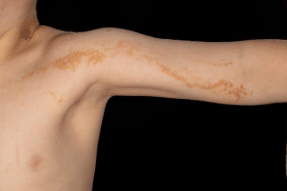
Clinical Image
Austin Pediatr. 2016; 3(2): 1031.
Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus
Kyparissou K¹* and Martinez AE²
¹Resident in Dermatology and Venereology, Andreas Syggros Hospital, Athens, Greece
²Consultant Paediatric Dermatologist, Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
*Corresponding author: Kyparissou K, Resident in Dermatology and Venereology, Andreas Syggros Hospital, Athens, Greece
Received: May 20, 2016; Accepted: May 26, 2016; Published: May 27, 2016
Clinical Image
What is the cause of this condition?
These lesions are a consequence of localised post-zygotic mutations (chromosomal mosaicism). Mutations in genes encoding keratin 1 and 10 have been identified but others have started to be recognized.
What are the clinical characteristics?
Most linear naevi are present from birth or in the first year of life as skin-colored warty papules. These may be solitary or multiple and of varying size. The lesions follow Blaschko lines. With age they can become darker and more verrucous in appearance.
Are there any symptoms and natural history?
The lesions are usually asymptomatic but pruritus and scaling is often present.
Management: Is difficult, surgical excision or other destructive procedures are possible for small lesions. Topical calcipotriol cream and keratolytic emollients may alleviate the dryness in older children. New topical targeted therapies are currently under research.
What is the differential diagnosis?
Lichen striatus, linear psoriasis, linear porokeratosis, incontinentia pigmenti, linear Darier disease.
Genetic counseling: Patients with the epidermolytic hyperkeratosis on histology may have gonadal mosaicism for the mutation responsible for Epidermolytic Ichthyosis (EI) and are at risk of having a child with EI.