
Case Presentation
Austin J Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 5(3): 1099.
Mucinous Cystadenoma of the Appendix Mimicking the Left Adnexal Mass
Tokgoz VY¹*, Sipahi M¹, Kesicioglu T², Ozen O³, Kozan R4 and Numan O5
¹Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Giresun, Turkey
²Department of General Surgery, Giresun, Turkey
³Department of Radiology, Giresun, Turkey
4Department of General Surgery, Istanbul, Turkey
5Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ordu, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Tokgoz Vehbi Yavuz, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Giresun University School of Medicine, Giresun/Turkey
Received: February 02, 2018; Accepted: February 22, 2018; Published: March 01, 2018
Abstract
Appendiceal mucocele is a cystic mass caused by accumulation of mucinous secretions and dilatation of appendix lumen. It occurs with mucosal hyperplasia, mucinous cystadenoma or mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. Mucinous cystadenoma of the appendix is the most common type and most frequent symptom is lower-quadrant pain. Mucocele may be misdiagnosed as ovarian cyst especially right adnexal mass. Differential diagnosis remains difficult and mucocele usually detected during surgery. Laparotomy is the most preferred surgical approach due to concerns about the rupture risk of appendiceal mucoceles, because spread of its contents produces pseudomyxoma peritonei. We presented a case of 52 year-old women who underwent laparotomy for a left adnexal mass. Mucocele was found and appendectomy was performed without any rupture.
Keywords: Appendix; Mucinous Cystadenoma; Adnexal mass; Mucocele
Case Presentation
A 52-year-old woman presented to our gynecology clinic with chronic pelvic pain since 6 months which increased during the last 2 weeks. Physical examination revealed bilateral lower quadrant tenderness with no rigidity. In the blood tests, there were no abnormal findings; Ca-125(cancer antigen 125), AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) and CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) were in normal range.
Transvaginal and trans abdominal ultrasound examination were performed. Ultrasonographic examination revealed a thick-walled left adnexal cystic mass measuring 77x22 mm in a tubular structure suggesting hydrosalpinx or paraovarian cyst (Figure 1D). There was no blood flow on doppler.
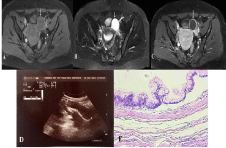
Figure 1: Pelvic MRI; 1A: axial fat suppressed T1A sequence showed
hypointense;
1B: axial fat suppressed T2A sequence showed hypointense well-defined
mass on left adnexa;
1C: After contrast injection; axial fat suppressed T1A sequence showed
peripheral contrast enhancement;
1D: A thick-walled left adnexal cystic mass measuring 77x22 mm in
ultrasound;
1E: Mucinous epithelium with no invasion and no atypia in histopathological
examination.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) with contrast showed a 42x35 mm thin-walled cystic lesion in the left adnexa with peripheral contrast enhancement without contrast uptake enhancement (Figure 1A, 1B, 1C). In MRI, there was no papillary projection, however no free fluid was seen in the Douglas pouch.
Operation was planned for patient, but within this period patient admitted to the clinic with severe abdominal pain and tenderness. The patient underwent laparotomy with pfannenstiel incision, the uterus and ovaries were atrophic. A 7x3 cm cystic mass with smooth surface which had mucous fluid was located and it was originated from the appendix. Appendectomy was performed without rupture of the cystic mass by general surgery.
Histopathologic evaluation of the specimen revealed fusiform appearance cystically dilated appendix, and filled with mucous material. It was diagnosed as mucinous cystadenoma of appendix and the resection margin of the lesion was free of dysplasia (Figure 1E).
Patient was discharged from the hospital with a good recovery 3 days later. After 2 months, the patient underwent colonoscopy, no pathological finding was found.
Discussion
Appendiceal mucocele is a rare lesion of the appendix, caused by obstruction of appendix lumen therefore cystic dilatation and intraluminal mucin accumulation of appendix arises [1]. Mucoceles may occur as a result of mucosal hyperplasia, mucinous cystadenoma or mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. Neoplastic lesions of the appendix with a mucocele are rare. Mucinous cystadenomas of the appendix is nearly 7% of all appendiceal neoplasms [2]. Diagnosis of appendiceal mucocele is difficult preoperatively and is often determined incidentally by surgery for other causes [3]. Twenty-five percent of cases are asymptomatic and the most frequent symptom is right lower quadrant abdominal pain [4]. Cystic dilatation of mucocele may resemble ovarian or paraovarian cystic structure in ultrasound, computed tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging so it can be misdiagnosed.
