Review Article
Austin J Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 2 (2). 1016
For and Against the use of Methylated Cyclodextrins in the Development of Midazolam Solution for Nasal Application
Snezana Agatonovic-Kustrin1*, Beverley D. Glass2, Michael E. Brown3, Mosimotsana L Lebete4
1Department of Pharmacy and Applied Science, La Trobe University, Edwards Rd, Bendigo 3550, Australia
2Department of Pharmacy and Molecular Sciences, James Cook University (JCU), Townsville, Qld 4811, Australia
3Department of Chemistry, Rhodes University, PO Box 94, Grahamstown.6140 South Africa
4Department of Pharmacy, Rhodes University, PO Box 94, Grahamstown.6140 South Africa
*Corresponding author: : Snezana Agatonovic- Kustrin, Department of Pharmacy and Applied Science, La Trobe University, Edwards Rd, Bendigo 3550, Australia
Received: February 03, 2014; Accepted: February 10, 2014; Published: February 13, 2014
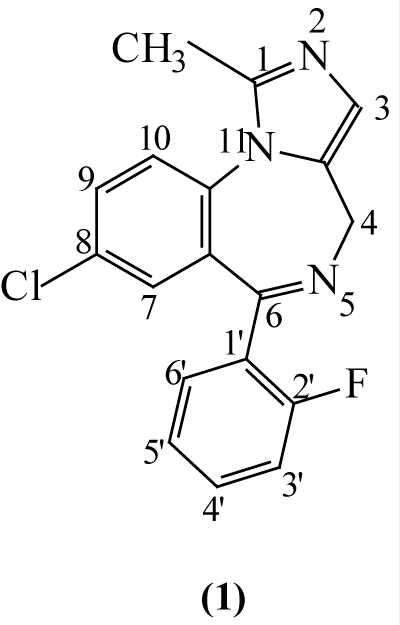
Midazolam (MDZ) is a high potent drug with anxiolytic, hypnotic, amnestic, anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant, and sedative properties. The drug differs from other benzodiazepines by the presence of an imidazole ring attached to benzodiazepine (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Chemical Structure of Midazolam.
Midazolam’s imidazole ring helps provide stability in solution to hydrolytic degradation and fast metabolic inactivation [1]. Because of its short half–life, myorelaxant, and amnesic properties, it is commonly used as a preoperative anesthetic agent, especially for the pediatric patients [2]. A growing interest in alternative forms of drug administration has led to the development of nasal formulations. Nasal administration, with transmucosal absorption, offers advantages of rapid onset of action, patient control and ease of administration. Nasal application of MDZ has been studied for a variety of indications, i.e. sedation before surgical, dental or diagnostic procedures, and for treatment of seizures in children and adult patients as safe and inexpensive means to rapidly achieve seizure control [3–6]. Since no nasal preparation is commercially available, midazolam solution for injection has been used [6–8]. However, due to the low concentration of the commercially available formulation for intravenous application, large application volumes exceeding limited nasal capacity have to be used to achieve adequate dosing. In order to deliver therapeutic midazolam doses in smaller volumes, nasal preparations with MDZ concentration, exceeding its solubility must be developed. MDZ is water–soluble at pH less than 4 and lipidsoluble at physiological pH. MDZ solubility is increased at pH <4 is due to ring opening to the corresponding benzophenone with a highly ionizable primary amino group [9]. At a pH > 5 the whole of the drug is present in a liposoluble, closed ring form. The ring is completely closed at physiological pH 7.4. Intranasal administration of the acidic midazolam solution can cause severe irritation and swelling in the nasal cavity. Since the solubility of midazolam is less than 0.1 mg⁄mL at pH 7, preparation of aqueous dosage formulations near physiological pH, requires the use of a solubilizer. Formulations of a 0.2% (w⁄v) oral solution of MDZ containing γ–cyclodextrin (γ– CD) and citric acid have been investigated [10]. More recently, the replacement γ–CD with partially methylated CDs was proposedwith the aim to improve the solubility and stability of MDZ in oral formulations and also for the development of a feasible buccal–nasal formulation [11]. Due to their high aqueous solubility (>500 mg⁄mL), and ability to form inclusion complexes, methylated CDs are widely used in pharmaceutical applications, to improve drug solubility [12], and drug stability to hydrolysis [13] and exposure to light [14]. Substitution of hydroxyl groups with methoxy groups increases lipophilic character, serve as a good absorption enhancer and therefore increase mucosal penetration [15]. However, cyclodextrins are known to alter the drug stability, either positively or negatively.
