
Research Article
Austin J Obstet Gynecol. 2017; 4(3): 1078.
The Impact of Endometriosis Symptoms on Health Related Quality of Life and Work Productivity in Egypt
Mohamed El-Maraghy¹*, Labib K¹, Waleed Salah El-Din² and Ahmed AB¹
¹Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ain Shams University, Egypt
²Department of Community Medicine, Ain Shams University, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Mohamed El-Maraghy, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ain Shams University, Egypt
Received: November 02, 2017; Accepted: November 27, 2017; Published: December 04, 2017
Abstract
Introduction: Endometriosis, usually called as “cancer of the careerwoman”, is being recognized as a “social disease” for its prevalence and its debilitating impact on young women, leading to a high socio-economic burden of the disease. It is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus and is found in women of all ethnic and social groups. The prevalence has been reported around 10% of the general female population and up to 50% in women with pelvic pain or infertility.
Aim of the Work: To assess the impact of endometriosis-related symptoms on work productivity and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in Egypt.
Materials and Methods: This is a cross sectional study that was performed from December 2016 to July 2017 at the Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics at Ain Shams University, anonymous questionnaires were administered individually to a total of 250 women with surgically diagnosed endometriosis. The questionnaires consisted of three sections: Patient Health Survey (SF-12), the Endometriosis Health Profile (EHP-5), and the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Survey (WPAI).
Results: The study confirm that endometriosis has a significant negative impact on work productivity and HRQoL of affected women, leading to high economic burden and huge costs to society, the WPAI showed absenteeism 16% of work time. Presenteeism 44% impairment. Percent overall work impairment due to health: 15.6%. Percent activity impairment due to health: 51% of regular daily activities disturbed.
Conclusion: Although endometriosis is not a life-threatening disease, this study confirmed that it can substantially affect women’s work productivity and HRQOL. Thus, endometriosis can be both physically and emotionally debilitating. Therefore it is time to make serious investment in preventing this debilitating condition in the next generation of women improving the collective level of awareness of endometriosis, its detection, and its treatment.
Keywords: Endometriosis; Work productivity; Quality of life; Pelvic pain; Egypt
Introduction
Endometriosis is a chronic disease, which is under diagnosed, under-reported, and under-researched Gao X et al. [1]. It is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus and is found in women of all ethnic and social groups. The prevalence has been reported around 10% of the general female population Giudice LC et al. [2], Berek JS et al. [3] and up to 50% in women with pelvic pain or infertility.
Endometriosis is often labeled ‘the missed disease’ Overton C et al. [4] and the average time between onset of pain and diagnosis is nearly 8 years in the United Kingdom, and 12 years in the United States of America Hadfield R et al. [5].
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus Kennedy et al. [6]. Like the uterine lining, this tissue builds up and sheds in response to monthly hormonal cycles. However, there is no natural outlet for the blood discarded from these implants. Instead, it falls onto surrounding organs, causing swelling and inflammation. Endometriosis triggers a chronic inflammatory reaction resulting in pain and adhesions. Adhesions develop when scar tissue attaches separate structures or organs together. The activity and the complaints due to endometriosis may vary during the woman’s menstrual cycle as hormone levels fluctuate. Consequently, symptoms may be worse at certain times in the cycle, particularly just prior to and during the woman’s menstrual period. While some women with endometriosis experience severe pelvic pain, others have no symptoms at all or regard their symptoms as simply being ‘ordinary menstrual pain’(Endometriosis association of Ireland).
The primary symptoms of endometriosis are pain and infertility. Endometriosis can be associated with dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, dysuria, chronic pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding Simoens S et al. [7]. The prevalence of endometriosis increases dramatically to as high as 25%–50% in women with infertility and 30-50% of women with endometriosis have infertility Verkauf BS et al. [8]. The severity of pain does not correspond with the number, location, or extent of endometriosis lesions. Some women with only a few small lesions experience severe pain; other women may have very large patches of endometriosis, but only experience little pain. (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2008), Stratton P et al. [9].
