
Research Article
Austin J Pharmacol Ther. 2024; 12(1): 1183.
In Silico Screening of Compounds Similar to Codeine, Tramadol, and Morphine with Better Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetics Profiles
Kamakia Faith*; Ouma Stephen; Richard Kagia
Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacognosy, Kabarak University School of Pharmacy, Kenya
*Corresponding author: Faith Muthoni Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacognosy, Kabarak University School of Pharmacy, Kenya. Email: wfaithmuthoni578@gmail.com
Received: November 27, 2023 Accepted: January 05, 2024 Published: January 12, 2024
Abstract
Introduction: Pain alleviation is the primary intervention in promoting quality of life. Among the compounds used in management of pain are opioids. Codeine is mostly used as antitussive and is commonly present in cough syrups. Tramadol and Morphine are used as analgesics based on severity of pain. Although these drugs provide instant pain relief, they are associated with many side effects and the most worrying once are addiction, respiratory depression and tolerance.
Methods: Codeine, Tramadol, and Morphine were used as query compounds to generate similar compounds using SwissSimilarity. Similar compounds were docked to mu, kappa, and delta receptors and those that showed better docking scores to mu receptor and lower scores to kappa and delta were analyzed for toxicity profiles using ProTox II and pharmacokinetics profiles using SwissADME.
Results: ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC03629718; 0. 995; ZINC03870350; 0.993; ZINC28256912; 0.992; and ZINC71774151; 0.977 showed highest binding score to mu receptors and lower to both kappa and delta. All compounds were predicted to inhibit CYP2D6 enzyme. All compounds permeated Blood Brain Barrier with the exceptions of ZINC04102208; 0.992; and ZINC13831510; 0.992. Tramadol, its zinc compounds and ZINC03629718; 0.995. were not substrates for P-glycoprotein. Tramadol and ZINC03639132; 0.976; were predicted immunoactive. All compounds conformed to Lipinski rule of five.
Conclusion: In conclusion, ZINC13831510; 0.992; showed the highest binding score to morphine. ZINC02509756; 0.986; and ZINC26259212; 0.995; were considered the safest as compared to Tramadol and Codeine and their zinc compounds respectively. Further invitro studies are recommended for the following promising compounds ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC03629718; 0. 995; ZINC03870350; 0.993; ZINC28256912; 0.992; and ZINC71774151; 0.977 ZINC02509756; 0.986; and ZINC26259212; 0.995;.
Keywords: Codeine; Tramadol, Morphine, docking score, SwissADME, Protox II, toxicity
Abbreviations: BBB: Blood Brain Barrier; AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor; A: Active; I: Inactive; GIT: Gastrointestinal Tract
Introduction
Opioids are majorly used to alleviate severe pain which is mediated through the mu receptor agonism in the brain [3]. Opioid use has however, been associated with abuse causing addiction leading to deaths of people due to respiratory depressant effects of opioids. Deaths related to synthetically manufactured opioids in United States in 2017, was 47,600, which was three quarter the number of total drug related deaths [18]. Opioids has become great concern in modern management of diseases. Physicians and Pharmacists are in dilemma in provision of patient centered care while maximizing benefits in pharmaceutical interventions and minimizing side effects of those interventions.
Major mechanism of action of opioids involves binding to their mu, delta and kappa receptors [16] on the presynaptic space of afferent sensory axon causing release of calcium channels that lead to loss of mitochondrion function of the cells and decreased in release of substance P. Opioids also bind postsynaptically to their respective receptors causing opening of potassium channels that hyperpolarize the cells increasing action potential required to generate pain impulse transmission.
Opioids are the mainstay in alleviating Pain and according to the WHO ladder of Pain, weak opioids such as tramadol are involved in the second step in pain management. The third step involves use of strong opioids such as morphine. Due to side effects, genetic polymorphism and abuse, there is a need to screen for new opioid analogues with improved metabolism, pharmacokinetics as well as pharmacodynamic properties.
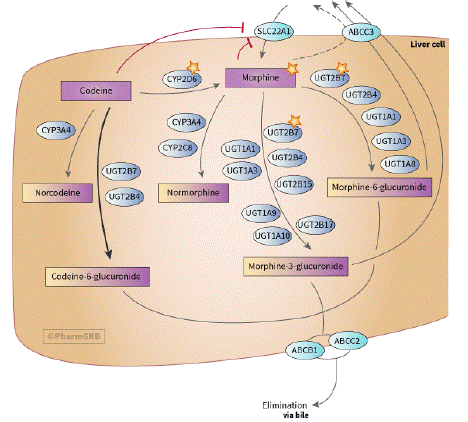
Figure 1: Codeine and morphine metabolism.(https://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA166117881/pathway)
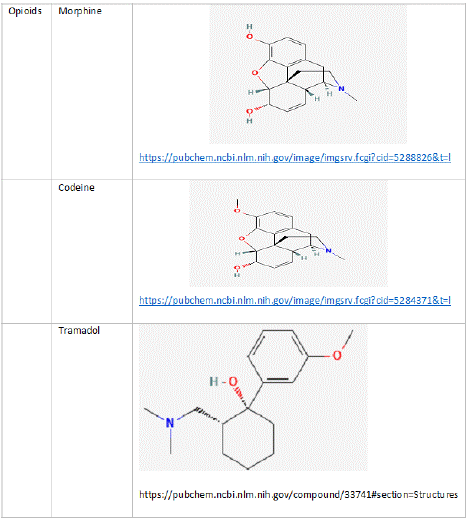
Figure 2: Structures of Codeine and Morphine.
Opioids cause respiratory depression, meiosis, constipation [6], dependence, and tolerance on chronic use. They increase the cost of therapy by the dditional cost of requiring an antidote to reverse the effects. They also cause hyperalgesia on chronic use. Tramadol lowers the seizure threshold [11].
