Case Report
Austin J Orthopade & Rheumatol. 2020; 7(3): 1093.
Treatment of Pipkin I Fracture by Watson-Jones Approach: A Case Report and Literature Review
Chen L*, Hou H, Pan Q and Zhang L
Department of Orthopedics, Suzhou Hospital of Anhui Medical University (Suzhou Municipal Hospital of Anhui Province), China
*Corresponding author: Li Chen, Department of Orthopedics, Suzhou Hospital of Anhui Medical University (Suzhou Municipal Hospital of Anhui Province), China
Received: November 19, 2020; Accepted: December 04, 2020; Published: December 11, 2020
Abstract
Objective: To explore the treatment of femoral head fracture with posterior dislocation of hip joint (Pipkin fracture).
Method: A case of the femoral head fracture with posterior dislocation of the hip (Pipkin I fracture) was reported in this paper, to review the literature of surgical treatment of Pipkin I fracture.
Result: The choice of operative approach in the treatment of Pipkin I fracture is still controversial.
Conclusion: Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are very important for patients with Pipkin I fracture, because the reasonable choice of treatment can significantly improve the prognosis,reduce the risk of necrosis of the femoral head and improve the function of the hip joint.
Keywords: Femoral head fracture; Posterior dislocation of hip joint; Pipkin classification; Literature review
Introduction
With the development of modern industry, the incidence of femoral head fracture with posterior dislocation of hip joint increases year by year. According to the literature, more than 11.7% of the patients with dislocation of the hip were posterior dislocation of the hip with femoral head fracture [1]. The higher incidence and the later stage of such fractures can lead to severe complications such as ischemic necrosis of the femoral head, ectopic ossification and traumatic arthritis [2]. So that this kind of injury is highly concerned by orthopedic doctors. However, in the course of treatment of Pipkin I type fracture, orthopedic doctors have not reached a consensus on the choice of conservative treatment or surgical treatment, as well as the timing and approach of the operation [3-5]. Among them, the choice of surgical methods is the most controversial. Ranging from traditional Kocher Langenbeck (K-L) and Smitll Peterson (SP) to improved Hueter approach, each surgical approach has its advantages and disadvantages [6-8]. This article introduces a case of Pipkin I fracture patient who take the Watson-Jones approach to further explore the choice of Pipkin fracture treatment options.
Case Report
Male, 58 year old farmer, “Left hip pain after tunnel collapse, deformity with limited movement for more than 1 hour” was admitted to hospital at 19:00 on January 12, 2020. The patient worked at the site tunnel an hour ago, because of the loose soil above the tunnel, the patient failed to escape in time, buried at the exit and rescued in time. At that time, the patient felt severe left hip pain, unable to stand on his own, immediately sent to the local township hospital emergency treatment. Pelvic plain film suggests a posterior dislocation of the left hip, no obvious signs of fracture around acetabular, the left medial femoral head cortical continuity was interrupted (Figure 1). The patient’s vital signs were stable, considering the patient’s condition and local medical conditions, patient and his families requested further treatment in orthopaedics of our hospital. Symptoms: pain in the left hip, active flexion and extension of the hip joint is significantly limited, no symptoms of numbness. The knee and ankle are limited by pain.
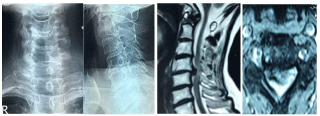
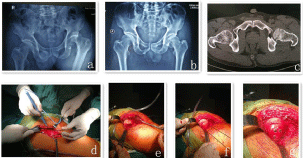
Figure 1: Male, 58 year old, femoral head fracture with posterior dislocation of hip joint (Pipkin I type); a: posterior dislocation of hip and femoral head fracture;
b: after manual reduction of posterior dislocation of hip; c: Hip CT suggested femoral head fracture; d: operative incision; e: the size of femoral head fracture; f:
fracture of femoral head temporarily fixed with Kirschner needle; g: anatomical reduction of femoral fracture.