Chronic pelvic pain is a debilitating condition that may affect millions of women worldwide with a significant financial cost to both the individual and society Mathias SD et al. [10]. Specifically, endometriosis-associated pain is the major cause of physical, psychosocial, emotional and work related impairment among these women Oehmke F et al. [11]. Therefore endometriosis can be considered a debilitating disease which has a detrimental effect on the healthrelated quality of life (HRQoL) Mathias SD et al. [10]. in a large number of patients, as reported by several studies Mathias et al. [10], Bodner et al.[11], Gao et al. [12], Bianconi et al. [12].
HRQoL is a multidimensional, dynamic concept that encompasses physical, Psychological and social aspects associated with a disease or its treatment Guyatt GH et al. [13]. Generic instruments most commonly used to assess HRQoL include the Patient Health Survey SF36v2, its abbreviated form SF12v2 capture practical, reliable and valid information about functional health and well-being from the patient’s point of view. Another generic instrument created to evaluate the impact of a disease on productivity loss and daily life activities is the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire (WPAI), validated for use in many diseases but not in endometriosis Reilly MC et al. [14]. The only validated disease-specific HRQoL scales for endometriosis are the Endometriosis Health Profile EHP- 30 and its shorter version, EHP-5 Jones G et al. [15].
The objectives of the study was to describe the effect of endometriosis-related symptoms on physical, mental health status, sexuality and work-related aspects (absenteeism, presenteeism, work productivity, and activity impairment) on a sample of 250 patients based on anonymous questionnaires.
Material and Methods
Study design
This is a cross-sectional study.
Place and duration of the study
The study was performed from December 2016 to July 2017 at the Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics at Ain Shams university hospitals.
Sample size
250 female patients attending to the Ob/Gyn clinics with laparoscopic or histological diagnosis of endometriosis aged 15-45, with no other chronic or debilitating disease were asked to participate in the study, the patients were asked to fulfill the questionnaires with the assistance of a trained medical supervisor.
Exclusion criteria
• Patients beyond the age limits
• Patients with no surgical prove of endometriosis
• Patients suffering from any form of chronic illness
• Patients with psychological disorders
Study questionnaires
Three questionnaires, the SF-12, EHP-5, and WPAI, have been administered: The SF-12 provides patient-reported outcomes (PRO) data by measuring patients’ perceptions of their general health status during the past 4 weeks in eight dimensions: physical functioning, social functioning, role limitations due to physical problems, role limitations due to emotional problems, mental health, energy and vitality, pain, and general perception of health.
Questions are subdivided into 10 questions that refer to the physical and emotional status during the past month, and whether patients felt that these had interfered with performing daily life activities Fourquet J et al. [16].
The Endometriosis Health Profile is a Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) patient self-report, used to measure the wide range of effects that endometriosis can have on women’s lives. The EHP is the only condition-specific designed from the patient’s perspective to assess health related quality of life in endometriosis. The EHP-5 consists of 11 questions that assess whether and how much symptoms of endometriosis interfere with work and daily activities during the past 4 weeks. Other aspects of the impact of endometriosis measured are mood and appearance changes, perception that others do not understand, and feelings that pain controls one’s life. Also, the impact on sexual life, childcare, relationship with doctor, treatment efficacy, and maternity are also measured.
The Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) is a 6-item questionnaire was used to measure the impact of health on work performance. The WPAI consists of six questions about work experiences and perceptions of productivity levels at work. The impact on work aspects is measured using a scale, from 0 (not affected) to 100 (could not work at all), and information is obtained regarding the total number of working hours, number of missed work hours due to symptoms, and perceived productivity at work.
The WPAI yields four types of scores expressed as impairment percentages: absenteeism (work time missed), presenteeism (impairment at work/reduced on-the-job effectiveness), work productivity (overall work impairment/absenteeism presenteeism), and activity impairments. Higher WPAI percentages indicate greater impairment and less productivity Fourquet J et al. [16].
Consent
The purpose of the study was explained to all participants and an oral informed consent was obtained.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the ethical committee of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Ain shams university.
