
Review Article
Austin J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2019; 7(2): 1056.
Nanoparticles as Safe and Effective Drug Delivery Systems for Wound Healing
Abousamra MM*
Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, National Research Centre, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Mona M Abousamra, Pharmaceutical Technology Department, National Research Centre, 33 El-Buhouth Street, Dokki, Giza, 12622, Egypt
Received: October 14, 2019; Accepted: November 01, 2019; Published: November 08, 2019
Abstract
Wound healing following skin injury is a natural phenomenon that usually lacks quality, rapidity, and aesthetics. Ignored wound treatment can conduct to cruel infections, unlimited time of hos-pitalization, damage and an overall noticeably decreased life feature. Recently, many researchers showed that the wound dressing materials have entered a new level of standards and there is a far better understanding based on the pathogenesis of chronic wounds. Wound care management mainly depends on the development of new and effective wound dressing materials. Consequently, an extensive percentage of nanomaterials are used in diverse biomedical applications for wound dressings, drug delivery and other medical purposes. This literature will focus on the existing nanotechnology- based therapies available in the field of wound healing and skin regeneration, in order to emphasize the significance of these innovative nano-systems, and to understand of their effect on the wound healing process.
Introduction
The skin represents the largest organ in the human body; it acts as the first defense line confronting the external environment. The skin protects the body against exogenous substances and/or organisms; therefore, any harm to it results in unpredicted defect in the immune system [1]. The wound is the result of disruption of normal anatomic structure and function as well as it affects the deep underlying tissues resulting in inflammation and infection [2,3]. A large numbers of patients suffer from poor wound healing which is considered as a key source of death [4]. Neglected wound treatment can guide to harsh infections, extended time of hospitalization, mutilation and an overall obviously decreased life feature.
Up until the present the most important problem in burn wounds has been chronic infections caused by some microorganisms such as P. aeruginosa, those are especially serious in deep burns with large areas involved. This is due to the intrinsic and acquired resistance of bacteria to antibiotics resulting in high mortality in burn wound patients [4].
The search is always about; repairing the resident structure, maintains role of the wounded organ, counting blood capillaries, accelerates the recovery process and minimizes the hazards of systemic infection. In addition to renewal of the skin in terms of function, reduce scar formation, and ameliorate aesthetics particularly in renovation surgeries and burns. Conventional agents such as sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, cetrimide solution, chlorhexidine and others revealed inadequate efficacy accompanying with unfavorable result during the progression of healing [5], and consequently they lack priority use. Additionally, scaring of the skin are results from treating the wound with the ordinary wound care products. For this reason, many studies have been established in order to develop alternating therapies in turn able to re-establish the vitality of the wounded skin [6]. Therefore, an attention is given to the nanotechnology and the use of nanomaterials as safe and effective way for wound healing.
Novel nano-preparations showed remarkable and significant advantages over traditional one including the enhancement of solubility, bioavailability, protection from toxicity, improvement of pharmacological activity, augmentation of stability, sustained delivery, and protection from both physical and chemical degradation [7]. Development of novel wound dressings from natural and synthetic bioactive such as metallic nanoparticles [8], polymeric nanoparticles [9], SLNs and NLCs [10], liposomes [11], nanoemulsions [12] and dendrimers [13] have been established. Nanoparticles and nano-formulations are useful as drug delivery systems with great achievement; and nano-particulate drug delivery systems still having a great potential for many applications.
This literature review will focus on the existing nanotechnologybased therapies available in the field of wound healing and skin regeneration, in order to emphasize the significance of these innovative nano-systems, and to understand of their effect on the wound healing process.
The Progression of Normal Wound Healing
The wound healing process is composed of four biological phases that each wound needs to pursue in order to heal normally: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling that each wound needs to go through in order to heal normally Figure 1 [14]. These phases are dissimilar in function and histological characteristics whatever the kind of the wound. However, the healing process revealed the appearance of essential elements such as cytokines, growth factors, chemokines, and chemical mediators to achieve physiological healing [15,16].
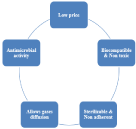
Figure 1: Properties of ideal wound healing material.
Hemostasis
Hemostasis is an immediate response following the skin injury in order to prevent bleeding and decrease hemorrhage. Vascular spasm, platelets plug formation and finally blood clotting are considered as main processes following the skin injury in order to seal the opening until tissues are repaired [17]. Once the platelet plug has been formed by the platelets, the clotting factors lead to the formation of fibrin. Thus, a fibrin mesh is produced all around the platelet plug to hold it in place. Beside to the vasoconstriction induced from platelets aggregation that in turn reduces blood flow to the wound bed. The coagulation process and thrombus formation which force blood cells and platelets to keep on trapped in the wounded region and nearby helping the deposition of collagen to promote repair the damaged tissue [18].
Inflammation
This phase begins directly after skin injury and may last for about 3 days .This phase focuses on destroying bacteria and removing debris in order to prepare the wound bed for the growth of new tissue [19,20]. Neutrophils are the first white blood cells released to destroy bacteria and remove debris. They are released in large number directly after injury and their number begin to reduce after 3 days from the injury [21]. After complete leaving of neutrophils, macrophages reach their destination to continue clearing of the debris. To catch the attention of the immune system cells, macrophages secrete growth factors and proteins to facilitate tissue repair [22]. This phase is accompanied with rising of the exudates levels causing skin swelling, erythema, pain and redness [23].
Proliferation
It occurs when the wound is “rebuilt” with new granulation tissue resulting from fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition in order to replace the fibrin mesh previously formed during the hemostasis phase. The aim of this phase is to fill and cover the wound. Proliferation starts with granulation of the wound with the connective tissues and ending by epithelialization [24].
Remodeling
The final phase occurring after wound closing is called maturation or remodeling phase. It starts 3 weeks after injury and can take up one year or more to complete [25]. In this final stage, dissimilar to intact skin, the arrangement of newly formed collagen fibers in the wound is random and disorganized. Fibroblasts secrete the lysyl enzyme oxidase, to allow collagen fiber accumulation. The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) maturation involves a balance between collagen synthesis and degradation, enzymes and glycoproteins, which are the key elements of wound repair [26].
Delay in Wound Curing
As recorded, wound healing takes two to three weeks in normal healthy persons. Chronic wounds build up because of a disturbance during the healing process.
They fail to heal within the normal period sufficient for the healing of acute one, in another meaning fail to close due to a problem in one or more of the wound healing stages [27,28]. Venous leg ulcers, pressure sores, ischemic ulcers, and diabetic foot ulcers are the main causes of chronic wounds which may be associated with individuals mortality [29,30].
Many signs characterize the chronic wounds such as increasing in inflammation, exudates accumulation, swelling, pain and stiffness in the affected area, hyper proliferative, so far non-advancing wound margin. Inflammation associated the wound may delay healing process. Also, the ulceration which appear as a result from chronic wound plays an important role in the pathogenesis of unhealed wounds [31].
