Special Article: Orthopedics: Clinical Cases and Images
Austin J Orthopade & Rheumatol. 2014;1(2): 1.
Patient with Bone Atrophy of the Feet
Pedro Carpintero*, Manuel Roman and Rocio Carpintero
Department of Orthopedics, University Hospital Reina Sofia, Spain
*Corresponding author: Pedro Carpintero, Department of Orthopedics, University Hospital Reina Sofia, Mejorana 45. 14012. Cordoba, Spain,
Received: November 28, 2014; Accepted: December 01, 2014; Published: December 04, 2014
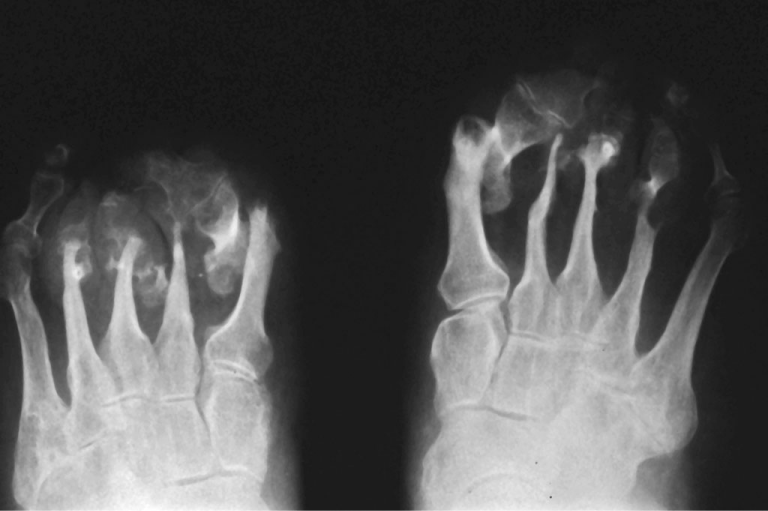
African patient of 34-year old admitted to hospital for foot deformity. Was treated ten years after in his country of leprous nepromatosy, in x-ray examination (Figure 1) was observed marked resorption of phalanges and metatarsals, with tapered appearance (“licked candy stick” or pencil like” osteolysis.
Figure 1: Text Here.
Mycobacterium leprae attacks the skin and peripheral nerves and has a predilection for the cooler appendages of the body with characteristic involvement of the small bones of the hands and feet.
Bone resorption in patients with Hansen´s disease is secondary to sensory impairment, complicated with repeated micro trauma and infection. Leprous bone disease can progress even several years after having completed specific treatment for the disease, meaning that such treatment is necessary, but that it is not sufficient to cure the bone lesions.
Patients should be instructed to examine their hands and feet periodically to search for any small wounds and to take adequate precautions both at home and at work.