Physical examination
Conscious, acute facial features, painful expression, medium size, left lower extremity flexion hip flexion knee, internal rotation short contraction deformity, left hip tenderness, percussive pain (+), Active and passive flexion and extension of the left hip, limited abduction, left lower extremity “4 characters” (+), stretching muscle strength 5. There was no significant difference in skin pain and touch, the dorsal foot artery of both lower limbs can touch obvious fluctuation. Auxiliary examination: January 12, 2020 pelvic plain film (local hospital) hint: left hip posterior dislocation, no obvious signs of fracture around acetabular, the left medial femoral head cortical continuity was interrupted (Figure 1).
Clinical diagnosis
Femoral head fracture with posterior dislocation of hip joint (type Pipkin I). Orthopaedics suggested immediate manual reduction of hip dislocation. If closed reduction fails, incision and restoration is performed to inform patient and his families of the importance of timely reduction of hip dislocation. Patient and his families understand and agree to reduction treatment.
Reduction process: after the patient’s general anesthesia is stable, take supine position, assistant press the pelvis with two hands, the operator straddles the affected limb with flexion and knee 90°, use forearm, elbow fossa to cover the popliteal part of the limb, slowly pull out, rotate the affected limb slightly while pulling upward, push the femoral head slide into acetabulum, feel the sound of acetabulum, straighten the affected limb, the left lower extremity internal rotation deformity disappear, C arm machine perspective to see that the femoral head is located in the acetabulum, confirm the successful reduction and fix the affected limb properly, the patient returns to the orthopedic ward after waking room. Manual reduction and postoperative treatment: the affected limb neutral skin traction fixation, eroxib 0.1 g twice a day oral, low molecular weight heparin sodium 2500 IU daily subcutaneous injection, Danhong injection 40 ml a day intravenous drip and other symptomatic treatment. A pelvic plain film and a further Hip CT scan on January 13, 2020 suggested that the left femoral head was located in the acetabulum, no dislocation, fracture separation and displacement of left femoral head, free bone mass can be seen in acetabular (Figure 1).
Considering that the femoral head fracture block was larger and accompanied by the relevant internal free bone mass, orthopedic surgeons recommend further open reduction and screw internal fixation of femoral head fracture+ removal of acetabular free bone mass. Inform the patient and his families of the advantages and disadvantages of conservative and surgical treatment.
Surgical process
The patient was treated with open reduction screw internal fixation of left femoral head fracture+ removal of acetabular free bone mass at 09:00 on January 15, 2020. Watson-Jones approach [9] (anterolateral approach) exposing the proximal femur, after satisfactory anesthesia, the patient lies sideways on the orthopedic bed, after iodophor disinfection and medical alcohol deiodization, the surgical field was covered with incision membrane, a slightly curved skin incision was performed on the femoral trochanter about 7-10 cm lateral slightly anterior (Figure 1), extending to the distal end to the femoral shaft (10 cm below the greater trochanter), after exposing the tensor fascia lata muscle, incision and blunt separation to the proximal end along the posterior boundary of the tensor fascia lata muscle, exposure of the femoral trochanter and gluteus medius, the tensor fascia lata and gluteus medius muscles were pulled forward and backward respectively, blunt separation of the gap between the two to the hip, notice the vascularization of this space, electrocoagulation and hemostasis. After exposing the hip sac, place Hoffmann retractor on the hip femoral head, plus a retractor in front and back, to reveal the hip sac more clearly after external rotation, Stripping the lateral femoral muscle from the base of the anterior trochanter reveals the underlying articular capsule, pull the muscle down, A T incision in the capsule, to expose the femoral head, the external rotation of the lower extremities increases the visual field, at this point, the femoral neck, femoral head and fracture site were completely exposed (Figure 1). At the end of the femoral head, after traction, flexion, abduction and external rotation of the hip joint, removal of broken blood clots, acetabular medial circular ligaments and free bone fragments, repeated saline irrigation of broken ends and hip joints, fracture reduction, screw pressurization (Figure 1), flush again, repair the articular capsule after reduction of the femoral head, implanted drainage tube, close the incision layer by layer.