Existing Wound Dressing Resources and their Restrictions
Many studies give attention to natural and bioactive materials used for the treatment of different types of wounds with the purpose to adjust one or more of the healing process. As increasing blood coagulation, decreasing exudates and speed up the closure of the wound. Thus, selecting a suitable wound dressing is very important.
The physiology of diabetic wounds shows dry texture and keratinized appearance, which leads to more susceptibility to suffering from fissures more easily, leading to an unlimited healing time [32]. Therefore, patients with diabetes are liable to cutaneous infections. At the present time, abundant wound dressing materials are accessible such as hydrocolloids, foam, hydrogels and hydrofibers are been used widely in clinical condition [33,34].
As wound, dressing types are abundant and different so when choosing a moist wound dressing we have to choose a dressing able to manage the associated symptoms such as inflammation and exudates [35]. In addition to the wound type, wound size, risk of infection and others factors should be taken in consideration during choosing the dressing type [36]. In order to choose an acceptable and helpful wound healing material, many criteria and conditions should be considered. The chosen material should be of low price, biocompatible, non-toxic, not strongly adhered to skin, should offer a moist wound environment, permission of diffusion of gases, thermal insulation (temperature and pH must be controlled), prevention of infection with antibacterial activity Figure 1.
The commonly available wound dressings don’t maintain a moist environment. They have poor absorption of wound exudates; poor gas exchange between wound and the environment. In addition, they show delay in wound healing process and difficulty in removal of the wound dressing after healing [37].
Recently, there was direction to incorporate bioactive antibacterial agents to wound dressing to reduce wound bacterial colonization and infection [38]. The use of bioactive compounds in wound dressings is significantly more effective in the medicinal treatment for non- healing chronic wounds. Bioactive compounds incorporated in the dressings are released through the hydrolysis activity of wound enzymes present in exudates or wound fluid [39]. As well, the possible modulation of the microenvironment of the healing wound from the point of view hydration, swelling and diffusion are used to release the bioactive compounds from the dressings to the site of injury [40]. Conversely, the bioactive agents in the dressings are found to be less effective due to the rapid absorption of compounds by wound exudates [41,42].
Recently, numerous researches are focused on the development of artificial wound dressing materials, as, no currently available material fulfils the requirements necessary for a speedy recovery of injured tissues [43]. For that reason, the seek for an ideal wound dressing material depending on the nanotechnology research represents an upcoming revolution evolution in this field.
Role of Nanotechnology in Promoting Wound Healing
Definitely, patients whose suffer from a delay in wound healing need innovative methods and novel strategies must be taken in consideration to resolve this problem. To enhance healing, the applied dressings must have bacterial lethal effect, stop bleeding, and absorb exudates [44]. In addition, they must be easy to use, have biodegradability properties, easily sterilized, non-toxic, good water vapor, and gas permeability [38].
For this reasons, great efforts are attributed by researchers for the development of new technologies able to clean the wound from microbes and deliver the antibiotics in a favorable microenvironment [38,37].
Worldwide, nanotechnology is considered as a fast growing and challenging research field. There are numerous talented products emerging from the application of nanotechnology intended for wound healing are under investigation.
Criteria of nanomaterials used in wound healing
The applied nanotechnology in the field of wound healing according to the produced formulations can be divided into:
1- Nano-materials employed as delivery vehicles for therapeutic agents
2- Nano-materials that exhibit intrinsic properties beneficial for wound treatment
3- Nano-materials that exhibit both as acting as delivery vehicle and in the same time possess property as wound healing material
Nanomaterials are typically (1-100 nm) in size, they are used in wound healing applications are materials which exhibit intrinsic properties promoting wound healing and materials used as transfer vehicles [45].
Considerable efforts have been made to develop drug delivery system using different types of biomaterials. The commonly used biomaterials are polymeric microspheres, polymeric Nano spheres, lipid nanoparticles, metal nanoparticles, nanoemulsions and dendrimers [46] (Figure 2).
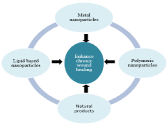
Figure 2: Potential role of nanoparticles in accelerating wound healing.
Nano-materials employed as delivery vehicles for therapeutic agents
These kinds of nanomaterials act only as a carrier for the active substance or the biomaterial used for wound healing.
Lipid based nanoparticles: Another attractive tool for topical wound healing is the application of lipid based nanoparticles because of their small particle size and lipoidic composition which ensures close contact with the wound sites.
Lipid nanoparticles: Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) are considered as good candidate for wound healing.
Both SLNs and NLCs are commonly prepared using the high shear homogenization method; however, the difference is that organic solvent is required for SLN preparation while a liquid lipid (oil) is used to formulate NLC as shown in Figure 3. In contrast to NLCs, SLNs exhibit a slower drug release, large surface area and low toxicity because the solid core of SLNs is hydrophobic with a monolayer coating of phospholipids and the drug is regularly dispersed or dissolved in the core [47,48]. For this reason, The SLN formulation was able to achieve more than eighty percent protein encapsulation efficiency and the solid lipid core prevented drug leakage and coalescence issue, resulting in a slow release. In addition to the ability of SLNs and NLCs to be, suitable carriers for both naturals and synthetic drugs to be useful to damaged and inflamed skin for accelerating wound healing. Regarding these properties, Gainza et al. studied the potential use of recombinant human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhEGF) loaded lipid nanoparticles for the managing of chronic wounds [49]. Encapsulation of rhEGF in lipid nanoparticles improve its stability and allowed its sustained delivery in wound healing.
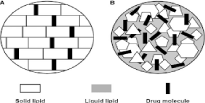
Figure 3: Schematic description of SLNs (A) and NLCs (B).
Liposomes: Liposomes have been chosen for transdermal drug delivery due to their superior drug penetration into the skin. They are formed of spherical vesicles made of one or more lamellar lipid-bilayers that spontaneously self-assemble when amphipathic precursors are mixed. Cholesterol and naturally occurring phospholipids are responsible for bilayers [50] as shown in Figure 4A. Considering structure and behavior, it was found that liposomes mimic biological membranes. However, topical use of the liposome is often hindered by their rapid drug release and coalescence of the particles. In order to overcome this drawback , advanced liposome-based formations such as semisolid phospholipid vesicles or gel core liposomes have been developed to have high drug loading level, long-term stability, and controlled drug release in wound sites [51,20]. Researchers succeeded to develop liposomes with a hydrogel core able to encapsulate the growth factor bfGF, which showed an accelerated wound closure of mice with deep second-degree scald [20].
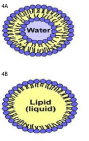
Figure 4: A). Liposome, Lipid bilayer enclosing an aqueous core; B).
Nanoemulsion, Lipid monolayer enclosing a liquid lipid core.