Opioids use in pregnant mothers causes neonatal abstinence syndrome of the infants characterized by CNS symptoms such as high pitch cry, shortening the sleep period of the infants after feeding, tremors and increase in muscle tone. Metabolic, respiratory and vasomotor systems are as well affected in the infants causing hyperthermia, sneezing and yawning frequently. GIT symptoms such as vomiting and passage of loose stools has been observed in the infants of mothers who took opioids during pregnancy (Proctor-Williams, 2018). Infants exposed to opioids in utero causes increase in cerebral blood flow to the brain and this causes derangements as seen during neural examination. Foetal brain development is affected and this causes neurological abnormalities in infants who have prenatal opioids exposure [1].
Metabolism of Codeine and Morphine is highly dependent on genetic polymorphism.
Genetic Polymorphism on Drug Metabolism
Different individuals metabolize drugs differently due to different genetic makeup. Codeine undergoes metabolism variability because it is metabolized to morphine by CYP2D6 polymorphism. This increases metabolism rate of codeine to morphine, which causes respiratory depression in individuals due to increase in exposure of the active drug morphine. Nursing mothers who are ultra-rapid metabolisers of codeine increases the rate of infant exposure to morphine causing death due to respiratory depression associated with codeine.
Glucose -6-phosphate dehydrogenase polymorphism in patients predispose the patients to haemolytic anaemia in patients taking tramadol and aspirin. Glucose-6-phosphate deficiency should therefore, be screened before instituting tramadol and aspirin to patients at high risk of haemolytic anaemia with this drug. CYP2C8*3, CYP2C9*1 and CYP2C9*2 polymorphism cause decrease in ibuprofen concentration in healthy individuals. Genetic determination of CYP2C9 is important in prescribing therapeutic agents to enhance optimal clinical outcome.
Codeine is metabolized to morphine by CYP2D6 gene in the liver and therefore, polymorphism in CY2D6 gene may cause ultra-rapid metabolism of codeine to morphine increasing morphine toxicities in the body. UDP glucuronyltransferase enzyme converts codeine to codeine-6-glucuronide, morphine is converted to morphine-3-glucuronide as well as morphine-6-glucuronide. Transporters such as ABC1 are implicated in transport of morphine across the cell and variability occurs due to decrease in efflux of morphine from the cells across the BBB causing increase in toxicities.
This study identified opioids analogues using Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine as query compounds to generate similar compounds. Compounds with better docking scores to the mu, kappa and delta receptors were identified and they were analysed for pharmacokinetic profiles as well as toxicity profiles. Compounds that showed promising results were highlighted.
Study Objectives
I. To identify similar compounds to Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine using SwissSimilarity.
II. To identify docking scores of identified compounds to mu, kappa and delta receptors in reference to codeine, Tramadol and morphine.
III. To identify pharmacokinetic properties of the Zinc compounds in reference to Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine using SwissADME.
IV. To identify toxicity profiles of Zinc compounds in reference to Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine using ProTox ii webserver.
Methods
Retrieval of Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine Structures
Three folders named Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine were generated on the desktop. PubChem tool (RRID:SCR_004284) was opened, Morphine, Tramadol and Codeine were searched separately. Summary was clicked and Morphine was saved as SDF format to Morphine folder, Codeine was saved as SDF format to Codeine folder and Tramadol was also saved as SDF format.
Identification of Similar compounds to Codeine, Tramadol, and Morphine using Ligand Based Virtual Screening
Canonical SMILES of Codeine and Morphine were copied from PubChem (RRID: SCR_004284) to SwissSimilarity (http://www.swisssimilarity.ch/index.php) online tool. Combined Zinc-Drug like property was clicked and the Zinc compounds for Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine were generated. Compounds that had 50% similarity score and above to Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine were selected and 20 compounds of each reference drugs were sampled in total for each reference compound. The 20 compounds were downloaded using PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov//edit3/index.html) sketcher online tool and the compounds were downloaded as SDF files and saved to respective folders.
Ligand Preparations
Avogadro (RRID: SCR_015983) software was opened and auto -optimization of Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine was done. Zinc compounds were also optimized by ensuring the compounds are in minimum energy state. These compounds were further minimized using Chimera (RRID: SCR_004097) by addition of hydrogen bonds and adding gasteiger charges.
Receptors Retrieval and Preparations
Drug Bank online tool (https://go.drugbank.com/) was opened and Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine were searched. UniProt IDs (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P41145/entry) were generated as P35372, P41143, P41145, for mu, delta and kappa receptors. Protein Data Bank (RRID: SCR_012820) (https://www.rcsb.org/) was opened and the specific IDs were searched and specific receptors were downloaded as PDF format and saved to both folders. Chimera (RRID: SCR_004097) software was opened and standardization of the receptors was done by eliminating non standard residues that would interfere with molecular dockings. The standard receptors were saved as PDB format to Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine folders.
Molecular Docking
Chimera (RRID: SCR_004097) software was opened, receptors were opened first followed by compounds. Grid box was generated followed by opening of Autodock vina (RRID: SCR_011958) version 1.2.0. All zinc compounds were docked to mu, kapa and delta receptors and docking scores were compared to docking scores of Codeine, Tramadol and Morphine. Compounds with best docking scores were further analyzed using Biovia Discovery studio and interactions between the compound’s pharmacophore and receptor binding sites were analyzed.
Pharmacokinetics Determination
Compounds that were promising were analyzed further for pharmacokinetics profiles using SwissADME (http://www.swissadme.ch/) online tool. Cytochrome P450 activity, Blood Brain Barrier penetration, P-glycoprotein activity, GIT absorption and conformation to Lipinski rule of five was determined.
Toxicity Analysis
ProTox II (RRID: SCR_018506) webserver was opened and canonical smiles of the compounds with promising results were analyzed for their oral toxicity, organ toxicities and end point toxicities.