Postoperative management
24 h after operation, the vein was given cefazolin 2.0 pentahydrate g to prevent wound infection. The second day after operation, when the drainage volume of 24 h in the joint was less than 50 mL, the drainage tube was pulled out and the pelvic plain film was rechecked (Figure 2). 8 h after surgery with low molecular weight heparin sodium subcutaneous injection to prevent lower extremity deep venous thrombosis, no weight on the limb within 8 weeks of surgery. After the operation, the patient was instructed to exercise the isometric contraction function of the quadriceps femoris, limiting hip abduction, internal rotation and flexion >60°; After 2 months, according to the clinical examination and X, The affected limb may gradually begin to carry weight, can gradually start hip joint abduction, internal rotation and flexion >60° of functional exercise; After 6 months, the Pelycogram showed that the femoral head fracture healed well (Figure 2). There was no apparent loosening of the screws, hip flexion and extension, adduction and abduction function are good.
Figure 2: Pelycogram and axial x-ray film of femoral neck after open reduction
and internal fixation of femoral head fracture; a1: radiographic feature2 days
after operation; b1: radiographic feature 6 months after operation.
Discussion
The fracture of femoral head belongs to intra-articular fracture. Ectopic ossification, ischemic necrosis of femoral head and traumatic arthritis are common complications in the healing process, which seriously affect the function of hip joint and reduce the quality of life of patients [2,10]. Therefore, reasonable treatment is essential for the prognosis of such trauma. The purpose of Pipkin fracture treatment is to restore the articular surface leveling and the anatomical relationship between acetabulum and femoral head as soon as possible, restore hip function as much as possible. Except for a very small number of fractures without displacement or displacement <2 mm and there is no free bone mass in the joint space, patients with a normal anatomical relationship between the acetabulum and the femoral head can be treated conservatively. Otherwise, most femoral head fractures need surgical treatment. The most commonly used classification of femoral head fracture combined with posterior dislocation of hip joint is proposed by Pipkin in 1957: Pipkin I type is posterior dislocation of hip joint with subfoveal fracture of femoral head; Pipkin I type fracture is posterior dislocation of hip joint with superior femoral head fracture; Pipkin I type is Pipkin I and II with femoral neck fracture; Pipkin I type of fracture with acetabular fracture [11]. The risk of post-traumatic arthritis or avascular necrosis of the femoral head is lower than other Pipkin types because the Pipkin I fracture site is located in the non-heavy area below the round ligament [12]. For the type of Pipkin I and type II fractures, if the fracture fragment is small or does not affect the weight bearing joint surface, the small fracture fragment can be removed intraoperatively, which does not affect the postoperative effect. If the fracture block is larger, the fracture should be treated with open reduction and internal fixation [13]. Stannard etc. [14] through the surgical treatment and literature review of 26 cases of femoral head fracture, it is considered that early anatomical reduction and strong fixation after femoral head fracture are the guarantee of good therapeutic effect. A consensus has not been reached on the choice of conservative or surgical treatment for the type of Pipkin I fracture, as well as the timing and approach [3- 5]. The choice of operative approach is the focus of internal fixation of femoral head fracture. The commonly used surgical approaches include anterior approach, posterior approach, lateral approach and combined approach [15]. The anterior hip approach (S-P approach) is commonly used in Pipkin I, II fractures. This approach may better expose the anterior articular surface of the femoral head, but S-P approach requires incision of the anterior articular capsule, which will further destroy the residual blood supply. Epstein, etc. [16] adopted S-P approach was used to treat 10 patients with femoral head fracture with posterior dislocation of hip joint and the prognosis was poor. But Gautier etc. [17] anatomical studies show that the blood supply of femoral head mainly comes from the deep branch of the medial circumflex femoral artery, so the anterior approach does not affect the blood flow of femoral head. Stannard etc. [14] adopted S-P and K-L approaches which were used to treat 26 patients with femoral head fracture. It was found that the K-L approach caused ischemic necrosis of femoral head 3.2 times that of the anterior approach. The study found that S-P approach had more advantages than the K-L approach in terms of operative time, blood loss and postoperative recovery, and the incidence of avascular necrosis of the femoral head was lower, but the incidence of ectopic ossification was higher than that of the K-L approach