Another technique to improve liposome delivery to wound sites is multi-functionalization of liposomal membranes with various bioactive molecules, such as ligands, receptors, polysaccharides or lipophilic drugs [48]. Manca et al., established that hyaluronanfunctionalized liposomes have shown to be superior to liposomes for lipophilic drug delivery [52]. In the present work, new highly biocompatible nanovesicles were developed using polyanion sodium hyaluronate to form polymer-immobilized vesicles, so called hyalurosomes. Curcumin, at high concentration was loaded into hyalurosomes and physico-chemical properties and in vitro/ in vivo performances of the formulations were compared to those of liposomes having the same lipid and drug content. Vesicles were prepared by direct addition of dispersion containing the polysaccharide sodium hyaluronate and the polyphenol curcumin to a commercial mixture of soy phospholipids, thus avoiding the use of organic solvents. An extensive study was carried out on the physico-chemical features and properties of curcumin-loaded hyalurosomes and liposomes. Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering showed that vesicles were spherical, uni- or oligolamellar and small in size (112-220 nm). The in vitro percutaneous curcumin delivery studies on intact skin showed an improved ability of hyalurosomes to favour a fast drug deposition in the whole skin. Hyalurosomes as well as liposomes were biocompatible, protected in vitro human keratinocytes from oxidative stress damages and promoted tissue remodelling through cellular proliferation and migration. Moreover, in vivo tests underlined a good effectiveness of curcumin-loaded hyalurosomes to counteract 12-O-tetradecanoilphorbol (TPA)-produced inflammation and injuries, diminishing oedema formation, myeloperoxydase activity and providing an extensive skin reepithelization. Thanks to the onestep and environmentally friendly preparation method, component biocompatibility and safety, good in vitro and in vivo performances, the hyalurosomes appear as promising nanocarriers for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications [52].
They found that hyaluronan stabilized dispersion of a lipophilic drug, curcumin, improved encapsulation as well as vesicle stability due to the surface exposure of polyanionic hyaluronan in comparison with liposomes. Furthermore, hyalurosomes without curcumin could improve skin re-epithelization due to its inherent tissue restoring properties from hyaluronan and synergistically accelerated in vivo wound regeneration with curcumin. This approach can be considered for further development of therapeutics that can effectively treat chronic wounds in different disease states.
Nanoemulsions (NEs): They are nano-sized amphiphilic molecules in the range of 20-200 nm prepared of oil-based and aqueous solutions [53]. As shown in Figure 4B, they have two parts including a hydrophobic core as well as a hydrophilic coating. The hydrophobic core can be efficiently loaded with insoluble agents, and the hydrophilic coating allows the NPs to be soluble in aqueous media [54]. They play an important role in many fields including drug delivery, cosmetics and cell culture [55]. They can be formulated using ultrasonication and mixing for the constituents.
As reported, chlorhexidine acetate formulated in a nanoemulsion was used against a Methicillin-Resistant S. Aurerus (MRSA) infection in a skin burn wound model. The nanoemulsion revealed successful and fast action against MRSA in-vitro and in-vivo. In addition, the formula allow delayed formation of biofilm, and disrupted MRSA cell walls, led to increased leakage of DNA, protein, Mg2+, K+ and alkaline phosphates out of the cells [12].
In another study, Alpha tocopherol combined with astaxanthin was impregnated in nanoemulsion form, which revealed a good antibacterial effect against S. aureus. Nanoemulsion formulation showed a significant damage to the bacterial cell membrane, facilitating its uses as an efficient antibacterial agent in addition to preventing them from developing resistance [48].
Dendrimers: Dendrimers are a type of nano-scale (1-10 nm), they are polymeric symmetric and spherical compounds which have applications in both diagnosis and therapy. Dendrimers possess a symmetric core, an inner shell and an outer shell as shown in Figure 5. They are prepared from phenyl acetylene subunits; they are formed from three major portions: a core, an inner shell, and an outer shell [56].
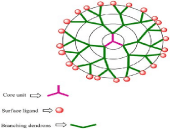
Figure 5: Structure of a typical dendrimer.
Moreover, the surface functional groups of dendrimers possess an antibacterial activity especially if cationic. Kalomiraki et al., revealed the disruption of the bacterial cell structure after dendrimers application due to the reaction occurring between the cationic group of the dendrimer (quaternary ammonium groups) and the anionic groups of the bacterial cell wall.
Kalomiraki et al., studied the antibacterial property resulting from the interaction between the water insoluble antibiotics (e.g. nadifloxacin and prolifloxacin) with polyamidoamine (water soluble dendrimer) [57]. Dendrimers loaded antibiotics revealed reduction of inflammation with disinfection for the wound and stimulating its healing.
Polymeric nanoparticles
Polymeric nanoparticles are pharmaceutical carriers for controlled and sustained released drugs. They are either nanospheres or nanocapsules. When the active molecule is integrated inside the core of the nanoparticulate system, the particles are named “nanocapsules”, while if the drug is adsorbed on the surface, the nanoparticles are named “nanospheres”.
Polymeric nanoparticles are composed of biodegradable and biocompatible polymers of synthetic or natural origin. In contrast to natural polymers, synthetic polymers can be modified by alterations the methodology of polymer synthesis, and can be adapted according to the specific requirements and the biological applications in order to overcome the limitations in the use of natural origin polymers [8].
The most widely used synthetic polymers are polylactide, polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polylactide-polyglycolide copolymers, polycaprolactones, and polyacrylates. Lactide-glycolide copolymer is an extensively explored copolymer. Among the various natural polymers, alginate, albumin, or chitosan have been widely used in drug formulation [58,59,60].
Many studies dealt with the use of synthetic polymers in tissue repair and wound healing; the effect of lipoic acid in ameliorating wound healing has been evaluated in poly (-caprolactone) nanoparticles. It was found that emulsified lipoic acid increased the healing rate and improved histological parameters [61,62].
Also, Polyurethanes (PU) showed amelioration in cellular proliferation through the stimulation of angiogenesis and reepithelization of injured rats [63,64].
On the other side, natural polymers are also integrated in the formulation of new easily applied in situ gel of cephadroxil loaded chitosan nanoparticles that could promote wound healing. Basha et al., succeeded to formulate an in situ gel possessing the ability to accelerate the healing process, encourage cell proliferation and allow matrix deposition [1].
Another study showing that the application of gelatin-based scaffolds to rat wounds resulted in faster wound closure and enhanced overall wound healing [65].
A same result was observed after application of fibrin scaffolds. Fibrin can reduce inflammation, increases immunological response and cell adhesion properties, and has been widely used for tissueengineering and wound healing [66].
Many others natural polymers including elastin [67], hyaluronic acid [68] have been investigated for wound healing.
Nano-materials that exhibit intrinsic properties beneficial for wound treatment
Metallic nanoparticles are nanomaterials characterized by their self-wound healing activity through directly applying on the site of the injured skin.
Metallic nanoparticles are characterized by their antibacterial activity such as magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4), silver and gold Nano particles [69], as well as, copper oxide, Zinc oxide, aluminum oxide, titanium oxide, and gallium nanoparticles which showed acceptable results on healing process [4].
