
Case Report
Austin J Orthopade & Rheumatol.2017; 4(1): 1049.
Spondyloarthritis in SLE-Therapeutic Challenge!
Subramanian N*
Department of Medicine and Rheumatology, Velammal Medical College Hospital, India
*Corresponding author: Subramanian N, Department of Medicine and Rheumatology, Velammal Medical College Hospital, Madurai, India
Received: February 07, 2017; Accepted: February 22, 2017; Published: February 27, 2017
Abstract
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a multisystem immune mediated disease and sometimes called as “disease of mimics”. It is the most common of the connective tissue diseases and most common presenting features are fever, rash, weight loss, lymphadenopathy and cytopenia. Inflammatory back pain and sacroileitis are uncommon in SLE and most commonly seen in HLA B27 positive males. We present this man with sacroileitis in SLE and the complexities in diagnosis and management.
Keywords: SLE; Spondyloarthritis; Adalimumab; Lupus nephritis
Introduction
Complex autoimmune diseases can manifest in different ways and SLE associated sacroileitis is rare. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE, lupus) is a highly complex and heterogeneous autoimmune disease that most often afflicts women in their child-bearing years. It is characterized by circulating self-reactive antibodies that deposit in tissues, including skin, kidneys, and brain, and the ensuing inflammatory response can lead to irreparable tissue damage. Inflammatory arthritis in ankylosing spondylitis causes pain and stiffness and progressively leads to new bone formation and ankylosis (fusion) of affected joints. SLE and Spondyloarthritis are two autoimmune rheumatologic diseases with different aetiopathogenesis as well as diverse clinical and genetic characteristics and are rarely seen together. To the best of our knowledge, there are only 9 reported cases of the coexistence of SLE and AS in the English literature [1]. I present a unique patient journey with challenging management decisions.
Case Presentation
A 24 yrs old male, PhD student, was referred with arthalgia, fever and cough. He had history of hair loss, mouth ulcers for a month. He had sacrolieitis diagnosed on CT Pelvis 2 yrs ago and had been continuing indomethacin for a year. His ANA and HLA B27 were negative.
At the time of hospitalization, he was febrile, tachypneic and in septic shock. He had features of pneumonia and ankle synovitis. His chest X ray showed pleural effusion with consolidation. He had hematoproteinuria and acute kidney injury.
Investigations
His blood test results showed neutrophilia, lymphopenia, ESR 110, platelets 410, CRP 48, Urea 74, creatinine 2.2, Urine PCR 5.2, ANCA, HLA B27, Rheumatoid Factor, ASO Titre, ACE levels all were negative, ANA 1 in 2560 positive and dsDNA high, Low c3, c4, Cardiolipin and antiphospolipid antibody normal, raised SGOT and SGPT with globulins too. ECHO was normal. CT chest showed consolidation with pleural effusion.
Management
He was diagnosed with sepsis due to Pneumonia and features of SLE. Following treatment for sepsis, he was given Methylpred and his renal functions improved. He was given Mycophenolate and steroids weaned. During his follow up, blood parameters, ANA, dsDNA normalized.
After 4 months he developed inflammatory back pain, His MRI showed asymmetric bilateral sacroileitis (Figure 1) and steroids was given with methotrexate instead of Mycophenolate. Although he improved with steroids he developed significant acne. His bloods showed raised CRP and no features of SLE.
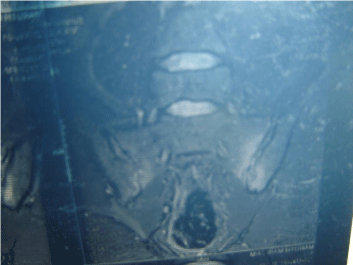
Figure 1: MRI Pelvis shows active Sacroileitis bilaterally.
He was screened for biologics and given Adalimumab for 3 months with both symptomatic and imaging benefit. However after 2 months he developed PIPJ synovitis and back pain, with increasing CRP. He then started having leg edema due to proteinuria and had renal biopsy. He had lupus nephritis WHO Class V. He achieved disease remission with mycophenolate and corticosteroids. His CRP and renal functions got normalized and urine PC ratio was 5.1
Discussion and Conclusion
Initially this gentleman had features of spondyloarthritis, then he developed evidence of SLE and was controlled on mycophenolate. However he noticed inflammatory back pain and sacroileitis and hence he was given Adalimumab (TNF alpha blocker). He couldn’t continue after 3 months and then he developed peripheral arthritis for which he had methotrexate. But his SLE got progressed to involve kidneys and he developed lupus nephritis (biopsy proven) and again he is on low dose steroids and mycophenolate.
His systemic disease had changed both clinically and immunologically. His unifying diagnosis is Spondyloarthritis in SLE.
Overlap syndromes define patients exhibiting enough features to meet the diagnosis of several CTDs at the same time [2]. Thus, they “overlap” two or more diseases. Any CTD can be a partner in an overlap disorder. For example, patients can have a combination of RA and SLE («rhupus»), or SSc and PM [3]. Most of the reported cases of SLE and AS coexistence are females and generally SLE precedes the occurrence of AS. To our knowledge this is the first patient with SLE and Spondyloarthritis in male [4,5] in India.
SLE in male and having spondyloarthritis are two faces of immunological diathesis in human system. Further long term review will throw more light on this complex disease.
Overall improvements in medical care including the availability of antibiotics, anti-hypertensive’s, and renal replacement therapy coupled with the judicious use of glucocorticoid, antimalarial, and immunosuppressive drugs have led to improved survival of SLE patients in the past 50 years [6]. Despite the improvements in care, patients often suffer long-term morbidity that can adversely affect their quality of life and their ability to work, resulting in substantial direct and indirect costs.
References
- Mahmood Akbaryan, Zahra Soltani, Overlap of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A case report. International Journal of Medical Research &Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 4: 100-103.
- Fernández M, Alarcón GS, Calvo-Alén J, Andrade R, McGwin G Jr, Vilá LM, et al. A multiethnic, multicenter cohort of patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) as a model for the study of ethnic disparities in SLE. Arthritis Rheum, 2007. 57: 576-584.
- Jury EC, D’Cruz D, Morrow WJ. Morrow, Autoantibodies and overlap syndromes in autoimmune rheumatic disease. J Clin Pathol. 2001. 54: 340- 347.
- Nasonova VA, Alekberova ZS, Folomeyev MY, Mylov NM. Sacroiliitis in male systemic lupus erythematosus. Scan J Rheumatol. 1984; 52: 23-29.
- Vivas J, Tiliakos NA. Sacroiliitis in male systemic lupus erythematous. Scan J Rheumatol. 1985; 14: 441.
- Tarhan F, Argin M, Can G, Özmen M, Keser G. Coexistence of systemic lupus erythematosus and ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2014; 1: 39-43.