Case Report
Austin Oncol Case Rep. 2022; 5(1): 1015.
Recurrent Intracranial Meningioma with Pulmonary Metastases: A Case Report
Rim A, Alia M*, Lina K and Chiraz N
Department of Radiation Therapy, Salah Azaiz Institute, Tunis, Tunisia
*Corresponding author: Mousli Alia, University Tunis El Manar, Campus Universitaire Farhat Hached, B.P. n° 94 - ROMMANA, Tunis 1068, Tunisia
Received: December 24, 2021; Accepted: January 21, 2022; Published: January 28, 2022
Abstract
We report a 40-year-old female diagnosed with histological grade III meningioma of OMS 2016 in the right side of the temporo-parietal region of skull vault. After a partial resection of the primary site, she rapidly developed unusual multiple metastasis in the pulmonary parenchyma. The patient received adjuvant radiotherapy on the residual volume with palliative decompressive intent due to the gross tumor volume. A review of the literature revealed well documented cases of benign meningiomas that metastasized in an interval of up to 10-12 years after primary tumor resection. This case illustrates that meningiomas Grade III WHO with progression disease of the primary tumor have the potential to develop hematogenous rapid metastases, emphasize the role of multimodal management and the role of genetic behavior to predict such evolution.
Keywords: Meningioma; Pulmonary metastases; Radiotherapy; Palliative
Introduction
Meningiomas represent 14-19% of all primary intracranial neoplasms [1]. They are slow-growing typically benign intracranial tumors that develop from the arachnoid membrane. After total resection, meningiomas represent a low rate of recurrence [2]. Numerous risk factors of recurrence were described in the literature such as histological grade, subtotal resection, young age, brain infiltration, and high proliferative rate [2]. Reportedly, 2-10% of meningiomas exhibit aggressive behaviour and the prevalence of distant metastases is estimated to 0.1-1% of all meningioma patients. [3]. Extracranial meningioma metastases have been reported to occur mostly in the lungs (61%), followed by the liver, lymph nodes, and bone [3].
We report a case of multiple pulmonary meningioma metastases developing after initial resection of right temporo-parietal World Health Organization Grade III intracranial meningioma
Case Presentation
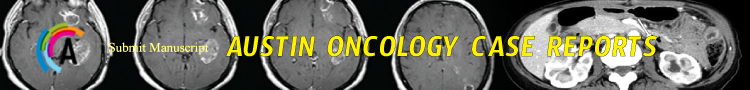
Miss Y.N is a 40-year-old woman, with no past medical and family history. A right cranial vault swelling appeared in May 2020 related to an ipsilateral temporo-parietal exteriorized mass with necrosis without any neurological symptoms. A Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) revealed osteolytic tissue process of the right temporo-parietal vault measuring 10cm in the greatest axis with intracranial invasion and ventricular junction’s compression. It showed a hydrocephalus of the temporal horn with deviation of the midline reaching the right transverse venous sinus (Figure 1). It was incompletely surgically removed with peripheral bone and dura infiltration. A cranioplasty with PALACOS® cement was made.
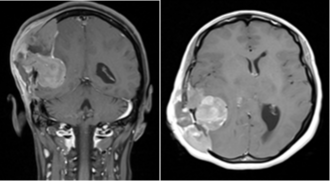
Figure 1: Pre-operative tumor.
The postoperative pathologic examination showed a poorly undifferentiated tumor proliferation of marked cell density, composed by anaplastic-looking cells with a nucleus provided chromatin arranged in a fine clod of vesicular appearance. The nuclear contours were irregular and the nucleocytoplasmic ratio was high. Cellular anaplasia was severe with the presence of atypical nucleus tumor cells. This concluded into aggressive anaplastic meningioma recurrence with infiltration of adjacent bone and adjacent glial parenchyma. The immunohistochemically study revealed cell Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), Vimentin and PS100 cell expression. The Ki 67 index proliferation was 30% in hot-spot zones. Finally, we don’t find actin and desmin expression excluding the diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma.