Nanoscale particles with antibacterial activity offer a high chance of interaction with biomolecules on the cell surfaces and penetration inside the cells into the wound [70]. These are referred to their small size, high surface area and shape [69]. Regarding these properties, nanoparticles are able to carry a sustained and controlled release therapeutics that results in an accelerated healing process [71].
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs): Silver has multifunctional bio-applications. It has antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiinflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and anti-cancer activities [11]. It is the best known as a bactericidal agent and is commonly used to treat burns, wound infection and a variety of ulcers [44]. The biological efficient antimicrobial activity of AgNPs depends on their large surface chemistry, size, shape, morphology, particle constituents, agglomeration, and dissolution proportion [72].
At first, AgNPs fix to the bacterial cell membrane which constitutes the biological cell barrier and penetrate and interact with sulphur and phosphorus groups forming bacterial proteins, as well as with DNA [73].
Application of Ag NP-based dressings on wound is associated with Ag NPs release and their penetration into the cells as agglomerates [74].
The nanoparticles initially release silver ions inside the bacterial cells, damage intracellular and nuclear membranes. This is followed by denaturing bacterial DNA and RNA [75]. The nanoparticles target and alter mitochondrial functionality and disturb cellular division, leading to cell death [76].
Silver nanoparticles can also accelerate the wound healing process as `they have anti-inflammatory effects and neovascularization. They reduce inflammation by modulating cytokines and enhances reepithelization [77].
Moreover, silver nanoparticles showed significant efficiency against microorganisms surrounded by biofilms, which represent a therapeutic challenge due to their resistance to conventional antimicrobial therapy [78]. Also, they have shown antimicrobial activity against many strains and other skin pathogens as S. aureus [78,79,80].
Currently, gold nanoparticles, nanoshells and nanocages [69] of silver coatings in wound dressings are available for efficient distribution of the drug [81,78].
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs): Topical applications of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), revealed antioxidative effects and could be helpful in wound healing [82]. Beside their usage in the field of diagnosis, AuNPs penetrate bacterial cells [83].
They alter their membrane and inhibit the enzyme ATP synthase. This is followed by of depletion of ATP and collapse in energy metabolism and bacterial cell death [84].
AuNPs enhance wound healing by promoting epithelialization, collagen deposition and fast vascularization [85] and regenerate the damaged collagen tissues [86].
In contrary to silver, gold nanomaterials as a single material alone does not offer any antimicrobial activity [87].
AuNPs must be incorporated with other biomolecules to be used successfully in biomedical applications. When AuNPs are cross linked with collagen, it can be easy integrated with other biomolecules like polysaccharides, growth factors, peptides, and cell adhesion molecules.
The modified AuNPs demonstrate properties like biocompatibility and biodegradability; it can be used widely in wound healing. Similar to collagen, gelatin and chitosan can also easily be incorporated with AuNPs showing safe and positive effects in enhancing wound healing [88,89].
Gold might be conjugated to existing antimicrobial drugs or with other nanoparticles, by this means increasing their potency to kill microbes [8]. Many studies were performed indicating that topical application of AuNPs to the wound site, reveal healing properties and improve wound healing and treat burns [90,91,92 93,86].
Copper nanoparticles (CuNPs)
Copper nanosized particles have been gained attention due to its antibacterial activity against intrinsically presented bacterial strains such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot ulcer and burn wound infections [94,95]. CUNPs reveal their action after their decomposition in protein solutions and on modification, Cu2+ ions are released which diminish the toxicity and fasten the healing efficacy of the wounded skin [45]. Tiwari et al. studied the biosynthesis and the use of CUNPs in wounded rats and observed an increase in the rate of wound healing [96]. Still important to introduce a biocompatible stabilizers such as chitosan are needed in order to increase the stability of CUNPs and defeat its rapid oxidation and agglomeration of during its use [97].
Others metal oxide nanoparticles [zinc oxide (ZnO), titanium oxide (TiO2), Cerium oxide (CeO2), yttrium oxide (Y2O3)]: Recently, nanoscaled metal oxide gained interest in the field of medical application. As known, a small amount of these essential mineral elements exhibited a strong activity to the human body. Both titanium oxide and zinc oxide have prevalent use in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical manufacturing as sunscreen protectors and also as a wound healing material [98]. Beside its usage as a cosmetic colorant, ZnoNPs are mostly used in skin creams because of its antiinflammatory and antiseptic properties. In addition to its effective use for wound healing as its nanoparticles possess powerful bacterial resistance ability and increases the wound healing procedure by staying at the wound site for a longer period of time [99]. Also, TiO2 NPs was found to be a promising agent in accelerating the rate of opened excision type wounds in vivo and in vitro [100,101]. Furthermore, CeO2NPs and Y2O3NPs were effectively used for the protection against oxidative stress damage for DFU [102].
Hazards of metal nanoparticles: Irrespective of the antibacterial activity of metallic NPs and their wide effectiveness in wound healing, current knowledge in the field of Nano toxicology reports their hazardous effect more than bulk materials [103].
The undesirable hazardous effects of metal Nano particles are related to their unique characteristic properties that promote wound healing. This double-edged sword to the human health risk is related to their small size, large surface area, chemical composition and solubility [104]. Nanoparticles have the capability of easy cellular penetration, crossing biological barriers, reaching the most sensitive organs and affect the vital body cellular metabolism due to their small size [105].
Botelho et al. [106] confirmed the appearance of tumor-like phenotypes in human gastric epithelial cells caused by TiO2NPs. Furthermore, they noted an inactivation of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes in an experiment done on Wistar rats. They analysed brain, skeletal muscle, and heart and liver of rat tissues after treatment with AgNPs.
Now a day, many studies were directed to decrease the toxicity related to NP by the introduction of carriers of natural origin namely of plant source [107].
Natural materials conjugated with nanoparticles
Currently, many skin wound dressings have been incorporated with compounds of natural sources in order to enhance its bactericidal effect [108,109]. Among these natural products displaying bactericidal activity and incorporated into wound dressings we can mention:
1- Natural substances possessing healing property delivered to the injured site through nanocarriers such as the honey and the essential oils.
2- Natural substance acting in the same time as a nano-carrier and a healing substance such as the chitosan.
Honey: Since the ancient times, honey was considered as a natural healing agent. The majority of the people are lacking information concerning honey’s wound care properties.
Honey possesses many bioactivities working in harmony to promote skin wound healing [110]. Honey has the properties to increase wound nutrition, minimize inflammation and stimulate angiogenesis with granulation tissue formation, epithelialization and repair [111].
Antimicrobial activity of honey is attributed to its osmolality, acidic nature due to hydrogen peroxide. These aid macrophage cells to destroy bacteria and avoid the formation of microbial biofilm [112].
When Honey is applied on the open wound, hydrogen peroxide is released causing cell growth inhibition [113]. Moreover, the low water content of honey less than 20% provides unfavorable environment for microorganism survival and development.