Results
Docking Scores
Morphine and Zinc compounds binding scores to mu, delta and kappa receptors: All the compounds except ZINC05966734; 0.990;( 6.6) showed higher binding score to delta receptor than the reference drug morphine, that has docking score of -6.8.
From the data in Table 1 below, all zinc compounds showed lower docking score to kappa receptor than morphine (-7.3) in exception of ZINC04217170; 0.988;(-7.8), ZINC26259212; 0.993;(-8.5), ZINC33839041; 0.993;(-7.9) and ZINC39949141; 0.997;(-7.5).
Serial no
Similarity score
Compound
Binding score to mu receptor
Binding score to delta receptor
Binding score to kappa receptor
Morphine_
-6.4
-6.8
-7.3
98.30%
ZINC03629718; 0.983;
-6.1
-7.0
-7.1
98.80%
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
-6.5
-7.4
-7.3
982%
ZINC03830598; 0.982;
-6.0
-7.4
-7.3
98.80%
ZINC03831152; 0.988;
-5.9
-7.3
-7.3
99.10%
ZINC03870349; 0.991;
-6.0
-7.3
-7.1
98.80%
ZINC03870350; 0.988;
-6.2
-7.2
-7.1
99.30%
ZINC03875420; 0.993;
-6.3
-8.0
-7.1
99.20%
ZINC04102208; 0.992;
-6.8
-7.8
-7.3
98.80%
ZINC04217170; 0.988;
-6.4
-7.0
-7.8
99.20%
ZINC05599925; 0.992;
-6.2
-7.1
-7.3
99.00%
ZINC05966734; 0.990;
-5.8
-6.6
-6.7
99.20%
ZINC13831510; 0.992;
-9.2
-8.1
-7.3
99.30%
ZINC26259212; 0.993;
-6.0
-7.5
-8.5
99.00%
ZINC26266464; 0.990;
-7.1
-9.6
-7.3
98.80%
ZINC27517251; 0.988;
-6.4
-8.2
-6.9
99.50%
ZINC28256912; 0.995;
-6.2
-8.3
-7.5
99.30%
ZINC33839041; 0.993;
-6.3
-8.2
-7.9
99.80%
ZINC33839042; 0.988;
-6.3
-7.2
-7.3
99.20%
ZINC37250136; 0.992;
-6.4
-8.5
-7
99.70%
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
-6.6
-8.3
-7.5
Note: From (Pettersen et al., 2004), (Eberhardt et al., 2021)
Table 1: Binding scores of morphine and zinc compounds to mu, delta and kappa receptors.
ZINC13831510; 0.992;(-9.2) had the highest binding score to mu receptor as compared to both the kappa and delta receptor. ZINC13831510; 0.992; was analysed for its pharmacokinetic profile.
Both morphine and ZINC13831510; 0.992 showed high GIT absorption, substrate of P-glycoprotein. They both showed CYP2D6 inhibition. Morphine showed permeation to BBB while ZINC13831510; 0.992 showed lack of BBB permeation. Morphine and ZINC13831510; 0.992 showed lack of CYP1A2, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 enzyme inhibition. They both complies with Lipinski rule of five.
Tramadol and Zinc compounds docking scores to mu, delta, and kappa receptors: ZINC02509756; 0.986;(-5.7), ZINC02510775; 0.995(5.7), ZINC02525883; 0.995; (5.6), ZINC03639132; 0.976; (5.9), ZINC05958052; 0.979; (-5.6) and ZINC71774151; 0.977; (-7.4) showed better docking score to mu receptor than tramadol (-5.5). These zinc compounds were further analysed for their pharmacokinetic properties and toxicity profiles.
All the zinc compounds shown higher binding scores to delta receptor. Three Zinc Compounds namely ZINC01849532; 0.994; (-6.6), ZINC02525883; 0.995; (-7.4), ZINC03639132; 0.976; (-6.5) and ZINC76734760; 0.977; (-6.8) showed higher binding score to kappa receptor than Tramadol (-6.4). ZINC71774151; 0.977; showed highest binding score to mu receptor than kappa and delta receptors therefore, it was further analysed for its pharmacokinetic properties as well as toxicity profiles.
Both tramadol and ZINC71774151; 0.977 showed high GIT absorption, BBB permeation and inhibition of CYP2D6 enzyme. They, however lack inhibition to CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4. They are not substrate to P-glycoprotein. They comply with Lipinski rule of five.
Codeine and zinc compounds binding scores to mu, delta and kappa receptors: ZINC03806721; 0.991; (-6.7) and ZINC37250136; 0.997; (-6.4) showed lower docking score to delta receptor than the reference codeine drug (-6.9). The rest of the Zinc compounds showed better docking scores than codeine.
ZINC03870349; 0.993; (-6.8), ZINC03870350; 0.993; (-6.8), ZINC04217170; 0.992; (-7.0), ZINC05599925; 0.997; (-7.0), ZINC27517251; 0.993; (-6.7) and ZINC33839042; 0.992; (-6.9) showed lower docking scores to kappa receptor as compared to reference codeine which showed docking score of (-7.1).
ZINC03629718; 0.995; (-8.3), ZINC03870350; 0.993; (-7.8) and ZINC28256912; 0.992; (-8.9) had the highest binding to mu receptors as compared to delta and kappa receptors. These Zinc compounds were further analysed for their pharmacokinetic profiles through SwissADME tool and toxicity using ProTox II server.
Codeine, ZINC03629718; 0.995; (-8.3), ZINC03870350; 0.993; (-7.8) and ZINC28256912; 0.992; (-8.9) showed high GIT absorption, BBB permeation P-glycoprotein substrates and CYP2D6 inhibition. ZINC03629718; 0.995; (-8.3) is an exception in that it is not a substrate to P-glycoprotein. Codeine and the Zinc compounds showed lack of enzyme inhibition to CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4.These compounds showed no violation to Lipinski rule of five.
