Now a days, these are being hot topics of researches in the whole world for the last decade.
25[OH]D is a stable form of vitamin D metabolized in the liver. Therefore, serum 25[OH]D concentrations currently becomes a hot interest in light of the bone and muscle metabolism as an indicator of vitamin D in human body.In the field of orthopedics, the threshold of insufficient serum 25[OH]D concentrations is determined by PTH reflection point of the relationship between serum PTH and 25(OH)D concentrations, and clinically identified as one of the risk factors which related to osteopenia and/or sarcopenia. Osteopenia and/or sarcopenia secondarily lead to hip and spinal vertebral fracture caused even by minor falls, and they finally result in disused syndrome or mortality in the elderly generations [2]. Vitamin D may play a key role to prevent from falls directly or indirectly in the elderly generations although the mechanism is still controversial [3]. In 2008, Suzuki et al. proposed that the serum 25[OH]D concentrations below 20ng/mL was a threshold of falls in the Japanese elderly generations (≧65yrs). As a positive study which supports vitamin D is associated with prevention from falls, in vitro, our colleagues, Miyakoshi and Sasaki have demonstrated that a vitamin D analog, alfacalcidol had an effect of strengthening muscle tonus in the rats [4].
The proportion of elderly people has been increasing in our globe. Out of all the advanced countries, Japan, in terms of the aging society phenomenon, is at the center of this problem. As of 2014, the rate of people over 65 years and 75 years is 25.7% and 12.5%, respectively in Japan. Moreover, the rate of people over 65 years is rapidly increasing and estimated to rise to 33.4% by 2034. This is unsurprising data, and one we must confront. Undoubtedly, the current situation of Japan is bound to develop in other countries in the near future [5].
In the western developed countries, especially in the United States, influence of 25[OH]D deficiency, insufficiency and Inadequency on the individual health is very concerned. What is deficiency, insufficiency and Inadequency of vitamin D?NIH, World Health Organization, Institute of Medicine, Centre for Disease Control and other organizations has suggested risks caused by lack of 25[OH]D. In particular, NIH has clearly proposed a guideline for the serum 25[OH]D concentrations (Table 1) [7]. On contrary to the United States there is no objective proposal of the normal or healthy range of the serum 25[OH]D concentrations from the medical associations in Japan. Dawson-Hughes B et al. have reported that 90% of Japanese and Korean population have serum 25[OH]D concentrations below 30ng/mL of which level is defined as a threshold off alls [6]. The guideline proposed by NIH is really available for Asian including Japanese? There may exist an ethnic difference of serum 25[OH]D concentrations in the healthy individuals.
nmol/L
ng/mL
Health status
<30
<12
Associated with vitamin D deficiency, leading to rickets
in infants and children and osteomalacia in adults
30 to <50
12 to <20
Generally considered inadequate for bone and overall health in healthy individuals
≥50
≥20
Generally considered adequate for bone and overall health
in healthy individuals
>125
>50
Emerging evidence links potential adverse effects to such
high levels, particularly >150 nmol/L (>60 ng/mL)
Table 1: Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentrations and health proposed by NIH [7].
Survey of Serum 25[OH]D Concentrations in Healthy Employed Workers at Latitude 40°Northin Japan
From November 2015 1st to August31st, 2016 in Odate, Japan. In our institute, the serum concentrations of 25[OH]D were investigated in the healthy employees, who mainly worked indoors. Geographically, Odate is located at approximately latitude 40° north. Odate annually has the shortest time of solar exposure in Japan. Three hundred and ten participants (Men 195, Women 63) were randomly scrutinized from the 1452 employed workers. Their mean age was 39.9±19.9 (mean ± standard deviation). Serum 25[OH]D2 and 25[OH]D3 were sampled in the all participants. The associations between serum concentration of 25[OH]D and health status including depressive mood, backache and so forth are being analyzed. The significance of difference was analysed by the Mann-Whitney U test (P<0.05= significant).
A Preliminary Result
Serum concentrations of 25[OH]D2 was below the limitation of detecting (<4ng/mL). The mean value of the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations was 15.1±6.9 ng/ml (Men ; 15.0±6.8 ng/ml, Women ; 13.5±6.4 ng/ml). There was no significant difference in the mean value of the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations between men and women (p<0.121). In the winter season, the mean value of the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations (13.6±6.9 ng/ml, n=155, from November 1st to March 30th) was significantly lower than that in the summer season (16.2±6.1 ng/ml, n=103, from April 1st to August 31st) (p<0.01) (Figure 1). Forty% (103/258) and 79% (204/258) of the participants have demonstrated the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations under 12ng/ml and 20ng/ml, respectively (Table 2). The participants with the serum of 25[OH]D3 concentrations under 10ng/ml have shown a significantly lower GH (45.4±8.8) and MC (42.7±10.3) adjusted national score in comparison to the mean value of GH (48.6±9.4) and MC (45.5±9.5) adjusted national score in the participants with the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations of 10ng/ml or more (P<0.05). The mean value of the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations was slightly decreased in the participants with backache (13.4±5.3 ng/ml, n=64) than that without backache (15.0±7.0 ng/ml, n=194) (P=0.051).