due to excessive dissection of muscles by the approach [6,15]. Swiontkowski etc. [6] made a retrospective analysis of femoral head fracture cases treated by two major trauma centers in the United States was carried out to compare the advantages and disadvantages of different surgical approaches of Pipkin I and II. The results showed that the operative time and bleeding volume of the S-P approach were significantly less and the visual field was better, but the incidence of ectopic ossification was higher than that of the K-L approach. From Wang etc. [15] the Meta analysis data show that in the treatment of type Pipkin I and II fractures, K-L approach greatly reduces the risk of ectopic ossification after operation. Other literature [18] reported the incidence of avascular necrosis of femoral head after K-L approach was 3.67 times that of S-P approach. A Ganz approach (trochanteric osteotomy approach) has been used in recent years to fully expose the femoral head and articular cavity and effectively reduce the occurrence of ectopic ossification of the hip joint [19-22]. Masse reported 13 patients with femoral head fracture treated by Ganz approach were followed up for 26-122 months and 8 patients received satisfactory reduction. To the end of the followup Harris, the average score was 82 points and the curative effect of 11 patients was excellent [23]. However, this method increases the time of trauma and surgery, and there is the possibility of nonunion of fracture at osteotomy. There are also scholars who use modified Heuter approaches to treat Pipkin I and II fractures, Kurtz, etc. [8] adopted a modified Hueter approach, which was used to treat 2 cases of femoral head fracture. The classical Heuter approach, through the gap between the tensor fascia lata and the sartorius muscles, partially dissociated the stop points of the tensor fascia lata, rectus femoris and piriformis muscles, while the modified Hueter approach for Pipkin I, I type fractures without dissecting the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, which has a clear surgical hierarchy and can effectively expose the femoral head fracture area. There are no complications such as lateral femoral skin injury and ectopic ossification after operation. Compared with the S.P approach, the surgical indications are the same as the femoral approach, but the visual field of exposure of the femoral head is worse than that of the S-P approach [8]. Because the plane of tensor fascia lata and gluteus medius muscle can show acetabulum more clearly and the femoral shaft reaming can be carried out safely, Watson-Jones approach [9] is often used in the treatment of hip replacement and complex femoral neck fracture. Antonio etc. [24] adopted randomly Watson-Jones approach and direct anterior approach to 1408 patients undergoing hip arthroplasty, the postoperative complications of the two surgical approaches were compared. The results showed that there was no significant difference in total volume of bleeding, recent infection rate, prosthetic dislocation and iatrogenic fracture between the two groups. Chen Hua etc. [25] adopted Watson-Jones approach was used to treat 15 patients with complex femoral neck fractures and all patients achieved bone healing 4.6 months after operation. Considering the fracture site, the size of the fracture block, the internal circular ligament of acetabulum, the free bone block and the internal fixation operation, the operator decided to use the Watson-Jones approach, which can completely expose the fracture end and fully expose the acetabulum, which is convenient for removing the free bone block and the broken circular ligament in the acetabulum. Although there is still much controversy about the surgical approach to the treatment of femoral head fracture, we should make early, accurate and comprehensive diagnosis of Pipkin fracture, formulate reasonable treatment plan and minimize the occurrence of complications.
Acknowledgment
The authors did not receive any outside funding or grants in support of their research for or preparation of this work. No commercial entity paid or directed, or agreed to pay or direct, any benefits to any research fund, foundation, division, center, clinical practice or other charitable or nonprofit organization with which the authors, or a member of their immediate families, are affiliated or associated.
References
- Giannoudis PV, Kontakis G, Christoforakis Z, Akula M, Tosounidis T, Koutras C. Management complications and clinical results of femoral head fractures. Injury. 2009; 40: 1245-1251.
- Oransky M, Martinelli N, Sanzarello I, Papapietro N. Fractures of the femoral head: a long-term follow-up study. Musculoskelet Surg. 2012; 96: 95-99.
- Holmes WJ, Solberg B, Bay BK, Laubach JE, Olson SA. Biomechanical consequences of excision of displaced Pipkin femoral head fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2000; l4: 149-150.
- Marchetti ME, Steinberg GG, Coumas JM. Intermediate-term experience of Pipkin fracture-dislocations of the hip. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10: 455-461.