Toxicity Profiles
Oral toxicity: None of the Morphine zinc compounds showed higher LD50 than Morphine, although all compounds belonged to toxicity Class IV with exceptions of ZINC04217170; 0.988;
ZINC27517251; 0.988; and ZINC37250136; 0.992 that belong to Toxicity class III. ZINC26259212; 0.995; was the safest with oral LD50 of 1140 mg/kg belonging to toxicity class IV compared to Codeine 85mg/kg and the rest of the zinc compounds belonging to class III.
Four of Tramadol’s zinc compounds were predicted to be in class IV as compared to Tramadol and other zinc compounds in Class III toxicity. These compounds include, ZINC05958052; 0.979; ZINC03639132; 0.976; ZINC02509756; 0.986 and ZINC71774151; 0.977. The safest compound with highest Oral LD50 was ZINC71774151; 0.977.
According to Drwal et al. (2014), Class I refers to death after swallowing (LD50 = 5); Class II refers to death after swallowing (5< LD50=50); Class III: toxic after swallowing (50< LD50=300); Class IV: harmful after swallowing (300<LD50=2000); Class V: harmful after swallowing (2000<LD50=5000) and Class VI: non-toxic (LD50>5000)
Hepatotoxicity and immunotoxicity: None of Morphine’s, Tramadol’s, and codeine’s zinc compounds were predicted hepatotoxic active. ZINC26266464; 0.990; ZINC26266464; 0.995; were predicted immunotoxic active with probability of 0.64. Tramadol and its zinc compound ZINC03639132; 0.976; were predicted immunoactive with probabilities of 0.87 and 0.81 respectively.
End point toxicities: None of the compounds were predicted active in causing carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and cytogenecity.
Morphine and its zinc compounds ZINC03812983; 0.988; and ZINC39949141; 0.997; were predicted active in nuclear receptor signalling with probability scores of 0.62, 0.62 and 0.66 respectively. Codeine and its zinc compounds namely ZINC28256912; 0.992, ZINC03830598; 0.991; ZINC05599925; 0.997 and ZINC39949141; 0.993 were also predicted active for nuclear receptor signaling with probability scores of 0.8, 0.62, 0.83, 0.93 and 0.62 respectively.
Phamacokinetic Profiles
P-glycoprotein substrates: Morphine and its zinc compounds were all predicted to be P-glycoprotein substrates. All Codeines zinc compounds were predicted substrates of P-glycoprotein with exceptions of ZINC03629718; 0.995. Tramadol and its zinc compounds were not substrates for P-glycoprotein.
1.6.2 BBB penetration
Morphine was predicted to cross BBB while its two zinc compounds were not. These compounds include ZINC04102208; 0.992; and ZINC13831510; 0.992. All other compounds were predicted to permeate BBB.
Enzyme inhibition: None of the compounds were predicted to inhibit CYP 1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4. All compounds were predicted to inhibit the CYP2D6 enzyme.
Post Docking Analysis
Codeine and zinc compounds 2D-Interactions with mu receptors: ZINC03870350; 0.993; ZINC03629718; 0.995 with -8.3 kcal/mol and -7.8 kcal/mol respectively showed binding to mu receptor with van der waals forces, pi-sigma bonds as well as pi-alkyl bonds. Codeine with -6.1 kcal/mol showed binding to active sites via van der waals forces-sigma-cation, pi-anion as well as pi-pi stacking amongst others.
Tramadol and zinc compound binding to mu receptor visualization [15]: ZINC71774151; 0.977; with binding affinity of -7.4kcal/mol as compared to Tramadol-5.5kcal/mol showed pi-pi stacking of the pharmacophore to mu binding site. Both compounds bonded with van der waals forces as well as pi–alkyl bonds to mu active sites.
Discussion
Opioids are currently used in pain management by acting via mu, kappa, and delta receptors [7]. The side effects of opioid agonists are propelling the urge to seek new analgesics with limited side effects. The effect on mu receptors is respiratory depression due to the binding of the agonists in the amygdala, brain stem, and thalamus (Imam et al., 2018). Through activation of the mu receptors, secretion of substance P and acetylcholine is inhibited leading to constipation [5]. Withdrawal and dependence effects occur on the activation of mu receptors. Kappa receptor activation produces aversion and euphoric effects [9] as well as pruritic effects due to their effects on the release of histamine. Both mu and kappa receptors produce sedation due to their effects on the CNS (Chung et al., 2017). Prior work by [14] showed that hyperalgesia effects of morphine are not attributable to the binding of morphine to peripheral receptors but to central mu receptors. Kappa receptors’ actions in hypothalamus and in the adrenal glands cause diuresis as a side effect [10]. Delta receptor is associated with convulsions due to actions on the thalamo-cortical areas and the hypothalamus [4].
Opioids (morphine, tramadol and codeine) and their zinc compounds were analysed in this study and compounds with better docking scores to mu receptor were highlighted. They produced positive compounds that can be discovered as potent analgesics. Based on results in Table 2, ZINC03812983; 0.988; ZINC04102208; 0.992; ZINC04217170; 0.988; ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC26266464; 0.990, ZINC27517251; 0.988; ZINC37250136; 0.992; and ZINC39949141; 0.997 showed better binding energies to mu receptor than morphine. Based on data in Table 3, ZINC02509756; 0.986; ZINC02510775; 0.995, ZINC02525883; 0.995, ZINC03639132; 0.976, ZINC05958052; 0.979; and ZINC71774151; 0.977; showed higher binding energies to mu receptor than tramadol. Table 5, highlights compounds with better docking scores to mu receptor than codeine. These Zinc compounds therefore, gives promising results in discovery of potent analgesic compounds but with serious side effects such as respiratory depression, constipation, vomiting and withdrawal effects.