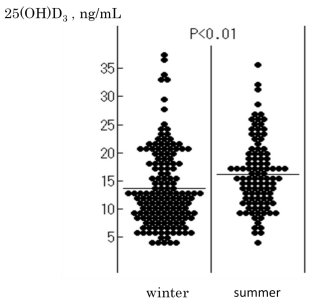
Figure 1: In the winter season (November 1st to March 30th), the mean value
of the serum 25(OH)D3 (13.6±6.9ng/mL, n=155) was significantly lower than
that in the summer season (April 1st to August 31st) (16.2±6.1ng/mL, n=103)
(p<0.01).
25(OH)D (ng/mL)
Numbers (%)
< 12
103 (40)
12~20
101 (39)
> 20
54 (21)
> 50
0 (0)
Table 2: Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D3] concentrations in healthy employed workers at latitude 40°north in Japan.
Personal Commentary
The mean value of the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations of the participants, that is 14.6±6.7 ng/ml (Men ; 15.0±6.8 ng/ml, Women ; 13.5±6.4 ng/ml ), is defined as being ‘inadequent’ for bone and overall health in healthy individuals according to NIH proposal [7]. This is surprising data, and what does it suggest?. All of the participants, who are being regularly engaged in the proper works, should be considered ‘sick or unhealthy’ and be recommended to take the supplementation or medication of vitamin D?. Is Serum 25[OH]D concentrations originally lower in healthy individuals of Japan?. It seems like very controversial, and needs a further discussion and consensus based on epidemiological and scientific researches.
Depression is a condition characterized by depressed mood or loss of interest or pleasure in nearly all activities most of every day for a period lasting at least 2 weeks. Poor health status and depression are common co-morbidity for patients with backache. Depressed patients without the diagnosis do not gain proper reference and treatment which may reduce their total illness burden. In the current preliminary result, no significant difference in the mean value of the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations between the participants with and without backache was shown (P=0.051). But the participants with serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations under 10ng/ ml have had a significantly lower GH (45.4±8.8) and MC (42.7±10.3) adjusted national score than the mean value of GH (48.6±9.4) and MC (45.5±9.5) adjusted national score in the participants with the serum 25[OH]D3 concentrations of 10ng/ml or more (P<0.05). In our ongoing research, SF-36 Ver. 2® has been used for evaluation of the health status of the participants. The GH and MC score from SF-36 Ver. 2® is an easy and valid predictor to detect general health status and depression [8]. Whether vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency is a causal or circumstantial risk factor for poor health status anddepression? Vitamin D likely has important functions in the human brain as a neuro-steroid, it still remains unclear whether these functions may be related to the occurrence of major depression. Recent studies have identified VDR in nearly all tissues, including both neuronal and glial cells in the central nervous system as well as the peripheral musculosketetal system [1,9]. Understanding of the function of vitamin D in the brain, is less known concerning how vitamin D may relate to the emotional mood. The current preliminary result has shown a possibility that vitamin D may be associated with depressive mood in the employed workers, but it is very controversial. A further longitudinal research is being carried out in our institute. Objective and persuading results are expected.
Ethics
This survey was approved by the Ethics Committee of Akita Rosai Hospital. The approval number was 32. A license to use Japanese language version’s SF-36 Ver. 2® was obtained from iHope International Company.
Conflict of Interest
This survey was financially supported as a dissemination project related to the occupational injuries and illness by Japanese Labour, Health and Welfare Organization in 2015-2016.
References
- Marks R. Vitamin D and Cartilage. Does Vitamin D Influence Cartilage Integrity? Austin J Musculoskelet Disord. 2016; 3: 1034.
- Shimizu K, Kim H, Yoshida H Shimada H,b Suzuki T. Serum25-hydroxyvitamin D level and risk of falls in Japanese community-dwelling elderly women : a 1 year follow-up study. Osteoporosis Int. 2015; 26: 2185-2192.
- Suzuki T, Kwon J, Kim H, Shimada H, Yoshida H, Iwasa H, et al. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels associated with falls among Japanese community-dwelling eldery. J Bone Miner Res. 2008; 23: 1309-1317.
- Miyakoshi N, Sasaki H, Kasukawa Y, Kamo K, ShimadaY. Effects of a vitamin D analog, alfacalcidol, on skeletal muscle in glucocorticoid-treated rats. Biomed Res.31; 2010: 329-336.
- Okuyama K, Miyakoshi N, Suzuki T Shimada Y. Current Tendencies of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with a Pedicle Screw in the Osteoporotic Spine-Advances and Concerns. Austin J Musculoskelet Disord. 2014; 1: 1011.
- Dawson-Hughes B, Mithal A, Bonjour JP, Boonen S, Burckhardt P, Fuleihan GH, et al. IOF statement: vitamin D recommended for older adults. Osteoporosis Int. 2010; 21: 1151-1154.
- Department of Health & Human Services National Institutes of Health.
- Walsh TL, Homa K, Hanscom B, Lurie J, Sepulveda MG, Abdu W. Screening for depressive symptoms in patients with chronic spinal pain using SF-36 health survey. Spine J. 2006; 6: 316-320.
- Elizabeth R, Bethtone J. Vitamin D and the occurrence of depression: Causal association or circumstantial Evidence? Nutr Rev. 2009; 67:481-492