Three months later, after surgery, the tumor progressed at the initial site. She had a voluminous increased temporo-parietal mass beyond the midline with new appearance of lesions associated with intracranial hypertension syndrome (Figure 2). A Brain MRI showed significant right hemispherical nodular tumor recurrence opposite to the cranioplasty, the largest one is a 40 x 30 mm cystic formation in the right temporal lobe. The cranioplasty implant was deviated outward with extension to the right hemispherical scalp beyond the midline to the left frontal scalp and invaded the ipsilateral temporal and occipital bone with partial extension to the right transverse sinus associated to oedema (Figure 3). The thoraco-abdominal CT scan showed multiple bilateral lung nodules.
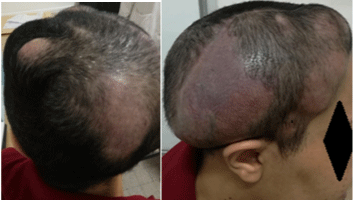
Figure 2: Voluminous increased temporoparietal mass.
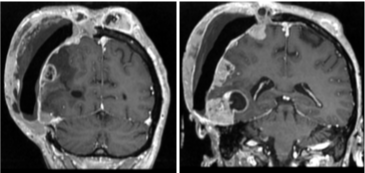
Figure 3: Post-operative MRI progression of the residual meningioma tumor.
In a multidisciplinary team, we performed a palliative cerebral radiotherapy given the metastatic status. The patient underwent a conformational whole brain radiation therapy at the dose of 40Gy in 20 fractions. A partial response was observed in the latest evaluation with clinical regression in number and size of lesions (Figure 4). For pulmonary progression, she received an anti-VEGF therapy by Bevacizumab.
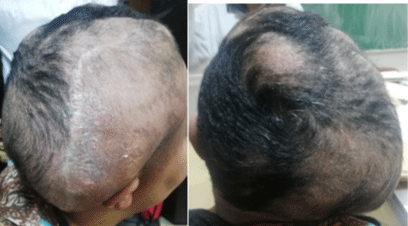
Figure 4: Clinical tumor regression after radiotherapy.
Discussion
Meningiomas annual incidence is about 4-5 cases in 100,000 people. They are commonly associated to genetic alterations in the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene. Diagnosis is based on MRI and confirmed by histopathological finding [4]. The World Health Organization (WHO) classified meningioma in 3 subtypes [5]. An atypical and anaplastic meningioma is present in 20% of cases [4].
Metastases outside the brain are an extremely rare entity less than 0.1% of all cases [6]. Metastatic meningioma may occur even a decade after initial tumor resection. The mean interval between diagnosis of the primary tumor and discovery of the first metastases ~6 years [7]. Metastases generally occur through haematogenous or lymphogenous way. Pulmonary metastases are the most frequent [8]. They rarely induce symptoms and are commonly present as a single lesion, or, less frequently, as multiple round noncalcified parenchymal nodules of different sizes. Multiple deposits are identified in 50% of cases [7]. High cellularity, cellular heterogeneity, high mitotic rate, nuclear pleomorphism, tumor necrosis and invasion of adjacent blood vessels are histological factors of metastases [9]. On the other hand, the authors showed that a higher cell proliferation is not a necessary factor of extra-cranial metastasis, and that metastases can occur in any type of individual meningioma. For recurrent intracranial meningioma, comprehensive examinations should be conducted for an early detection of distant metastasis even when the primary tumor is benign [10].
There is a relationship between metastasis and tumor location. Especially, parasagittal and falcine located meningioma metastasized more frequently than other location [11]. Another hypothesis of tumor spread is the blood-brain barriers damage at the moment of primary craniotomy. Intracranial tumor recurrence as well as papillary morphology and histological malignancy may predict of multiple metastases [12].