Data management
Data collected were entered into Excel, then Data were analyzed using Stata® version 14.2 (Stata Corp LLC, College Station, TX, USA). Normality of numerical data distribution was examined using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Non-Normally distributed numerical data were presented as median and interquartile range and categorical data as number and percentage.
Results
The questionnaire was completed by 250 women. The mean age of the population was 37.3 years (range: 24 to 45 years).188 participants of the 250 only were employers, while 162 participants of the 250 had children.
SF-12 results
The majority of participants rated their general health status as, ata minimum, ‘‘good’’ (n 197 of 250; 78%). More than half of the participants reported daily activities have been extremely (n 79 of 250; 31.6%) or moderately (n 84 of 250; 33.6%) limited by symptoms.
The majority of women reported that work-related activities were affected due to their physical health; (66.4%) accomplished less than expected, (56.8%) reported physical limitations.
Most of the women (n 137 of 250; 54.8%) reported that pain did interfere a little bit or moderately, while (n 74 of 250; 29.6%) reported that pain did interfere quite a bit or extremely on normal work (Table 1). The majority of the participants were employed (n 171of 250; 68.4%) were employed for a mean of 27.2 hours during the last week (standard deviation {SD} 7.1 hours).
Frequency
Percent
Valid Percent
Cumulative Percent
Valid Not at all
39
15.6
15.6
15.6
A little bit
84
33.6
33.6
49.2
Moderately
53
21.2
21.2
70.4
Quite a bit
47
18.8
18.8
89.2
Extremely
27
10.8
10.8
100
Total
250
100
100
Table 1: During the past 4 weeks, how much did pain interfere with your normal work (including both work outside the home and housework)?
Patients were asked to rate the impact of endometriosis-related symptoms on productivity loss and daily life using a scale of 0 to 10. Out of the 171 participants only 25th percentile choose 2 and below, while 50th percentile scored between 2 and 7, and 25th percentile choose above 7 which is severely affected, Based on this scale, loss of productivity had a mean score of 4.4 (SD_2.8) (Figure 1). As for daily activities out of the 250 participants; 25th percentile choose scores above 7, with a mean score of 5.1 (SD_2.7).
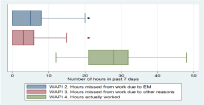
Figure 1: Box plot showing the response to WAPI Q2 to Q4. Box represents
the range from the 25th to 75th percentiles (interquartile range). Line inside
the box represents the 50th percentile. Whiskers represent the minimum and
maximum values excluding outliers (dots). Minimum value and 25th percentile
are overlapping in the plots of WAPI Q2 and WAPI Q3 As for daily activities
out of the 250 participants; 25th percentile choose scores above 7, with a
mean score of 5.1 (SD_2.7).
Out of the 171 working participants, 123 reported missing hours from work in the past seven days due their health problem (mean loss in work time 5.2 hours; SD_ 4.7 hours). The effects of endometriosis symptoms on the four domains measured by WPAI were quantified as,
• Percent work time missed due to health (absenteeism): 16% of work time.
• Percent impairment while working due to health (presenteeism): 44% impairment.
• Percent overall work impairment due to health: 15.6%
• Percent activity impairment due to health: 51 % of regular daily activities disturbed (activity impairment).
EHP results
Many participants (47.2%) reported that pain severely interfered with walking substantially (i.e., often or always) during the last month. Many participants (37.2%) reported that the symptoms of endometriosis severely controlled their life (i.e., often or always) during the last month (Table 2).
Frequency
Percent
Valid Percent
Cumulative Percent
Valid Never
37
14.8
14.8
14.8
Rarely
51
20.4
20.4
35.2
Sometimes
69
27.6
27.6
62.8
Often
56
22.4
22.4
85.2
Always
37
14.8
14.8
100
Total
250
100
100
Table 2: During the last 4 weeks, how often, because of your endometriosis, have you felt as though your symptoms are ruling your life?