Many honey-incorporated wound dressings are commercialized. Among the marketed products: Algivon, MediHoney, Activon Tulle and Actilite [111].
Volatile natural mixtures: Volatile natural mixtures called Essential Oils (EOs), emerged as feasible routes to decrease skin wound bacterial colonization and proliferation. They are of plant origin formed of secondary metabolites that display important medicinal characteristics [114].
The essential oils have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antiviral, anticancer, insecticidal, and antimicrobial properties [114]. They are impregnated as antibacterial agents in skin wound dressings. Authors reverted the antimicrobial activity of EOs to the phenolic compounds, specifically to thymol and carvacrol [115, 116].
The antimicrobial effect of EOs is through troubling the function of the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, by distracting the active transport of nutrients through the cell membrane, and coagulation of bacterial cell contents [3].
Many researchers demonstrated the efficiency of EOs incorporation in wound dressing and their significant efficacy as antimicrobial agents.
Prepared lipid nanoparticles loaded with eucalyptus or rosemary essential oils in order to be used as a natural tool for skin wound healing [117].
In another study, Liakos et al. [118] reported the antibacterial effectiveness of 1% and 5% of EOs consisting of cinnamon, lemongrass and peppermint in fibrous dressings against E. Coli [118].
Chitosan: Many reports have indicated the antimicrobial effects of chitosan, and its derivatives on wound healing [119]. Figure 6 elucidates the mechanisms of the bactericidal effect of CS [120].
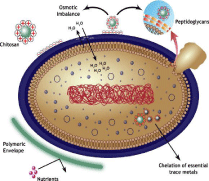
Figure 6: Representation of the mechanisms proposed to explain the
antibacterial activity of Chitosan.
The chitosan antibacterial activity is due to the positively-charged amine groups of chitosan glucosamine. This initiates electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged surface components of the bacterial cell wall [121].
As a result to this contact, the permeability of the microorganism’s cell wall is affected leading to internal osmotic imbalance causing inhibition of the microorganism’s growth [119].
Alternatively, this electrostatic interactions promote the hydrolysis of the peptidoglycans constituting the microorganisms cell wall leading to the release of intracellular electrolytes [104]. A second proposed mechanism of CS bactericidal activities is realized by the formation of a polymeric sachet around the bacterial wall. This envelop prevents cell exchanges and nutrients absorption [121]. The third postulated mode of CS action is related to the interaction occurring between the CS’s amino groups with the essential trace metals needed for bacterial growth and thereby inhibition of toxins production and microbial growth happened [121]. Many wound dressings containing CS are existing in the market, such as Chitopack, HidroKi Patch, Tegasorb and KytoCel [122].
Conclusion and Perspectives
Wound healing technologies and delivery of wound dressing care supplies for acute and chronic skin wounds constitute one of foremost commercial enterprise.
The new innovations in dressing nanotechnology-based therapies reported in this review clarified the impact on accelerated wound healing.
Although many metallic nanoparticles and others Nano carriers such as lipid NPs, liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles and dendrimers were industrialized, yet resort to the incorporated wound dressings with natural product were raised and flourished in last few years.
Regardless of the reached progress, further developments of these types of dressings are expected. The innovation of new NPs or the loading of antimicrobial agents into Nano devices is a new avenue to treat infected wounds. In addition, dressings containing sensors and therapeutic molecules are the novelty for future improvement of wound dressing industry.
References
- Lee SH, Jeong SK, Ahn SK. An update of the defensive barrier function of skin. Yonsei Med J. 2006; 47: 293-306.
- Lazarus GS. “Definitions and guidelines for assessment of wounds and evaluation of healing”. Arch Dermatol. 1994; 130: 489-493.
- Altiok D, Altiok E, Tihminlioglu F. “Physical, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan films incorporated with thyme oil for potential wound healing applications.” J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010. 21: 2227-2236.
- Chellappan DK, Yenese Y, Wei CC, Gupta G. “Nanotechnology and Diabetic Wound Healing: A Review”. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2017; 17: 87-95.
- Moore D. “Hypochlorites: a review of the evidence”. J Wound Care. 1992; 1: 44-53.
- Razavi S, Partoazar A, Takzaree N, Fasihi-Ramandi M, Bahador A, Darvishi MH. “Silver sulfadiazine nanoethogel for burn healing: characterization and investigation of its in vivo effects”. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2018; 13: 1319- 1331.
- Amini-Nik, S, Yousuf Y, Jeschke MG. “Scar management in burn injuries using drug delivery and molecular signaling: Current treatments and future directions”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018; 123: 135-154.
- Kumar SSD, Rajendran NK, Houreld NN, Abrahamse H. “Recent advances on silver nanoparticle and biopolymer-based biomaterials for wound healing applications.” Int J Biol Macromol. 2018; 115: 165-175.
- Basha M, AbouSamra MM, Awad GA, Mansy SS. “A potential antibacterial wound dressing of cefadroxil chitosan nanoparticles in situ gel: Fabrication, in vitro optimization and in vivo evaluation”. Int J Pharm. 2018; 544: 129-140.
- Fumakia M, Ho EA. “Nanoparticles Encapsulated with LL37 and Serpin A1 Promotes Wound Healing and Synergistically Enhances Antibacterial Activity”. Mol Pharm. 2016; 13: 2318-2331.
- Zhang XF, Liu ZG, Shen W, Gurunathan S. “Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches.” Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17.
- Song Z, Sun H, Yang Y, Jing H, Yang L, Tong Y, et al. “Enhanced efficacy and anti-biofilm activity of novel nanoemulsions against skin burn wound multi-drug resistant MRSA infections”. Nanomedicine. 2016; 12: 1543-1555.
- Liu X, Hao W, Lok CN, Wang YC, Zhang R, Wong KK. “Dendrimer encapsulation enhances anti-inflammatory efficacy of silver nanoparticles”. J Pediatr Surg. 2014; 49: 1846-1851.
- Greaves NS, Ashcroft KJ, Baguneid M, Bayat A. Current understanding of molecular and cellular mechanisms in fibroplasia and angiogenesis during acute wound healing”. J Dermatol Sci. 2013; 72: 206-217.
- Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M. “Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation”. Sci Transl Med. 2014; 6: 265sr266.
- You HJ, Han SK. “Cell therapy for wound healing”. J Korean Med. 2014; 29: 311-319.
- Saghazadeh S, Rinoldi C, Schot M, Kashaf SS, Sharifi F, Jalilian E, et al. “Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018; 127: 138-166.
- Miyata T. “Guest editorial: Current understanding of thrombosis and hemostasis-from bench to bedside”. Int J Hematol. 2012; 95: 331-332.
- Senior RM, Skogen WF, Griffin GL, Wilner GD. “Effects of fibrinogen derivatives upon the inflammatory response. Studies with human fibrinopeptide B”. J Clin Invest. 1986; 77: 1014-1019.