Serial no
Similarity score
Compound
Binding score to mu receptor
Binding score to delta receptor
Binding score to kappa receptor
Tramadol
-5.5
-5.7
-6.4
99.70%
ZINC00000853; 0.997;
-5.3
-6.4
-6.3
98.10%
ZINC00020781; 0.981;
-4.8
-5.9
-6.3
99.40%
ZINC01849532; 0.994;
-5
-6.8
-6.6
99.80%
ZINC02015652; 0.998;
-5.1
-6.9
-6.1
97.90%
ZINC02243733; 0.979;
-5.5
-6
-5.9
98.60%
ZINC02509756; 0.986;
-5.7
-6.1
-6
99.50%
ZINC02510775; 0.995;
-5.7
-6.3
-6.1
99.50%
ZINC02525883; 0.995;
-5.6
-6.4
-7.4
97.60%
ZINC03639132; 0.976;
-5.9
-7.1
-6.5
99.50%
ZINC03643419; 0.995;
-5.4
-6.6
-6.2
99.50%
ZINC03643421; 0.995;
-5.5
-7.3
-6.1
97.90%
ZINC05958019; 0.979;
-5.5
-7
-5.9
97.90%
ZINC05958052; 0.979;
-5.6
-6.7
-6.3
97.70%
ZINC21986241; 0.977;
-5.4
-6.4
-6
98.90%
ZINC33979435; 0.989;
-5.1
-6.2
-5.3
98.80%
ZINC33979436; 0.988;
-4.8
-6.3
-6.1
99.00%
ZINC33979437; 0.990;
-5.3
-6.4
-6.2
97.70%
ZINC71774151; 0.977;
-7.4
-6.9
-6.4
97.70%
ZINC76734760; 0.977;
-5.5
-6.3
-6.8
Note: From (Pettersen et al., 2004), (Eberhardt et al., 2021)
Table 2: Tramadol and zinc compounds binding scores to mu, delta and kappa receptors.
Serial no
Similarity score
Compound
Binding score to mu receptor
Binding score to delta receptor
Binding score to kappa receptor
Codeine
-6.1
-6.9
-7.1
99.10%
ZINC00402777; 0.991;
-6.1
-7.4
-7.3
99.10%
ZINC00490120; 0.991;
-6
-7.4
-7.1
99.10%
ZINC02039583; 0.991;
-6.4
-6.4
-7.3
99.50%
ZINC03629718; 0.995;
-8.3
-7.8
-7.1
99.10%
ZINC03806721; 0.991;
-5.7
-6.7
-7.8
99.10%
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
-6.3
-7.1
-7.5
99.30%
ZINC03870349; 0.993;
-6
-7.1
-6.8
99.30%
ZINC03870350; 0.993;
-7.8
-7.2
-6.8
99.50%
ZINC03875420; 0.995;
-6
-7.6
-7.8
99.20%
ZINC04217170; 0.992;
-5.9
-7.2
-7
99.70%
ZINC05599925; 0.997;
-6.4
-6.9
-7
99.50%
ZINC26259212; 0.995;
-6.6
-7.7
-7.2
99.50%
ZINC26266464; 0.995;
-6.5
-8.5
-7.4
99.30%
ZINC27517251; 0.993;
-6.3
-6.9
-6.7
99.20%
ZINC28256912; 0.992;
-8.9
-8.3
-7.5
99.50%
ZINC33839041; 0.995;
-6.3
-8.3
-7.9
99.20%
ZINC33839042; 0.992;
-6
-7.2
-6.9
99.00%
ZINC34275567; 0.990;
-6.1
-7.8
-7.7
99.70%
ZINC37250136; 0.997;
-6.3
-6.4
-7.1
99.30%
ZINC39949141; 0.993;
-6.2
-8.3
-7.5
Note: From (Pettersen et al., 2004), (Eberhardt et al., 2021)
Table 3: Codeine and zinc compounds binding scores to mu, delta and kappa receptors.
Compound name
Oral LD50 (mg/kg)
Predicted toxicity class
Predicted Accuracy %
Morphine
461
IV
23
ZINC13831510; 0.992
335
IV
100
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
335
IV
100
ZINC04102208; 0.992;
335
IV
100
ZINC04217170; 0.988;
85
III
100
ZINC26266464; 0.990;
335
IV
100
ZINC27517251; 0.988;
85
III
100
ZINC37250136; 0.992;
85
III
100
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
335
IV
72.9
Codeine
85
III
100
ZINC03629718; 0.995
85
III
100
ZINC02039583; 0.991;
85
III
100
ZINC03870350; 0.993;
85
III
100
ZINC28256912; 0.992
335
IV
100
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
85
III
100
ZINC05599925; 0.997
85
III
100
ZINC26259212; 0.995;
1140
IV
100
ZINC26266464; 0.995;
335
IV
100
ZINC27517251; 0.993;
85
III
100
ZINC33839041; 0.995;
85
III
100
ZINC37250136; 0.997;
85
III
100
ZINC39949141; 0.993
N/A
N/A
0
Tramadol
228
III
100
ZINC71774151; 0.977
388
IV
100
ZINC02509756; 0.986;
387
IV
100
ZINC02510775; 0.995;
228
III
100
ZINC02525883; 0.995;
228
III
100
ZINC03639132; 0.976;
318
IV
100
ZINC05958052; 0.979;
387
IV
100
Note: From; (ProTox-II - Prediction of TOXicity of Chemicals, 2021).
Table 4: Codeine and zinc compounds binding scores to mu, delta and kappa receptors.