Discussion
This cross-sectional study on 250 Egyptian women with endometriosis supports the evidence gathered by other studies conducted in other populations, indicating that endometriosis-related symptoms have a negative impact on HRQoL and work productivity.
Nowadays this issue is of growing interest in a society where increased health care costs and limited resources are of increasing concern. For this reason in recent years, the studies quantifying the costs of endometriosis Nnoaham KE et al. [17], Simoens S et al. [7] and the impact of the disease on health, work productivity, and daily life activities have increased. Damario MA et al. [18], Oehmke F et al. [11], Reilly MC et al. [14], Fourquet J et al. [16]. To quantify the impact of endometriosis-related symptoms in these important aspects of a person’s life, we compiled questions from three validated, standardized questionnaires into one instrument. The questionnaires used were (SF-12, WPAI, and EHP 5+6), these questionnaires were previously for assessment of endometriosis in different countries but this is the first to be done in Egypt or the Middle east.
There were 17 papers (14 quantitative and 3 qualitative) which reported findings relating to the impact of endometriosis on QoL and everyday activities. All of the studies demonstrate reduced QoL among women with endometriosis Marques A et al. [19], Petrelluzzi KF et al. [20], Siedentopf F et al. [21], Bernuit D et al. [22], Tripoli TM et al. [23], and one study demonstrated that a minority of women consider themselves to have a current state of health ‘worse than death’ Simoens S et al. [7].
Pain is consistently reported as a central and destructive feature of life with endometriosis and several studies report a negative correlation between pain and QoL Sepulcri et al. [24], Nnoaham et al. [18], Souza et al. [25], Tripoli et al. [23]. Endometriosis symptoms, and specifically pain, have a detrimental impact on daily life and physical functioning (e.g. sleeping, eating, moving) Jones G et al. [15], Petrelluzzi KF et al. [19]. Between 16% and 61% of women experience difficulties with mobility, daily activities and/or self-care. Fourquet J et al. [16], Simoens et al. [16]. Fourquet et al [16]. also found that women had SF-12 scores denoting statistically significant disability in physical and mental health components, indicating that the women in this study experienced substantial disability and Nnoaham et al. [18] found that women with endometriosis had reduced physical health compared with the normative population. Sleeping has also been found to be negatively affected by endometriosis Fourquet. et al. [16].
A focus on the impact of endometriosis on education has been included in a small number of papers with inconclusive findings. Whilst some studies reported that endometriosis had affected women’s study activity and grades, and had caused some to leave education before completion Huntington et al. [20], Gilmour et al. [18], others reported that only a minority of women had experienced negative consequences on their education Fagervold et al. [26].
More commonly, researchers have explored how endometriosis has impacted on women’s working lives. Several papers suggest that women’s endometriosis symptoms, particularly pain symptoms, impact on productivity at work with between 23 and 66% reporting limitations in their ability to perform work-related activities Fourquet et al. [16]; 2011, Bernuit et al. [17]. Fourqu et al. [16] so reported that 84–85% of women described a decrease in their quality of work, and elsewhere these authors report an average rate of work impairment and reduced effectiveness of 65% (presenteeism) and an average loss of efficiency levels of 64% (work productivity loss) Fourquet et al. [16]. Informing employers of their diagnosis of endometriosis and of its symptoms causes tensions for women, as while it is felt to be a private condition, women also need support in employment Gilmour et al. [18]. Women do not always inform employers of their diagnosis or symptoms for a range of reasons including the potential implications of this and because they find it difficult to discuss a gender-specific condition with male employers Gilmour et al. [18]. The study by Gilmour suggested that the decision to disclose may be affected by women’s past experiences of being disbelieved.
WPAI was used to measure the impact of health on work performance. WPAI results showed a substantial impact of symptoms in both work productivity (moderately affected) and daily life activities (extremely affected).