- Liu S, Long Q, Xu Y, Wang J, Xu Z, Wang L, et al. “Assessment of antimicrobial and wound healing effects of Brevinin-2Ta against the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae in dermally-wounded rats”. Oncotarget. 2017; 8: 111369-111385.
- Choi J, Kim R, Kim J, Jeong W, Park SW, Lee HW, et al. “Nicorandil reduces burn wound progression by enhancing skin blood flow”. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018; 71: 1196-1206.
- Kloc M, Ghobrial RM, Wosik J, Lewicka A, Lewicki S, Kubiak JZ. “Macrophage functions in wound healing”. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019; 13: 99-109.
- Kim SY, MG Nair. “Macrophages in wound healing: activation and plasticity”. Immunol Cell Biol. 2019.
- Fronza M, Caetano GF, Leite MN, Bitencourt CS, Paula-Silva FW, Andrade TA, et al. “Hyaluronidase modulates inflammatory response and accelerates the cutaneous wound healing.” PLoS One. 2014; 9: e112297.
- Rosenbaum AJ, Banerjee S, Rezak KM, Uhl RL. “Advances in Wound Management”. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018; 26: 833-843.
- Zhang C, Feinberg D, Alharbi M, Ding Z, Lu C, O’Connor JP, et al. “Chondrocytes Promote Vascularization in Fracture Healing Through a FOXO1-Dependent Mechanism”. J Bone Miner Res. 2018.
- Frykberg RG, J Banks. “Challenges in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds”. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015; 4: 560-582.
- Zelga PJ, Górnicz MM, Gluszkiewicz JM, Piasecka-Zelga J, et al. “Outcomes of acute dermal irritation and sensitisation tests on active dressings for chronic wounds: a comparative study”. J Wound Care. 2016; 25: 722-729.
- Izadi K, Ganchi P. “Chronic wounds”. Clin Plast Surg. 2005; 32: 209-222.
- Sinno H, S Prakash. “Complements and the wound healing cascade: an updated review”. Plast Surg Int. 2013: 146764.
- McDaniel JC, Roy S, Wilgus TA, et al. “Neutrophil activity in chronic venous leg ulcers--a target for therapy?”. Wound Repair Regen. 2013; 21: 339-351.
- Hobizal KB, DK Wukich. “Diabetic foot infections: current concept review”. Diabet Foot Ankle. 2012; 3.
- Dhaliwal K, N Lopez. “Hydrogel dressings and their application in burn wound care”. Br J Community Nurs. 2018; 23: S24-S27.
- Hussain Z, Thu HE, Shuid AN, Katas H, Hussain F. “Recent Advances in Polymer-based Wound Dressings for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: An Overview of State-of-the-art”. Curr Drug Targets. 2018; 19: 527-550.
- Cutting KF, White RJ. “Avoidance and management of peri-wound maceration of the skin”. Prof Nurse. 2002; 18; 33: 35-36.
- Shao M, Hussain Z, Thu HE, Khan S, de Matas M, Silkstone V, et al. “Emerging Trends in Therapeutic Algorithm of Chronic Wound Healers: Recent Advances in Drug Delivery Systems, Concepts-to-Clinical Application and Future Prospects”. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2017; 34: 387-452.
- Dabiri G, Damstetter E, Phillips T. “Choosing a Wound Dressing Based on Common Wound Characteristics”. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016; 5: 32-41.
- Simoes D, Miguel SP, Ribeiro MP, Coutinho P, Mendonça AG, Correia IJ, et al. “Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review”. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 127: 130-141.
- Boateng J, O Catanzano. “Advanced Therapeutic Dressings for Effective Wound Healing--A Review”. J Pharm Sci. 2015; 104: 3653-3680.
- Dias AM, Braga ME, Seabra IJ, Ferreira P, Gil MH, de Sousa HC, et al. “Development of natural-based wound dressings impregnated with bioactive compounds and using supercritical carbon dioxide”. Int J Pharm. 2011; 408: 9-19.
- Azuma K, Izumi R, Osaki T, Ifuku S, Morimoto M, Saimoto H, et al. “Chitin, chitosan, and its derivatives for wound healing: old and new materials”. J Funct Biomater. 2015; 6: 104-142.
- Das S, Singh G, Majid M, Sherman MB, Mukhopadhyay S, Wright CS, et al. “Syndesome Therapeutics for Enhancing Diabetic Wound Healing”. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016; 5: 2248-2260.
- Silva MMP, Aguiar MIF, Rodrigues AB, Miranda MDC, Araújo MÂM, Rolim ILTP, et al. “The use of nanoparticles in wound treatment: a systematic review”. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2018; 51: e03272.
- Junker JP, Kamel RA, Caterson EJ, Eriksson E, et al. “Clinical Impact upon Wound Healing and Inflammation in Moist, Wet, and Dry Environments”. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013; 2: 348-356.
- Vijayakumar V, Samal SK, Mohanty S, Nayak SK. “Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management”. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 122: 137-148.
- Gainza G, Villullas S, Pedraz JL, Hernandez RM, Igartua M. “Advances in drug delivery systems (DDSs) to release growth factors for wound healing and skin regeneration”. Nanomedicine. 2015; 11: 1551-1573.
- Gomes FLT, Maranhão RC, Tavares ER, Carvalho PO, Higuchi ML, Mattos FR, et al. “Regression of Atherosclerotic Plaques of Cholesterol-Fed Rabbits by Combined Chemotherapy with Paclitaxel and Methotrexate Carried in Lipid Core Nanoparticles”. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 23: 561- 569.
- Shanmugapriya K, Kim H, Saravana PS, Chun BS, Kang HW, et al. “Astaxanthin-alpha tocopherol nanoemulsion formulation by emulsification methods: Investigation on anticancer, wound healing, and antibacterial effects”. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018; 172: 170-179.
- Gainza G, Pastor M, Aguirre JJ, Villullas S, Pedraz JL, Hernandez RM, et al. “A novel strategy for the treatment of chronic wounds based on the topical administration of rhEGF-loaded lipid nanoparticles: In vitro bioactivity and in vivo effectiveness in healing-impaired db/db mice”. J Control Release. 2014; 185: 51-61.
- Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, et al. “Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications”. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013; 8: 102.
- Manca ML, Manconi M, Falchi AM, Castangia I, Valenti D, Lampis S, et al. “Close-packed vesicles for diclofenac skin delivery and fibroblast targeting.” Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013; 111: 609-617.
- Manca ML, Castangia I, Zaru M, Nácher A, Valenti D, Fernàndez-Busquets X, et al. “Development of curcumin loaded sodium hyaluronate immobilized vesicles (hyalurosomes) and their potential on skin inflammation and wound restoring”. Biomaterials. 2015; 71: 100-109.
- Jaiswal M, Dudhe R, Sharma PK. “Nanoemulsion: an advanced mode of drug delivery system”. 3 Biotech. 2015; 5: 123-127.
