
Review Article
Austin J Pharmacol Ther. 2021; 9(4).1142.
Cytochrome C and COI Sequence of O.laetus Review
Mazhar MW*, Raza A, Sikandar M, Mahmood J, Saif S, Waqas N, Tahir H and Mazhar F
Department of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology, Government Collage University, Faisalabad, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Muhammad Waqar Mazhar, Department of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology, Government Collage University, 38000 Faisalabad, Pakistan
Received: May 28, 2021; Accepted: June 18, 2021; Published: June 25, 2021
Introduction
The COI sequence of O.laetus was submitted to the Genbank database holding an accession number HQ908084 (Figure1). The amino acid sequence of the corresponding COI gene was also updated under the accession number ADZ05746, which turned out to contain 222 amino acids. Base statistics of the O.laetus COI are presented in Figure 2. It can be seen from the table that the fragment is rich in AT content as expected with thymine occurring most frequently followed by the others in the order A, C & G. The AT% stood at 67.2 in comparison to GC% at 32.8. The protein entry was subjected to family confirmation by searching the InterProScan database and the results indicate a very high and significant match confirming our sequence to be a part of Cytochrome C.
Cytochrome C
Cytochrome c is hemi protein that is presnt in the mitochondrial intermembrane space. It found in both animal and plant and many unicellular, this along with small size molecular weight is about 12000 Daltons [1]. Its amino acid sequence is highly conserved in mammals differing by only few residues. Sequence of the in human and chimpanzees is similar but more different from the sequence of the horses.
It is capable of undergoing oxidation reduction but does not bind to oxygen. The cytochrome is electron carrier that do not transfer proton. It transfer the electron between the complex III and complex IV. Cytochrome b, c1, a and a3 are integral membrane protein but cytochrome c is associated with the inner membrane of mitochondria. Cytochrome c is highly water soluble its water solubility is 100g/L [1]. Cytochrome is not a part of large complex it can diffuse more rapidly due to this key property it role in transferring of electron between protein complexes. In human cytochrome c is encoded by the CYCS gene [1] (Figure 1).
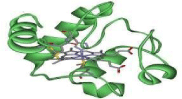
Figure 1: Structure of cytochromes C (green) with a hemi molecule
coordinating acentral Iron atom (orange).
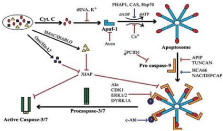
Figure 2: Signal transduction and pathways involved in apoptosis.
Classification of Cytochrome C
Cytochrome C is classified in four class:
Class I: it is low spine soluble cytochrome of mitochondria and bacteria.
Class II: it include the high spine cytochrome.
Class III: it contain low redox potentials and multiple heme Cytochromes.
Class IV: it is the complex proteins that have other prosthetic groups as well as heme c [2].
Function of cytochrome
Cytochrome play major role in many important processes like electron transport chain, LLLT, apoptosis. LLLT (low level laser therapy) is use for repairing of by increasing rate of cellular regeneration. In LLLT (low level laser Therapy) red light and near infrared wavelength is use. It penetrates in tissue and increase cytochrome c activity which cause increase metabolic activity and produce more free energy for cellular regeneration [3].
Cytochrome c is also responsible for apoptosis (apoptosis is cell death mechanisms) [4]. In mitochondria cytochrome c is attached with cardiolipin, which prevent the cytochrome from the releasing out and apoptosis. cytochrome c initially interact with the cardiolipin due to electrostatic interaction because on cytochrome c is extremely positive charge present, final interaction between cytochrome c and cardiolipin is hydrophobic interaction, hydrophobic tail of cardiolipin is inserted in the hydrophobic portion of cytochrome c. In first step of apoptosis cardiolipin is oxidized by per oxidize. The hemoprotein is detached from the inner mitochondrial membrane and release into the soluble cytoplasm through the outer membrane pore. Cytochrome c release from mitochondria by elevation level of calcium. When small amount of cytochrome is release it interacts with the IP3 receptor on endoplasmic reticulum and this cause the release of calcium. The overall increase in calcium level it cause the increase the then acts in the positive feedback loop to maintain endoplasmic reticulum calcium release through the IP3. Cytochrame cause the activation of caspase 9 which is a cysteine protease. Caspase 9 activates the caspase 3 and caspase 7 and these are responsible for cell death or apoptosis [5] (Figure 2).
Beside this cytochrome c is also present in normal cellular condition at extra mitochondrial locations. In pancreatic acinar, strong and specific detection of cytochrome c was detected in zymogene granules and growth hormones granules [6].