Compound
Hepatotoxicity
Probability
Immunotoxicity
Probability
Morphine
I
0.99
I
0.87
ZINC13831510; 0.992
I
0.89
I
0.96
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
I
0.99
I
0.87
ZINC04102208; 0.992;
I
0.89
I
0.96
ZINC04217170; 0.988;
I
0.9
I
0.97
ZINC26266464; 0.990;
I
0.99
A
0.64
ZINC27517251; 0.988;
I
0.9
I
0.97
ZINC37250136; 0.992;
I
0.99
I
0.94
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
I
0.99
I
0.98
Codeine
I
0.99
I
0.94
ZINC03629718; 0.995
I
0.97
I
0.94
ZINC02039583; 0.991;
I
0.99
I
0.94
ZINC03870350; 0.993;
I
0.9
I
0.97
ZINC28256912; 0.992
I
0.99
I
0.87
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
I
0.99
I
0.94
ZINC05599925; 0.997
I
0.99
I
0.94
ZINC26259212; 0.995;
I
0.98
I
0.7
ZINC26266464; 0.995;
I
0.99
A
0.64
ZINC27517251; 0.993;
I
0.9
I
0.97
ZINC33839041; 0.995;
I
0.9
I
0.97
ZINC37250136; 0.997;
I
0.99
I
0.94
ZINC39949141; 0.993
I
0.99
I
0.87
Tramadol
I
0.92
A
0.87
ZINC71774151; 0.977
I
0.84
I
0.84
ZINC02509756; 0.986;
I
0.94
I
0.86
ZINC02510775; 0.995;
I
0.86
I
0.7
ZINC02525883; 0.995;
I
0.86
I
0.7
ZINC03639132; 0.976;
I
0.95
A
0.81
ZINC05958052; 0.979;
I
0.94
I
0.86
Key I=Inactive, A=Active
Table 5: Hepatotoxic and immunotoxic profiles of Morphine, Codeine, and Tramadol.
Zinc compound ZINC05966734; 0.990; showed the lowest docking score to delta receptor than the rest of the zinc compounds and the morphine drug used as the standard. Data in Table 3 shows all the zinc compounds showed higher binding energies to delta receptor than Tramadol. ZINC03806721; 0.991; and ZINC37250136; 0.997; showed lowest docking scores to delta receptor than Codeine based on Table 5. ZINC05966734; 0.990; ZINC03806721; 0.991; and ZINC37250136; 0.997; are promising in developing opioid agonist with least convulsive side effects associated with delta receptor.
In Table 1, ZINC04217170; 0.988, ZINC26259212; 0.993, ZINC33839041; 0.993; and ZINC39949141; 0.997; showed higher docking energies to kappa receptor than morphine. Data on Table 3 showed that these zinc compounds showed higher binding score to kappa receptor than tramadol, ZINC01849532; 0.994, ZINC02525883; 0.995, ZINC03639132; 0.976; and ZINC76734760; 0.977; These zinc compounds therefore, have higher propensity than the rest of the zinc compounds to produce euphoria and diuresis. Table 5 shows that ZINC03870349; 0.993, ZINC03870350; 0.993, ZINC04217170; 0.992; ZINC05599925; 0.997; ZINC27517251; 0.993; and ZINC33839042; 0.992; showed lower binding energies to kappa receptor than codeine and therefore, shows promising results in discovery of opioid agonists with little euphoria side effects.
ZINC13831510; 0.992; showed the highest docking score to mu receptor than Morphine, equal binding energy to kappa receptor as Morphine and higher delta receptor binding than Morphine. ZINC03629718; 0. 995; ZINC03870350; 0.993; and ZINC28256912; 0.992; showed better docking energies to mu receptor than both delta and kappa to codeine as outlined in Table 5. Table 3 indicates that ZINC71774151; 0.977 with the highest binding score to mu than both kappa and delta receptors as compared to Tramadol.
In Tables 10 and 11, Pharmacokinetics profiles of opioids and Zinc compounds were analysed. Opioid analgesics that lack BBB permeation lack the CNS side effects and therefore would lead to better tolerability to the patients and lack of abuse. ZINC13831510; 0.992 and ZINC04102208; 0.992 zinc compounds lack BBB permeation as compared to reference Morphine compound. Codeine, Tramadol and their zinc compounds showed BBB permeation therefore, it is expected that they will have CNS side effects. Table 10 outlines the compounds, which were predicted to be substrates for P-glycoprotein.
Morphine, tramadol, codeine and their zinc compounds showed CYP2D6 inhibition as indicated in Table 11. These compounds also showed absence of CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 inhibition. All Zinc compounds analysed for pharmacokinetic profile and their standard drugs complied with Lipinski rule of five, which indicates drug likeness.
In Table 6, ZINC27517251; 0.988;, ZINC37250136; 0.992; and ZINC04217170; 0.988; showed the most toxic compounds having LD50 of 85mg/kg as compared to Morphine which showed LD50 of 461mg/kg.ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC03812983; 0.988;, ZINC04102208; 0.992; and ZINC39949141; 0.997 showed LD50 of 335mg/kg. Codeine and these zinc compounds ZINC03629718; 0.995, ZINC03870350; 0.993; and ZINC28256912; 0.992; were the most lethal with LD50 of 85mg/kg. The safest zinc compound was ZINC26259212; 0.995; predicted to have LD50 of 1140mg/kg. Tramadol, ZINC02510775; 0.995 and ZINC02525883; 0.995 were predicted to be the most lethal with LD50 of 228mg/kg.Tramadol was predicted to be toxic when swallowed while ZINC71774151; 0.977 was considered harmful when swallowed. ZINC71774151; 0.977 was predicted to be the safest with LD50 of 387mg/kg followed by ZINC02509756; 0.986; with LD50 of 387mg/kg.