- Jabbarzadegan M, Rajayi H, Mofazzal Jahromi MA, Yeganeh H, Yousefi M, Muhammad Hassan Z, et al. “Application of arteether-loaded polyurethane nanomicelles to induce immune response in breast cancer model”. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017; 45: 808-816.
- Hu Q, Gerhard H, Upadhyaya I, Venkitanarayanan K, Luo Y. “Antimicrobial eugenol nanoemulsion prepared by gum arabic and lecithin and evaluation of drying technologies”. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016; 87: 130-140.
- Abbasi E, Aval SF, Akbarzadeh A, Milani M, Nasrabadi HT, Joo SW. “Dendrimers: synthesis, applications, and properties”. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014; 9: 247.
- Kalomiraki M, Thermos K, Chaniotakis NA. “Dendrimers as tunable vectors of drug delivery systems and biomedical and ocular applications”. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2016; 11: 1-12.
- Moreira-Teixeira LS, Georgi N, Leijten J, Wu L, Karperien M. “Cartilage tissue engineering”. Endocr Dev. 2011; 21: 102-115.
- Ngo YH, Li D, Simon GP, Garnier G. “Paper surfaces functionalized by nanoparticles”. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2011; 163: 23-38.
- Ramasamy M, J Lee. “Recent Nanotechnology Approaches for Prevention and Treatment of Biofilm-Associated Infections on Medical Devices”. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016: 1851242.
- Kulkamp-Guerreiro IC, Souza MN, Bianchin MD, Isoppo M, Freitas JS, Alves JA, et al. “Evaluation of lipoic acid topical application on rats skin wound healing”. Acta Cir Bras. 2013; 28: 708-715.
- Sahana TG, PD Rekha. “Biopolymers: Applications in wound healing and skin tissue engineering”. Mol Biol Rep. 2018; 45: 2857-2867.
- Younan GJ, Heit YI, Dastouri P, Kekhia H, Xing W, Gurish MF, et al. “Mast cells are required in the proliferation and remodeling phases of microdeformational wound therapy”. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011; 128: 649e-658e.
- Heit YI, Dastouri P, Helm DL, Pietramaggiori G, Younan G, Erba P, et al. “Foam pore size is a critical interface parameter of suction-based wound healing devices”. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012; 129: 589-597.
- Bilgi H, Demiriz M, Ozler M, Ide T. “Gelatin based scaffolds and effect of EGF dose on wound healing”. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2013; 3: 2205-2211.
- Cho SW, Jeon O, Lim JE, Gwak SJ, Kim SS, Choi CY, et al. “Preliminary experience with tissue engineering of a venous vascular patch by using bone marrow-derived cells and a hybrid biodegradable polymer scaffold”. J Vasc Surg. 2006; 44: 1329-1340.
- Lee J, Baek SE, Lee S, Cho YW, Jeong YJ, Kim KJ, et al. “Wound-healing effect of adipose stem cell-derived extracellular matrix sheet on full-thickness skin defect rat model: Histological and immunohistochemical study”. Int Wound J. 2019; 16: 286-296.
- Schneider HP, Landsman A. “Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Hyaluronic Acid in Wound Care: A Case Series and Literature Review”. Wounds. 2019; 31: 41-48.
- Mody VV, Siwale R, Singh A, Mody HR. “Introduction to metallic nanoparticles”. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010; 2: 282-289.
- Mody VV, Nounou MI, Bikram M. “Novel nanomedicine-based MRI contrast agents for gynecological malignancies”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009; 61: 795- 807.
- Arvizo RR, Bhattacharyya S, Kudgus RA, Giri K, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee P. “Intrinsic therapeutic applications of noble metal nanoparticles: past, present and future”. Chem Soc Rev. 2012; 41: 2943-2970.
- Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, et al. “Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species.” J Phys Chem B. 2008; 112: 13608- 13619.
- Salvioni L, Galbiati E, Collico V, Alessio G, Avvakumova S, Corsi F, et al. “Negatively charged silver nanoparticles with potent antibacterial activity and reduced toxicity for pharmaceutical preparations”. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12: 2517-2530.
- Rigo C, Ferroni L, Tocco I, Roman M, Munivrana I, Gardin C, et al. “Active silver nanoparticles for wound healing”. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14: 4817-4840.
- Lansdown AB. “Silver. I: Its antibacterial properties and mechanism of action”. J Wound Care. 2002; 11: 125-130.
- Fayaz AM, Balaji K, Girilal M, Yadav R, Kalaichelvan PT, Venketesan R. “Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: a study against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria”. Nanomedicine. 2010; 6: 103-109.
- Hamdan S, Pastar I, Drakulich S, Dikici E, Tomic-Canic M, Deo S, et al. “Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications”. ACS Cent Sci. 2017; 3: 163-175b.
- Yildirimer L, Thanh NT, Loizidou M, Seifalian AM. “Toxicology and clinical potential of nanoparticles”. Nano Today. 2011; 6: 585-607.
- Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ, et al. “Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles”. Nanomedicine. 2007; 3: 95-101.
- Ruparelia JP, Chatterjee AK, Duttagupta SP, Mukherji S, et al. “Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles”. Acta Biomater. 2008; 4: 707-716.
- Ayata M, Kaptan Z, Uzunkulaoglu H, Akyildiz I, Tüzüner A, Ünverdi H, et al. “Effect of Enoxaparin Sodium on Experimentally-Induced Myringosclerosis in Rats”. J Int Adv Otol. 2015; 11: 192-195.
- Leu JG, Chen SA, Chen HM, Wu WM, Hung CF, Yao YD, et al. “The effects of gold nanoparticles in wound healing with antioxidant epigallocatechin gallate and alpha-lipoic acid”. Nanomedicine. 2012; 8: 767-775.
- Guo R, Song Y, Wang G, Murray RW. “Does core size matter in the kinetics of ligand exchanges of monolayer-protected Au clusters?”. J Am Chem Soc. 2005; 127: 2752-2757.
- Gobin AM, O’Neal DP, Watkins DM, Halas NJ, Drezek RA, West JL. “Near infrared laser-tissue welding using nanoshells as an exogenous absorber”. Lasers Surg Med. 2005; 37: 123-129.
- Oyarzun-Ampuero F, Vidal A, Concha M, Morales J, Orellana S, Moreno- Villoslada I. “Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Wounds”. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21: 4329-4341.
- Volkova N, Yukhta M, Pavlovich O, Goltsev A. “Application of Cryopreserved Fibroblast Culture with Au Nanoparticles to Treat Burns”. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2016; 11: 22.
- Lau P, Bidin N, Islam S, Shukri WNBWM, Zakaria N, Musa N, et al. “Influence of gold nanoparticles on wound healing treatment in rat model: Photobiomodulation therapy”. Lasers Surg Med. 2017; 49: 380-386.
- Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Sudheesh Kumar PT, Nair SV, Tamura H, et al. “Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications”. Biotechnol Adv. 2011; 29: 322-337.