Cytochrome c play major role in electron transport chain. In electron transport chain energy rich molecule such as glucose are metabolized by series of oxidation reduction reaction ultimately yield carbon dioxide and water. The reduce enzyme NADH and FADH2 each donate a pair of electron to specialized set of electron carrier, consisting of FMN, co enzyme Q and series of Cytochromes (cytochrome a, b, c) collectively known as electron transport chain. Cytochrome c is capable of undergoing oxidation reduction but does not bind with oxygen. It transfer electron between complex III (coenzyme Q-cytochrome c reductase) and complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase).
Pathway
Electron transport chain pathway
Mitochondrial respiration an important bioenergetics process relies on operation of four membranous enzymatic complexes linked functionally by mobile freely diffusible elements, quinone molecules in the membrane and water-soluble Cytochromes c in the intermembrane space of mitochondria. One of the mitochondrial complexes, complex III (cytochrome bc1 or ubiquinol cytochrome c oxidoreductase) provides an electronic connection between these two diffusible redox pools linking in a fully reversible manner two electron of quinine undergo oxidation reduction with one electron of cytochrome c reduction oxidation. Several features of this homodimeric enzyme implicate that in addition to its well defined function of contributing to generation of proton motive force, cytochrome bc1 may be a physiologically important point of regulation of electron flow acting as a sensor of the redox state of mitochondria that actively responds to changes in bioenergetics conditions. These features include the following: the opposing redox reaction at Quinone catalytic sites located on the opposite sides of the membrane, the inter monomer electronic connection that functionally links four quinone binding sites of a dimmer into an H-shaped electron transfer system as well as the potential to generate super oxide and release it to the intermembrane space where it can be engaged in redox signaling pathways (Figure 3).
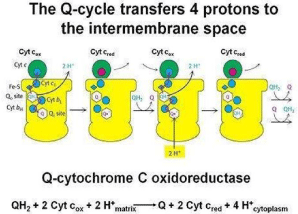
Figure 3: Electron transport chain mechanism in mitochondrial intermembrane.
Here we highlight recent advances in understanding how cytochrome bc1 may accomplish this regulatory physiological function, what is known and remains unknown about catalytic and side reactions within the Quinone binding sites and electron transfers through the cofactor chains connecting those sites with substrat redox pools.
Apoptotic pathway
Mitochondria Is essential for multicellular organisms because without mitochondria cell cannot respirate aerobically, quick die. This fact makes the basis for apoptosis. Apoptotic protein targets the mitochondrial membrane and increase the permeability of mitochondrial membrane through pore formation and leak out the apoptotic factor [7]. Nitric oxide induce the apoptosis by helping to dissipate the membrane potential [8].
Mitochondrial protein is known as the SMACs protein (second mitochondria derived activator of caspase) are releases into the cell cytoplasm following to increase permeability of mitochondrial membrane. SMACs bind to the protein that inhibits apoptosis and deactivating them and Prevent Inhibit Apoptosis (IPAs) and precede the apoptosis. Cytochromes c is also release from mitochondria due to a channel, the mitochondrial Apoptosis Induce Channel (MAC) in the outer mitochondrial membranes and function as morphological change associated with apoptosis [7]. Once cytochrome c is release it binds with apoptotic protease Activating Factor-1 (Apaf-1) and ATP which then bind to pro-caspase-9 to create a protein complex known as an apoptosome [9].
The apoptosome cleave the pro-caspase-9 to its active form caspase-9 which is turn activate the caspase-3 [10].
Two theories of the direct initiation of apoptotic mechanisms in mammals have been suggested the TNF-induced (tumors necrosis factor) model and the Fas-Fas ligand-mediated model both involving receptors of the TNF Receptor (TNFR) family coupled to extrinsic signals [11].
TNF pathway
TNF-alpha is a cytokine produced mainly by activated macrophages and is the major extrinsic mediator of apoptosis. Most cells in the human body have two receptors for TNFalpha TNFR1 and TNFR2. The binding of TNF-alpha to TNFR1 initiate the pathway that leads to caspase activation via the intermediate membrane proteins TNF Receptor Associated Death Domain (TRADD) and Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD). CIAP1/2 can inhibit TNF-a signaling by binding to TRAF2. FLIP inhibits the activation of caspase-8 [12]. Binding of this receptor can also indirectly lead to the activation of transcription involved in cell survival and inflammatory responses [13]. Signaling through TNFR1 might also induce apoptosis in a caspase independent manner [12]. The link between TNF-alpha and apoptosis shows why an abnormal production of TNF-alpha plays a fundamental role in several human diseases, especially in autoimmune disease.
Fas pathway
The Fas receptor first apoptosis signal (Fas) binds the Fas ligand (FasL) a transmembranes part of the TNF family [11]. The interaction between Fas and FasL results in the formation of the death inducing signaling complex (DISC) which contains the FADD caspase-8 and caspase10. In some types of cells (type I) processed caspase-8 directly activates other members of the caspase family and triggers the execution of apoptosis of the cell. In other types of cells (type II) the Fas-DISC starts a feedback loop that spirals into increasing release of proapoptotic factors from mitochondria and the amplified activation of caspase-8 [11].