Our WPAI results showed the mean loss in work time was (5.2hours; SD_4.7hours) with a mean of 27.2 hours actually worked during the last 7 days, which were compared to other studies using the same utilities, one Study held at University of Rome, Sant’ Andrea Hospital, Rome, Italy by Donatella showed the mean loss in work time was (2.3 hours; SD_ 5.3 hours) with a mean of 36.4 hours actually worked during the last 7 days. While another study held by Fourqu et at. [16] Ponce School of Medicine and Health Sciences in Puerto Rico showed that the mean loss in work time (7.41 hours; SD_ 8.97 hours) with a mean of 24.6 hours actually worked during the last 7 days.
In order to extrapolate the total annual societal burden of endometriosis, a recent multi-center study was conducted by Simoens et al. [17] in 10 countries. The authors, using a theoretical model, reported that the average annual total cost per woman affected by endometriosis was €9579 (95% confidence interval €8559-€10599) and costs of productivity loss of €6298 per woman were double the health care costs of €3113 per woman, showing that the economic burden of endometriosis arises predominantly from productivity loss. They also extrapolated the total annual societal costs for endometriosis in Italy, which was € 9.3 billion.
Regarding the impact of the disease on HRQoL, Jia et al. [19] recently reviewed all the available literature on the subject and the authors concluded that HRQoL is impaired in such women, and medical or surgical treatment to alleviate pain could partially restore this impairment Jia et al. [19].
Although endometriosis is not a life-threatening disease, this study confirmed that it can substantially affect women’s work productivity and HRQOL. Thus, endometriosis can be both physically and emotionally debilitating. Physically, endometriosis pain can impair work and daily activities. Psychologically, the disease can lead to depression, anxiety and feelings of low self-esteem, which in turn lead to impairment in work productivity and HRQoL Lemaire et al. [25].
Conclusion
This cross sectional quantitative study provides tangible evidence of the negative impact of endometriosis on important aspects related to work and daily life, as shown before qualitatively and the review has identified a large number of studies which address the psychological and social impact of endometriosis on women’s lives, with the majority identifying a significant impact across several domains [26- 30].
Endometriosis generally affects women during the most productive years of their lives, when they should be finishing education, starting a career and probably have a family. Although endometriosis is known to have relevant impact on different aspects of patients’ daily lives, the disease often remains misdiagnosed. Consequently, the burden of endometriosis on women and society remains under-estimated. For these women to have their productivity impaired, their quality of life compromised and their chances for starting a family reduced, is something society can no longer afford to ignore. Therefore it is time to make serious investment in preventing this debilitating condition in the next generation of women improving the collective level of awareness of endometriosis, its detection, and its treatment.
References
- Gao X, Yeh YC, Outley J, Simon J, Botteman M, Spalding J. Health-related quality of life burden of women with endometriosis: a literature review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006; 22: 1787-1797.
- Giudice LC. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 36: 2389-2398.
- Berek JS. Berek& Novak’s Gynecology. 15th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, North American Edition edition. 2012.
- Overton C, Park C. Endometriosis: more on the missed disease. BMJ. 2010; 341: c3727.
- Hadfield R, Mardon H, Barlow D, Kennedy S. Delay in the diagnosis of endometriosis: a survey of women from the USA and the UK. Hum Reprod. 1996; 11: 878-880.
- Kennedy S, Bergqvist A, Chapron C, D’Hooghe T, Saridogan E. ESHRE Special Interest Group for Endometriosis and Endometrium Guideline Development Group. ESHRE guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2005; 20: 2698-2704.
- Simoens S, Dunselman G, Dirksen C, Hummelshoj L, Bokor A, Brandes I, et al. The burden of endometriosis: costs and quality of life of women with endometriosis and treated in referral centres. Hum Reprod. 2012; 2: 1292- 1299.
- Verkauf BS. Incidence, symptoms, and signs of endometriosis in fertile and infertile women. J Fla Med Assoc. 1987; 74: 671-675.
- Stratton P, Berkley KJ. Chronic pelvic pain and endometriosis: Translational evidence of the relationship and implications. Hum Reprod Update. 2011; 17: 327-346.
