
Clinical Image
Austin J Otolaryngol. 2015;2(6): 1051.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) as an Effective Instrument in Therapy of Recurrent, Symptomatic Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa (HGM Type II) in the Cervical Esophagus
Richter-Schrag HJ*, Thimme R and Walker C
Department of Medicine II, University of Freiburg, Germany
*Corresponding author: Hans-Juergen Richter- Schrag, Department of Medicine II, Interdisciplinary Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, University of Freiburg, Sir- A-Krebs Street, Freiburg D-79106, Germany
Received: July 18, 2015; Accepted: August 26, 2015; Published: August 28, 2015
Clinical Image
Heterotopic gastric mucosa in the cervical esophagus remains asymptomatic (HGM I) in most cases, and varies from microscopic to macroscopically visible lesions. Prevalence ranges from 1-13.8 % [1]. Laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms like dysphagia or odynophagia (HGM II) or severe complications, like fistula, strictures or malignant transformation (HGM III,-V) seldom occur [2]. Available studies indicate argon plasma coagulation (APC) being an effective treatment [3].
In July 2014 a 30-year old man underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) due to odynophagia persisting despite taking proton pump inhibitors. Ear-nosethroat examination showed no pathologies. Impedanz (Impedanz, Tecnomatix, Germany), showed no gastroesophageal reflux whereas laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) was shown (RestechTM, Promedics, Germany). At a threshold of pH <6,40 pharyngeal reflux events were seen in 24h. Additionally EGD with narrow-band imaging system (NBI) and histological examination revealed a 0.25 mm large HGM Type II of the oxyntic cell type (Figure 1, A1). Repeated APC-therapy achieved a significant improvement of symptoms and pharyngeal acid exposure (Figure 1, B1/2). However symptoms and measured pharyngeal acid reappeared. Successive exploration showed multiple micro-HGMs again, partially overlaid with squamous epithelium (Figure 2, A1). Hence, circular treatment with radiofrequency ablation (Barrx™ 90, Covidien, Germany) was performed (Figure 2, B1). Until now the patient is free from symptoms and LPR (Figure2, B2).
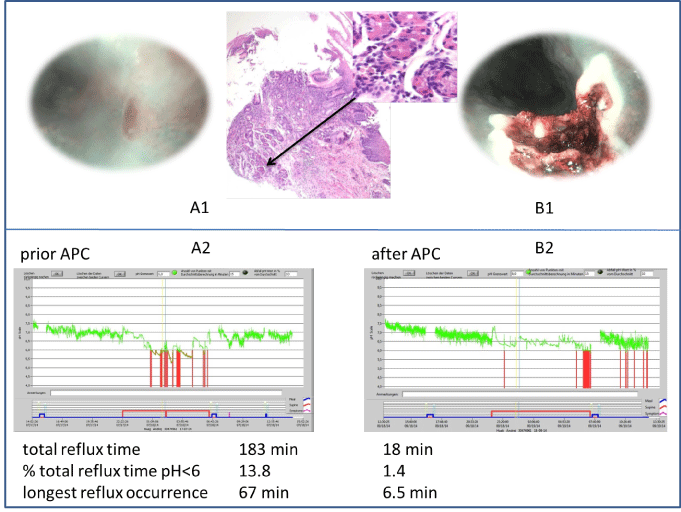
Figure 1: A1- HGM Type II just below the upper esophagus sphincter, detected by narrow-band-imaging and HE 4x/60x with a parietal cell highlighted by arrow.
Prior and after argon plasma coagulation (B1). A2/B2 Pharyngeal acid exposure prior and after therapy.
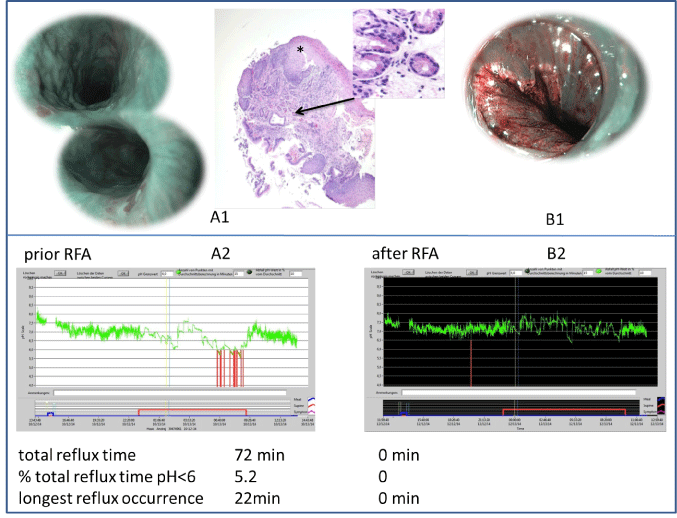
Figure 2: A1- Multiple lesions of recurrent HGM, 4 month after APC, partially overlaid with squamous epithelium (*) and after treatment with circular BarxxTM-RFA
focal catheter (B1). A2/B2 Pharyngeal acid exposure prior and after therapy. The Rayan-score showed normal values in all measurements.
In conclusion HGM should be taken into account as a differential diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms. As the lesions are often difficult to detect during EGD– NBI is recommended [4].
Recurrent or residual HGM after APC therapy poses a relevant problem [3]. Not knowing the origin, it is difficult to differentiate residual HGM in multifocal lesions from recurrent HGM evolving from erupted cysts in the esophagus [5]. Our EGD series supports the hypothesis of erupted cysts as the HGM showed a heterogeneous size and shape. RFA seems to be effective if APC Therapy remains unsuccessful or if, like in our case, subepithelial HGM parts could macroscopically not be evaluated. And therefore sub-epithelial HGM parts and / or immature precursors according to the theory of erupted cysts have to be assumed to be the course of the symptoms, and an extensive thermal ablation is indicated.
References
- Chong VH. Clinical significance of heterotopic gastric mucosal patch of the proximal esophagus. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19: 331-338.
- von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Becker K, Liebermann-Meffert D, Siewert JR. Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the esophagus: literature-review and proposal of a clinicopathologic classification. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004; 99: 543-551.
- Klare P, Meining A, von Delius S, Wolf P, Konukiewitz B, Schmid RM, et al. Argon plasma coagulation of gastric inlet patches for the treatment of globus sensation: it is an effective therapy in the long term. Digestion. 2013; 88: 165-171.
- Chung CS, Lin CK, Liang CC, Hsu WF, Lee TH. Intentional examination of esophagus by narrow-band imaging endoscopy increases detection rate of cervical inlet patch. Dis Esophagus. 2014.
- Meining A, Bajbouj M. Erupted cysts in the cervical esophagus result in gastric inlet patches. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72: 603-605.