Caspases
Caspase play the important role in the transduction of apoptosis. There are two type caspases, one is initiator caspases, caspase 2, 8, 9, 11, 12 and second type is the effector caspase 3, 6, 7.
Activation of initiator caspase requires binding to specific oligomeric activator [14].
LLLT Pathway
Mitochondria are considered the power generators of the eukaryotic cell, converting oxygen and nutrients through the oxidative phosphorylation process and electron transport chain into Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) [15]. Various in vitro experiments, such as those that use rat liver isolates, found that cellular respiration was upregulated when mitochondria were exposed to a He Ne laser or other forms of illumination. Laser irradiation caused an increase in mitochondrial products (such as ATP, NADH, protein, Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) and a reciprocal augmentation in oxygen consumption. A similar effect is produced when tissue that contains mitochondria is exposed to low-level radiation. Visible and Near-Infrared (NIR) light is absorbed by the organelle, and an upregulation of cellular respiration is observed .Four membrane-bound complexes have been identified in mitochondria, each constituting an extremely complex transmembrane structure embedded in the inner membrane. Complex IV, also known as CCO, is a large transmembrane protein complex found in mitochondria, which is a component of the respiratory electron transport chain. CCO appears to absorb the same spectrum of light as that observed for the action spectra for the biological response to light in the NIR range. Thus it is reasonable to assume that CCO acts as an important chromophore in LLLT [16]. CCO consists of 2 copper centers and 2 heme-iron centers that are capable of absorbing light over a wide range, including NIR.
Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase) is the principal chromophore involved in low-level light therapy. It has 2 copper centers and 2 heme prosthetic groups. Cytochrome c is oxidized and oxygen is reduced to water during respiration.
On the cellular level, LLLT may cause photodissociation of nitric oxide (NO) from CCO. In a stressed cell, NO produced by mitochondrial NO synthase displaces oxygen from CCO, which results in a downregulation of cellular respiration and a subsequent decrease in the production of energy-storing compounds, such as ATP. By dissociating NO from CCO, LLLT prevents the displacement of oxygen from CCO and thereby promotes unhindered cellular respiration. Increased CCO enzyme activity can be measured increased ATP production and increased electron transports also have been reported. The basic idea behind cellular respiration is that high-energy electrons are passed from electron carriers, such as NADH and FADH2, through a series of transmembrane complexes (including CCO) to the final electron acceptor. Increased cellular ATP produced by LLLT may contribute to the positive effects, both by raising cellular energy levels and by upregulating the cyclic AMP molecule (biochemically formed from ATP) that is involved in many signaling pathways.
Nitric oxide can bind to copper (heme) centers in cytochrome c oxidase and inhibit respiration. The nitric oxide may be photo dissociated by absorption of red or near infrared light, allowing oxygen to return and sharply increasing respiration and adenosine.
Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor and is, in the process, converted to water. Part of the oxygen that is metabolized produces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as a natural by-product. ROS (e.g. superoxide and hydrogen peroxide) are chemically active molecules that play an important role in cell signaling, regulation of cell cycle progression, enzyme activation, and nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Because LLLT promotes the metabolism of oxygen, it also acts to increase ROS production. In turn, ROS activates certain redox-sensitive transcription factors which lead to the upregulation of various stimulatory and protective genes [17]. Because of a few confinements in morphological-based identification system, molecular approach was favored over the morphological approach for species identification. The sequence of standard region of mitochondrial gene cytochrome c oxidase (CO1) was established as a barcode for identification among eight of the most diverse orders of insects. Utilization of CO1 for recognition in lapidopterans was all the more difficult because sequence divergence was low in this order. CO1 based identification system could be used at large scale for animals [18]
In plants, DNA barcoding was a difficult task because COI gene was not as good as in animals, because that it had lower subsititution rate in plants. Utilization of multiloci of plastid areas as standardized barcode was a suitable solution of this problem. This genome had large number of the desirable qualities as that of animal mitochondrial DNA for barcoding, such as conserved gene order and high copy number for easy amplification of DNA for PCR and sequencing. First there was need to recognize a short sequence which had conserved sites for primer binding but showed high variability within it [19].
In animals, the barcoding is good task for recognizing species including birds, fish, insects [20-24]. The short sequence of 648- bp region of the mitochondrial gene cytochrome c oxidase (COI), serve as a DNA barcode for the recognition of animal species. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) has been mostly used in evolutionary studies of animal because it advances substantially more quickly than nuclear DNA, bringing about the aggregation of contrasts between nearly related species [20].
DNA barcoding had an incredible success in animal groups by utlizing mitochondrial gene, cytochrome c oxidase (CO1). Two more DNA regions could be utilized as DNA barcode along with some drawbacks, that were plasted spacer trnH-psbA and nuclear ribosomal ITS region. Barcode had short length and simple enhancement was considered as a perfect one. Best standardized barcodes were being searching. A plant barcode after its establishment was used in biodiversity inventories, preservation evaluations, and scientific investigation.