Compound name
Carc
P
Mut
P
Cyt
P
Morphine
I
0.74
I
0.93
I
0.68
ZINC13831510; 0.992
I
0.74
I
0.93
I
0.68
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
I
0.63
I
0.78
I
0.63
ZINC04102208; 0.992;
I
0.62
I
0.78
I
0.61
ZINC04217170; 0.988;
I
0.6
I
0.73
I
0.58
ZINC26266464; 0.990;
I
0.62
I
0.78
I
0.61
ZINC27517251; 0.988;
I
0.81
I
0.93
I
0.69
ZINC37250136; 0.992;
I
0.75
I
0.89
I
0.69
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
I
0.81
I
0.93
I
0.69
Codeine
I
0.73
I
0.85
I
0.62
ZINC03629718; 0.995
I
0.73
I
0.85
I
0.62
ZINC03870350; 0.993;
I
0.62
I
0.78
I
0.61
ZINC28256912; 0.992
I
0.74
I
0.93
I
0.68
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
I
0.81
I
0.93
I
0.69
ZINC05599925; 0.997
I
0.81
I
0.93
I
0.69
ZINC26259212; 0.995;
I
0.6
I
0.81
I
0.58
ZINC26266464; 0.995;
I
0.6
I
0.73
I
0.58
ZINC27517251; 0.993;
I
0.62
I
0.78
I
0.61
ZINC33839041; 0.995;
I
0.62
I
0.78
I
0.61
ZINC37250136; 0.997;
I
0.81
I
0.093
I
0.69
ZINC39949141; 0.993
I
0.74
I
0.93
I
0.68
Tramadol
I
0.62
I
0.8
I
0.76
ZINC71774151; 0.977
I
0.69
I
0.71
I
0.65
ZINC02509756; 0.986;
I
0.67
I
0.8
I
0.77
ZINC02510775; 0.995;
I
0.65
I
0.77
I
0.97
ZINC02525883; 0.995;
I
0.65
I
0.77
I
0.97
ZINC03639132; 0.976;
I
0.55
I
0.8
I
0.69
ZINC05958052; 0.979;
I
0.67
I
0.8
I
0.77
Key Carc=Carcinogenicity, Mut=Mutagenicity, Cyt=Cytotoxicity, I=Inactive, A=Active
Note: From; (ProTox-II - Prediction of TOXicity of Chemicals, 2021)
Table 6: Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and cytogenecity toxicity predictions.
Compound
Ahr
p
Morphine
A
0.62
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
A
0.62
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
A
0.66
Codeine
A
0.8
ZINC28256912; 0.992
A
0.62
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
A
0.83
ZINC05599925; 0.997
A
0.93
ZINC39949141; 0.993
A
0.62
Key A= Active, AhR=Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor=probability
Note: From; (ProTox-II - Prediction of TOXicity of Chemicals, 2021)
Table 7: Nuclear receptor signaling toxicity pathways.
Compound
P-gp substrate
Compound
Morphine
Yes
ZINC03870350; 0.993;
Yes
ZINC13831510; 0.992
Yes
ZINC28256912; 0.992
Yes
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
Yes
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
Yes
ZINC04102208; 0.992;
Yes
ZINC05599925; 0.997
Yes
ZINC04217170; 0.988;
Yes
ZINC26259212; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC26266464; 0.990;
Yes
ZINC26266464; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC27517251; 0.988;
Yes
ZINC27517251; 0.993;
Yes
ZINC37250136; 0.992;
Yes
ZINC33839041; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
Yes
ZINC37250136; 0.997;
Yes
Codeine
Yes
ZINC39949141; 0.993
Yes
ZINC02039583; 0.99;
Yes
Note: From; (SwissADME, 2017)
Table 8: P-glycoprotein substrates predictions.
Compound
CYP2D6 inhibition
Morphine
Yes
ZINC03629718; 0.995
Yes
ZINC13831510; 0.992
Yes
ZINC02039583; 0.991;
Yes
ZINC03812983; 0.988;
Yes
ZINC03870350; 0.993;
Yes
ZINC04102208; 0.992;
Yes
ZINC28256912; 0.992
Yes
ZINC04217170; 0.988;
Yes
ZINC03830598; 0.991;
Yes
ZINC26266464; 0.990;
Yes
ZINC05599925; 0.997
Yes
ZINC27517251; 0.988;
Yes
ZINC26259212; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC37250136; 0.992;
Yes
ZINC26266464; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC39949141; 0.997;
Yes
ZINC27517251; 0.993;
Yes
Codeine
Yes
ZINC33839041; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC37250136; 0.997;
Yes
ZINC03639132; 0.976;
Yes
ZINC39949141; 0.993
Yes
ZINC02525883; 0.995;
Yes
Tramadol
Yes
ZINC02510775; 0.995;
Yes
ZINC71774151; 0.977;
Yes
ZINC02509756; 0.986;
Yes
ZINC05958052; 0.979;
Yes
Note: From; (SwissADME, 2017)
Table 9: CYP inhibition by opioids.
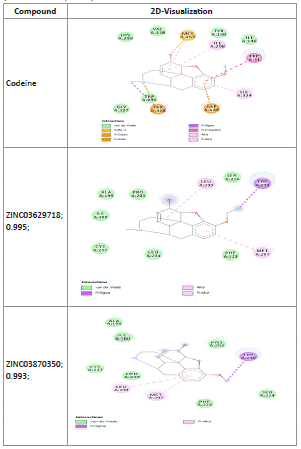
Table 10: Codeine and zinc compounds 2D-interactions with receptors (Shaweta et al., 2021).