- Roeder LF, DeLee JC. Femoral head fractures associated with posterior hip dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980; 147: 121-130.
- Swiontkowski MF, Thorpe M, Seiler JG, Hansen ST. Operative management of displaced femoral head fractures: case-matched comparison of anterior versus posterior approaches for Pipkin I and Pipkin I fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1992; 6: 437-442.
- Ganz R, Gill TJ, Gautier E, Ganz K, Krugel N, Berlemann U. Surgical dislocation of the adulthip. A technique with full access to the femoral head and acetabulum without the risk of avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint SurgBr. 2001; 83: 1119-1124.
- Kurtz WJ, Vrabec GA. Fixation of femoral head fractures using the modified Heuter direct anterior approach. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23: 675-680.
- De jong L, Klem T, Kuijper TM, Roukema GR. The minimally invasive anterolateral approach versus the traditional anterolateral approach (Watson- Jones) for hip hemiarthroplastic after a female neckfracture: analysis of clinical outcomes. IntOrthop. 2018; 42: 1943-1948.
- Marchetti ME, Steinberg GG, Coumas JM. Intermediate-term experience of Pipkin fracture-dislocations ofthe hip. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10: 455-461.
- Mostafa MF, E1 Adl W, E1-Sayed MA. Operative treatment of displaced Pipkin type I and II femoral head fractures. Arch OrthopTrauma Surg. 2014; 134: 637-644.
- Lin S, Tian Q, Liu Y, Shao Z, Yang S. Mid-and long-term clinical effects of trochanteric flip osteotomy for treatment of Pipkin I and II femoral head fractures. J South Med Univ. 2013; 33: 1260-1264.
- Yoon TR, Rowe SM, Chung JY, Song EK, Jung ST, Anwar IB. Clinical and radiographic outcome of femoral head fractures: 30 patients followed for 3 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001; 72: 348-353.
- Stannard IP, Harris HW, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Functional outcome of patients with femoral head fractures associated with hipdislocations. C1in Orthop Relat Res. 2000; 377: 44-56.
- Wang CG, Li YM, Zhang HF, Li H, Li ZJ . Anterior approach versus posterior approach for Pipkin I and II femoral head fractures: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2016; 27: 176-181.
- Epstein HC, Wiss DA, Cozen L. Posterior fracture dislocation of the hip with fractures of the femoral head. CIin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; 201: 9-17.
- Gautier E, Ganz K, Krtigel N, Ganz R. Anatomy of the medial femoral circumflex artery and its surgical implications. Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2000; 82: 679-683.
- Giannoudis PV, Kontakis G, Christoforakis Z, Akula M, Tosounidis T, Koutras C. Management complications and clinical results of femoral head factures. Injury. 2009; 40:1245-1251.
- Henle P, Kloen P, Siebenrock KA. Femoral head injuries: Which treatment strategy can be recommended? Injury. 2007; 38: 478-488.
- Gardner MJ, Suk M, Pearle A, Buly RL, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. Surgical dislocation of the hip for fractures of the femoral head. I Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19: 334-342.
- Solberg BD, Moon CN, Franco DP. Use of a trochanteric flip osteotomy improves outcomes in Pipkin IV fractures. C1in Orthop RelatRes. 2009; 467: 929-933.
- Hadjicostas PT, Thielemann FW. The use of trochanteric slide osteotomy in the treatment of displaced acetabular fractures. Injury. 2008; 39: 907-913.
- Masse A, Aprato A, Alluto C, Favuto M, Ganz R. Surgical hip dislocation is a reliable approach for treatment of femoral head fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473: 3744-3751.
- Klasan A, Neri T, Oberkircher L, Malcherczyk D, Heyse TJ, Bliemel C. Complications after direct anterior versus Watson-Jones approach in total hip arthroplasty: results from a matched pair analysis on 1408 patients. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2019; 20: 77.
- Chen H, Li J, Chang Z, Liang X, Tang P. Treatment of femoral neck nonunion with a new fixation construct through the Watson-Jones approach. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation. 2019; 19: 126-132.