Furthermore, loss of heterozygosity at 9p, 1p and 22q has been reported to be a potential predictor of multiple pulmonary metastases [12]. The molecular properties of meningiomas have identified genetic biomarkers that effect tumor behaviour. Analyses of genetic and epigenetic changes may reveal better understanding of meningioma progression mechanisms [13].
In our case MRI found that the tumor invades the transverse venous sinus and we found also an infiltration of bone and adjacent glial parenchyma. The pathologic examination showed hypercellularity and infiltration of cranial bone and adjacent normal parenchyma. Ki67 was also high. Some author mentioned that Ki67 was related to the potential risk of recurrences but also metastases [11].
Nowadays, there are no established guidelines for optimal treatment in the case of extensive pulmonary metastatic meningioma. In the present case the brain tumor recurrence was early detected with synchronous diffuse pulmonary metastases. This emphasizes the need for an early detection of distant metastases. We performed a whole brain irradiation with partial response and start bevacizumab for pulmonary Metastasis.
Conclusion
Atypical meningiomas, sinus invasion and tumor recurrence may be the more predictive factors of pulmonary metastases. For early detection, enhanced pulmonary computed tomography is recommended for recurrent intracranial meningioma. There are no established guidelines for the optimal management of extensive pulmonary metastatic meningioma and it should be considered as part of the differential diagnosis.
Declaration
Acknowledgements: I am very thankful to all contributors, who were very helpful and without their support this case study would have never come into its present form.
Ethics approval and consent to participate Consent for publication written informed consent for publication of clinical details and clinical images was done.
Consent for publication: A written consent for publication is given by the patient.
Authors’ contributions: Both authors contributed equally to the final version of the publication, have read, and approved the manuscript.
Availability of data and material: The data sets supporting the conclusion of this article are included within the article.
References
- Rampurwala M, Pazooki M, Schauer P. Delayed hepatic metastasis from a benign fibroblastic meningioma thirty-one years after surgical resection of the intracranial tumor. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29: e214-215.
- Abboud M, Haddad G, Kattar M, et al. Extraneural metastases from cranial meningioma: a case report. Radiat Oncol. 2009; 4: 2.
- Kaminski JM, Movsas B, King E, et al. Metastatic meningioma to the lung with multiple pleural metastases. Am J Clin Oncol. 2001; 24: 579-582.
- Riemenschneider MJ, Perry A, Reifenberger G. Histological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5: 1045-1054.
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016; 131: 803-820.
- Nakano M, Tanaka T, Nakamura A, Watanabe M, Kato N, Arai T, et al. Multiple pulmonary metastases following total removal of a bilateral parasagittal meningioma with complete occlusion of the superior sagittal sinus: Report of a case. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2012: 121470.
- Kovoor JM, Jayakumar PN, Srikanth SG, Indiria B, Devi MG. Solitary pulmonary metastasis from intracranial meningiothelial meningioma. Australas Radiol. 2002; 46: 65-68.
- Incarbone M, Ceresoli GL, Di Tommaso L, Cappuzzo F, InzirilloFnfante M, et al. Primary pulmonary meningioma: Report of a case and review of the literature. Lung Cancer. 2008; 62: 401-407.
- Surov A, Gottschling S, Bolz J, Kornhuber M, Alfieri et al. Distant metastases in meningioma: an underestimated problem. J Neurooncol. 2013; 112: 323- 327.
- KE-DA Wang, YI-Bing Su and Yan. Recurrent intracranial meningioma with multiple pulmonary metastases: A case report. Oncology Letters. 2015; 10: 2765-2768.
- Drummond KJ, Bittar RG, Fearnside MR. Metastatic atypical meningioma: case report and review of the literature. J ClinNeurosci. 2000; 7: 69-72.
- Gladin CR, Salsano E, Menghi F, et al. Loss of heterozygosity studies in extracranial metastatic meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2007; 85: 81-85.
- He N, Zhong L, Lei K. Multiple Pulmonary and Pleural Metastases in Recurrent Intracranial Meningioma with Genetic Changes: Case Report and Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2020; 136: 337-340.