RM–β–CD might affect the degradation kinetics of midazolam in aqueous solution result in the formation of different photodegradants from those observed in the absence of RM–β–CD.
Midazolam is a light sensitive drug. Light sensitive drugs decompose to form radical intermediates and highly reactive products, which react with the tissue cells resulting in adverse effects, making the detection and identification of photodegradants important. In general, photosensitivity reactions that have occurred in patients to whom light sensitive drugs are administered have been associated with the formation of toxic photodegradants. Although the photostability of MDZ is well documented [9,16,17] in the literature, the rate of photodegradation and distribution of photodegradents may be altered in the presence of cyclodextrin [18–20]. CDs have the potential to control chemical and photochemical reactions. This has been attributed to the microplanarity of the host cavity and limited molecular mobility of the guest molecule due to steric constraints. The nature of the lowest excited states of the guest molecule, deactivation pathways and the fate of the reaction may be modified by the CD microenvironment. Structural changes in drug molecules that occur when they complex with cyclodextrin may also accelerate drug degradation [21]. The rate of secondary reactions may alsobe influenced and the chemical evolution of reaction intermediates controlled [20].
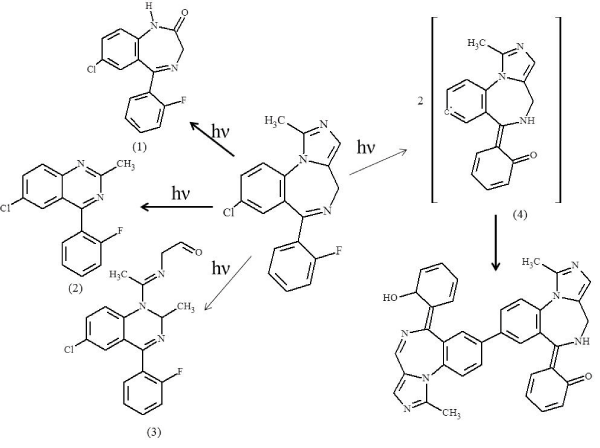
Photodegradation study [22] has shown that RM–β–CD slightly decreases the photostability of midazolam. Degradation of midazolam with time, both in the presence and absence of RM–β–CD is not linear. The initial stages are acceleratory, suggesting autocatalysis by the degradants. The decreased stability is also accompanied by the appearance of a new degradant, compound (5) (Figure 2), unique to the cyclodextrin presence. The proposed structure is a dimer of a major degradation product of midazolam that is identified in theaqueous solution [16]. The dimer is formed through loss of Cl atom from each molecule, resulting in free radicals which then combine with each other. The reactions are made possible by the ability of cyclodextrin to stabilize free radicals, and by conformational control inside cyclodextrin cavity which results in stabilization of certainreaction intermediates. Important part of the degradant products is formed from the recombination of radicals which are not present in the solvent surrounding the inclusion complex but are trapped inside the cyclodextrin cavity.
Figure 2: Proposed photodegradation of midazolam in aqueous solution containing 30% w⁄v of RM–β–CD, at pH 5.
Figure 2: Proposed photodegradation of midazolam in aqueous solution containing 30% w⁄v of RM–β–CD, at pH 5.
Taking into consideration the lower photostability of the MDZ in the presence of RM–β–CD, the use of CD may not be the best approach to enhance the MDZ aqueous solubility. Although, RM–β–CD improves the aqueous solubility of midazolam as desired, and suitable packaging might reduce the appearance of these photodegradants in the final formulation, descovery of new photodegradants should be further investigated. Further work could involve the isolation and structural elucidation of the photodegradation products to confirm the proposed structures and to establish the phototoxicity of these photodegradants.
References
- Gerecke M. Chemical structure and properties of midazolam compared with other benzodiazepines. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983; 16: 11S-16S.