Here we presented a case of mucinous cystadenoma of appendix mimicking adnexal cyst in preoperative radiological and gynecologic evaluation.
Mucinous cystadenoma of the appendix usually presents as appendiceal mucocele that characterized mucin accumulation in the appendix lumen due to obstructive process and cystadenomas is the most common cause of mucocele [1]. Appendiceal mucocele is usually diagnosed in elderly patients who are in their fifth decades and more frequent in women than men [5]. One fourth of patients have no symptoms and most common presentation is acute or chronic right lower quadrant abdominal pain [4].
There is no specific clinical symptom of mucocele because of this preoperative diagnosis is difficult and most of the cases are diagnosed by surgery incidentally. In gynecologic evaluation, transvaginal ultrasonography is routinely performed and in these patients cystic mass of the appendiceal mucocele in the right lower abdomen can be misjudged as an adnexal mass [6]. Interestingly we revealed left adnexal cyst instead of right adnexa in our ultrasonographic and MRI evaluation.
Mucoceles have some specific ultrasonographic findings like ‘onion sign’ that is echogenic layers within the cystic mass, despite it is high suggestive for appendiceal mucocele, purely cystic mass or complex hyperechoic mass can be seen depend on its contents [7,8]. MRI also reveals some specific signal intensities on T1-weigted scan and T2-weighted scan, low signal intensity and high signal intensity respectively [9].Choice of appropriate surgical treatment is controversial. Some authors suggested open surgical procedure for the possibility of malignant tumor because rupture of the malign cyst during surgery can cause pseudomyxoma peritonei which is difficult to treat [10]. On the contrary, others established that laparoscopic approach is suitable if it is performed carefully [3].
We presented a rare case of mucinous cystadenome of the appendix mimicking left adnexal cyst. We performed open surgical procedure and excised the appendix without any rupture.
Conclusion
Differential diagnosis of appendiceal mucocele is very difficult due to lack of specific symptoms. Cystic structures of lower abdomen resemble hydrosalpinx, ovarian/paraovarian cysts, mesenteric cysts, enteric duplication cysts. We suggested that mucinous cystadenoma should be considered in differential diagnosis of cystic mass on lower abdomen though it is in left adnexal region in ultrasound and MRI.
References
- Maa J, Kirkwood K. The appendix. Townsend C, Beauchamp R, Ever B, Mattox K, editors. In: Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. 2012; 1279-1293.
- Connor S, Hanna G, Frizelle F. Appendiceal tumors: retrospective clinicopathologic analysis of appendiceal tumors from 7,970 appendectomies. Dis Colon Rectum. 1998; 41: 75-80.
- Sikar HE, Cetin K, Gundogan E, Gundogan GA, Kaptanoglu L. Retroperitoneal mucinous cystadenoma of the appendix mimicking hydatid cyst: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016; 5: 345-347.
- Aho AJ, Heinonen R, Laur´en P. Benign and malignant mucocele of the appendix. Histological types and prognosis. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica. 1973; 139: 392-400.
- Ruiz-Tovar J, Teruel DG, Castineiras VM, Dehesa AS, Quindos PL, Molina EM. Mucocele of the appendix. World J Surg. 2007; 31: 542-548.
- Ahmed N, Vimplis S, Deo N. A mucocele of the appendix seen as an adnexal mass on ultrasound scan. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017; 37: 116-117.
- Caspi B, Cassif E, Auslender R, Herman A, Hagay Z, Appelman Z. The onion skin sign: a specific sonographic marker of appendiceal mucocele. J Ultrasound Med. 2004; 23: 117-121.
- Honnef I, Moschopulos M, Roeren T. Appendiceal mucinous cystadenoma. Radiographics. 2008; 28: 1524-1527.
- Cois A, Pisanu A, Pilloni L, Uccheddu A. Intussusception of the appendix by mucinous cystadenoma. Report of a case with an unusual clinical presentation. Chir Ital. 2006; 58: 101-104.
- Skaane P, Ruud TE, Haffner J. Ultrasonographic features of mucocele of the appendix. J Clin Ultrasound. 1988; 16: 584-587.