- Mathias SD, Kuppermann M, Liberman RF, Lipschutz RC, Steege JF. Chronic pelvic pain: prevalence, health-related quality of life, and economic correlates. Obstet Gynaecol. 1996; 87: 321-327.
- Oehmke F, Weyand J, Hackethal A, Konrad L, Omwandho C, Tinneberg HR. Impact of endometriosis on quality of life: a pilot study. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2009; 25: 722-725.
- Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Patrick DL. Measuring health-related quality of life. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 118: 622-629.
- Reilly MC, Gooch KL, Wong RL, Kupper H, van der Heijde D. Validity, reliability and responsiveness of theWork Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49: 812-819.
- Jones G, Jenkinson C, Kennedy S. The impact of endometriosis upon quality of life: a qualitative analysis. J Psychosom ObstGyn. 2004; 25: 123-133.
- Fourquet J, Báez L, Figueroa M, Iriarte RI, Flores I. Quantification of the impact of endometriosis symptoms on health-related quality of life and work productivity. Fertil Steril. 2011; 1: 107-112.
- Nnoaham KE, Hummelsho JL, Webster P, d’Hooghe T, de Cicco Nardone F, Jenkinson C, et al. Impact of endometriosis on quality of life and work productivity: a multicenter study across ten countries. Fertil Steril. 2011; 2: 366-373.
- Damario MA, Rock JA. Pain recurrence: a quality of life issue in endometriosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1995; 50: S27-42.
- Gilmour J, Huntington A, Wilson H. The impact of endometriosis on work and social participation. Int J Nurs Pract. 2008; 6: 443-448.
- Jia SZ, Leng JH, Shi JH, Sun PR, Lang JH. Health-related quality of life in women with endometriosis: a systematic review. J Ovarian Res. 2012; 5: 29.
- Marques A, Bahamondes L, Aldrighi JM, Petta CA. Quality of life in Brazilian women with endometriosis assessed through a medical outcome questionnaire. J Reprod Med. 2004; 2: 115-120.
- Petrelluzzi KF, Garcia MC, Petta CA, Grassi-Kassisse DM, Spadari-Bratfisch RC. Salivary cortisol concentrations, stress and quality of life in women with endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain. Stress. 2008; 5: 390-397.
- Siedentopf F, Tariverdian N, Ru··cke M, Kentenich H, Arck PC. Immune status, psychosocial distress and reduced quality of life in infertile patients with endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008; 5: 449-461.
- Bernuit D, Ebert AD, Halis G, Strothmann A, Gerlinger C, Geppert K, et al. Female perspectives on endometriosis: findings from the uterine bleeding and pain women’s research study. J Endometriosis. 2011; 2: 73-85.
- Tripoli TM, Sato H, Sartori MG, de Araujo FF, Girão MJ, Schor E. Evaluation of quality of life and sexual satisfaction in women suffering from chronic pelvic pain with or without endometriosis. J Sex Med. 2011; 2: 497-503.
- Sepulcri RD, Amaral VF. Depressive symptoms, anxiety, and quality of life in women with pelvic endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009; 1: 53-56.
- Souza CA, Oliveira LM, Scheffel C, Genro VK, Chaves MF, Filho J. Quality of life associated to chronic pelvic pain is independent of endometriosis diagnosis: a crosssectional survey. Health Qual Life Out. 2011; 1: 41-45.
- Fagervold B, Jenssen M, Hummelshoj L, Moen MH. Life after a diagnosis with endometriosis: a 15 years follow-up study. ActaObstetGyn Scan. 2009; 8: 914-919.
- Lemaire GS. More than just menstrual cramps: symptoms and uncertainty among women with endometriosis. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2004; 33: 71-79.
- Huntington A, Gilmour J. A life shaped by pain: women and endometriosis. J Clin Nurs. 2005; 9: 1124-1132.
- Donatella C, Giulia B, Eleonora R, Eleonora M, Flaviano M. Impact of Endometriosis on Work Productivity and Quality of Life: a Survey from Italy. Int J Manage Scien Busin Res. 2013; 2: 42-48.