- Wermeling DP, Record KA, Kelly TH, Archer SM, Clinch T. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a new intranasal midazolam formulation in healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg. 2006; 103: 344-349.
- Björkman S, Rigemar G, Idvall J. Pharmacokinetics of midazolam given as an intranasal spray to adult surgical patients. Br J Anaesth. 1997; 79: 575-580.
- Burstein AH1, Modica R, Hatton M, Forrest A, Gengo FM. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam after intranasal administration. J Clin Pharmacol. 1997; 37: 711-718.
- Wolfe TR, Macfarlane TC. Intranasal midazolam therapy for pediatric status epilepticus. Am J Emerg Med. 2006; 24: 343-346.
- Mahmoudian T, Zadeh MM. Comparison of intranasal midazolam with intravenous diazepam for treating acute seizures in children. Epilepsy Behav. 2004; 5: 253-255.
- Lahat E, Goldman M, Barr J, Bistritzer T, Berkovitch M. Comparison of intranasal midazolam with intravenous diazepam for treating febrile seizures in children: prospective randomised study. BMJ. 2000; 321: 83-86.
- Burstein AH, Modica R, Hatton M, Forrest A, Gengo FM. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam after intranasal administration. J Clin Pharmacol. 1997; 37: 711-718.
- Andersin R. Solubility and acid-base behaviour of midazolam in media of different pH, studied by ultraviolet spectrophotometry with multicomponent software. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1991; 9: 451-455.
- Marçon F, Mathiron D, Pilard S, Lemaire-Hurtel AS, Dubaele JM. Development and formulation of a 0.2% oral solution of midazolam containing gamma- cyclodextrin. Int J Pharm. 2009; 379: 244-250.
- Mathiron D, Marçon F, Dubaele JM, Cailleu D, Pilard S. Beneits of methylated cyclodextrins in the development of midazolam pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm Sci. 2013; 102: 2102-2111.
- Mannila J, Järvinen T, Järvinen K, Tarvainen M, Jarho P. Effects of RM-beta- CD on sublingual bioavailability of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rabbits. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005; 26: 71-77.
- Loftsson T, Brewster ME. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J Pharm Sci. 1996; 85: 1017-1025.
- Scalia S, Tursilli R, Iannuccelli V. Complexation of the sunscreen agent, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor with cyclodextrins: effect on photostability and human stratum corneum penetration. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007; 44: 29-34.
- Loftsson T, Vogensen SB, Brewster ME, Konrádsdóttir F. Effects of cyclodextrins on drug delivery through biological membranes. J Pharm Sci. 2007; 96: 2532-2546.
- Andersin R, Ovaskainen J, Kaltia S. Photochemical decomposition of midazolam. III--Isolation and identiication of products in aqueous solutions. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1994; 12: 165-172.
- Andersin, R. and S. Tammilehto, Photochemical Decomposition of Midazolam. 2. Kinetics in Ethanol. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 1989; 56: 175-179.
- Mielcarek J. Photochemical stability of the inclusion complexes formed by modiied 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives with beta-cyclodextrin. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1997; 15: 681-686.
- Tadanobu Utsuki, Keiko Imamura, Fumitoshi Hirayama, Kaneto Uekama. Stoichiometry-dependent changes of solubility and photoreactivity of an antiulcer agent, 2’-carboxymethoxy-4,4’-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyloxy) chalcone, in cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1993; 1: 81-87.
- P. Bortolus, G. Grabner, G. Köhler, S. Monti. Photochemistry of Cyclodextrin Host-Guest Complexes. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 1993; 125: 261- 268.
- Sortino S, Giuffrida S, De Guldi G, Chillemi R, Petralia S. The photochemistry of lutamide and its inclusion complex with beta-cyclodextrin. Dramatic effect of the microenvironment on the nature and on the eficiency of the photodegradation pathways. Photochem Photobiol. 2001; 73: 6-13.
- Mosimotsana Leah L. The inluence of a methylated-ß-Cyclodextrin on the solubility and photostability of midazolam in aqueous solution, in Faculty of Pharmacy. 2001, Rhodes University. 116.