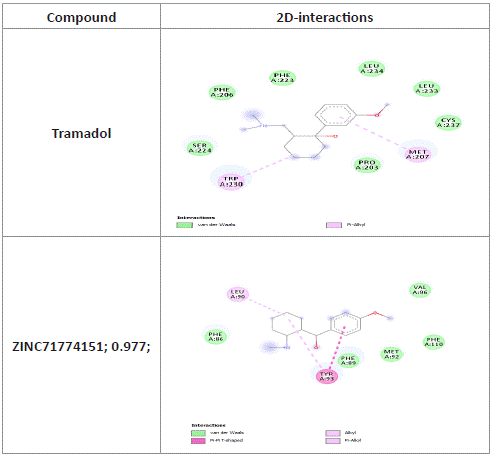
Table 11: Tramadol and zinc compounds 2D-interactions with receptors.
Morphine, ZINC03812983; 0.988, ZINC39949141; 0.997, Codeine, ZINC28256912; 0.992 and ZINC03830598; 0.991 were predicted active against AR with probability scores of 0.62,0.62,0.66,0.8,0.62 and 0.83 respectively. ZINC00409844; 0.992; ZINC01651927; 0.991; ZINC01747085; 0.985; ZINC00394165; 0.987; ZINC00406627; 0.980; ZINC01557001; 0.987 and ZINC71451975; 0.975 were predicted active against AhR with probability scores of 0.5,0.5,0.55,0.72,0.81,0.59 and 0.56 respectively. The rest of the compounds were predicted to be inactive in signaling AR-LBD, Aromatase, ER-LBD.
Conclusion
Compounds with the highest docking scores to mu receptor and lower docking scores to both kappa and delta will produce better analgesic effects than rest of the compounds. ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC03629718; 0. 995; ZINC03870350; 0.993; ZINC28256912; 0.992; and ZINC71774151; 0.977 showed the highest binding score to mu receptors and lower to both kappa and delta.
All compounds except ZINC04102208; 0.992; and ZINC13831510; 0.992 were predicted to penetrate Blood Brain Barrier. All compounds and reference compounds were predicted to inhibit the CYP2D6 enzyme.
In conclusion, ZINC13831510; 0.992; showed the highest binding score to morphine. ZINC02509756; 0.986; was considered the safest as compared to Tramadol and its zinc compounds. ZINC26259212; 0.995; was considered the safest as compared to the rest of the Codeine’s zinc compounds.
Author Statements
1. ReccommendationsFurther studies such as quantitative structure-activity analysis and ease of synthesizability of ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC02509756; 0.986, ZINC26259212; 0.995, ZINC71774151; 0.977, ZINC03629718; 0. 995; ZINC03870350; 0.993; and ZINC28256912; 0.992 should be done.
2. In vitro analysis of ZINC13831510; 0.992, ZINC02509756; 0.986, ZINC26259212; 0.995, ZINC71774151; 0.977, ZINC03629718; 0. 995; ZINC03870350; 0.993; and ZINC28256912; 0.992 should be done.
Funding Sources
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Benninger KL, Peng J, Ho ML, Newton J, Wang DJJ, Hu HH, et al. Cerebral perfusion and neurological examination characterise neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome: a prospective cohort study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022; 107: 414-20.
- Eberhardt J, Santos-Martins D, Tillack AF, Forli S. AutoDock vina 1.2.0: new docking methods, expanded force field, and python bindings. J Chem Inf Model. 2021; 61: 3891-8.
- Ehrlich AT, Kieffer BL, Darcq E. Current strategies toward safer Mu Opioid receptor drugs for pain management. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019; 23: 315-26.
- Faouzi A, Varga BR, Majumdar S. Biased opioid ligands. Molecules. 2020; 25: 4257.
- Galligan JJ, Akbarali HI. Molecular physiology of enteric opioid receptors. Am J Gastroenterol Suppl. 2014; 2: 17-21.
- Gasner N, Ouanounou A. Analgesics and pain management following root canal therapy. Essent Dent. 2021; 1: 1-11.
- Hartrick CT, Poulin D, Molenaar R, Hartrick A. Dual-acting peripherally restricted delta/kappa opioid (CAV1001) produces antinociception in animal models of sub-acute and chronic pain. J Pain Res. 2020; 13: 2461-74.
- Kamakia F, Stephen O, Kagia R. Computational analysis of morphine, codeine and tramadol. Harv Dataverse. 2023.
- Lazenka ML, Moerke MJ, Townsend EA, Freeman KB, Carroll FI, Negus SS. Dissociable effects of the kappa Opioid receptor agonist nalfurafine on pain/itch-stimulated and pain/itch-depressed behaviors in male rats. Psychopharmacology. 2018; 235: 203-13.
- Meariman JK, Sutphen JC, Gao J, Kapusta DR. Nalfurafine, a G-protein–biased KOR (kappa Opioid receptor) agonist, enhances the diuretic response and limits electrolyte losses to standard-of-care diuretics. Hypertension. 2022; 79: 379-90.
- Nakhaee S, Hoyte C, Dart RC, Askari M, Lamarine RJ, Mehrpour O. A review on tramadol toxicity: mechanism of action, clinical presentation, and treatment. Forensic Toxicol. 2021; 39: 293-310.
- Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, et al. UCSF Chimera--A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comp Chem. 2004; 25: 1605-12.
- ProTox II. Prediction of TOXicity of chemicals. 2021.
- Roeckel LA, Utard V, Reiss D, Mouheiche J, Maurin H, Robé A et al. Morphine-induced hyperalgesia involves mu opioid receptors and the metabolite morphine-3-glucuronide. Sci Rep. 2017; 7: 10406.
- Shaweta S, Akhil S, Utsav G. Molecular Docking studies on the anti-fungal activity of Allium sativum (Garlic) against Mucormycosis (black fungus) by BIOVIA discovery studio visualizer 21.1.0.0. Ann Antivir Antiretrovir. 2021; 028-032: 28-32.
- Stein C. New concepts in opioid analgesia. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018; 27: 765-75.
- Swiss A DME; 2017.
- Wilson N, Kariisa M, Seth P, Smith H, Davis NL. Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths – United States, 2017-2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020; 69: 290-7.