DNA barcoding in animals was generally used for the identification of organisms and the revelation of new species. A lot of criticism was rewarded to this method. Numerious studies demonstrated that biodiversity exploration should be possible by the sequencing of a single organelle region. Achievement of this tool was declined by substitution in mitochondrial DNA in plants, and search for similar region to animal COI had focused on chloroplast DNA.
DNA barcoding on CO1 cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene) was considered a wellorganized method for the recognition of species in animal life and learned at a geographical scale particularly within tropical regions. Overview was made on potential species differing qualities utilizing DNA barcodes by collecting 163 species of geotropically bats. That largest survey was relevent to any animal group like land vertebrates. DNA barcoding utilized over great geographical regions and across extremely varied habitats. 98.8% sets of CO1, from those of 163, were haplotypes and easily identifiable at that locus. 1.38 % of intraspecific diversity was marked relating to birds as compared to other bats. 44 cases out of 163 supported the existence of cryptic species while intraspecific divergence was not predictors of their existence. Further investigaton was required for intraspecific lineage using other techniques.
References
- Tafani M, Karpinich NO, Hurster KA, Pastorino JG, Schneider T, Russo MA, et al. Cytochrome c release upon Fas receptor activation depends on translocation of full-length bid and the induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem. 2002; 2: 7.
- Ambler RP. Sequence variability in bacterial cytochromes c. Biochem Biophy Acta. 1991; 1058: 42-47.
- Karu TI, Pyatibrat LV, Afanasyeva NI. Cellular effects of low power laser therapy can be mediated by nitric Lasers. J Surg Med. 2005; 36: 307.
- Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome C. Cell Press. 1996; 86: 147-157.
- Boehning D, Patterson RL, Sedaghat L, Glebova NO, Kurosaki T, Snyder SH. Cytochrome c binds to inositol (1,4,5) trisphosphate receptors, amplifying calciumdependent apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2003; 5: 1051-1061.
- Soltys BJ, Gupta RS. Mitochondrial-matrix proteins at unexpected locations: are they exported. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999; 24: 174-177.
- Cotran RS, Kumar D, Collins F. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders Company. 1998.
- González D, Bejarano I, Barriga C, Rodríguez AB, Pariente RJ. Oxidative Stress-Induced Caspases are Regulated in Human Myeloid HL-60 Cells by Calcium Signal. Current Signal Transduction Therapy. 2010; 5: 181-186.
- Dejean LM, Martinez-Caballero S, Manon S, Kinnally KW. Regulation of the mitochondrial apoptosis-induced channel, MAC, by BCL-2 family proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006; 1762: 191-201.
- Lodish H, Baltimore D, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaira P, Darnell J. Molecular cell biology. Scientific American Books New York. 1995.
- Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S. Cardiolipin oxidation sets cytochrome c free. Nat Chem Biol. 2005; 1: 188-189.
- Chen G, Goeddel DV. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science. 2002; 296: 1634-1635.
- Goeddel DV. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science. 2007; 296: 1634-1635.
- Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 1999; 397: 441-446.
- Brosseau L, Welch V, Wells GA, Bie DR, Gam A, Harman K, et al. Low level laser therapy (Classes I, II and III) for treating rheumatoid arthritis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005; 19: 20-49.
- Karu TI. Mitochondrial Signaling in Mammalian Cells Activated by Red and Near-IR Radiation. Photochemistry and Photobiology. 2005; 84: 1091-1099.
- Afanasyeva NI, Karu TI, Pyatibrat LV. "Cellular effects of low power laser therapy can be mediated by nitric oxide". Lasers Surg Med. 2005; 36: 307- 314.
- Hebert PD, Cywinska A, Ball SL. "Biological identifications through DNA barcodes." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences. 2003; 270: 313-321.
- Chase MW, Cowan RS. A proposal for a standardised protocol to barcode all land plants Taxon. 2007; 56: 295-299.
- Hebert PD, Stoeckle MY. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS biology. 2004; 2: 1657-1663.
- Janzen DH, Hajibabaei M. Wedding biodiversity inventory of a large and complex Lepidoptera fauna with DNA barcoding. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. Biological Sciences. 2005; 360: 1835-1845.
- Paul D, Hebert N, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, Francis CM. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS biology. 2004; 2: 1657-1663.
- Dejean LM, Martinez-Caballero S, Kinnally KW. Is MAC the knife that cuts cytochrome c from mitochondria during apoptosis? Cell Death & Differentiation. 2006; 13: 1387-1395.
- Wajant H. The Fas signaling pathway: more than a paradigm. Science. 2002; 296: 1635-1636.