- Akturk O, Kismet K, Yasti AC, Kuru S, Duymus ME, Kaya F, et al. “Collagen/ gold nanoparticle nanocomposites: A potential skin wound healing biomaterial”. J Biomater Appl. 2016; 31: 283-301.
- Wilson M. “Lethal photosensitisation of oral bacteria and its potential application in the photodynamic therapy of oral infections”. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2004; 3: 412-418.
- Norman RS, Stone JW, Gole A, Murphy CJ, Sabo-Attwood TL. “Targeted photothermal lysis of the pathogenic bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with gold nanorods”. Nano Lett. 2008; 8: 302-306.
- Hsu SH, Chang YB, Tsai CL, Fu KY, Wang SH, Tseng HJ, et al. “Characterization and biocompatibility of chitosan nanocomposites”. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011; 85: 198-206.
- Sherwani MA, Tufail S, Khan AA, Owais M. “Gold Nanoparticle- Photosensitizer Conjugate Based Photodynamic Inactivation of Biofilm Producing Cells: Potential for Treatment of C. albicans Infection in BALB/c Mice”. PLoS One. 2015; 10: e0131684.
- Bowler PG, Duerden BI, Armstrong DG, et al. “Wound microbiology and associated approaches to wound management”. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001; 14: 244-269.
- Boateng JS, Matthews KH, Stevens HN, Eccleston GM, et al. “Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: a review”. J Pharm Sci. 2008; 97: 2892-2923.
- Tiwari M, Narayanan K, Thakar MB, Jagani HV, Venkata Rao J, et al. “Biosynthesis and wound healing activity of copper nanoparticles”. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014; 8: 230-237.
- Gopal A, Kant V, Gopalakrishnan A, Tandan SK, Kumar D. “Chitosan-based copper nanocomposite accelerates healing in excision wound model in rats”. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014; 731: 8-19.
- Newman MD, Stotland M, Ellis JI. “The safety of nanosized particles in titanium dioxide- and zinc oxide-based sunscreens”. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 61: 685-692.
- Fu F, Li L, Liu L, Cai J, Zhang Y, Zhou J, et al. “Construction of cellulose based ZnO nanocomposite films with antibacterial properties through onestep coagulation”. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015; 7: 2597-2606.
- Sankar R, Dhivya R, Shivashangari KS, Ravikumar V, et al. “Wound healing activity of Origanum vulgare engineered titanium dioxide nanoparticles in Wistar Albino rats”. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014; 25: 1701-1708.
- Archana D, Singh BK, Dutta J, Dutta PK, et al. “Chitosan-PVP-nano silver oxide wound dressing: in vitro and in vivo evaluation”. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015; 73: 49-57.
- Becker S, Soukup JM, Gallagher JE, et al. “Differential particulate air pollution induced oxidant stress in human granulocytes, monocytes and alveolar macrophages”. Toxicol In Vitro. 2002; 16: 209-218.
- Suliman YA, Ali D, Alarifi S, Harrath AH, Mansour L, Alwasel SH. “Evaluation of cytotoxic, oxidative stress, proinflammatory and genotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells”. Environ Toxicol. 2015; 30: 149- 160.
- Adibhesami M, Ahmadi M, Farshid AA, Sarrafzadeh-Rezaei F, Dalir- Naghadeh B. “Effects of silver nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus contaminated open wounds healing in mice: An experimental study”. Vet Res Forum. 2017; 8: 23-28.
- Bahadar H, Maqbool F, Niaz K, Abdollahi M. “Toxicity of Nanoparticles and an Overview of Current Experimental Models”. Iran Biomed J. 2016; 20: 1-11.
- Botelho MC, Costa C, Silva S, Costa S, Dhawan A, Oliveira PA, et al. “Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human gastric epithelial cells in vitro”. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014; 68: 59-64.
- Yadi M, Mostafavi E, Saleh B, Davaran S, Aliyeva I, Khalilov R, et al. “Current developments in green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts: a review”. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018; 1-8.
- Saleem M, Nazir M, Ali MS, Hussain H, Lee YS, Riaz N, et al. “Antimicrobial natural products: an update on future antibiotic drug candidates”. Nat Prod Rep. 2010; 27: 238-254.
- Essa MM, Vijayan RK, Castellano-Gonzalez G, Memon MA, Braidy N, Guillemin GJ. “Neuroprotective effect of natural products against Alzheimer’s disease”. Neurochem Res. 2012; 37: 1829-1842.
- Molan P, T Rhodes. “Honey: A Biologic Wound Dressing”. Wounds. 2015; 27: 141-151.
- Carter DA, Blair SE, Cokcetin NN, Bouzo D, Brooks P, Schothauer R, et al. “Therapeutic Manuka Honey: No Longer So Alternative”. Front Microbiol. 2016; 7: 569.
- Cutting KF. “Honey and contemporary wound care: an overview”. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2007; 53: 49-54.
- Bayron J, Gallagher K, Cardenas L. “Medical-grade Honey as an Alternative to Surgery: A Case Series”. Wounds. 2019; 31: 36-40.
- Seow YX, Yeo CR, Chung HL, Yuk HG. “Plant essential oils as active antimicrobial agents”. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2014; 54: 625-644.
- Packer JM, Irish J, Herbert BR, Hill C, Padula M, Blair SE, et al. “Specific non-peroxide antibacterial effect of manuka honey on the Staphylococcus aureus proteome”. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012; 40: 43-50.
- Kavanagh S, Gunnoo J, Marques Passos T, Stout JC, White B. “Physicochemical properties and phenolic content of honey from different floral origins and from rural versus urban landscapes”. Food Chem. 2019; 272: 66-75.
- Saporito F, Sandri G, Bonferoni MC, Rossi S, Boselli C, Icaro Cornaglia A, et al. “Essential oil-loaded lipid nanoparticles for wound healing”. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018; 13: 175-186.
- Liakos IL, Holban AM, Carzino R, Lauciello S, Grumezescu AM. “Electrospun Fiber Pads of Cellulose Acetate and Essential Oils with Antimicrobial Activity”. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017; 7.
- Freire PL, Albuquerque AJ, Farias IA, da Silva TG, Aguiar JS, Galembeck A, et al. “Antimicrobial and cytotoxicity evaluation of colloidal chitosan - silver nanoparticles - fluoride nanocomposites”. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016; 93: 896-90.
- Sahariah P, Masson M. “Antimicrobial Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives: A Review of the Structure-Activity Relationship”. Biomacromolecules. 2017; 18: 3846-3868.
- Arkoun M, Daigle F, Heuzey MC, Ajji A. “Mechanism of Action of Electrospun Chitosan-Based Nanofibers against Meat Spoilage and Pathogenic Bacteria”. Molecules. 2017; 22.
- Coimbra P, Santos P, Alves P, Miguel SP, Carvalho MP, de Sá KD, et al. “Coaxial electrospun PCL/Gelatin-MA fibers as scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering”. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017; 159: 7-15.